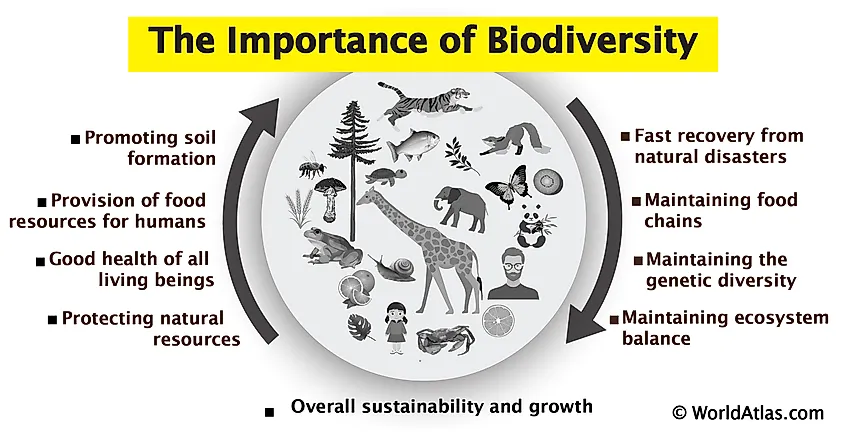
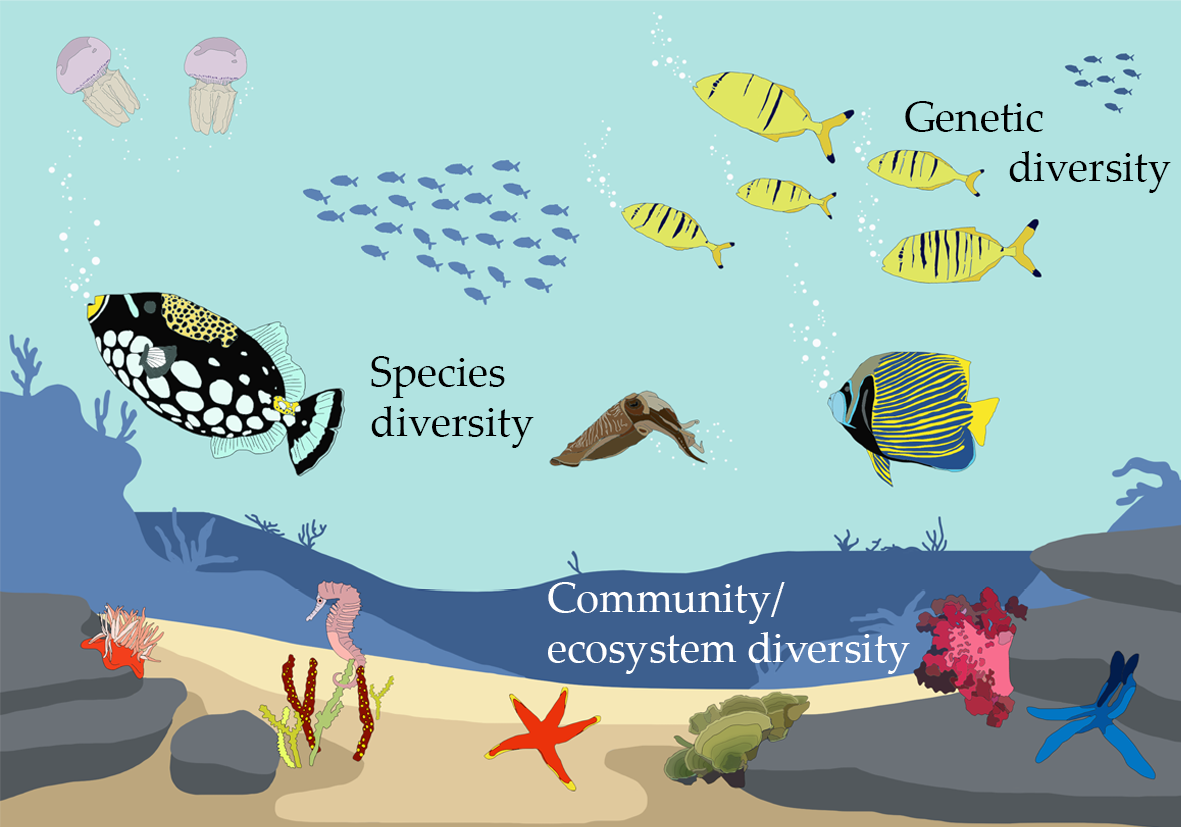
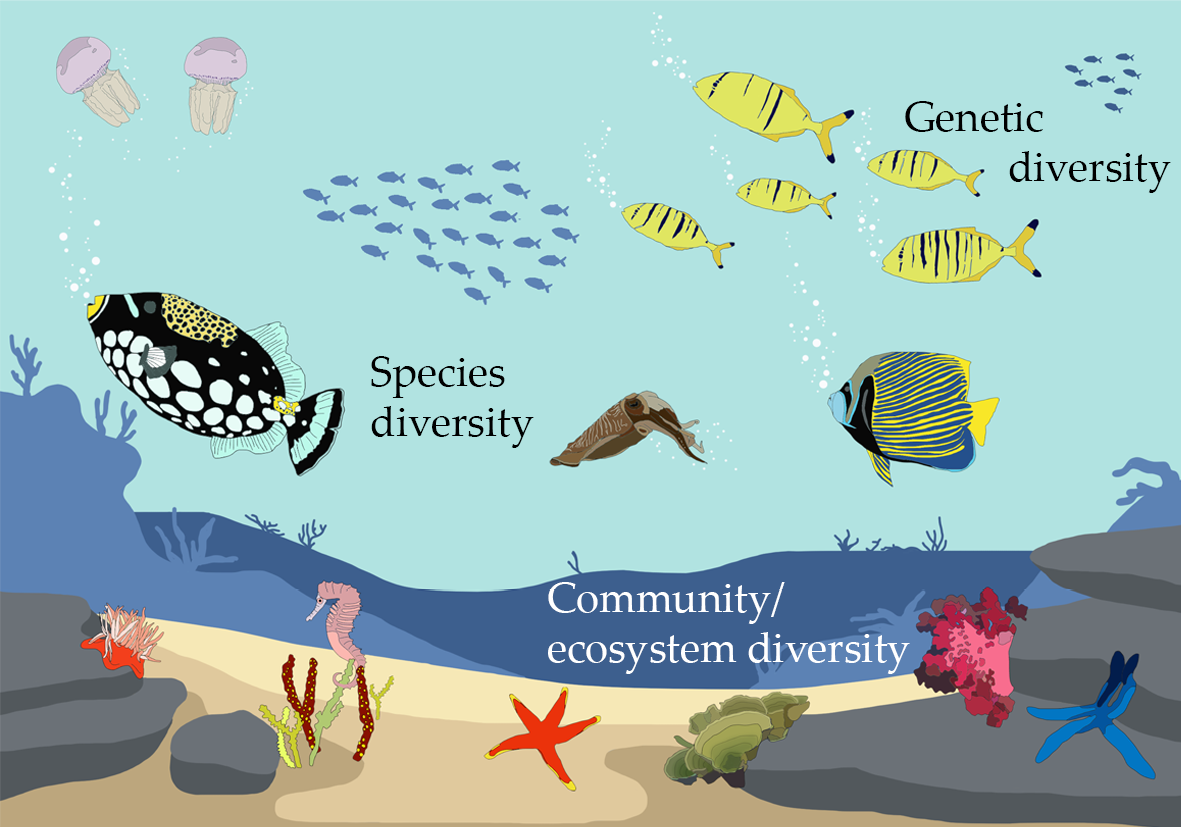
Topic diversity ecosystem: Explore the captivating world of diversity ecosystems, where the intricate interplay of life forms creates a resilient and vibrant planet, fostering sustainability and balance in our global environment.
Table of Content
- How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the stability of an environment?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Unique Characteristics
- Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Biodiversity
- Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
- The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the stability of an environment?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems within a specific geographic location. It encompasses both biotic and abiotic components of these ecosystems. Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in contributing to the stability of an environment in several ways:
- Enhanced resilience: A diverse range of ecosystems provides a greater capacity for resilience in the face of disturbances or changes in environmental conditions. Different ecosystems may have varying responses to disturbances, which reduces the overall vulnerability of the environment.
- Increased productivity: Ecosystems with higher biodiversity tend to exhibit greater productivity. This is because diverse ecosystems are better equipped to utilize resources efficiently, leading to a more efficient cycling of nutrients and energy within the ecosystem.
- Improved ecosystem services: Ecosystem diversity ensures the provision of a wide range of ecosystem services. For example, diverse ecosystems contribute to carbon sequestration, water purification, pollination, and soil fertility. These services are essential for the well-being of both ecological systems and human populations.
- Greater genetic diversity: Ecosystem diversity also contributes to genetic diversity within populations. Genetic diversity enables populations to adapt and evolve in response to changing environmental conditions, improving their ability to withstand threats such as diseases, invasive species, or climate change.
