Topic biodiversity ecosystem diversity: Explore the wonders of biodiversity ecosystem diversity, where the intricate balance of life showcases the earth"s incredible natural variety and the vital importance of preserving this richness for future generations.
Table of Content
- How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the overall biodiversity of a geographic location?
- Understanding Biodiversity and Ecosystem Diversity
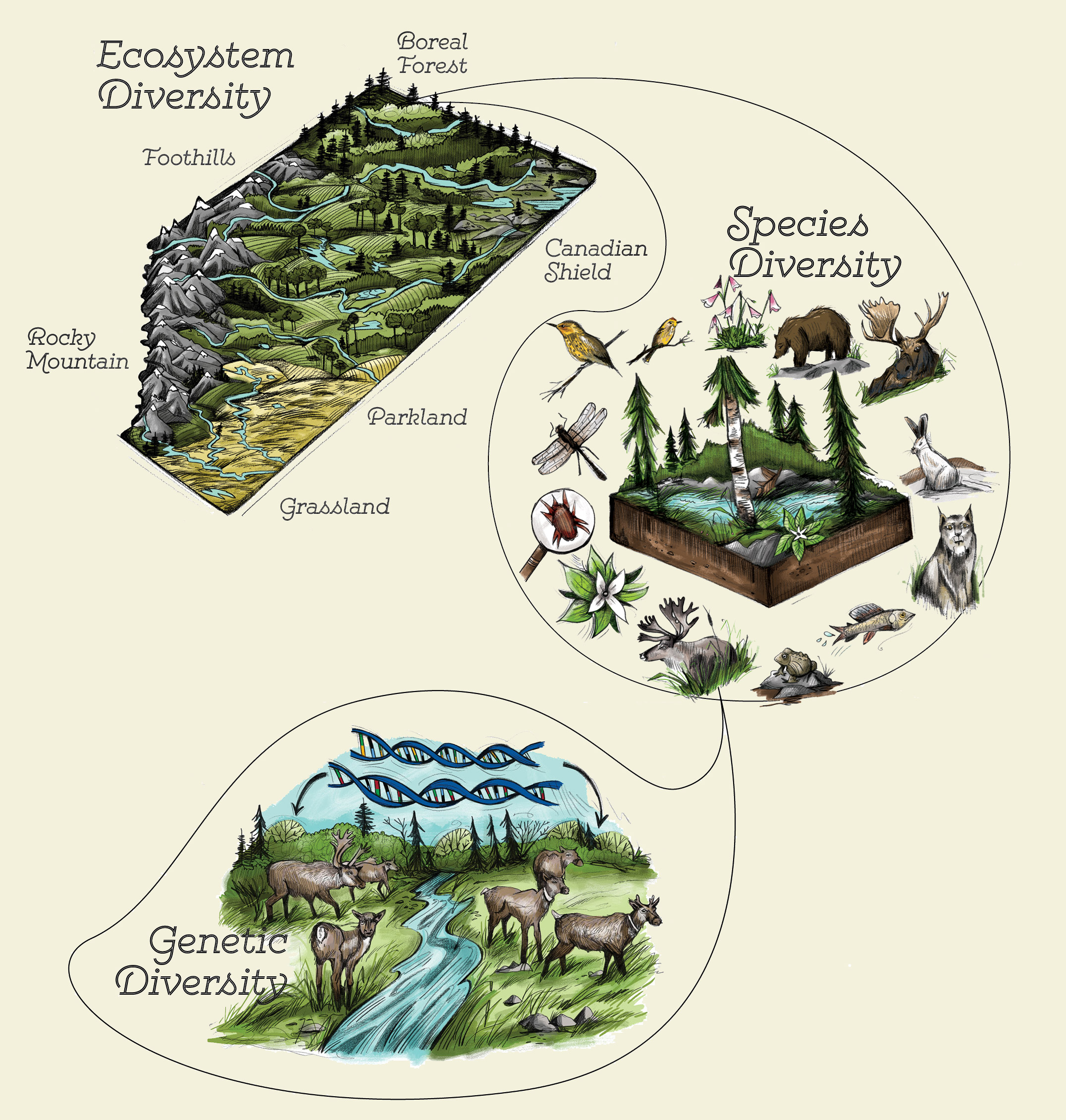
- Types of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Diversity
- The Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Examples of Ecosystem Diversity: From Terrestrial to Aquatic
- Threats to Biodiversity and Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Protecting Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- The Role of Ecosystem Services in Human Well-being
- Global Initiatives and Policies for Biodiversity Conservation
- Emerging Research and Innovations in Biodiversity
- Community Involvement and Education in Biodiversity Conservation
How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the overall biodiversity of a geographic location?
Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in supporting and maintaining overall biodiversity in a geographic location. Here is how it contributes:
- Provides a Variety of Habitats: Ecosystem diversity encompasses different types of habitats, such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, and marine environments. Each habitat supports a unique set of species, allowing for a wide range of biodiversity.
- Supports Different Communities: Within each habitat, various communities of organisms coexist. These communities consist of different species, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. Ecosystem diversity ensures the presence of diverse communities, thereby promoting overall biodiversity.
- Enhances Species Richness: A higher number of ecosystems in a geographic location leads to increased opportunities for different species to thrive. This increases species richness and contributes to overall biodiversity.
- Facilitates Interactions and Dependencies: Ecosystem diversity fosters complex ecological interactions and dependencies among species. These interactions include predation, symbiosis, and competition. By facilitating these connections, ecosystem diversity supports the overall maintenance of biodiversity.
- Promotes Genetic Diversity: Genetic diversity, an essential component of biodiversity, is influenced by ecosystem diversity. By providing a range of habitats and communities, ecosystems create opportunities for species to adapt and evolve, leading to greater genetic diversity.
- Provides Ecosystem Services: Each ecosystem contributes to the overall functioning of the environment through ecosystem services such as air and water purification, pollination, and soil fertility. These services are crucial for the survival and well-being of organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity.
Thus, ecosystem diversity is integral to the overall biodiversity of a geographic location, supporting a wide array of habitats, communities, species, and ecological processes.
READ MORE:
Understanding Biodiversity and Ecosystem Diversity
Biodiversity, or biological diversity, refers to the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the differences among organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part. Ecosystem diversity, a crucial aspect of biodiversity, involves the variety of habitats, natural communities, and ecological processes in the living world, as well as the diversity within species, between species, and of ecosystems.
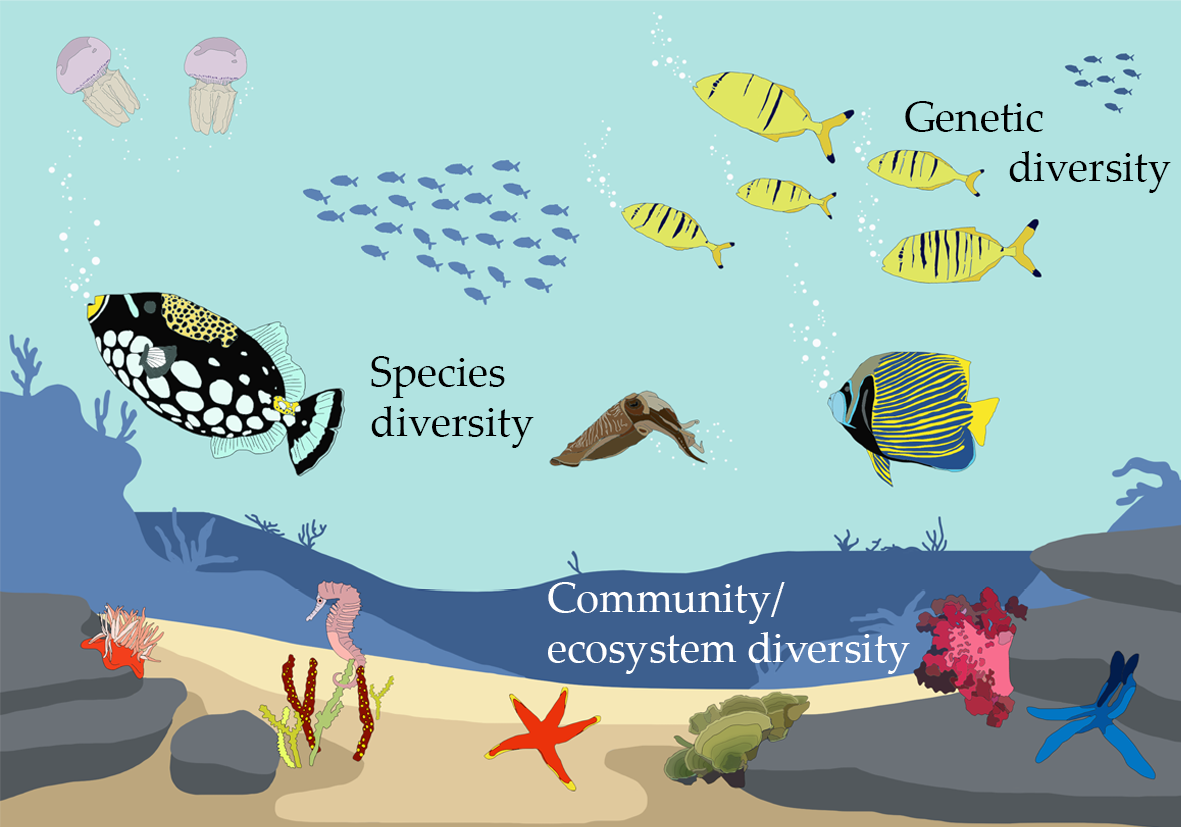
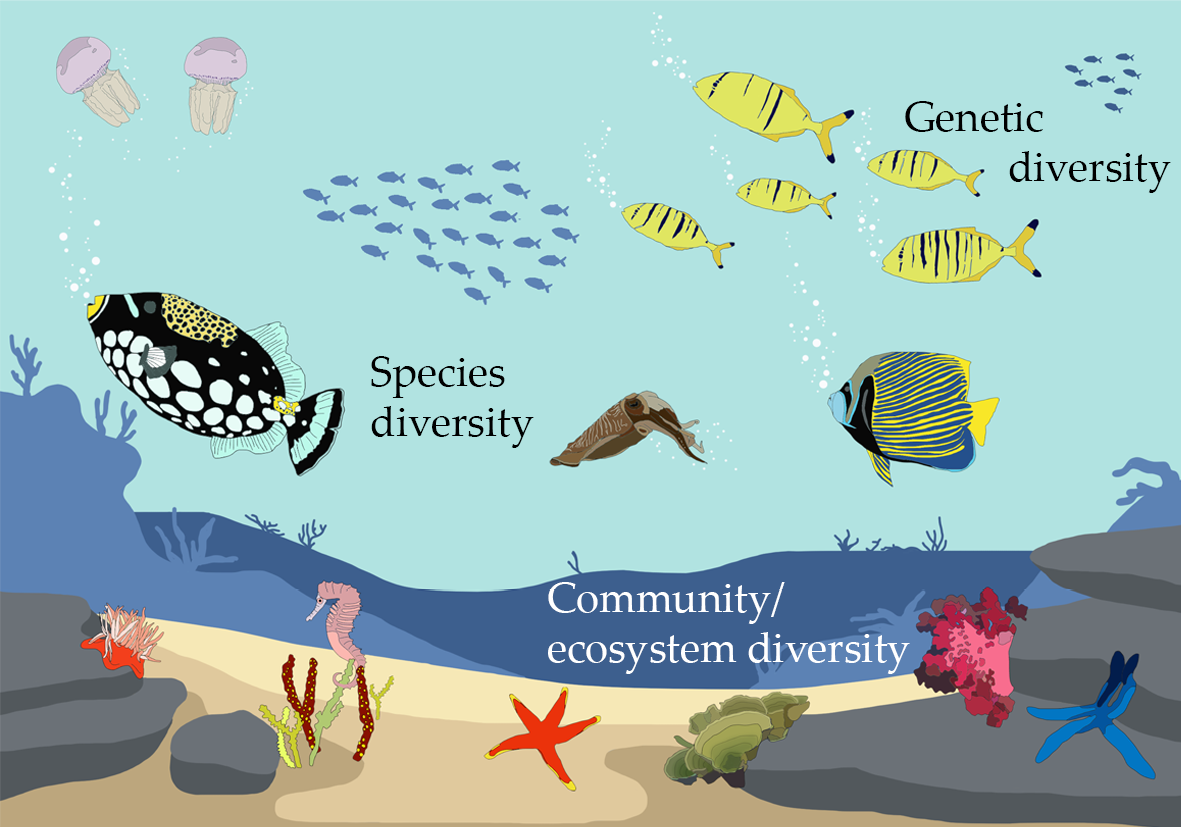
- Species Diversity: This refers to the variety of species within a habitat or a region. It includes the number of species and their relative abundance.
