Topic diversity in ecosystem: Explore the vibrant tapestry of life through "Diversity in Ecosystems", where each thread intertwines to create the dynamic, complex fabric of our planet"s biology and habitats.
Table of Content
- What is ecosystem diversity and how does it impact the stability of ecosystems?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Diversity
- Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Ecosystem Diversity Around the World
- Future Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
What is ecosystem diversity and how does it impact the stability of ecosystems?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and species present in a specific geographic location. It encompasses both the biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living factors like climate, soil, and topography) components of an ecosystem.
There are several ways in which ecosystem diversity impacts the stability of ecosystems:
- Enhanced resilience: Ecosystems with high diversity are generally more resilient and able to adapt to changes in their environment. This is because diverse ecosystems have a greater range of species with different traits, which allows them to respond to environmental disturbances effectively.
- Increased productivity: In diverse ecosystems, different species play unique roles, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and seed dispersal. This specialization leads to increased efficiency and productivity within the ecosystem, providing greater stability in terms of energy flow and resource availability.
- Better resistance to invasive species: High ecosystem diversity can act as a barrier against the establishment and spread of invasive species. In a diverse ecosystem, native species have a better chance of outcompeting invaders due to their specific adaptations and interactions with each other.
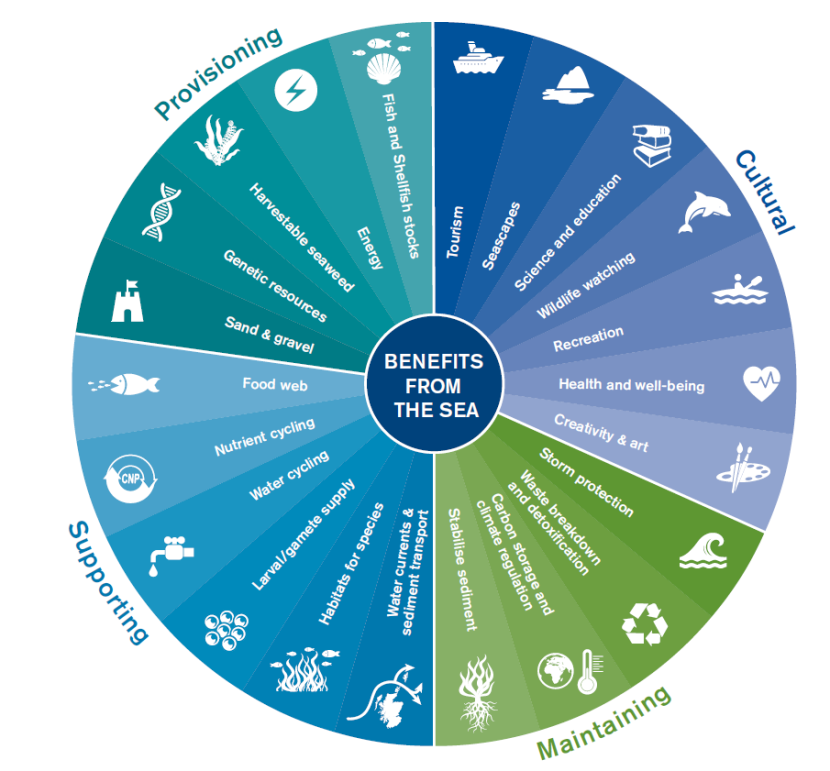
- Improved ecosystem services: Ecosystem diversity provides a wide range of ecosystem services, including air and water purification, soil formation, climate regulation, and flood control. These services contribute to the stability and functioning of ecosystems, benefiting both nature and human well-being.
