Topic ecosystem diversity def: Explore the essence of ecosystem diversity, a critical component of our planet"s health, offering insights into the complex interplay of life forms across varied habitats.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
- What is Ecosystem Diversity?
- Types of Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: What is Ecosystem Diversity? || La Excellence
- Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change Mitigation
- Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
- Future Directions in Ecosystem Diversity Research
What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in a given geographical area. It encompasses the range of different ecosystems present, including terrestrial, aquatic, and transitional ecosystems such as wetlands or mangroves.
Key components of ecosystem diversity include:
- 1. Habitats: Ecosystem diversity includes the different types of habitats or physical environments found within an area. These can range from forests, grasslands, deserts, mountains, rivers, lakes, coral reefs, and more.
- 2. Communities: It also takes into account the diversity and variety of biological communities, which are composed of different species and their interactions within a specific ecosystem. Communities can include plants, animals, microorganisms, and other organisms.
- 3. Ecological Processes: Ecosystem diversity is also characterized by the various ecological processes that occur within and between ecosystems. These processes include energy flow, nutrient cycling, pollination, seed dispersal, predator-prey dynamics, and more.
- 4. Beneficial Services: Ecosystem diversity provides numerous beneficial services to human societies, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, climate regulation, waste decomposition, and cultural values.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the health and functioning of ecosystems, as well as ensuring sustainable use of natural resources and the conservation of biodiversity.
READ MORE:
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
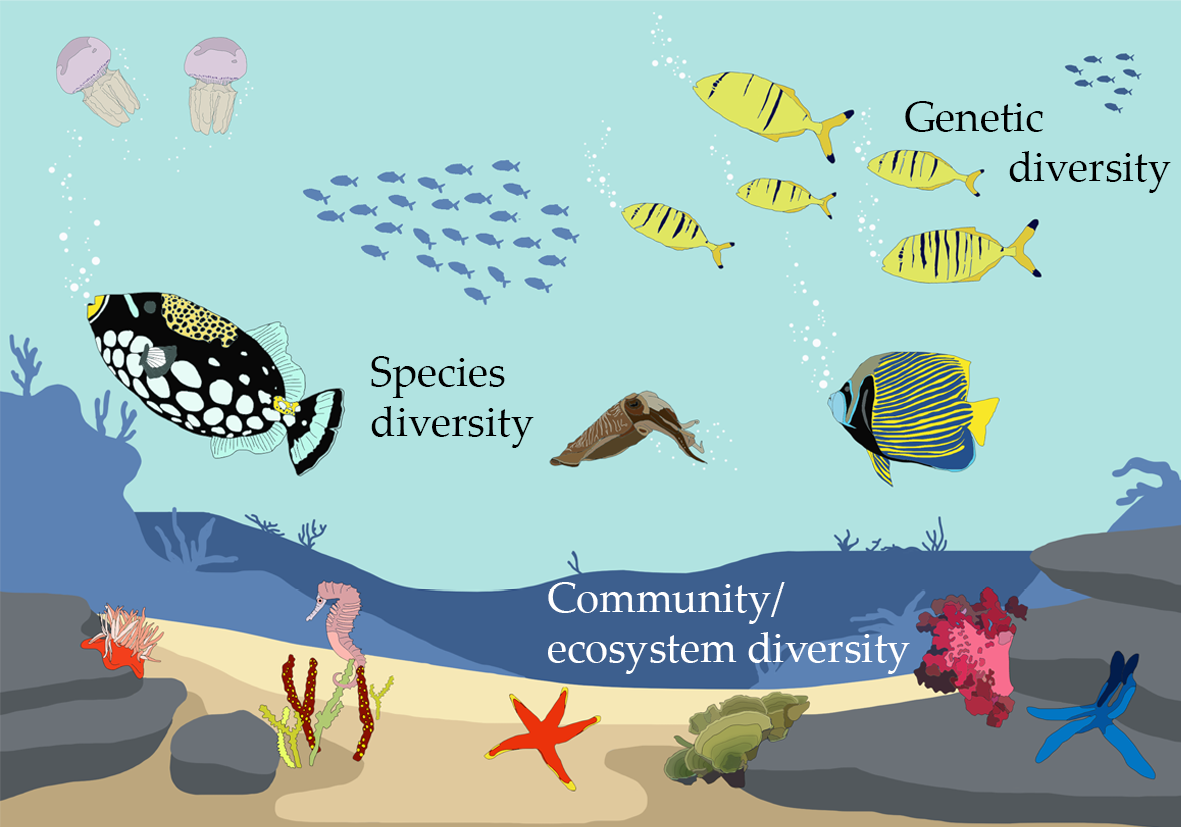
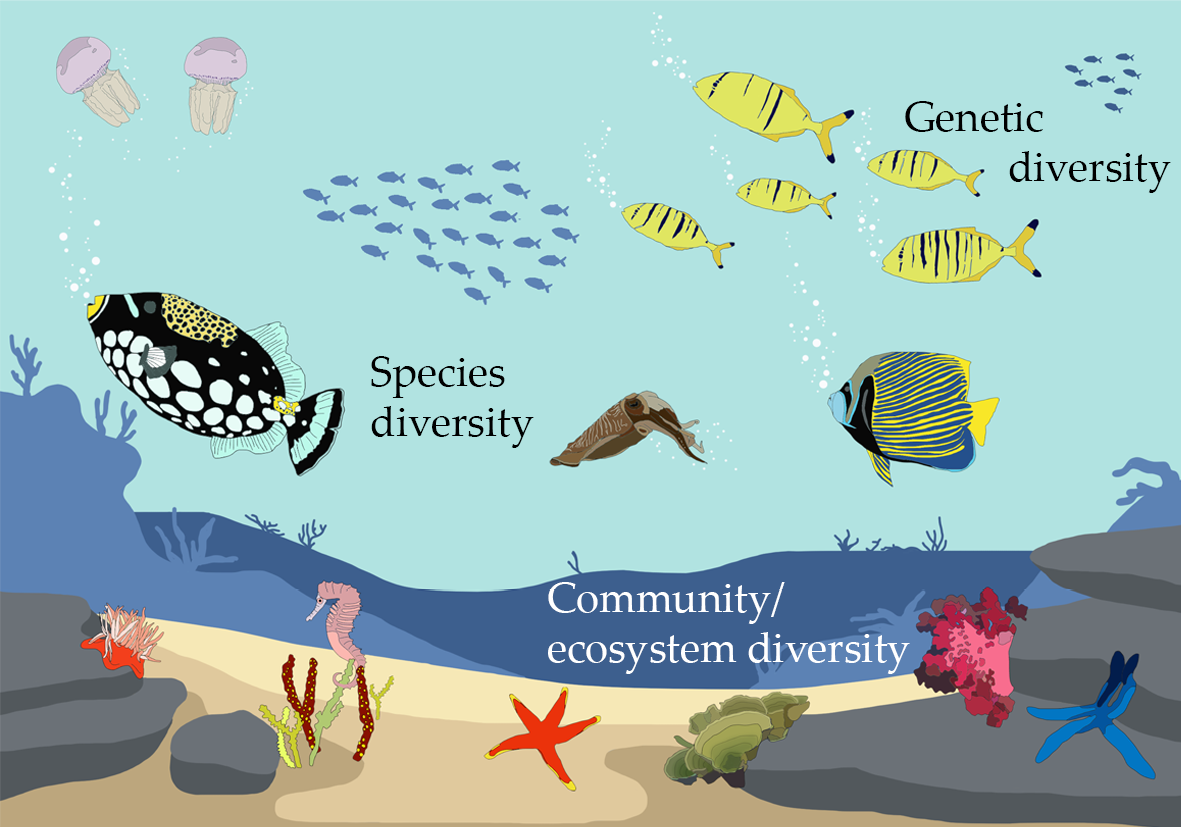
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems within a given geographical area, encompassing the myriad of living organisms, their physical environments, and the complex interactions that occur within and between these systems. It is a crucial aspect of biodiversity, alongside species and genetic diversity, highlighting the richness of life forms and ecological processes on Earth.
- It underscores the range of different habitats, from forests and oceans to deserts and wetlands, each hosting unique communities of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- This diversity not only includes the variety of ecosystems but also the ecological processes that sustain them, such as nutrient cycling, energy flow, and climate regulation.
