Topic explain ecosystem diversity: Explore the fascinating world of ecosystem diversity, where the variety of life interconnects to form the complex, vibrant tapestry that sustains our planet.
Table of Content
- What is ecosystem diversity and why is it important?
- What is Ecosystem Diversity?
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
- The Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
- Measuring Ecosystem Diversity
- Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
- The Role of Climate Change in Shaping Ecosystem Diversity
- Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
What is ecosystem diversity and why is it important?
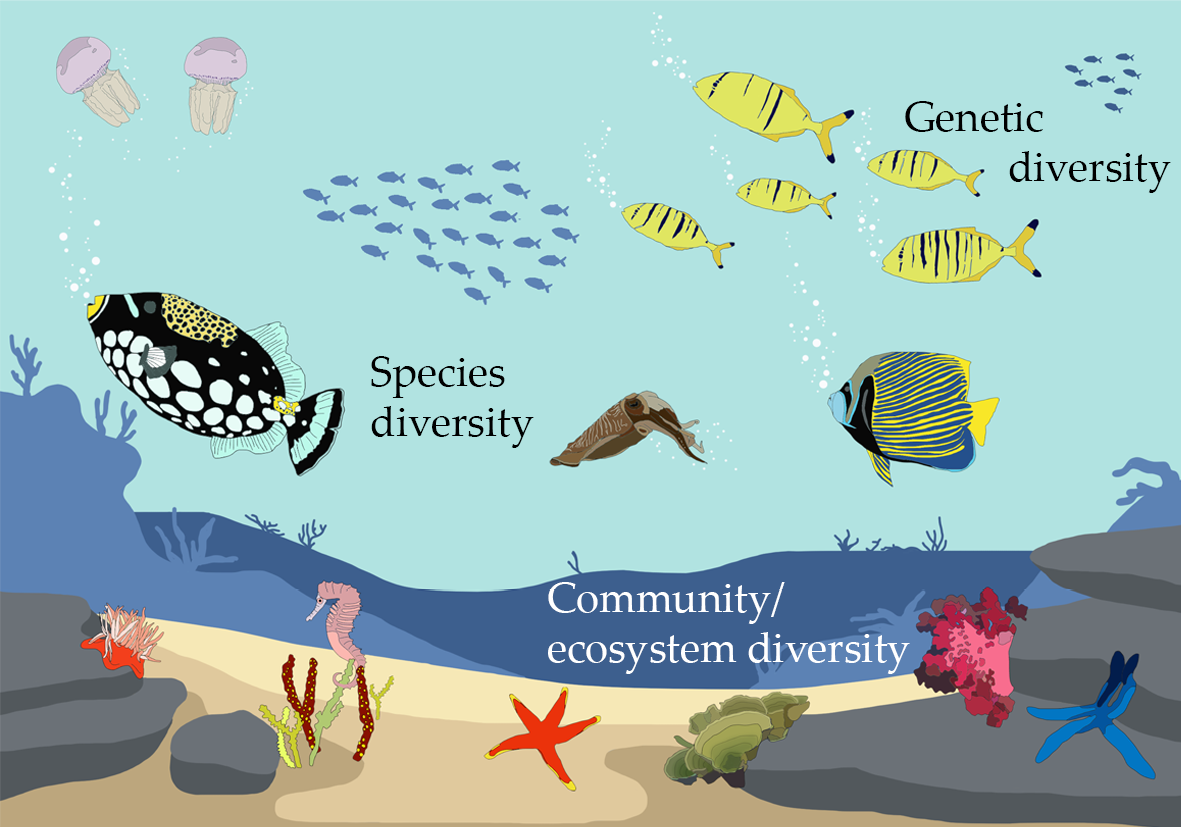
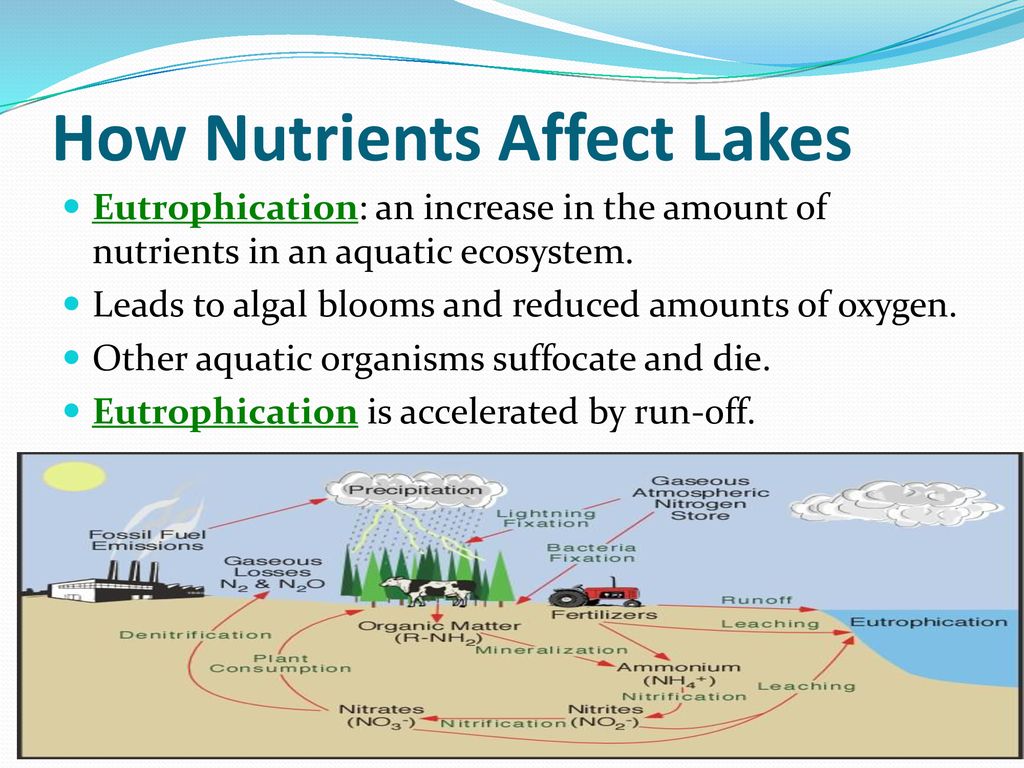
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems present in a particular geographic area or the entire planet. It encompasses different types of habitats, communities, and ecological processes that exist within these ecosystems.
Ecosystems are composed of various living organisms, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the non-living components of their environment, like soil, water, and climate. Ecosystem diversity highlights the differences in these components and their interactions across different ecosystems.
Here are some key points that explain the importance of ecosystem diversity:
- Promotes resilience: Ecosystems with high diversity are more resilient to disturbances and environmental changes. A variety of species within an ecosystem allows for greater adaptability and ensures functions and processes continue even if some species are affected.
- Enhances ecosystem services: Each ecosystem provides numerous services essential for human well-being, such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation. Ecosystem diversity contributes to an increased range and effectiveness of these services.
- Supports food security: Diversity in ecosystems enables a variety of plant and animal species to thrive, providing a more stable and reliable food supply. A loss of ecosystem diversity can lead to a decrease in available food sources.
- Preserves genetic diversity: Different ecosystems support the survival and evolution of distinct species with unique genetic characteristics. The preservation of ecosystem diversity is vital for maintaining genetic diversity, which is important for species adaptation and resilience.
- Provides cultural and recreational value: Ecosystems exhibit unique characteristics, scenic beauty, and biodiversity that have cultural and recreational significance. Preserving diverse ecosystems allows for the enjoyment and exploration of natural environments by people.
Overall, ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, supporting human well-being, and preserving the planet\'s natural heritage.
READ MORE:
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different habitats, natural communities, and ecological processes in the natural world. This diversity encompasses the variation in ecosystems within a geographical location and its overall impact on human existence and the global environment. It includes everything from large-scale ecosystems like forests, deserts, and coral reefs to smaller ecosystems such as ponds, streams, and even microenvironments like the soil.
