Topic what is diversity in an ecosystem: "Diving into the heart of nature, "What is Diversity in an Ecosystem?" unveils the intricate web of life that sustains our planet, highlighting the importance and beauty of biodiversity."
Table of Content
- What is the significance of diversity in an ecosystem?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity for Environmental Stability
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Unique Characteristics
- Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Efforts to Protect Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Success Stories in Ecosystem Preservation
- Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Conservation
What is the significance of diversity in an ecosystem?
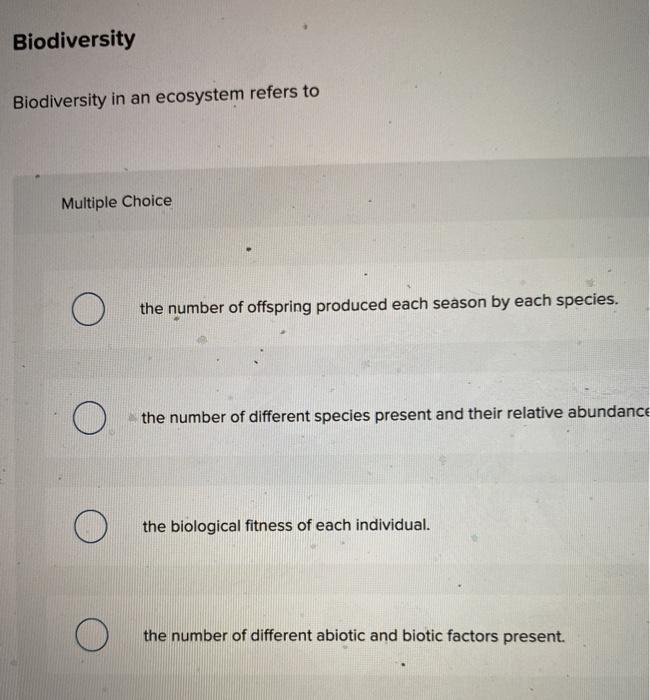
The significance of diversity in an ecosystem is crucial for its stability, resilience, and overall health. It encompasses both biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living factors) elements, and plays a vital role in maintaining the balance and functionality of the ecosystem.
- Biodiversity: Diversity in living organisms is known as biodiversity, and it is a fundamental aspect of ecosystem diversity. Biodiversity includes various species, genes, and ecosystems within a particular area. It provides several benefits for the ecosystem, such as:
- Enhanced productivity and ecosystem functioning: Different species perform unique roles, such as plant pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control, which collectively contribute to the overall productivity and functioning of the ecosystem.
- Resilience to environmental changes: Ecosystems with higher biodiversity have a greater capacity to adapt and recover from disturbances, such as climate change, pollution, and disease outbreaks. The presence of diverse species ensures that even if some are affected negatively, others may thrive and maintain ecosystem stability.