- Ecosystem diversity plays a vital role in providing essential services to humanity, including clean air and water, fertile soil for agriculture, and the regulation of climate and diseases.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is paramount for maintaining the balance of our planet"s life-support systems, ensuring the sustainability of natural resources and the resilience of life forms to environmental changes.

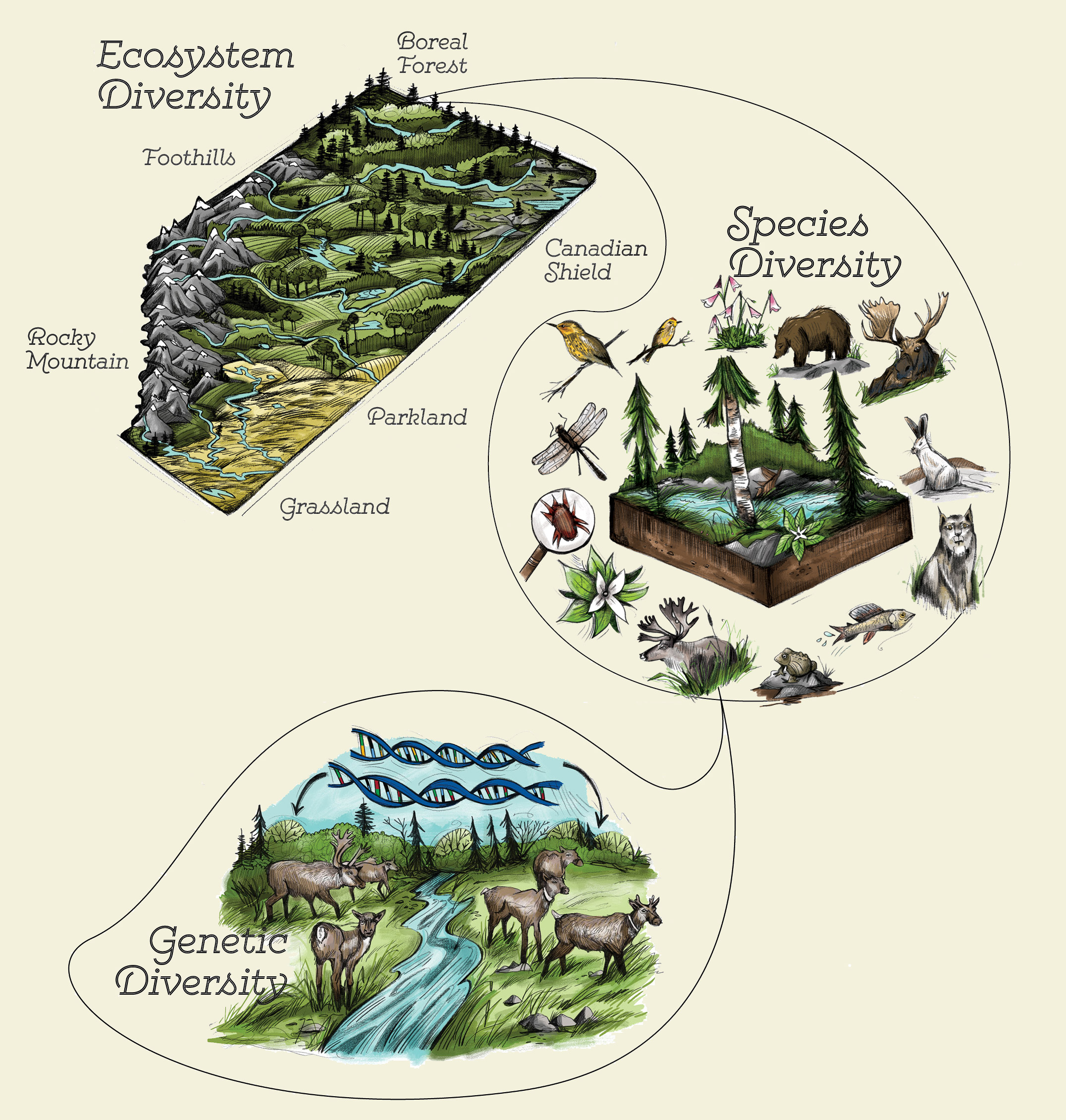
Types of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of ecosystems within a particular region, reflecting the richness of Earth"s habitats. This diversity can be classified into several types, each providing unique environments and supporting diverse forms of life.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These include forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundras, each characterized by distinct climates, soil types, and biological communities.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater (lakes, rivers, and wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries) systems, each with specialized flora and fauna adapted to water-based environments.