- Variety of Habitats: Ranging from terrestrial and aquatic environments to deserts and forests, each with unique flora and fauna.
- Natural Communities: The complex interactions between different species, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
- Ecological Processes: Fundamental processes such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and decomposition that sustain life.
This diversity is crucial for the resilience and functionality of the Earth"s ecosystems, providing essential services for human survival, including clean air and water, fertile soil for agriculture, and the regulation of climate.

Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
Ecosystem diversity encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, each with distinct characteristics and life forms. Understanding these different types is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of our planet. Below are some of the major types of ecosystems and their unique features:
- Forest Ecosystems: Characterized by a high density of trees, these ecosystems are critical for carbon storage, biodiversity, and regulating global climate. They are subdivided into tropical, temperate, and boreal forests.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Including both freshwater (lakes, rivers, and wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries) environments, these ecosystems are vital for water regulation, providing habitat for marine life, and supporting fisheries.
- Desert Ecosystems: Defined by their dry conditions, deserts support a unique set of life forms adapted to low water availability. They are important for biodiversity and have a unique beauty.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants, grasslands are key for supporting a variety of wildlife, including many herbivores and their predators, and are crucial for agriculture.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Characterized by cold temperatures and short growing seasons, the tundra supports hardy species adapted to extreme conditions. It plays a significant role in global climate regulation.
- Urban Ecosystems: Human-made environments that include cities and towns. Despite being heavily modified by human activity, these ecosystems support a range of plants, animals, and microbes and are increasingly recognized for their biodiversity.
Each ecosystem type plays a crucial role in the global ecosystem, contributing to the Earth"s biodiversity, climate stability, and human well-being.
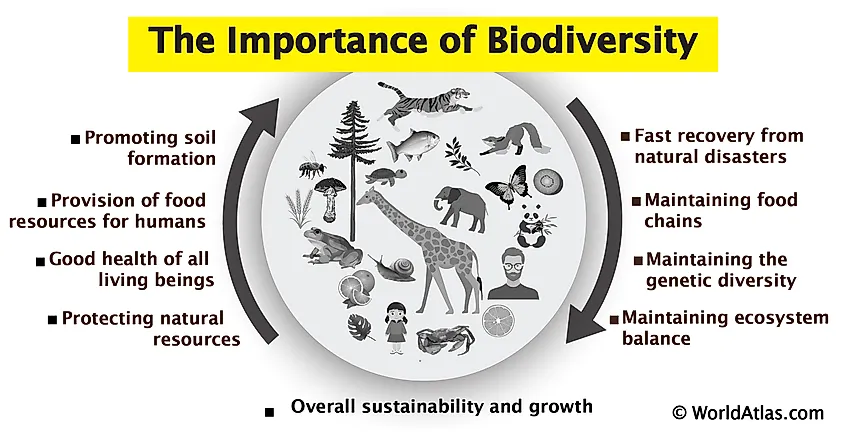
The Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is a cornerstone of environmental health and human prosperity. It encompasses the variety of ecosystems within a region, offering numerous benefits crucial for survival and well-being. Here are some key reasons why ecosystem diversity is so important:
- Supports Biodiversity: Diverse ecosystems provide habitats for a wide range of species, supporting global biodiversity and contributing to the richness of life on Earth.
- Enhances Resilience: A variety of ecosystems can better withstand and recover from environmental stresses, such as climate change, natural disasters, and human disturbances.
- Provides Ecosystem Services: Ecosystems deliver essential services such as air and water purification, pollination of crops, carbon sequestration, and nutrient cycling that are vital for human survival.
- Drives Economic Benefits: Many industries, including agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism, rely heavily on diverse ecosystems for resources, raw materials, and income.
- Promotes Cultural and Recreational Values: Ecosystem diversity enriches cultural identities and provides recreational opportunities, enhancing the quality of life and human well-being.