In summary, ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the stability and functioning of ecosystems. It ensures that ecological processes are well-regulated and minimizes the risk of ecological collapse. By valuing and protecting the diversity of species and habitats, we can contribute to the conservation and sustainable management of ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
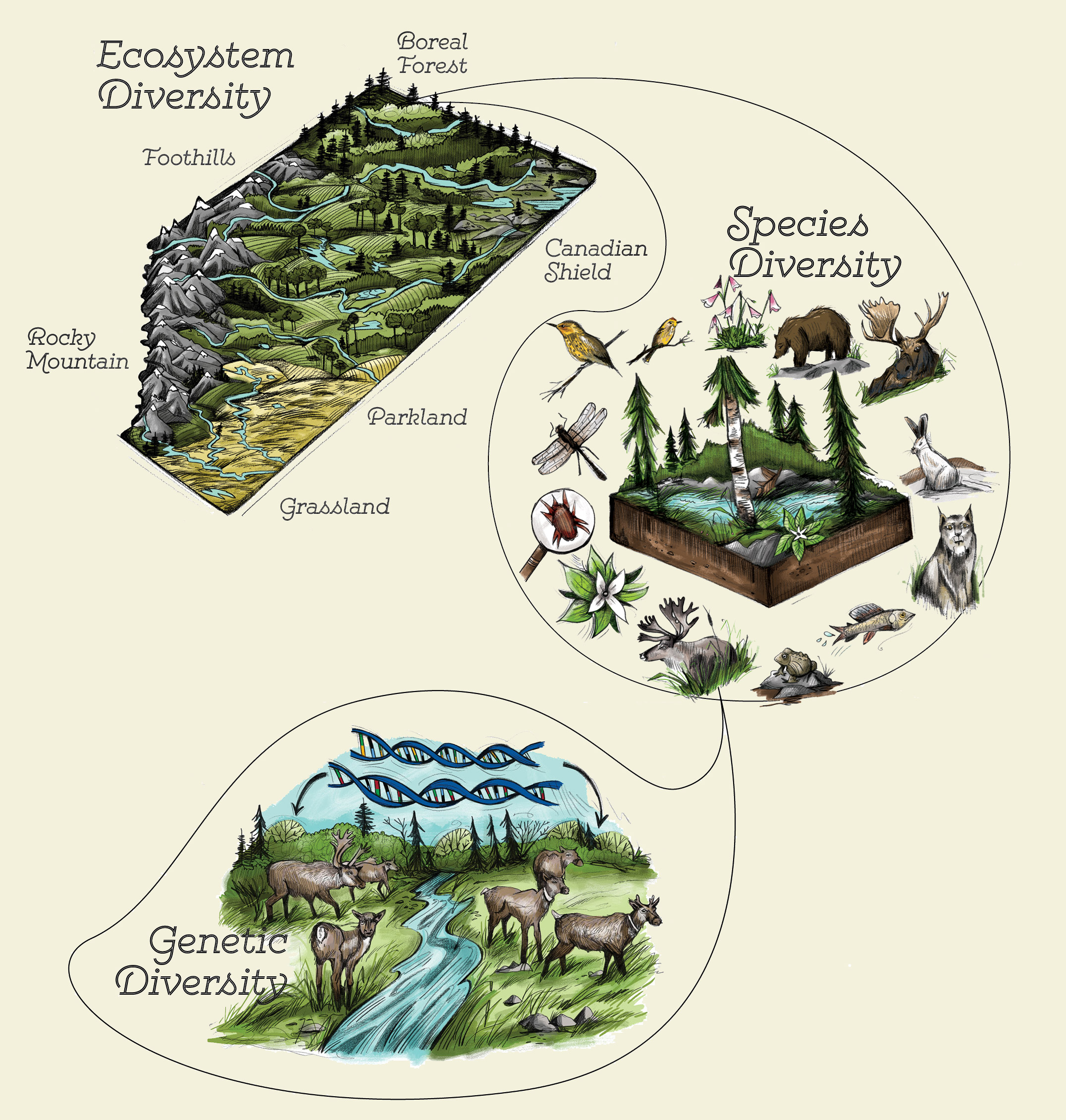
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of environments, living organisms, and the complex processes in the natural world, including their interactions and energy flow. It is a cornerstone of our planet"s health and stability, influencing everything from local climates to global biodiversity.
- Variety of Ecosystems: Includes forests, deserts, coral reefs, wetlands, and urban areas, each with unique species and ecological processes.
- Species Diversity: The range of different species within an ecosystem, contributing to its complexity and resilience.