- Urban Ecosystems: Urban areas, though heavily modified by humans, host unique ecosystems where wildlife, plants, and humans interact in complex ways.
- Managed Ecosystems: These include agricultural lands and managed forests, where human intervention shapes the environment but still supports biodiversity.
Understanding the types of ecosystem diversity is crucial for conservation efforts, as each ecosystem type supports specific services essential for human well-being, including air and water purification, climate regulation, and pollination.
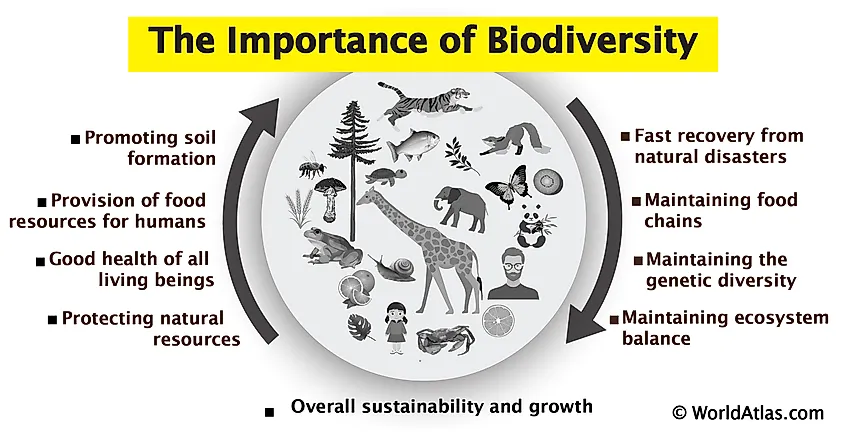
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and sustainability of our planet. It is fundamental to the provision of ecosystem services that are crucial for human survival and the overall health of the environment.
- Supports a Wide Range of Life: By providing varied habitats, ecosystem diversity ensures the survival of a vast array of species, contributing to species diversity.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances, such as climate change, pests, and diseases, helping to sustain the environment over time.
- Drives Ecological Services: Essential services like air and water purification, pollination of crops, climate regulation, and carbon sequestration are all supported by ecosystem diversity.
- Promotes Human Well-being: Beyond ecological benefits, diverse ecosystems support agriculture, fisheries, and forestry, and are the foundation for many economies. They also offer recreational, cultural, and spiritual benefits.
- Facilitates Adaptation and Evolution: The interaction between different ecosystems encourages genetic diversity, adaptation, and evolution, ensuring the survival of species in changing environments.
The conservation of ecosystem diversity is thus essential for the sustainability of life on Earth, highlighting the need to protect and preserve our natural habitats.

Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is exemplified by the vast array of habitats found across the globe, each supporting unique communities of organisms and ecological processes. Here are some notable examples:
- Tropical Rainforests: Rich in biodiversity, these ecosystems are home to a significant portion of the world"s species, including numerous plants, animals, and insects not found elsewhere.
- Coral Reefs: Often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," coral reefs support a diverse range of marine life and are crucial for the health of the world"s oceans.
- Deserts: Despite harsh conditions, deserts have a unique set of organisms adapted to survive with minimal water, showcasing the adaptability of life.
- Arctic Tundra: Characterized by cold temperatures and short growing seasons, the tundra supports species adapted to extreme conditions, including migratory birds, mammals, and a variety of plant life.
- Wetlands: Crucial for water purification and flood control, wetlands are breeding grounds for many species and serve as important stopover points for migratory birds.
- Grasslands: These areas support a variety of plants and animals, including many large herbivores and the predators that feed upon them, and are important for agriculture.