- Facilitates Scientific Research and Education: Diverse ecosystems are living laboratories that offer opportunities for scientific research, education, and the discovery of new medicines and technologies.
Protecting ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of nature, ensuring sustainable development, and safeguarding our planet for future generations.

Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is influenced by a range of natural and human-induced factors. These factors can either contribute to the richness and variety of ecosystems or pose threats to their stability and existence. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective conservation efforts:
- Natural Climate and Geography: The climate, topography, and soil type of an area naturally determine the types of ecosystems that can develop, influencing their diversity and distribution.
- Biological Interactions: Predation, competition, and symbiosis among species can affect ecosystem structure and function, shaping the diversity within and across ecosystems.
- Human Activities: Land use changes, urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution significantly alter and often reduce ecosystem diversity by destroying habitats and polluting environments.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompete native species, and lead to a loss of biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Global warming and changing weather patterns can shift ecosystems" geographic ranges, alter habitats, and threaten species adapted to specific climate conditions.
- Conservation Efforts: Protected areas, restoration projects, and sustainable management practices can help preserve and enhance ecosystem diversity.
Addressing these factors through informed policy, conservation, and sustainable practices is essential for maintaining and enhancing ecosystem diversity for future generations.
Measuring Ecosystem Diversity
Measuring ecosystem diversity is critical for understanding the health and functionality of our planet"s environments. It involves assessing the variety and abundance of species, the distribution of ecosystems, and the ecological processes that maintain life. Here are key methods used to measure ecosystem diversity:
- Species Richness and Evenness: Evaluating the number of species (richness) and the distribution of individuals among those species (evenness) within an ecosystem.
- Habitat Diversity: Assessing the variety of habitats within a given area, including the range of terrestrial, aquatic, and atmospheric environments.
- Genetic Diversity: Analyzing the genetic variation within and between species populations to understand resilience and adaptability to environmental changes.
- Functional Diversity: Measuring the range of different biological functions and processes within an ecosystem, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and food chain dynamics.
- Landscape Diversity: Examining the diversity of ecosystems at a larger geographical scale, including the pattern of ecosystems across a landscape and the connectivity between habitats.
- Remote Sensing and GIS Technologies: Utilizing satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for large-scale analysis of ecosystem types, changes, and trends over time.
These measurements provide valuable insights into the health and sustainability of ecosystems, guiding conservation efforts and policy decisions to protect our planet"s biodiversity.

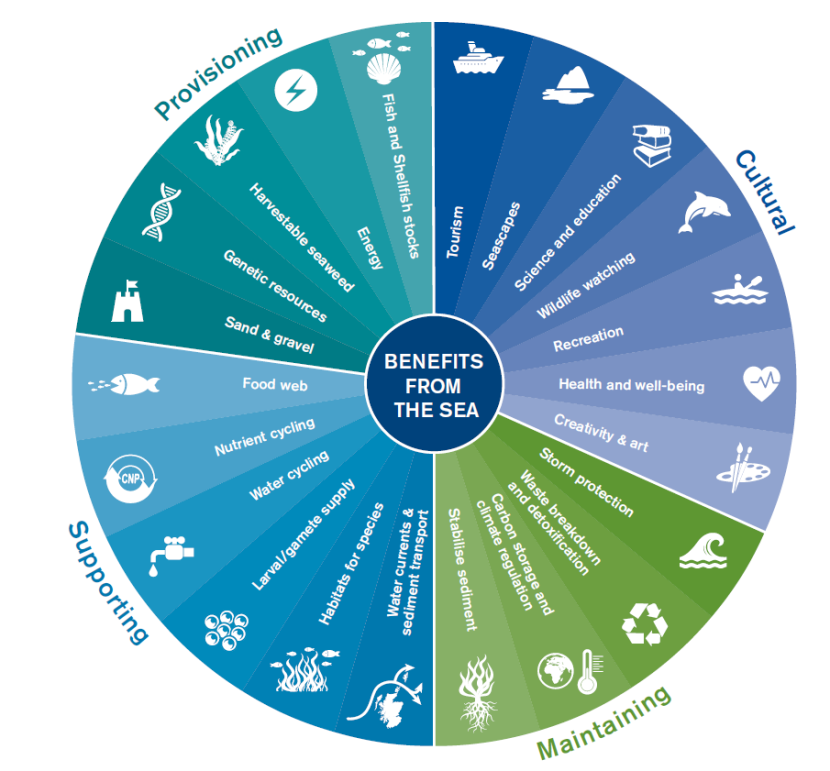
Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
Ecosystems provide a myriad of services that are indispensable for human survival and well-being. These services are the benefits that humans freely gain from the natural functioning of healthy ecosystems. Understanding and valuing these services is crucial for sustainable development and ensuring a quality life for future generations. Here are some of the key ecosystem services and their impact on human well-being:
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood and fiber, and genetic resources. Ecosystems play a vital role in food security, medicine, and raw materials.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality. They help mitigate natural disasters, control pests and diseases, and purify water and air.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production. They support the processes that enable life on Earth.