- Genetic Diversity: This aspect highlights the genetic variation within and between populations of species. It is crucial for species" adaptability to changing environments.
- Ecosystem Diversity: It encompasses the broad range of ecosystems found within an area, each with its own network of organisms and environmental conditions.
Ecosystem diversity not only adds to the Earth"s biodiversity but also supports multiple ecosystem services essential for human survival, including air and water purification, pollination of crops, climate regulation, and the cycling of nutrients. Understanding and preserving biodiversity and ecosystem diversity is vital for sustaining the natural environment for future generations.

Types of Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Diversity
Biodiversity is a complex and vibrant feature of our planet, crucial for the survival and resilience of ecosystems. It can be categorized into three primary types, each playing a unique role in maintaining the ecological balance and supporting life in myriad forms.
- Genetic Diversity: This refers to the variation of genes within species. It encompasses the differences in DNA among individuals of a species, which can lead to variations in traits such as size, color, and resistance to diseases. Genetic diversity is fundamental for a species" adaptability and survival in changing environments.
- Species Diversity: This dimension involves the variety of species within a particular habitat or the entire planet. It includes the number of different species (species richness) and their distribution or abundance (species evenness). Species diversity ensures ecosystem resilience, as diverse communities are better equipped to withstand environmental changes.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This type covers the diversity of ecosystems within a geographical location and includes forests, deserts, wetlands, mountains, lakes, rivers, and agricultural landscapes. Each ecosystem supports its own set of species and interactions among them, contributing to global biodiversity and offering a wide range of ecosystem services essential for human well-being, such as water filtration, oxygen production, and climate regulation.
Understanding the types of biodiversity is crucial for conservation efforts, as it highlights the importance of each level in sustaining life and the need for comprehensive strategies to protect our planet"s natural heritage.
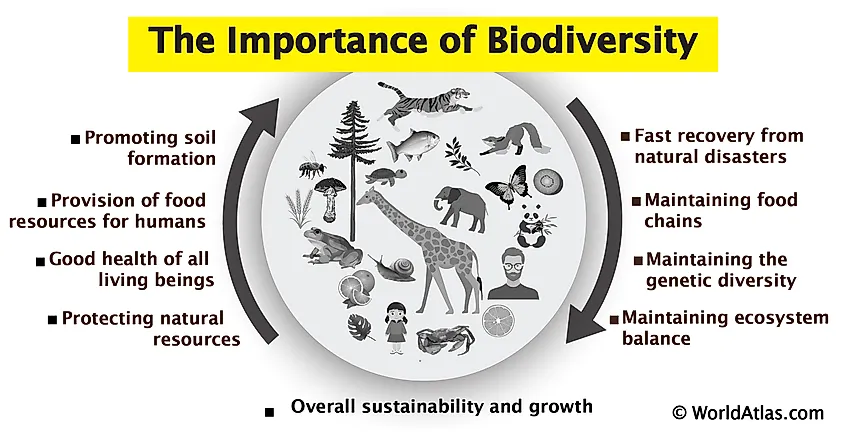
The Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity plays a critical role in maintaining the balance and health of our planet. It encompasses the variety of ecosystems within a region, each providing unique services and functions essential for the survival of life. Understanding the significance of ecosystem diversity helps in recognizing its value to humanity and the natural world.