- Genetic Diversity: The genetic variation within and between species, enabling adaptation and survival through changing conditions.
- Functional Diversity: The variety of processes such as energy flow and matter recycling that sustain ecosystems.
This diversity ensures ecosystem productivity, resilience, and adaptability, making it fundamental for ecosystem services that support life on Earth, including air and water purification, pollination of crops, and climate regulation.

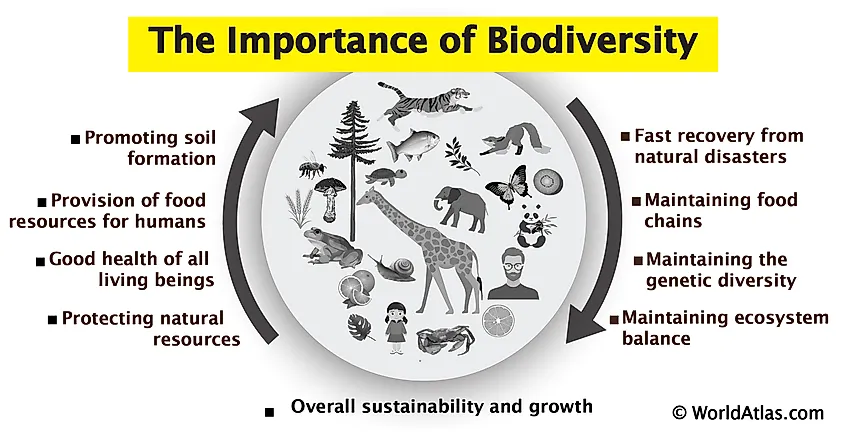
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is vital for the health and sustainability of our planet. It underpins the resilience of the environment, supporting all forms of life through a variety of services. Understanding its importance is key to preserving our natural world for future generations.
- Supports Biodiversity: A diverse range of ecosystems supports a wider variety of species, contributing to global biodiversity.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand and recover from environmental stresses, such as climate change and natural disasters.
- Provides Ecosystem Services: Essential services such as air and water purification, pollination of plants, and carbon sequestration are all supported by ecosystem diversity.
- Contributes to Human Wellbeing: Besides providing basic needs (food, clean water, and air), diverse ecosystems also offer cultural, aesthetic, and recreational benefits.
- Promotes Economic Benefits: Many industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, directly benefit from the goods and services provided by diverse ecosystems.
Preserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the balance of nature, ensuring the survival of species, and securing the well-being and prosperity of human societies across the globe.
Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is influenced by a combination of natural and anthropogenic factors. These factors shape the complexity, resilience, and productivity of ecosystems worldwide.
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations significantly affect ecosystem types and species distributions.
- Geography: Landforms, soil types, and water bodies determine the physical environment and habitats available for organisms.
- Altitude: Changes in altitude affect climate conditions, leading to different ecosystems at various elevations.
- Human Activities: Urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution drastically alter and often reduce ecosystem diversity.
- Biological Factors: Interactions among species, such as competition, predation, and symbiosis, influence the structure and function of ecosystems.
- Evolutionary Processes: Evolution through natural selection and genetic drift drives the emergence of new species and ecosystems over time.
Understanding these factors is crucial for the conservation and management of ecosystem diversity, ensuring the sustainability of environments and the services they provide to humanity.

Types of Ecosystems and Their Diversity
Ecosystems vary widely across the globe, each harboring unique forms of life and ecological processes. The diversity of these ecosystems is fundamental to the richness of life on Earth. Here are some of the main types of ecosystems and their characteristics.
- Forest Ecosystems: Including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests, these ecosystems are characterized by high levels of biodiversity and are crucial for carbon storage.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Covering freshwater (lakes, rivers, wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs) environments, aquatic ecosystems support diverse life forms and complex food webs.
- Desert Ecosystems: Found in arid regions, these ecosystems are adapted to extreme dry conditions, showcasing unique flora and fauna adapted to low water availability.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Including savannas and temperate grasslands, these areas are dominated by grasses and support a variety of large herbivores and predators.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Characterized by cold, dry conditions, the tundra is home to hardy species of plants and animals adapted to survive with minimal warmth and moisture.
