Topic diverse ecosystem definition: Discover the essence of diverse ecosystems, their critical role in Earth"s balance, and how they underpin the survival and prosperity of all living beings.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of a diverse ecosystem?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Importance
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Environmental Stability
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Examples of Diverse Ecosystems Around the World
- Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
- The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
What is the definition of a diverse ecosystem?
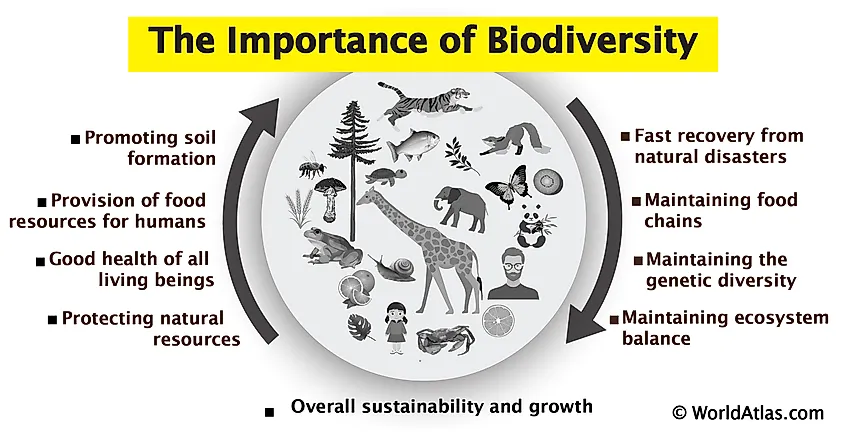
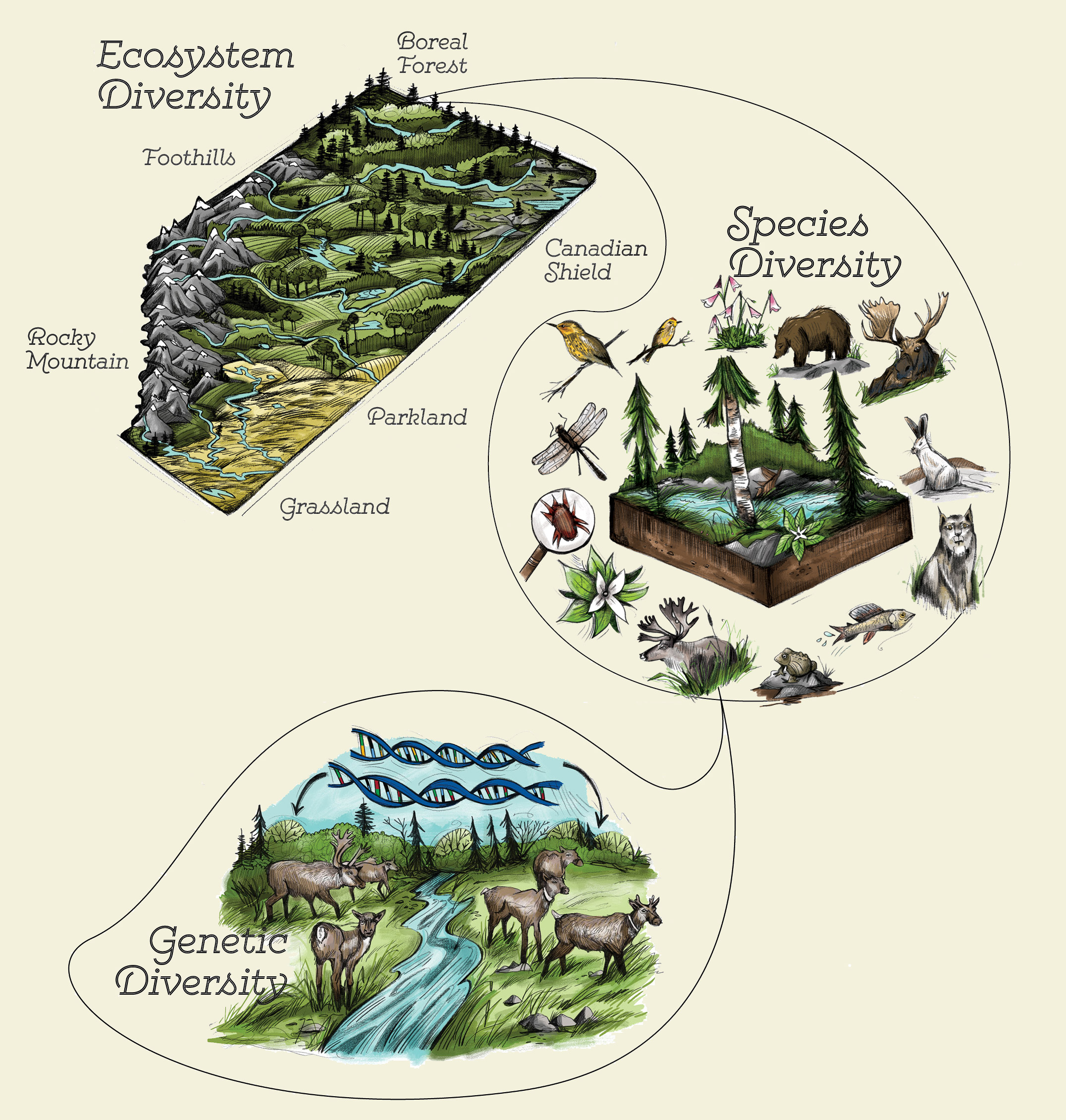
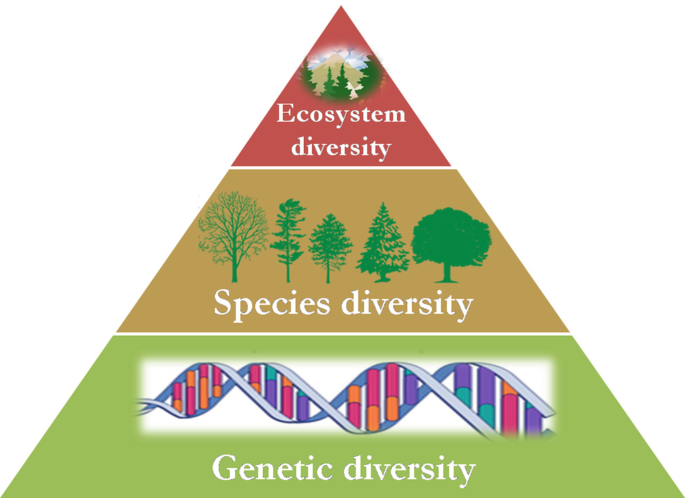
A diverse ecosystem refers to an environment that contains a wide range of different species, habitats, and ecological processes. It is characterized by high biodiversity, both in terms of the number of species present and the variety of genetic, functional, and ecological roles they play.
Diverse ecosystems have a multitude of interconnected relationships among different organisms and their physical surroundings. These relationships contribute to the stability and resilience of the ecosystem, as well as the provision of numerous ecosystem services such as carbon storage, nutrient cycling, water purification, and habitat provisioning.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the definition of a diverse ecosystem:
- An ecosystem is a complex community of living organisms (biotic factors) and their physical environment (abiotic factors).
- Diversity in an ecosystem refers to the variety of different species, habitats, and ecological processes present within it.