- Cultural Services: Ecosystems provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits. They support tourism, recreation, and cultural and artistic inspiration, enhancing mental and physical health.
The preservation of ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining these services. As ecosystems are degraded, their ability to provide these services diminishes, threatening human health, livelihoods, and future prosperity. Therefore, protecting and restoring ecosystem diversity is not just an environmental issue but a crucial socio-economic challenge and opportunity.
Ecosystem Diversity
Experience the beauty and wonder of ecosystem diversity in this captivating video. Immerse yourself in breathtaking landscapes and discover the incredible array of plants, animals, and habitats that make our world so remarkable.
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
Curiosity piqued? Let us explain complex concepts in a simple and engaging way. Join us for an enlightening video where we break down intricate topics, ensuring that you not only understand but also enjoy the learning process.
Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is under threat from a variety of sources, many of which are exacerbated by human activities. Understanding these threats is the first step toward mitigating their impact and protecting the invaluable diversity of life on Earth. Here are some of the most significant threats to ecosystem diversity:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urban expansion, agriculture, and mining lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, which is the primary cause of biodiversity loss.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect ecosystems" ability to support life, leading to species migration, extinction, and changes in habitat types.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade ecosystems and harm the species that depend on them.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, prey upon, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balances and reducing biodiversity.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, logging, and harvesting at unsustainable rates deplete resources faster than they can regenerate, leading to loss of species and ecosystems.
- Land Use Changes: Converting natural landscapes into agricultural or urban areas reduces the variety of habitats available for different species, diminishing ecosystem diversity.
Addressing these threats requires coordinated global efforts, including conservation, sustainable management practices, and policies that promote the protection of ecosystem diversity.
Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Preserving ecosystem diversity is vital for the health of the planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants. Effective conservation strategies require a multifaceted approach, combining science, policy, and community engagement. Here are key strategies that can help protect and restore ecosystem diversity:
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing national parks, nature reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries to safeguard habitats and species from human exploitation and development.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and the reintroduction of native species to restore ecological balance.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing practices that allow for the sustainable use of natural resources, ensuring that ecosystems can regenerate and maintain their functions.
- Combating Climate Change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting climate resilience through conservation efforts and sustainable practices to protect ecosystems from the impacts of climate change.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in the preservation of natural resources, and empowering them to act as stewards of biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policy: Enacting and enforcing laws and policies that protect ecosystems, regulate pollution, and manage land use to minimize human impact on the environment.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, since many ecosystems extend beyond national boundaries and require a global effort for their protection.
By implementing these strategies, we can work towards a sustainable future where ecosystem diversity is valued and preserved for the benefit of all life on Earth.
Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
Ecosystem restoration projects around the world demonstrate the potential for human intervention to facilitate the recovery of degraded environments and conserve biodiversity. These case studies highlight the success stories of ecosystem restoration, providing valuable lessons and inspiration for future efforts:
- The Loess Plateau, China: Once one of the most eroded regions in the world, extensive reforestation and sustainable agricultural practices have transformed it into fertile land, increasing local incomes and biodiversity.