- Urban Ecosystems: Human-made environments that incorporate natural, semi-natural, and artificial systems, urban ecosystems are increasingly recognized for their biodiversity and ecological services.
Each ecosystem type plays a vital role in the global ecosystem, contributing to Earth"s overall biodiversity and ecological balance.
Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems. The variety of life forms within a given ecosystem ensures its health and functioning, providing numerous benefits that are essential for life on Earth.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse ecosystems are more efficient at recycling nutrients, ensuring the sustainability of life processes.
- Pollination Services: A variety of insects and birds in biodiverse ecosystems enhances the pollination of plants, crucial for food production and maintaining healthy flora.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiversity can help regulate diseases by supporting a wide range of species, some of which can keep potential pests and pathogens in check.
- Climate Regulation: Ecosystems like forests and oceans play a key role in regulating the Earth"s climate by sequestering carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Resilience to Environmental Changes: Biodiverse ecosystems are better able to withstand environmental stress and recover more quickly from disturbances such as fires, storms, and human impacts.
The stability provided by biodiversity is not just crucial for ecosystems but also underpins human well-being, offering solutions to many of the challenges faced by society, including climate change, food security, and health.

Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
The impact of human activities on ecosystem diversity has been profound, with both negative and positive influences. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to protect and enhance ecosystem diversity.
- Deforestation: The removal of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban expansion reduces habitat for countless species and decreases biodiversity.
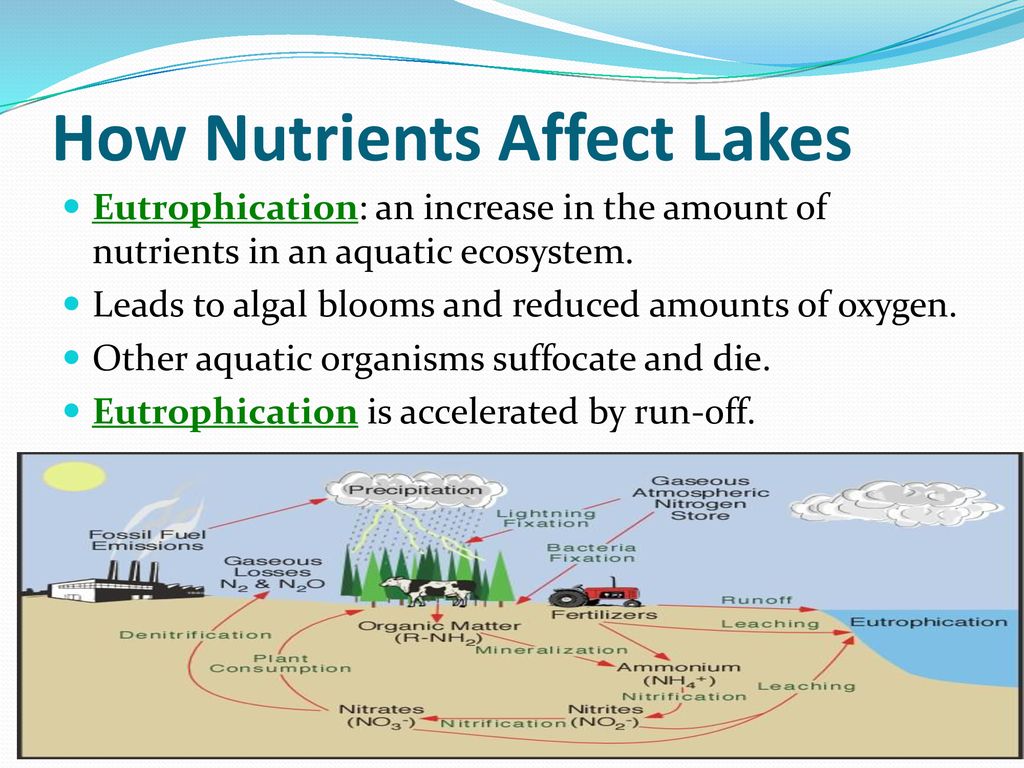
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade ecosystems, harming species and reducing biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects ecosystems globally, altering habitats, and threatening species with extinction.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompete native species, and reduce biodiversity.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable harvesting of resources, including fishing, hunting, and logging, can lead to the decline of species and ecosystem services.