- Supports a Wide Range of Life: Diverse ecosystems offer habitats for a wide variety of species, contributing to species and genetic diversity. This diversity within and across ecosystems is crucial for food security, medicinal resources, and the health of the global ecosystem.
- Ensures Natural Sustainability: Each ecosystem has its own natural processes, such as carbon and nitrogen cycling, water filtration, and soil formation, which are vital for the sustainability of life on Earth. The diversity in ecosystems ensures that these processes can occur under various conditions and locations.
- Provides Ecosystem Services: Ecosystems deliver essential services that benefit humanity, including provisioning (food, fresh water), regulating (climate regulation, disease control), supporting (nutrient cycling, oxygen production), and cultural (recreational, spiritual) services. The diversity of ecosystems enhances the resilience of these services.
- Buffers Against Environmental Changes: Ecosystem diversity acts as a natural buffer against environmental changes and disasters, reducing the impact of events such as floods, hurricanes, and droughts. A variety of ecosystems means that some can maintain their functions even when others are affected.
- Promotes Ecological Stability and Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to changes and disturbances, ensuring ecological stability over time. This resilience is crucial for adapting to climate change and recovering from natural and human-induced disturbances.
The importance of ecosystem diversity cannot be overstated, as it underpins the health of the planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants. Conserving ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of life and ensuring the survival of future generations.
Examples of Ecosystem Diversity: From Terrestrial to Aquatic
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the vast array of ecosystems that exist on our planet, from dry deserts to lush rainforests, from deep ocean trenches to sparkling freshwater lakes. Here are some examples that illustrate the richness and variety of ecosystems around the world, highlighting the importance of preserving this diversity.
- Tropical Rainforests: Located near the equator, these ecosystems are known for their high biodiversity, with millions of species of plants, animals, and insects. They play a crucial role in regulating global weather patterns and carbon dioxide levels.
- Coral Reefs: Often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," coral reefs provide habitat for approximately a quarter of all marine species. They are vital for marine life, protect coastlines from erosion, and support fishing industries.
- Deserts: Characterized by their dry conditions, deserts are home to a unique set of plants and animals adapted to survive with minimal water. They cover about one-fifth of the Earth"s surface and include both hot and cold environments.
- Grasslands: These areas, including savannas and prairies, are dominated by grasses and have fewer trees. They support a variety of wildlife and are important for agriculture and grazing.
- Wetlands: Including marshes, swamps, and bogs, wetlands are critical for water purification, flood protection, and providing habitat for birds and many other species.
- Temperate Forests: These forests experience four distinct seasons and are home to a wide variety of plants and animals. They are important for wood and paper products and provide recreational opportunities.
- Tundra: Found at the highest latitudes and altitudes, the tundra is a cold, treeless landscape where the subsoil is permanently frozen. It supports a community of hardy vegetation and wildlife.
- Freshwater Ecosystems: Including rivers, lakes, and streams, these ecosystems are vital sources of drinking water, support diverse life forms, and are key for agriculture and industry.
These examples highlight the incredible variety of ecosystems that exist on our planet, each playing a unique role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life. Preserving ecosystem diversity is essential for the health of our planet and the well-being of future generations.
Threats to Biodiversity and Ecosystem Diversity
Biodiversity and ecosystem diversity face numerous threats that can significantly impact their health and sustainability. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Here are some of the major challenges to biodiversity and ecosystem diversity:
- Habitat Destruction: The leading cause of biodiversity loss, habitat destruction includes deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion, leading to the fragmentation and loss of habitats for many species.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events disrupt ecosystems, affecting species" distribution, reproduction, and survival rates.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade ecosystems and harm or kill the species that inhabit them.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced to new areas can outcompete, prey upon, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem balance and reducing native biodiversity.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable logging, fishing, hunting, and harvesting of wild species reduce populations and genetic diversity, and can lead to species extinction.
- Pesticides and Chemicals: The use of pesticides and chemicals in agriculture can harm non-target species, pollute ecosystems, and reduce biodiversity.
