Topic ecosystem diversity examples: Discover the wonders of our world through ecosystem diversity examples, showcasing the beauty and complexity of nature"s varied landscapes and the life they support.
Table of Content
- What are some examples of ecosystem diversity?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems
- Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Efforts
- YOUTUBE: Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies on Ecosystem Diversity
- Future of Ecosystem Diversity
What are some examples of ecosystem diversity?
Some examples of ecosystem diversity include:
- Forests
- Grasslands
- Deserts
- Wetlands
- Oceans
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
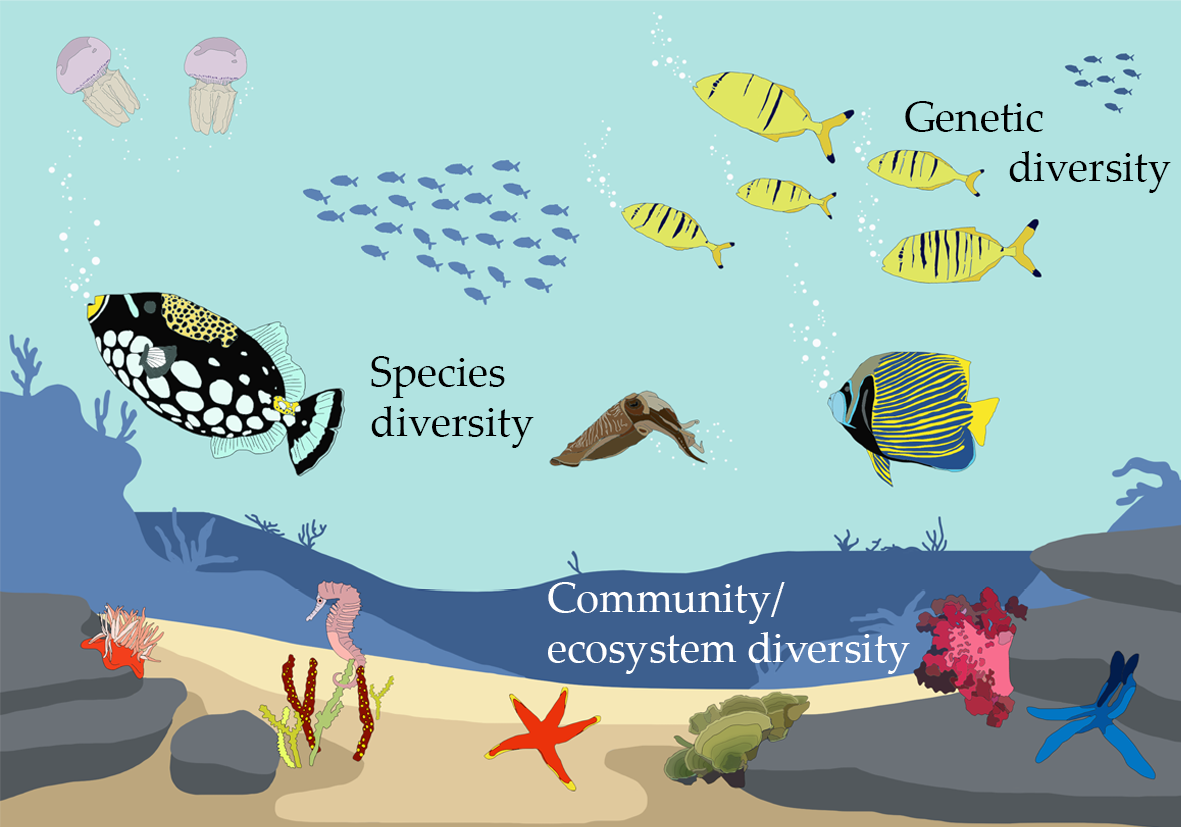
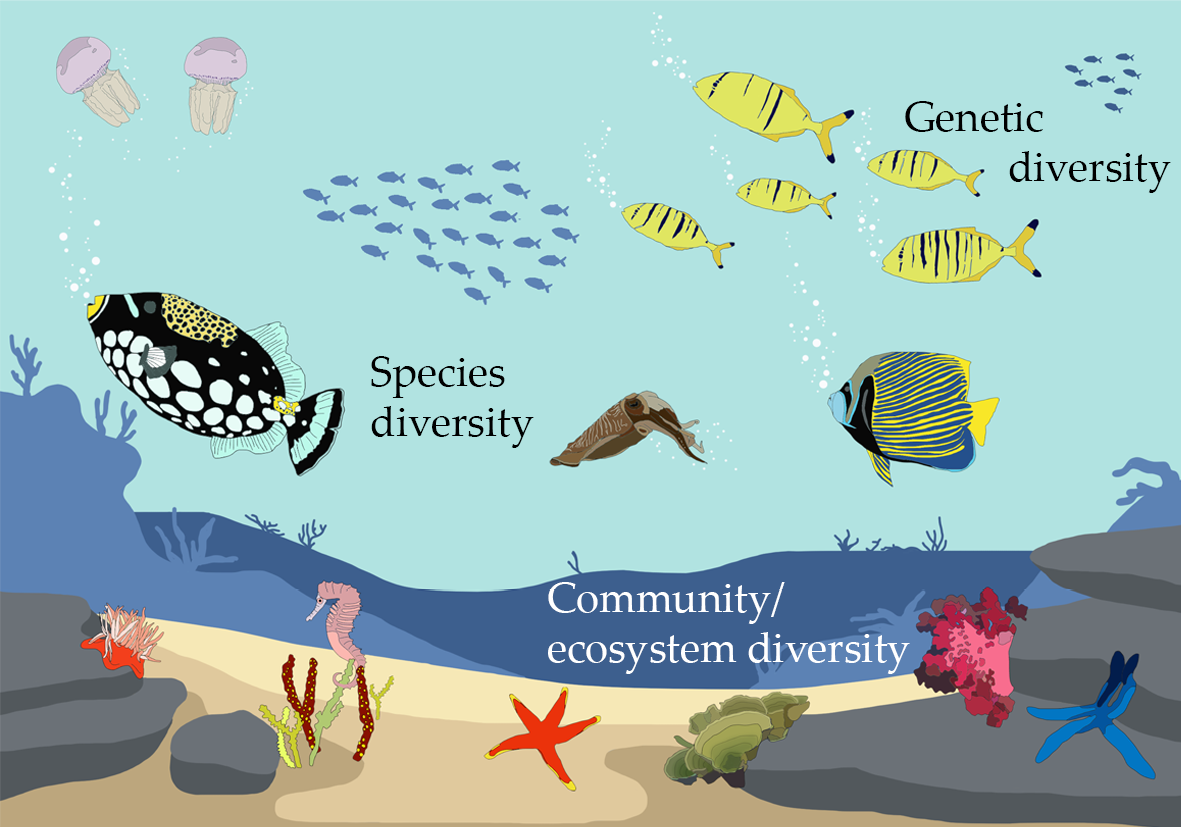
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems within a certain region. It encompasses different habitats, living communities, and ecological processes. This diversity not only includes terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems but also the distinctions between them, such as forests, deserts, grasslands, rivers, lakes, coral reefs, and wetlands.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These are land-based ecosystems like forests, deserts, and grasslands. Each has unique soil types, climates, and life forms.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Includes freshwater bodies like lakes and rivers, and marine environments such as oceans and coral reefs. These ecosystems are defined by their salt content.
- Transitional Ecosystems: Such as estuaries and wetlands, which serve as the transition zones between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and are crucial for biodiversity.
This diversity is vital for human survival, providing essential services like clean air and water, fertile soil for agriculture, and resources for medicines and materials. It also offers resilience to environmental changes and disasters, contributing to the planet"s overall health and stability.

Types of Ecosystems
The Earth"s biosphere is teeming with a vast array of ecosystems, each playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. These ecosystems can broadly be classified into two main types: terrestrial and aquatic, with further subdivisions based on distinct characteristics such as climate, geography, and the species they support.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These ecosystems are found on land and are categorized into several types, including:
- Forests: Diverse in types such as rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests, each housing a unique array of flora and fauna.
- Deserts: Characterized by low precipitation, they support life forms adapted to aridity.
- Grasslands: Known for vast open spaces covered by grasses, they include savannas and temperate grasslands.
- Mountains: Ecosystems that vary greatly over short distances due to changes in altitude and slope.