Each of these ecosystems plays a vital role in maintaining the Earth"s biological and ecological balance, highlighting the importance of preserving ecosystem diversity.
Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is influenced by a variety of factors, both natural and anthropogenic, that can alter the composition, structure, and function of ecological communities. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective conservation and management strategies.
- Natural Factors:
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation patterns largely determine the types of ecosystems that can exist in a region.
- Geography: Physical features like mountains, rivers, and soil types influence the distribution of ecosystems.
- Biological Interactions: Predation, competition, and symbiosis among species shape ecosystem structure.
- Anthropogenic Factors:
- Land Use Change: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation significantly modify ecosystem diversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution can degrade ecosystems and reduce their diversity and resilience.
- Climate Change: Global warming and altered weather patterns are shifting ecosystems and their species compositions.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predominate, and disrupt native ecosystems.
Addressing these factors through sustainable practices and policies is essential for preserving ecosystem diversity and the benefits it provides to humanity and the natural world.

Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the Earth"s resilience and productivity. Effective strategies involve a multifaceted approach, engaging local communities, governments, and international bodies. Here are key conservation strategies:
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing protected areas like national parks and wildlife reserves to safeguard habitats and species.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetlands restoration, and the reintroduction of native species.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and preserve biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect ecosystems, restrict harmful activities, and promote sustainable resource use.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their traditional knowledge and ensuring they benefit from biodiversity conservation.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing the root causes of climate change to protect ecosystems from its adverse effects, including promoting renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity and the need for conservation among the public and policymakers.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, especially for ecosystems that span multiple countries or global biodiversity hotspots.
These strategies, when implemented effectively, can help preserve the intricate balance of our planet"s ecosystems, ensuring a sustainable future for all species, including humans.
What is Ecosystem Diversity? || La Excellence
Discover the wonders of the ecosystem and dive into a breathtaking journey through lush forests, sparkling rivers, and thriving wildlife. Uncover the delicate balance of nature and marvel at the interconnections that make our planet truly magnificent - this video will leave you in awe of our incredible ecosystem.
Ecosystem Diversity | Nature World
Embrace the beauty of diversity as we take you on an inspiring exploration of different cultures, perspectives, and ways of life. Celebrate the richness that comes from embracing our differences and gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for the world\'s diverse tapestry - this video is a captivating celebration of diversity.
Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the Earth"s resilience and productivity. Effective strategies involve a multifaceted approach, engaging local communities, governments, and international bodies. Here are key conservation strategies:
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing protected areas like national parks and wildlife reserves to safeguard habitats and species.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetlands restoration, and the reintroduction of native species.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and preserve biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect ecosystems, restrict harmful activities, and promote sustainable resource use.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their traditional knowledge and ensuring they benefit from biodiversity conservation.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing the root causes of climate change to protect ecosystems from its adverse effects, including promoting renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity and the need for conservation among the public and policymakers.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, especially for ecosystems that span multiple countries or global biodiversity hotspots.
These strategies, when implemented effectively, can help preserve the intricate balance of our planet"s ecosystems, ensuring a sustainable future for all species, including humans.
Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change Mitigation
Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by maintaining healthy ecosystems that can absorb and store carbon dioxide, a primary greenhouse gas. This diversity ensures a variety of habitats, species, and genetic variation, contributing to the resilience and adaptive capacity of ecosystems to climate change impacts. Below are key points highlighting the role of ecosystem diversity in climate change mitigation:
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests, wetlands, and oceans are examples of diverse ecosystems that act as carbon sinks. Through photosynthesis, plants in these ecosystems absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, storing it in biomass and soil, thereby reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases.
- Climate Regulation: Diverse ecosystems contribute to climate regulation by influencing global and local climate patterns. For example, forests can moderate temperatures, increase humidity through transpiration, and contribute to cloud formation, all of which can mitigate climate change effects.
- Supporting Biodiversity: Biodiversity is integral to ecosystem resilience. A diverse ecosystem can better withstand environmental stress and adapt to changes, ensuring the stability of services such as pollination, water purification, and disease regulation that are vital for carbon cycling and sequestration.