- Yellowstone National Park, USA: The reintroduction of wolves in 1995 restored the park"s ecological balance, demonstrating the importance of top predators in ecosystem health.
- The Great Green Wall, Africa: An ambitious initiative to combat desertification across the Sahara and Sahel by planting a belt of trees across Africa, improving food security and resilience to climate change for millions.
- Kissama National Park, Angola: Following civil war, the park"s wildlife was decimated. A large-scale translocation project, "Operation Noah"s Ark," successfully reintroduced various species, revitalizing the park"s biodiversity.
- New Zealand"s Island Restoration: Predator-free islands have been created through the eradication of invasive species, leading to the recovery of native bird populations and ecosystem restoration.
These examples underscore the potential for positive change through concerted restoration efforts, offering hope and a roadmap for future projects aimed at preserving our planet"s invaluable ecosystem diversity.
The Role of Climate Change in Shaping Ecosystem Diversity
Climate change is a significant global challenge that has profound effects on ecosystem diversity. Alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events directly impact the distribution, structure, and function of ecosystems worldwide. Understanding the role of climate change in shaping ecosystem diversity is crucial for developing effective conservation and adaptation strategies. Here are some ways in which climate change influences ecosystem diversity:
- Shifts in Species Distribution: As temperatures rise, species migrate to cooler areas, altering the composition of ecosystems and potentially leading to mismatches in ecological interactions.
- Changes in Ecosystem Boundaries: Warming temperatures can lead to the expansion of some ecosystems, such as deserts, at the expense of others, like tundra and boreal forests, thereby changing global biodiversity patterns.
- Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events: Storms, droughts, and wildfires can devastate ecosystems, leading to loss of species and habitats and altering ecosystem services.
- Acidification and Warming of Oceans: These phenomena threaten marine ecosystems, particularly coral reefs, which are biodiversity hotspots, affecting fish populations and the livelihoods of people who depend on them.
- Altered Phenological Events: Changes in timing of natural events, such as flowering, breeding, and migration, can disrupt ecological balance and the interdependencies among species.
Addressing the impact of climate change on ecosystem diversity requires global cooperation and the implementation of policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, protecting habitats, and supporting species adaptation to new climate realities.
READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
The conservation of ecosystem diversity faces numerous challenges in the face of global change, but it also presents opportunities for innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. Addressing these challenges and seizing these opportunities are crucial for the sustainability of our planet"s ecosystems and the services they provide. Here are key future challenges and opportunities in ecosystem diversity conservation:
- Climate Change Adaptation: Developing strategies to help ecosystems adapt to the changing climate, mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events, and shifting temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Urbanization and Land Use Change: Balancing the needs of growing urban populations with the conservation of natural habitats and the sustainable use of land resources.
- Invasive Species Management: Implementing effective measures to prevent the introduction of invasive species and to control or eradicate those already established.
- Integrating Biodiversity in Policy and Planning: Embedding ecosystem conservation priorities within local, national, and international policy frameworks and development plans.
- Technological Advances: Leveraging technology for monitoring biodiversity, restoring ecosystems, and enhancing public awareness and education on conservation issues.
- Community Engagement and Indigenous Knowledge: Involving local communities and recognizing the value of traditional ecological knowledge in conservation practices and decision-making.
- International Cooperation: Strengthening global partnerships and collaborations to address transboundary conservation challenges and share best practices and resources.
The future of ecosystem diversity conservation is a shared responsibility that requires innovative thinking, collaborative action, and a commitment to sustainable development. By addressing these challenges and embracing opportunities, we can ensure the preservation and resilience of the world"s ecosystems for future generations.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is pivotal for our planet"s health and our future. By embracing conservation efforts, we can safeguard this invaluable treasure, ensuring a rich, resilient Earth for generations to come.