- Conservation Efforts: Positive impacts include the establishment of protected areas, restoration projects, and sustainable management practices that help preserve and restore ecosystem diversity.
Addressing human impacts on ecosystem diversity requires concerted global efforts towards sustainable development, conservation, and restoration initiatives.
Ecosystem Diversity
Biodiversity: Discover the incredible world of biodiversity in our latest video! Join us as we explore the wonders of nature, showcasing the vast array of plant and animal species that make our planet so unique. Get ready to be amazed by the beauty and complexity of the natural world!
The Importance of Biodiversity
Importance: Uncover the true importance of our subject in this thought-provoking video. We delve into the significance of our topic, highlighting its crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance and providing essential resources for our survival. Prepare to gain a new appreciation for the impact this subject has on our lives and the planet as a whole.
Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Effective conservation strategies involve a combination of global, regional, and local efforts designed to protect, restore, and manage ecosystems wisely.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats and species.
- Restoration Projects: Restoring degraded ecosystems, such as reforestation projects and wetlands restoration, to revive biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and conserve biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and regulations to protect endangered species and habitats, control pollution, and manage natural resources sustainably.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their traditional knowledge and ensuring their benefits from conservation.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, such as biodiversity treaties and climate agreements, to address global environmental challenges.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research and monitoring ecosystems to inform conservation strategies and adapt them as necessary.
By integrating these strategies, we can work towards a more sustainable future, preserving the intricate mosaic of life that makes our planet unique.
Case Studies: Ecosystem Diversity Around the World
Ecosystem diversity is a global treasure, with examples from every corner of the planet illustrating the richness and complexity of nature. These case studies highlight the variety of ecosystems and the efforts to conserve them.
- The Amazon Rainforest: Home to about 10% of the world"s known species, this vast tropical rainforest showcases the importance of conserving biodiversity for ecological balance and human wellbeing.
- The Great Barrier Reef: The world"s largest coral reef system, located off the coast of Australia, is a marine biodiversity hotspot, facing threats from climate change, pollution, and overfishing.
- Serengeti National Park: This African savanna ecosystem is renowned for its large mammal migrations, demonstrating the interconnectedness of species and habitats.
- The Arctic Tundra: Characterized by its cold, dry conditions, the Arctic tundra supports unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme environments, highlighting the effects of climate change on ecosystem diversity.
- The Sundarbans Mangrove Forest: Located at the delta of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers on the Bay of Bengal, this forest is an example of a coastal ecosystem providing critical protection against flooding and habitat for diverse species.
These case studies underscore the urgent need for global conservation efforts to protect ecosystem diversity, ensuring the health and sustainability of our planet.
READ MORE:
Future Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
As we move forward, the preservation of ecosystem diversity faces numerous challenges. Addressing these will be crucial for maintaining the health and resilience of our planet.
- Climate Change: Rapid climate change poses a significant threat to ecosystems, altering habitats and species distributions faster than organisms can adapt.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Ongoing deforestation, urban expansion, and agriculture continue to degrade and fragment habitats, reducing biodiversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources continue to harm ecosystems and the species that depend on them.
- Invasive Species: The spread of non-native species can disrupt ecosystems, outcompete native species, and lead to biodiversity loss.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable extraction of natural resources, including logging, fishing, and hunting, threatens ecosystem health and biodiversity.
- Lack of Awareness and Engagement: Insufficient understanding and involvement by the public and policymakers can hinder conservation efforts.
- Need for Global Cooperation: Biodiversity conservation is a global issue that requires coordinated international efforts, which can be challenging to achieve.
Overcoming these challenges will require innovative solutions, increased public awareness, and strong political will, ensuring the preservation of ecosystem diversity for future generations.
Embracing the diversity of ecosystems enriches our planet, offering endless benefits and beauty. Together, we can preserve this precious diversity for future generations, fostering a healthier, more resilient Earth.