- Protecting Coastal Areas: Coastal ecosystems like mangroves, salt marshes, and seagrass beds provide natural barriers against storm surges and coastal erosion. Their preservation and restoration enhance carbon storage capacity while protecting shorelines from the impacts of sea-level rise.
- Enhancing Soil Quality: Diverse ecosystems contribute to soil formation and fertility, which in turn supports plant growth and carbon sequestration. Healthy soils store more carbon and help mitigate the greenhouse effect.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Conservation and sustainable management of diverse ecosystems encourage practices that reduce emissions, such as reduced deforestation, sustainable agriculture, and forestry practices that enhance carbon sinks.
In conclusion, maintaining and enhancing ecosystem diversity is essential for climate change mitigation. It is a natural solution that complements technological and policy measures aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The conservation of diverse ecosystems, therefore, should be a key component of global strategies to combat climate change.
Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have significantly impacted ecosystem diversity across the globe, leading to habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and a decrease in species diversity. These changes threaten the stability and services provided by ecosystems, essential for human survival and the planet"s health. Here, we explore the various ways in which human actions affect ecosystem diversity:
- Deforestation: The removal of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban development reduces habitat for millions of species, leading to a loss in biodiversity and disrupting carbon and water cycles essential for life.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal introduce harmful substances into ecosystems, affecting species health, reproductive rates, and leading to ecosystem degradation.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change, resulting from the emission of greenhouse gases, affects ecosystems by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to habitat shifts, species extinction, and decreased resilience of ecosystems.
- Overexploitation: The excessive harvesting of resources, such as overfishing and hunting, depletes populations faster than they can recover, leading to a loss of species and negatively affecting ecosystem balance and functionality.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species, whether intentionally or accidentally, can outcompete native species for resources, leading to a decline in native biodiversity and altering ecosystem structure and function.
- Land Use Change: The conversion of natural habitats into agricultural or urban areas not only reduces the area available for native species but also fragments habitats, making it difficult for species to migrate, find food, or mate.
Addressing the impact of human activities on ecosystem diversity requires concerted efforts towards sustainable practices, including protecting natural habitats, restoring degraded areas, and adopting sustainable resource management. Through awareness, education, and policy changes, we can mitigate these impacts and ensure the preservation of ecosystem diversity for future generations.
READ MORE:
Future Directions in Ecosystem Diversity Research
As the global community becomes increasingly aware of the importance of biodiversity and ecosystems to human well-being and planetary health, ecosystem diversity research is evolving with new focuses and methodologies. Future directions in this field aim to address current challenges, improve understanding, and provide actionable solutions for conservation and sustainable management. The following points highlight key areas of focus for future research in ecosystem diversity:
- Integrated Approaches: Combining traditional ecological research with advances in technology, such as remote sensing, molecular biology, and big data analytics, to better understand the complexities of ecosystems and their functions.
- Climate Change Impacts: Focusing on how climate change alters ecosystem diversity, including shifts in species distributions, changes in phenology, and the emergence of new ecosystem types, to inform adaptation and mitigation strategies.
- Human-Ecosystem Interactions: Investigating the reciprocal effects between human activities and ecosystem diversity to develop sustainable practices that benefit both ecosystems and human societies.
- Restoration Ecology: Expanding research on ecosystem restoration and rehabilitation methods to enhance resilience, recover endangered species, and restore ecosystem services in degraded landscapes.
- Policy and Governance: Exploring the effectiveness of policies, governance structures, and conservation strategies in preserving ecosystem diversity and promoting sustainable use of natural resources.
- Transdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration among ecologists, social scientists, policymakers, and local communities to address complex conservation challenges and implement ecosystem-based management approaches.
- Novel Ecosystems: Understanding and managing novel ecosystems—those significantly altered by human activity—recognizing their potential contributions to biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
These future research directions underscore the necessity for a holistic and inclusive approach to studying and conserving ecosystem diversity. By embracing technological advancements, interdisciplinary collaboration, and inclusive governance, the scientific community can enhance its ability to safeguard ecosystem diversity amidst changing global conditions.
Exploring ecosystem diversity reveals the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. By understanding, valuing, and protecting this diversity, we can ensure a resilient and vibrant world for future generations to cherish and inhabit.