- Tundra: Cold, treeless regions found in the Arctic and high mountains, supporting hardy species adapted to extreme conditions.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Covering about 75% of the Earth"s surface, these include:
- Freshwater Ecosystems: Lakes, rivers, streams, and wetlands, which are vital for the water cycle and biodiversity.
- Marine Ecosystems: Oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries, home to a diverse range of marine life.
Each ecosystem type supports unique communities of plants and animals, adapted to their specific environments. Understanding these types helps in appreciating the complexity of life on Earth and the importance of conserving these natural habitats.
Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of ecosystems within a region or the planet as a whole. Here are some striking examples that illustrate the vast diversity of ecosystems on Earth, each with its unique flora, fauna, and environmental conditions:
- Amazon Rainforest: One of the most biodiverse regions on Earth, this tropical rainforest spans several countries in South America and is home to millions of species.
- Great Barrier Reef: The world"s largest coral reef system, located in Australia, it harbors thousands of marine species, including fish, corals, and birds.
- Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, covering much of North Africa, it features a unique ecosystem adapted to arid conditions.
- Serengeti Plains: Located in East Africa, this grassland ecosystem is famous for its large mammal migrations and high biodiversity.
- Arctic Tundra: A cold, treeless biome found in the Arctic, it supports life forms adapted to extreme cold and permafrost conditions.
- Antarctic Ice Sheets: Though seemingly inhospitable, these ice-covered ecosystems support a variety of life, including penguins, seals, and a diverse range of marine organisms.
- Amazon Basin Wetlands: These freshwater ecosystems are critical for biodiversity, water purification, and flood control.
- Mangroves: Coastal ecosystems found in tropical and subtropical regions, mangroves are crucial for protecting shorelines and supporting marine life.
These examples highlight the importance of preserving ecosystem diversity to ensure the health and survival of our planet.

Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
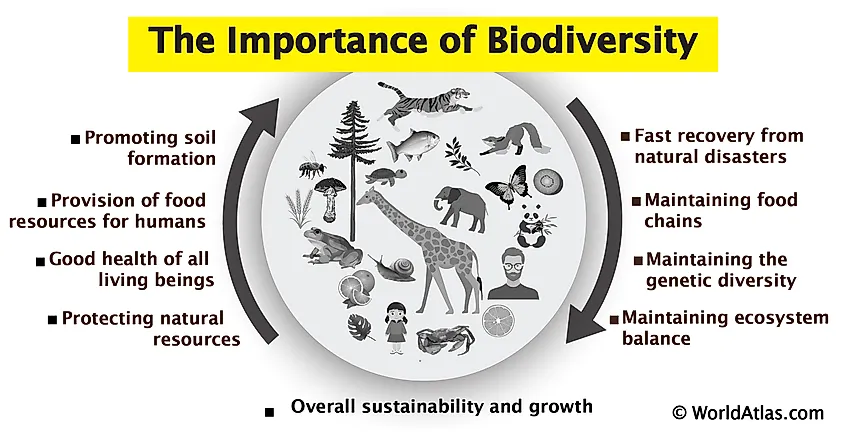
Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the balance of the planet"s environments and life forms. It offers a myriad of benefits, from supporting basic life processes to providing economic and cultural values. Here"s why ecosystem diversity is so important:
- Supports Biodiversity: Diverse ecosystems create habitats for a wide range of species, contributing to genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
- Ensures Natural Sustainability: Healthy ecosystems perform essential services like purifying air and water, pollinating crops, and decomposing wastes, which are vital for life on Earth.
- Provides Resources: Ecosystems supply a wealth of resources such as food, fiber, medicine, and materials that humans rely on for survival and economic activities.
- Regulates Climate: Ecosystems like forests and oceans play a key role in regulating the Earth"s climate by sequestering carbon dioxide and influencing local weather patterns.
- Cultural and Recreational Value: Many ecosystems offer spiritual, educational, and recreational benefits, enhancing human well-being and cultural heritage.
- Resilience to Environmental Changes: A diverse range of ecosystems can better withstand and recover from natural disasters and human-induced changes, ensuring ecological stability.
Preserving ecosystem diversity is therefore essential for sustaining the planet"s health, ensuring the well-being of all its inhabitants, and maintaining the natural systems upon which life depends.
Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is under threat from a variety of human activities and environmental changes. These threats not only endanger the habitats and species within these ecosystems but also compromise the essential services they provide to humanity and the environment. Key threats include:
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture expansion lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, one of the primary threats to biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events disrupt ecosystems, affecting their ability to support life.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources can degrade ecosystems and harm the species that depend on them.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable harvesting of resources, such as overfishing and logging, depletes populations and alters ecosystem structures.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predation, or bring diseases to native species, significantly altering ecosystem dynamics.
- Land Use Change: Converting natural habitats into urban or agricultural areas reduces the space available for native species and ecosystems.
Addressing these threats requires coordinated global efforts, including conservation, sustainable management practices, and policies aimed at protecting the planet"s vital ecosystem diversity.

Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are crucial in protecting ecosystem diversity and ensuring the sustainability of our planet for future generations. These efforts range from local initiatives to global agreements, all aimed at preserving the natural world. Here are some key conservation strategies:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats and species.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate pollution, and manage natural resources sustainably.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and coral reef restoration to restore biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in preserving natural resources.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and protect biodiversity.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research and monitoring ecosystems to understand their health, threats they face, and effectiveness of conservation measures.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation projects and agreements, recognizing that ecosystem diversity and environmental challenges are global issues.
Through these and other efforts, conservation aims to balance human needs with the protection of the natural world, ensuring the preservation of ecosystem diversity for the health of the planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Examples: Watch this captivating video filled with amazing examples that will broaden your knowledge and leave you inspired. From jaw-dropping feats to incredible achievements, these examples showcase the limitless capabilities of the human mind.
Exploring Ecosystem Diversity
Exploring: Embark on an extraordinary journey of exploration with this captivating video. Discover new horizons, immerse yourself in uncharted territories, and witness breathtaking discoveries that will ignite your curiosity and fuel your desire for adventure.
Case Studies on Ecosystem Diversity
Exploring case studies on ecosystem diversity reveals the complex interactions within ecosystems and the impacts of human activities on them. These studies offer insights into the importance of conservation and sustainable practices. Here are several notable examples:
- The Amazon Rainforest: Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," this case study highlights the critical role of tropical rainforests in global biodiversity and climate regulation, as well as the threats from deforestation and climate change.
- The Great Barrier Reef: This study examines the world"s largest coral reef system, its significance to marine biodiversity, and the challenges it faces from coral bleaching, ocean acidification, and pollution.
- The Serengeti-Mara Ecosystem: An example of grassland ecosystems, focusing on the annual wildebeest migration, its significance for biodiversity, and the pressures from human encroachment and climate variability.
- The Galápagos Islands: Showcasing unique species and evolutionary processes, this case study emphasizes the importance of isolation in ecosystem diversity and the impacts of invasive species and tourism.
- The Arctic Tundra: Highlighting the effects of climate change on cold ecosystems, including permafrost thawing, changes in species distribution, and challenges for indigenous communities.
These case studies underscore the need for targeted conservation efforts and sustainable management to protect ecosystem diversity and the services it provides.

READ MORE:
Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on the actions taken today to mitigate threats and promote conservation. While challenges are significant, there is hope for preserving and enhancing ecosystem diversity through collective efforts. Here are key points shaping the future:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting climate-resilient practices are critical for protecting ecosystems from the adverse effects of climate change.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating biodiversity conservation into economic development plans to ensure ecosystems are preserved and restored for future generations.
- Innovative Conservation Strategies: Utilizing technology and science to enhance conservation efforts, including habitat restoration, genetic diversity preservation, and the creation of wildlife corridors.
- Global and Local Partnerships: Strengthening collaboration between governments, NGOs, indigenous communities, and the private sector to implement effective conservation measures.
- Public Awareness and Education: Increasing awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity and encouraging public participation in conservation activities.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing stronger policies and regulations that protect ecosystems and biodiversity at both national and international levels.
Optimism for the future of ecosystem diversity is grounded in our growing understanding of the importance of biodiversity and the increasing commitment to sustainable practices worldwide. The continued dedication to conservation and sustainable management is essential for ensuring the health and diversity of ecosystems for future generations.
Embracing the richness of ecosystem diversity illuminates the path to a sustainable future, inspiring collective action to protect our planet"s invaluable natural heritage for generations to come.