- Land Use Changes: Converting natural habitats into agricultural or urban areas not only reduces the space available for wildlife but also alters the natural processes and services ecosystems provide.
Addressing these threats requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and policies that protect natural habitats and the species that depend on them. By taking action to mitigate these threats, we can preserve biodiversity and ecosystem diversity for future generations.

Conservation Strategies for Protecting Biodiversity
Protecting biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the survival of countless species, including humans. Effective conservation strategies are essential to safeguard our planet"s biodiversity. Here are several key approaches:
- Establishing Protected Areas: Designating national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve natural habitats and provide sanctuaries for species to live and reproduce without human interference.
- Restoring Damaged Ecosystems: Undertaking reforestation, wetlands restoration, and other ecosystem rehabilitation projects to restore biodiversity and ecological functions.
- Implementing Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable agriculture, forestry, fishing, and urban planning to reduce environmental impact and promote the conservation of resources and biodiversity.
- Combating Climate Change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing adaptation measures to protect ecosystems and biodiversity from the adverse effects of climate change.
- Controlling Invasive Species: Managing or eradicating invasive species to protect native biodiversity and prevent ecosystem disruption.
- Legislation and Policies: Enacting and enforcing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate hunting and trade, and promote biodiversity conservation.
- Community Involvement and Education: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity through education and outreach programs.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, sharing knowledge, and resources to address global biodiversity challenges.
Through these and other strategies, it is possible to mitigate threats to biodiversity and ensure the preservation of the natural world for future generations. The collective effort of governments, organizations, communities, and individuals is vital for the success of biodiversity conservation.
Ecosystem Diversity
\"Dive into the mesmerizing world of biodiversity and unlock the secrets of nature\'s incredible variety! Watch this captivating video to witness the breathtaking beauty and importance of preserving and celebrating the diverse life forms that make our planet so magical.\"
Ecosystem Biodiversity
\"Discover the delicate balance of nature\'s masterpieces with this awe-inspiring video on ecosystems! Immerse yourself in the wonders of interconnected habitats, learn about the fascinating relationships between species, and unravel the mysteries behind the resilience of our planet\'s ecosystems.\"
The Role of Ecosystem Services in Human Well-being
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides to humanity, underpinning our well-being, economy, and survival. These services are crucial for making life on Earth possible and enjoyable. Here"s how ecosystem services contribute to human well-being:
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood and fiber, and other natural resources. They are the basis of most agricultural and industrial activities that support human survival and economic activities.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality among other environmental hazards. Healthy ecosystems help mitigate the impacts of natural disasters and disease outbreaks, protecting communities and supporting resilience.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production. These services enable the Earth to sustain basic life forms and contribute to the fertility and productivity of the environment.
- Cultural Services: Ecosystems provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits that contribute to human well-being. Natural landscapes and biodiversity are sources of inspiration, relaxation, and cultural identity.
The role of ecosystem services in human well-being is immense, offering both direct and indirect benefits that improve quality of life, support economic development, and ensure environmental sustainability. Recognizing and preserving these services through sustainable management and conservation efforts is essential for the health of the planet and the prosperity of future generations.

Global Initiatives and Policies for Biodiversity Conservation
Conserving biodiversity is a global imperative that requires coordinated international efforts and policies. Numerous global initiatives and policies have been established to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable development. Here are some of the key efforts:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): An international treaty with 196 parties aiming to conserve biological diversity, promote sustainable use of its components, and ensure fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Specifically, SDG 15 aims to protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, manage forests sustainably, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
- Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES): Provides assessments on biodiversity and ecosystem services for decision-makers, emphasizing the critical importance of biodiversity and ecosystems to human well-being and survival.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Regulates international trade in over 35,000 species of plants and animals, ensuring that such trade does not threaten their survival in the wild.
- World Conservation Strategy: Launched by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the strategy aims to promote the conservation of living resources crucial for human well-being and for maintaining ecological processes.
- Global Biodiversity Framework: Adopted by countries to guide actions worldwide through 2030 to preserve and protect nature and its essential services to people.