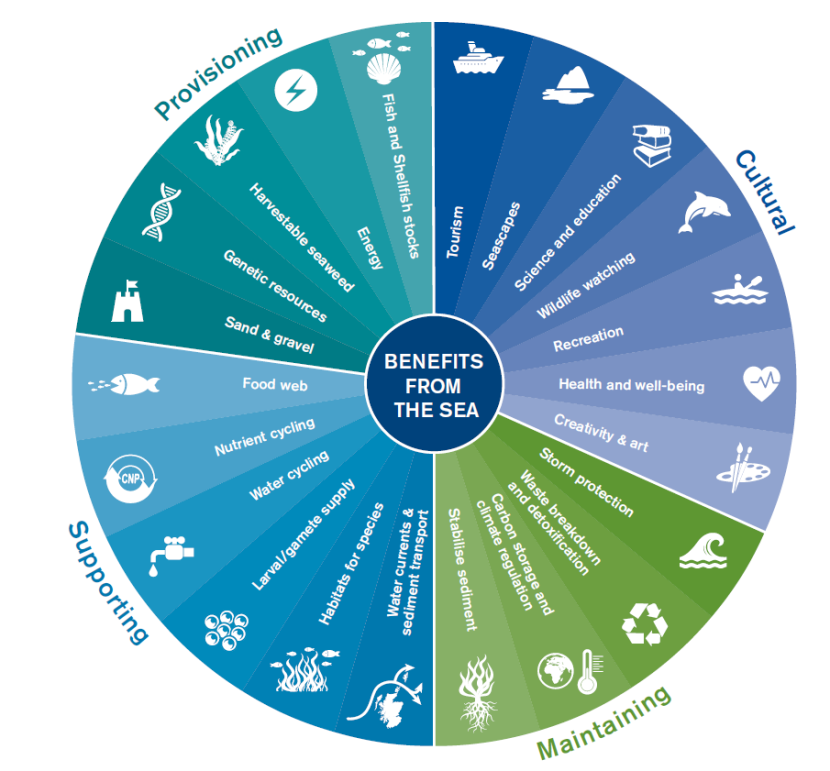
- Improved ecosystem services: Biodiversity supports the provision of essential ecosystem services, including air and water purification, soil fertility, and regulation of climate and natural disasters. These services are vital for human well-being and the sustainability of economies.
- Geodiversity: In addition to biodiversity, geodiversity refers to the abiotic aspects of ecosystem diversity, such as geology, landforms, soil types, and climatic conditions. Geodiversity influences the distribution and abundance of species, shapes ecosystem structure, and provides important habitats for various organisms.
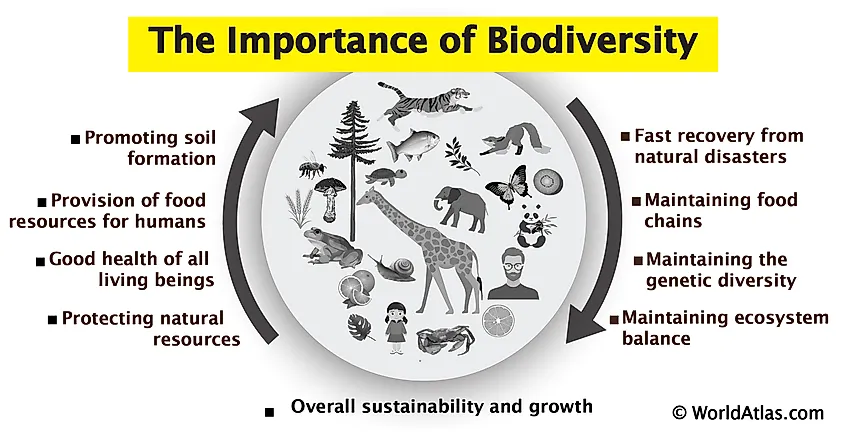
Overall, diversity in an ecosystem is significant as it ensures the maintenance of ecological processes, stability, and resilience, as well as the provision of vital services for both the environment and human societies.