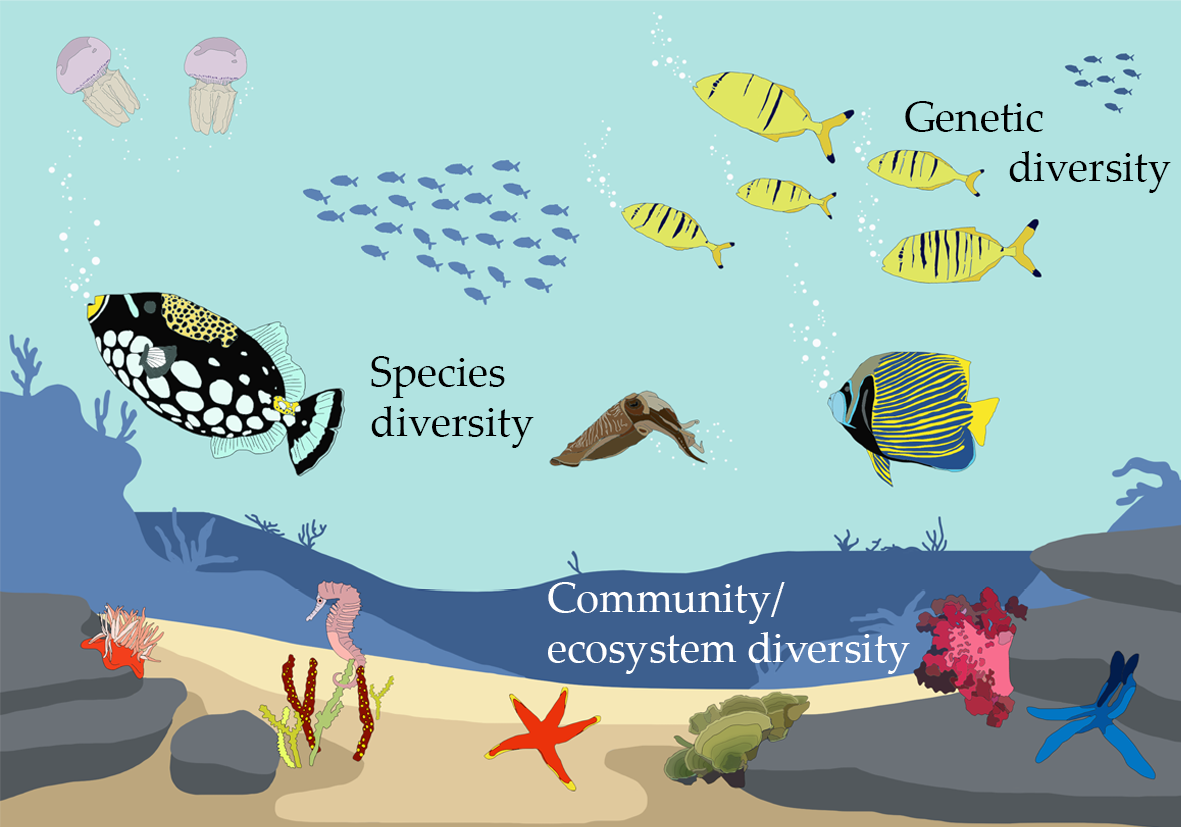
- Biodiversity encompasses the number of different species (species richness) as well as the variety of genetic, functional, and ecological characteristics among them.
- Habitat diversity refers to the range of different physical conditions, such as temperature, moisture levels, and topography, that exist within the ecosystem and provide diverse niches for different species.
- Ecological processes include interactions between species, energy flow through food webs, and nutrient cycling.
- A diverse ecosystem is characterized by high levels of biodiversity, both in terms of the number of species and the variety of genetic, functional, and ecological roles they play.
- Such ecosystems have a greater capacity to withstand disturbances, adapt to changes, and maintain functioning over time.
- They provide a wide range of ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being, including the provision of food, clean water, climate regulation, and cultural and recreational values.
In summary, a diverse ecosystem is a complex and interconnected web of life, featuring a wide array of species, habitats, and ecological processes. It is essential for the health and functioning of the planet and supports numerous benefits for both humans and the environment.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of environments, living organisms, and the complex interactions within and among these systems across the Earth. It"s a fundamental component of Earth"s overall biodiversity, including not just the range of ecosystems but also the genetic diversity within species and the variety of species themselves. This diversity ensures natural sustainability for all living things and provides the essential services that support life, including air and water purification, pollination of crops, and climate regulation.
- The variety of ecosystems includes forests, deserts, wetlands, grasslands, oceans, and coral reefs, each supporting unique communities of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Ecosystem diversity is measured in terms of the variety of habitats, the number of species, and the range of ecological processes, including energy flow and nutrient cycling.
- This diversity plays a critical role in maintaining the resilience and adaptive capacity of the environment, helping ecosystems withstand and recover from disturbances.
- Conservation efforts focus on protecting ecosystem diversity to ensure the long-term health of our planet and the well-being of people who depend on these systems for resources, livelihoods, and quality of life.