These initiatives and policies reflect the global consensus on the urgency of biodiversity conservation. They provide frameworks for action at international, national, and local levels, emphasizing the interconnectedness of human well-being, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
Emerging Research and Innovations in Biodiversity
The field of biodiversity is witnessing rapid advancements and innovations, driven by the urgent need to address the loss of biodiversity and to understand the complexities of ecosystems. Emerging research and technological breakthroughs are providing new ways to conserve and restore biodiversity. Here are some notable areas of innovation:
- Genetic and Genomic Technologies: Advances in genetic and genomic research are enhancing our understanding of species diversity and evolutionary relationships. This technology is being used for conservation genetics, to identify and protect endangered species, and to restore genetic diversity in populations.
- Bioinformatics and Data Science: The use of bioinformatics and big data analytics is revolutionizing biodiversity research by enabling the processing and analysis of vast amounts of ecological and genomic data. This helps in mapping and monitoring biodiversity at unprecedented scales.
- Remote Sensing and GIS Technologies: Satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS) are critical tools for tracking changes in land use, habitat loss, and ecosystem dynamics over time. They provide valuable data for conservation planning and management.
- Ecological Modelling and Simulations: Models and simulations are being developed to predict the impacts of climate change, land-use change, and other stressors on biodiversity. These tools are crucial for planning conservation strategies and assessing the efficacy of intervention measures.
- Conservation Drones and Automated Monitoring: Drones and automated sensors are increasingly used for wildlife monitoring, habitat mapping, and enforcing protected areas. They offer a non-invasive way to gather accurate data across large and inaccessible areas.
- Synthetic Biology and Biotechnology: These fields hold the potential for restoring species and habitats. For example, techniques like gene editing are being explored for potential use in conservation, such as controlling invasive species or enhancing the resilience of native species to environmental changes.
Emerging research and innovations in biodiversity are crucial for developing effective conservation strategies, restoring ecosystems, and ensuring the sustainable use of natural resources. As these technologies continue to evolve, they offer hope for reversing the trend of biodiversity loss and securing a sustainable future for our planet.

READ MORE:
Community Involvement and Education in Biodiversity Conservation
Engaging local communities and promoting education on biodiversity conservation are crucial for the sustainable management and protection of ecosystems. Empowering people with knowledge and involving them in conservation efforts can lead to more effective and long-lasting outcomes. Here"s how community involvement and education play a key role in biodiversity conservation:
- Community-Based Conservation Projects: Local communities often have traditional knowledge and a vested interest in the health of their surrounding ecosystems. Involving them in conservation projects, such as reforestation and wildlife monitoring, can leverage this knowledge for effective ecosystem management.
- Environmental Education Programs: Education initiatives that focus on the importance of biodiversity and ecosystems can raise awareness among the public and foster a sense of responsibility towards the environment. This includes programs in schools, community centers, and through media.
- Citizen Science Projects: Engaging the public in data collection and scientific research helps gather valuable information on biodiversity and fosters a deeper connection between individuals and their environment. Citizen science projects can range from bird counts to monitoring water quality.
- Ecotourism: Well-managed ecotourism initiatives can provide economic benefits to local communities while promoting conservation awareness. Visitors gain an appreciation for biodiversity, and revenues can be reinvested into conservation efforts.
- Policy and Decision-Making Involvement: Ensuring community voices are heard in policy and decision-making processes related to land use and natural resource management can lead to more sustainable outcomes and protect the rights and livelihoods of indigenous peoples and local communities.
- Conservation Awareness Campaigns: Campaigns that highlight the value of biodiversity and the steps individuals can take to protect it can mobilize community action and support for conservation initiatives.
Community involvement and education are fundamental to achieving biodiversity conservation goals. By fostering a collective understanding and appreciation of nature, we can encourage actions that contribute to the protection and restoration of our planet"s ecosystems.
In embracing the vital importance of biodiversity and ecosystem diversity, we forge a path toward a sustainable and flourishing future, highlighting our collective responsibility to cherish and protect our planet"s precious natural heritage.