READ MORE:
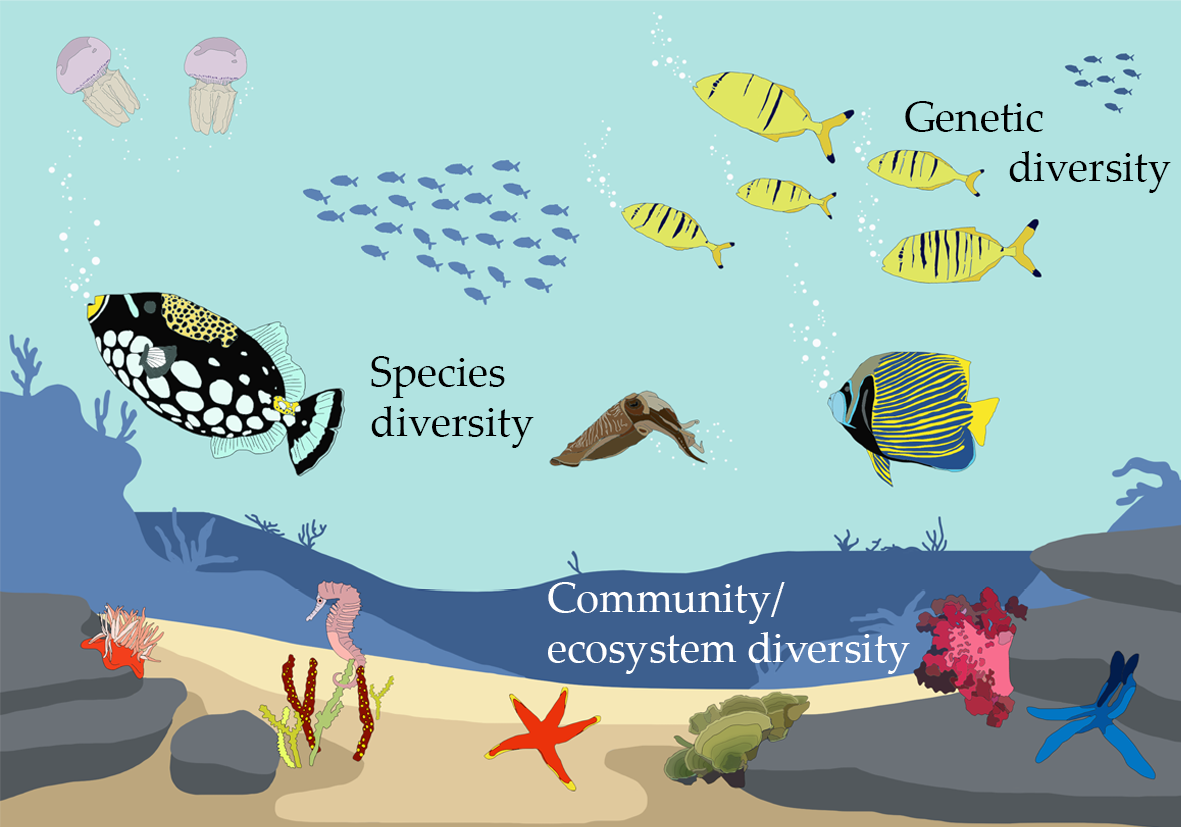
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of habitats, living organisms, and ecological processes in the natural world. It encompasses the range of different ecosystems within a region, each with its own unique combination of plants, animals, and microorganisms. This diversity is crucial for the stability and health of the planet, offering resilience against environmental changes and providing a wide range of ecological services.
- Types of Ecosystems: From forests and oceans to deserts and wetlands, the Earth is home to countless distinct ecosystems, each supporting diverse forms of life.
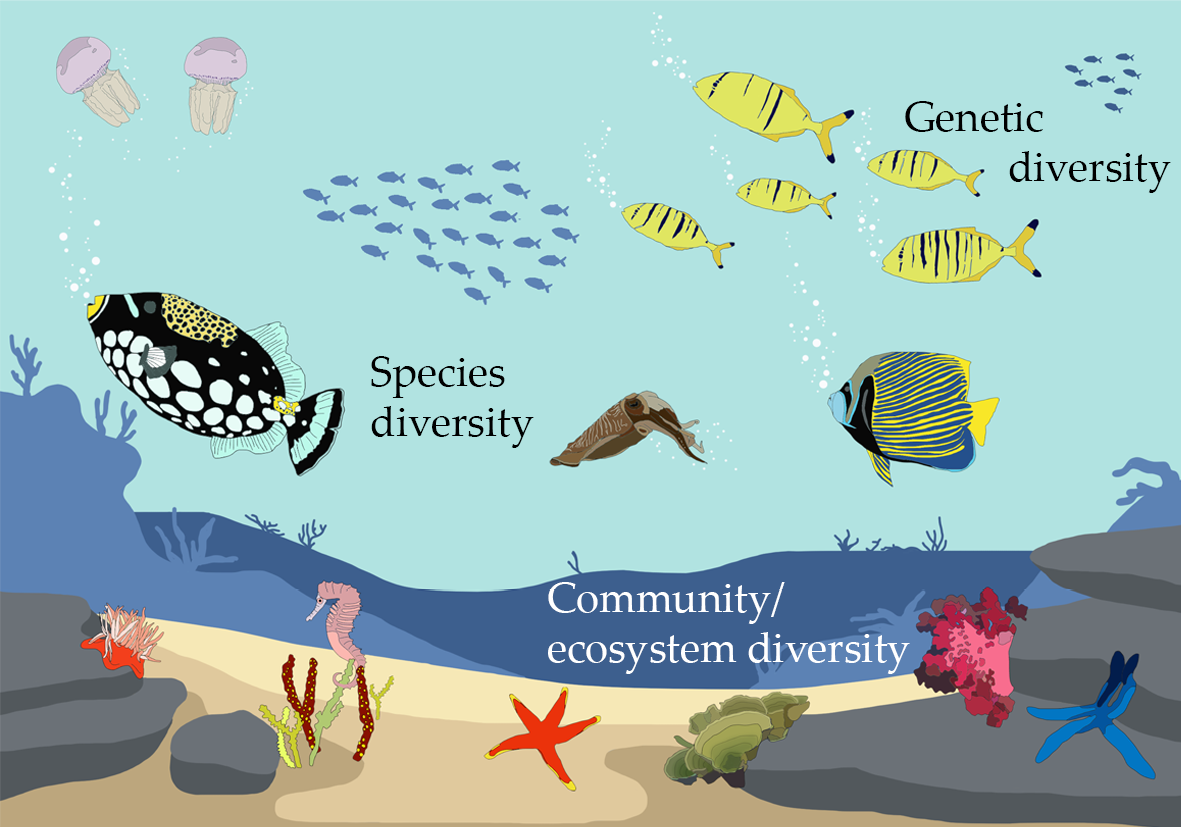
- Species Diversity: Within each ecosystem, there exists a multitude of species interacting with each other and their environment, contributing to the overall biodiversity.
- Genetic Diversity: Ecosystem diversity also includes the genetic variation within species, enabling populations to adapt to changing conditions and resist diseases.
- Ecological Processes: The intricate ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and predation, are vital components of ecosystem diversity, ensuring the sustainability and productivity of ecosystems.
Understanding ecosystem diversity is essential for conservation efforts, as it helps identify critical areas for protection and the restoration of habitats. By appreciating and preserving the variety of ecosystems, we support the complex web of life upon which we all depend.
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity for Environmental Stability
Ecosystem diversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining environmental stability and resilience. It ensures that natural systems are robust enough to withstand and recover from disturbances, such as climate change, natural disasters, and human activities. Here"s how ecosystem diversity underpins environmental stability:
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to cope with environmental changes. If one ecosystem is affected, others can help maintain the overall balance.
- Supports Species Survival: Varied habitats allow for a wide range of species to thrive, reducing the risk of extinctions caused by habitat loss or climate change.
- Promotes Genetic Diversity: The more diverse an ecosystem, the greater the genetic diversity within species, enhancing their adaptability to changing conditions.
- Ensures Ecological Services: Ecosystem diversity guarantees the provision of essential ecological services, including air and water purification, pollination of crops, and carbon sequestration, which are vital for human survival.
- Fosters Productivity: Diverse ecosystems are often more productive because they utilize resources more efficiently, supporting a wider range of organisms.