Understanding ecosystem diversity is crucial for developing strategies for its conservation and sustainable use, highlighting the interconnectedness of all living organisms and their environments.

Types of Ecosystems and Their Importance
Ecosystems are broadly categorized into two types: terrestrial and aquatic. Each type plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance and offers essential resources for human survival and biodiversity conservation.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These include forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundra, each characterized by distinct climates, vegetation types, and animal species. Forests are crucial for carbon sequestration, grasslands for soil preservation and supporting herbivores, deserts for unique biodiversity adaptations, and tundra for permafrost research.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Divided into freshwater (lakes, rivers, and wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs) ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems are vital for drinking water, agriculture, and habitat diversity, while marine ecosystems regulate climate, support a vast array of life, and drive global economic activities like fishing and tourism.
Each ecosystem type not only supports a wealth of biodiversity but also provides critical ecosystem services such as air and water purification, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. The importance of preserving these ecosystems cannot be overstated, as they are foundational to human health, economic prosperity, and environmental sustainability.
Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is influenced by a variety of natural and human-induced factors that affect the complexity and richness of biological communities. Understanding these factors is essential for effective conservation strategies.
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight play a critical role in shaping ecosystems. Different climates support different types of ecosystems, from lush rainforests to arid deserts.
- Geography: Geographic features such as mountains, rivers, and soil types determine the distribution of flora and fauna, influencing ecosystem diversity.
- Altitude: Ecosystems vary with altitude, from lowland tropical forests to high-altitude tundra, each supporting unique species adapted to their environments.
- Human Activities: Urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution significantly alter habitats, reduce biodiversity, and influence ecosystem dynamics.
- Biological Interactions: Predation, competition, and symbiosis among species affect ecosystem structure and function, promoting diversity through ecological niches.
Preserving ecosystem diversity requires addressing these factors through sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and global cooperation to mitigate human impacts and protect natural habitats.
Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Environmental Stability
Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining environmental stability, supporting life on Earth through a variety of mechanisms. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it affects everything from local weather patterns to global climate regulation.
- Supports Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand environmental stressors and disturbances, such as natural disasters or human activities, thereby maintaining ecological balance.
- Ensures Sustainable Services: A variety of ecosystems means a broader range of ecosystem services, including water filtration, air purification, carbon sequestration, and soil fertility, which are essential for human survival.
- Promotes Biodiversity: Ecosystem diversity creates habitats for a wide range of species, contributing to genetic diversity which is crucial for adaptation and evolution.
- Regulates Climate: Ecosystems like forests and oceans play key roles in carbon cycling and storage, helping to regulate the Earth"s climate and mitigate climate change.
- Supports Pollination and Food Production: Various ecosystems support pollinators and other species that are vital for food production and agricultural productivity.
By preserving ecosystem diversity, we ensure environmental stability, which is fundamental for the health of the planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have profound impacts on ecosystem diversity, some of which threaten the very fabric of global biodiversity. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing measures to protect and preserve ecosystem health.
- Deforestation: The removal of forests for agriculture, logging, and development reduces habitat diversity, leading to species loss and altered ecosystem functions.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources degrade ecosystems, affecting species health and reducing biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting habitat suitability for many species and leading to shifts in biodiversity distribution.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at unsustainable rates deplete species and disrupt food webs, impacting ecosystem balance.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can outcompete, predominate, and destabilize native species and ecosystems.
- Land Use Change: Converting natural habitats into urban or agricultural areas fragments ecosystems, reducing their size and connectivity, which diminishes species diversity and resilience.
Addressing these impacts requires concerted global efforts towards sustainable development, conservation initiatives, and policies that promote environmental stewardship and biodiversity protection.

Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
Conservation of ecosystem diversity is vital for maintaining the planet"s health and ensuring sustainable resources for future generations. A variety of strategies and initiatives are being employed globally to protect and restore ecosystems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, nature reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats and species from human activities.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and coral reefs to restore their ecological functions and biodiversity.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts to ensure sustainable land use and protect indigenous knowledge.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to minimize environmental impact and preserve biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate pollution, and manage natural resources sustainably.
- International Agreements: Participating in global agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) to commit to biodiversity conservation and sustainable development goals.
- Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity and how individuals can contribute to its conservation.
Through these and other efforts, we can hope to mitigate the impacts of human activity on ecosystems and preserve the diversity that is essential for life on Earth.
Ecosystem Diversity
Explore the beauty of diversity in this captivating video that celebrates the many cultures, traditions, and perspectives that make our world so fascinating and vibrant. Discover the power of embracing our differences and learn how they can bring us together as one global community.
Nature World
Immerse yourself in the breathtaking wonders of nature with this awe-inspiring video that showcases the mesmerizing landscapes, majestic creatures, and awe-inspiring phenomena that our planet has to offer. Journey through lush forests, towering mountains, and crystal-clear waters, and witness the incredible harmony and resilience of the natural world.
Examples of Diverse Ecosystems Around the World
The Earth is home to a vast array of ecosystems, each unique in its biodiversity and ecological functions. Here are examples of some of the most diverse and vital ecosystems found around the globe.
- Amazon Rainforest, South America: Known as the "lungs of the Earth," this tropical rainforest boasts the highest biodiversity in the world, housing millions of species of plants, animals, and insects.
- Great Barrier Reef, Australia: The world"s largest coral reef system, providing habitat for thousands of marine species, including fish, corals, and birds.
- Serengeti Plains, Africa: Famous for its annual wildebeest migration, the Serengeti is a vast ecosystem that supports a wide range of wildlife, from lions and elephants to giraffes and zebras.
- Arctic Tundra, Polar Regions: Characterized by its cold, desert-like conditions, the tundra supports unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme temperatures, including polar bears and arctic foxes.
- Sundarbans Mangrove Forest, South Asia: The largest tidal halophytic mangrove forest in the world, crucial for protecting coastal areas from erosion and home to the Bengal tiger.
- Galápagos Islands, Ecuador: This volcanic archipelago is renowned for its endemic species, which played a key role in the development of Darwin"s theory of evolution by natural selection.
These examples highlight the incredible diversity of ecosystems on our planet, each playing a critical role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life.
Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
While the importance of preserving ecosystem diversity is widely recognized, several challenges complicate these conservation efforts. Addressing these issues is crucial for the sustainability of our planet"s ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Global warming and changing weather patterns threaten ecosystems by altering habitats, leading to species migration and extinction.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture expansion result in the loss of habitats and the fragmentation of ecosystems, which diminishes biodiversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources contaminate ecosystems, affecting the health and survival of species.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced by human activity can outcompete, prey upon, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balances.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable extraction of resources, including logging, fishing, and hunting, depletes populations and alters ecosystem structures.
- Lack of Public Awareness: Insufficient understanding and appreciation of the value of biodiversity and ecosystem services among the public and policymakers hinder conservation efforts.
- Political and Economic Constraints: Conservation often competes with other land uses that are prioritized for their immediate economic benefits, making sustainable practices challenging to implement.
Overcoming these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including stronger environmental policies, international cooperation, scientific research, and community engagement.
READ MORE:
The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on the actions taken today to conserve and restore natural habitats. With concerted efforts from individuals, communities, and governments worldwide, there is hope for maintaining and enhancing the richness of life on Earth.
- Increased Conservation Initiatives: Expanding protected areas and investing in ecosystem restoration projects are critical for preserving biodiversity.
- Climate Action: Global efforts to combat climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy, are vital for protecting ecosystems.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fisheries will reduce human impact on natural environments and support ecosystem health.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in science and technology offer new ways to monitor and protect ecosystems, including remote sensing and bioengineering.
- Education and Awareness: Enhancing public understanding of the importance of ecosystem diversity through education can drive support for conservation efforts.
- International Cooperation: Global challenges require global solutions. International agreements and collaborations are essential for addressing threats to ecosystem diversity.
The preservation of ecosystem diversity is not only a moral imperative but also a practical necessity for sustainable development and the well-being of future generations. Optimism, action, and resilience can shape a future where ecosystem diversity thrives.
Embracing the beauty and necessity of diverse ecosystems is key to our planet"s future. Let"s commit to preserving this richness for the health, prosperity, and legacy of generations to come.