Recognizing the importance of ecosystem diversity is crucial for environmental conservation and sustainability. Protecting and restoring diverse ecosystems is not just about preserving wildlife; it"s about safeguarding the future of our planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
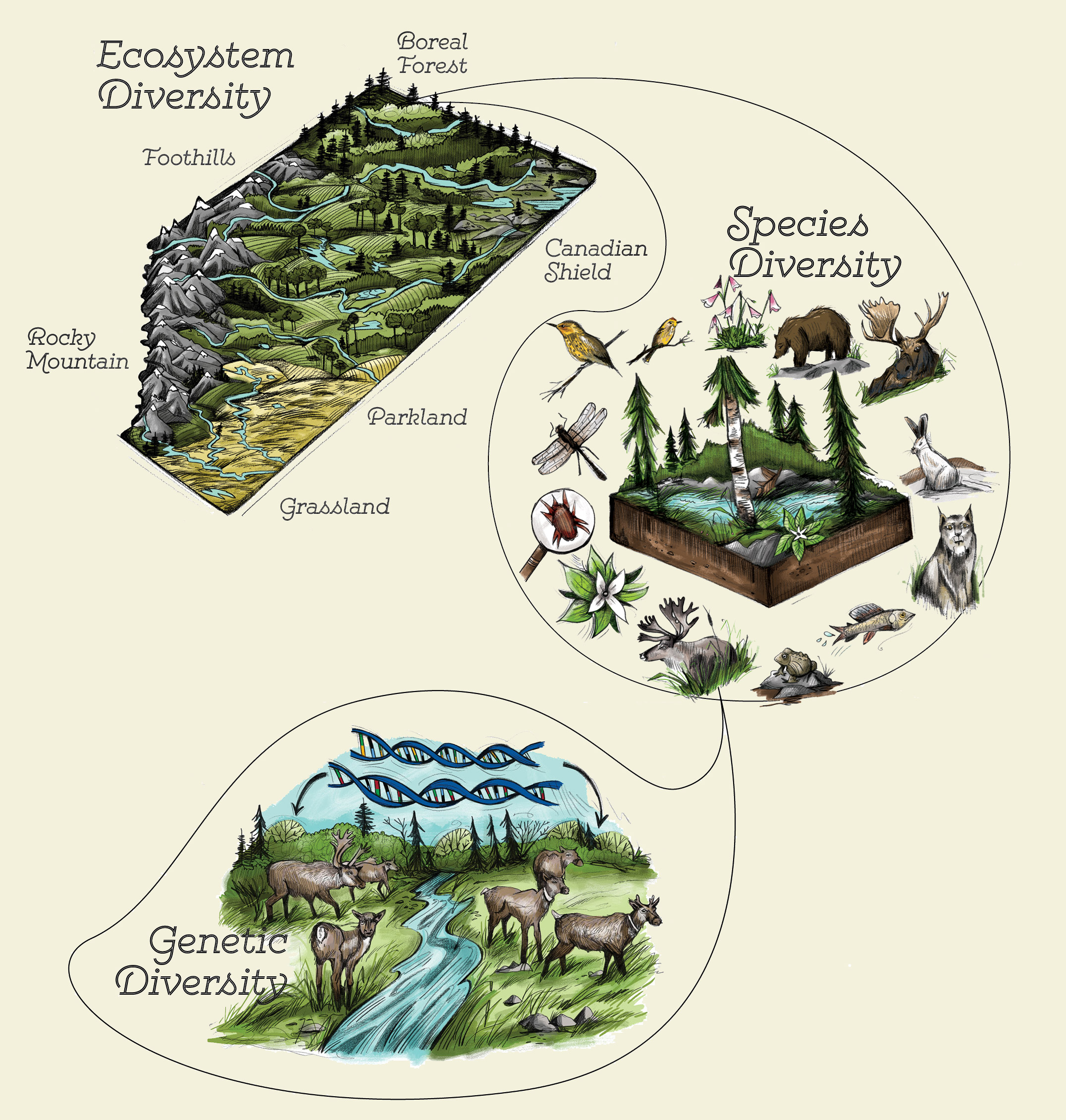
Types of Ecosystems and Their Unique Characteristics
The Earth is adorned with a mosaic of ecosystems, each with distinct environments and life forms. Understanding the types of ecosystems and their unique characteristics sheds light on the diversity of our planet. Below are some of the major types of ecosystems and what makes them unique:
- Forests: Including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests. They are characterized by high levels of rainfall and biodiversity, serving as the home for over half of the terrestrial species.
- Deserts: Known for their extreme dryness, deserts can be hot or cold. They host species adapted to harsh conditions, with specialized plants and animals that conserve water.
- Grasslands: Including savannas and temperate grasslands, these areas are dominated by grasses. They support a variety of herbivores, predators, and migratory species due to their open landscapes.
- Wetlands: Encompassing marshes, swamps, and bogs, wetlands are crucial for water purification, flood protection, and as breeding grounds for many species.
- Oceans: Covering over 70% of the Earth"s surface, oceans are key to climate regulation and support diverse marine life from microscopic plankton to the largest whales.
- Freshwater Ecosystems: Including rivers, lakes, and streams, these ecosystems are essential for drinking water, agriculture, and habitat for many species.
- Tundra: Characterized by cold temperatures and minimal vegetation, tundra ecosystems are found in the Arctic and high mountains, hosting hardy species adapted to extreme cold.
- Coral Reefs: Often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," coral reefs support an immense variety of life, providing shelter and food for thousands of marine species.
Each ecosystem plays a critical role in the Earth"s biological and ecological balance, showcasing the importance of diversity in sustaining life across different environments.
Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity is the foundation upon which ecosystems operate and flourish. The variety of life forms within an ecosystem, from genes to species to communities, plays a critical role in how ecosystems function and provide services essential to human survival. Below are key aspects of how biodiversity contributes to ecosystem functioning:
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, soil fertility, and climate regulation, directly impacting human welfare.
- Enhances Resilience: A diverse ecosystem can better withstand environmental stress and is more resilient to disturbances like disease outbreaks, natural disasters, and climate change.
- Improves Productivity: Biodiverse ecosystems are more productive because they utilize resources more efficiently, leading to greater ecological stability and outputs, such as biomass and oxygen production.
- Fosters Ecological Balance: The interaction among different species in varied ecosystems helps to control population sizes, maintain health of habitats, and cycle nutrients effectively.
- Promotes Adaptation: Genetic diversity within and among species increases the likelihood of organisms" adapting to environmental changes, thereby supporting the long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
The role of biodiversity in ecosystem functioning is a testament to the intricate and interconnected nature of life on Earth. Protecting biodiversity is not only a moral obligation but a necessary step to ensure the health and stability of ecosystems upon which we depend.
Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have profoundly impacted ecosystem diversity across the globe, often leading to significant alterations and declines in biodiversity. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative effects and promote sustainable interactions with the natural world. Here are the main ways humans have affected ecosystem diversity:
- Land Use Change: Agriculture, urbanization, and deforestation have transformed habitats, reducing their size and quality, and leading to habitat fragmentation and loss of species.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources have degraded ecosystems, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Global warming and climate variability affect ecosystems" structure and function, altering species distributions and interactions, and threatening sensitive habitats like coral reefs and wetlands.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at unsustainable rates have led to the depletion of many species, affecting ecosystem balance and functionality.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species to new environments can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompeting or preying on native species and altering ecosystem processes.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for positive human influence through conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and restoration projects aimed at preserving and enhancing ecosystem diversity. Recognizing the interconnectedness of human well-being with the health of ecosystems is a crucial step towards fostering a harmonious relationship with our planet.

Conservation Efforts to Protect Ecosystem Diversity
Protecting ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the Earth"s resilience, productivity, and biological richness. Conservation efforts worldwide aim to safeguard these vital systems through a variety of strategies and initiatives. Here"s how conservation efforts are making a difference:
- Establishing Protected Areas: National parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas are designated to preserve critical habitats and provide sanctuaries for species.
- Restoration Projects: Efforts to restore degraded habitats, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, help to rebuild ecosystem functions and biodiversity.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation activities ensures the sustainable management of resources and raises awareness of the importance of ecosystem diversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Enforcing environmental laws and policies, including those related to land use, pollution control, and endangered species protection, is crucial for conservation success.
- International Agreements: Global initiatives and treaties, such as the Convention on Biological Diversity, foster cooperation among countries to address biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research and monitoring of ecosystems help to understand their complexity, inform conservation decisions, and track the effectiveness of protection measures.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices minimizes environmental impact and supports ecosystem health.
Through these concerted efforts, we can ensure the preservation and enhancement of ecosystem diversity, which is crucial for the well-being of our planet and future generations.
Ecosystem Diversity
\"Discover the beauty of diversity as we explore the vibrant and colorful world of nature in this mesmerizing video. Get ready to be mesmerized by the incredible variety of plants, animals, and landscapes that make our planet so unique and precious.\"
What Is An Ecosystem?
\"Embark on a visual journey through the intricate web of life in our awe-inspiring ecosystem video. Dive into the depths of the ocean, trek through lush rainforests, and witness the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. Prepare to be captivated by the wonders and interconnectedness of our planet\'s diverse ecosystems.\"
Case Studies: Success Stories in Ecosystem Preservation
In the global effort to preserve ecosystem diversity, there have been notable success stories that demonstrate the positive impact of conservation initiatives. These case studies highlight the effectiveness of targeted actions in restoring and protecting vital ecosystems:
- The Amazon Rainforest, Brazil: Through a combination of protected areas, sustainable land use practices, and international cooperation, significant portions of the Amazon have been preserved, maintaining its incredible biodiversity and mitigating climate change impacts.
- Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Conservation and restoration efforts, including water quality improvements and species protection programs, have helped to preserve this iconic marine ecosystem, home to thousands of species of marine life.
- Serengeti National Park, Tanzania: Effective wildlife management and anti-poaching efforts have protected this vast ecosystem, ensuring the survival of many species and the continuation of the annual wildebeest migration.
- Yellowstone National Park, USA: The reintroduction of wolves has restored the natural balance of the ecosystem, demonstrating the importance of top predators in ecological health.
- New Forest National Park, UK: Conservation of this ancient woodland and heathland has preserved its unique biodiversity, including rare bird species and native plants, through community engagement and sustainable tourism.
These case studies exemplify how dedicated conservation efforts can lead to significant achievements in ecosystem preservation, offering hope and a roadmap for future initiatives aimed at protecting the planet"s natural heritage.

READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Conservation
As we move forward, ecosystem conservation faces both significant challenges and opportunities. Addressing these effectively will be crucial for the sustainability of our planet"s diverse ecosystems. Here"s what lies ahead:
- Climate Change: Global warming presents a profound challenge, altering habitats and threatening species with extinction. Adaptation and mitigation strategies will be key in conserving ecosystems affected by climate shifts.
- Urbanization and Land Use Change: Expanding urban areas and changing land use for agriculture and development continue to fragment and degrade ecosystems. Innovative solutions for sustainable development and urban planning are needed.
- Biodiversity Loss: Halting the loss of biodiversity requires enhanced protection efforts, restoration of degraded ecosystems, and the sustainable management of natural resources.
- Pollution: Tackling pollution in all its forms is essential for the health of ecosystems. Initiatives to reduce plastic waste, curb emissions, and clean up polluted habitats will be crucial.
- Engagement and Education: Raising awareness and engaging communities in conservation efforts are vital for success. Education can foster a deeper connection with nature and a commitment to its protection.
- Technological Advances: Technology offers new tools for monitoring biodiversity, restoring ecosystems, and reducing human impacts. Leveraging these tools can enhance conservation efforts.
- International Cooperation: Ecosystem conservation is a global issue that requires coordinated international efforts. Strengthening global partnerships and agreements can address cross-border conservation challenges.
The future of ecosystem conservation is filled with challenges, but also abundant opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and progress. By embracing these opportunities, we can ensure the preservation of ecosystem diversity for future generations.
"Embracing the kaleidoscope of ecosystem diversity is our path to a resilient and flourishing planet. Together, we can forge a future where nature"s symphony continues to inspire and sustain life in all its forms."