- Support for interconnectedness: Different ecosystems are often interconnected and function as part of larger ecological networks. This interconnectedness allows for the movement of species, nutrients, and energy between ecosystems, promoting overall stability and sustainability.
In summary, ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the stability of an environment. It enhances resilience, increases productivity, provides valuable ecosystem services, supports genetic diversity, and promotes interconnectedness between ecosystems. By valuing and protecting ecosystem diversity, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of our environment.
READ MORE:
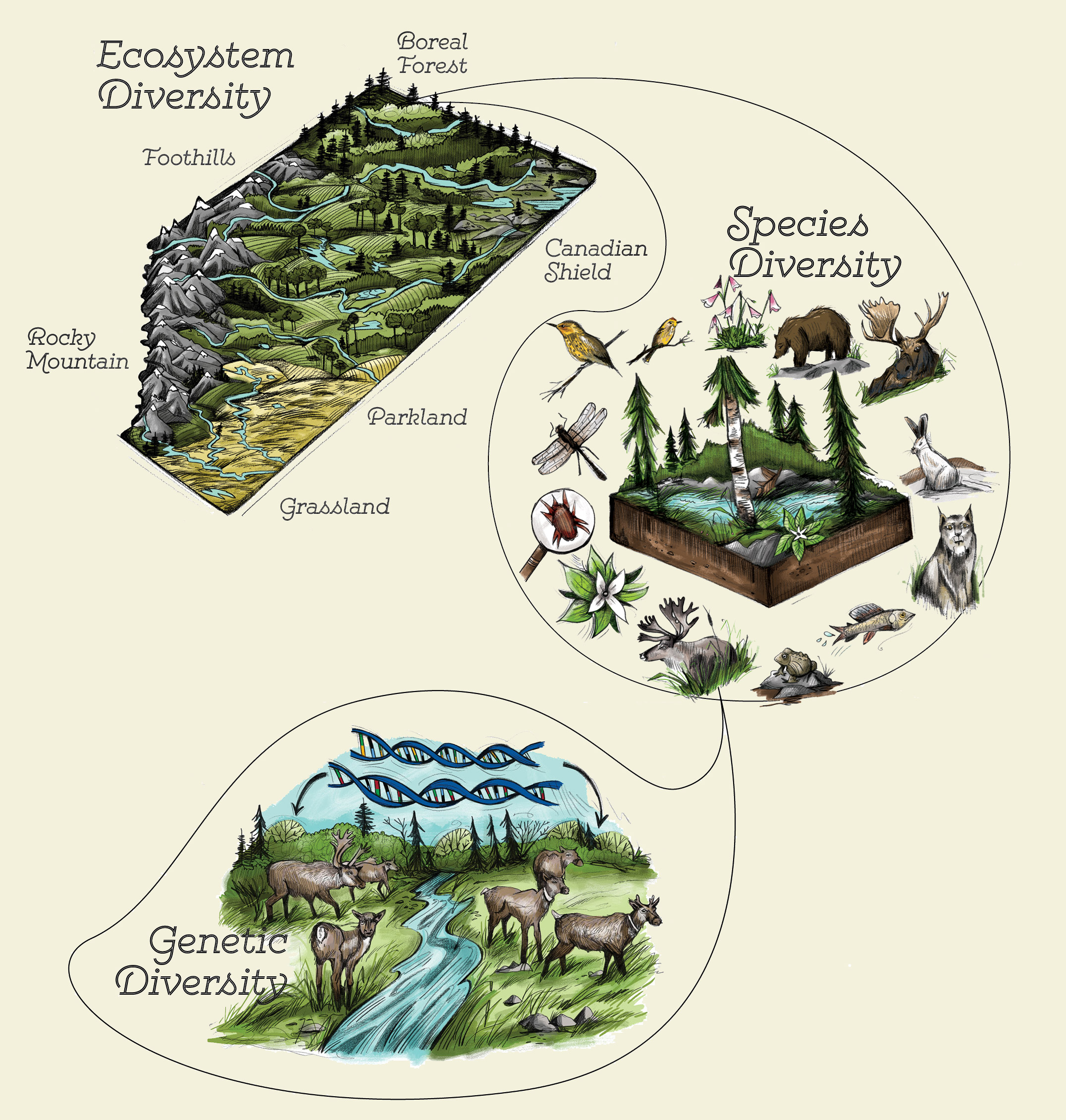
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of environments, living organisms, and the complex processes in their habitats including forests, deserts, wetlands, oceans, lakes, and rivers. It encompasses the diversity of interactions among organisms and their environments, forming a web of life that supports, regulates, and enriches our planet.
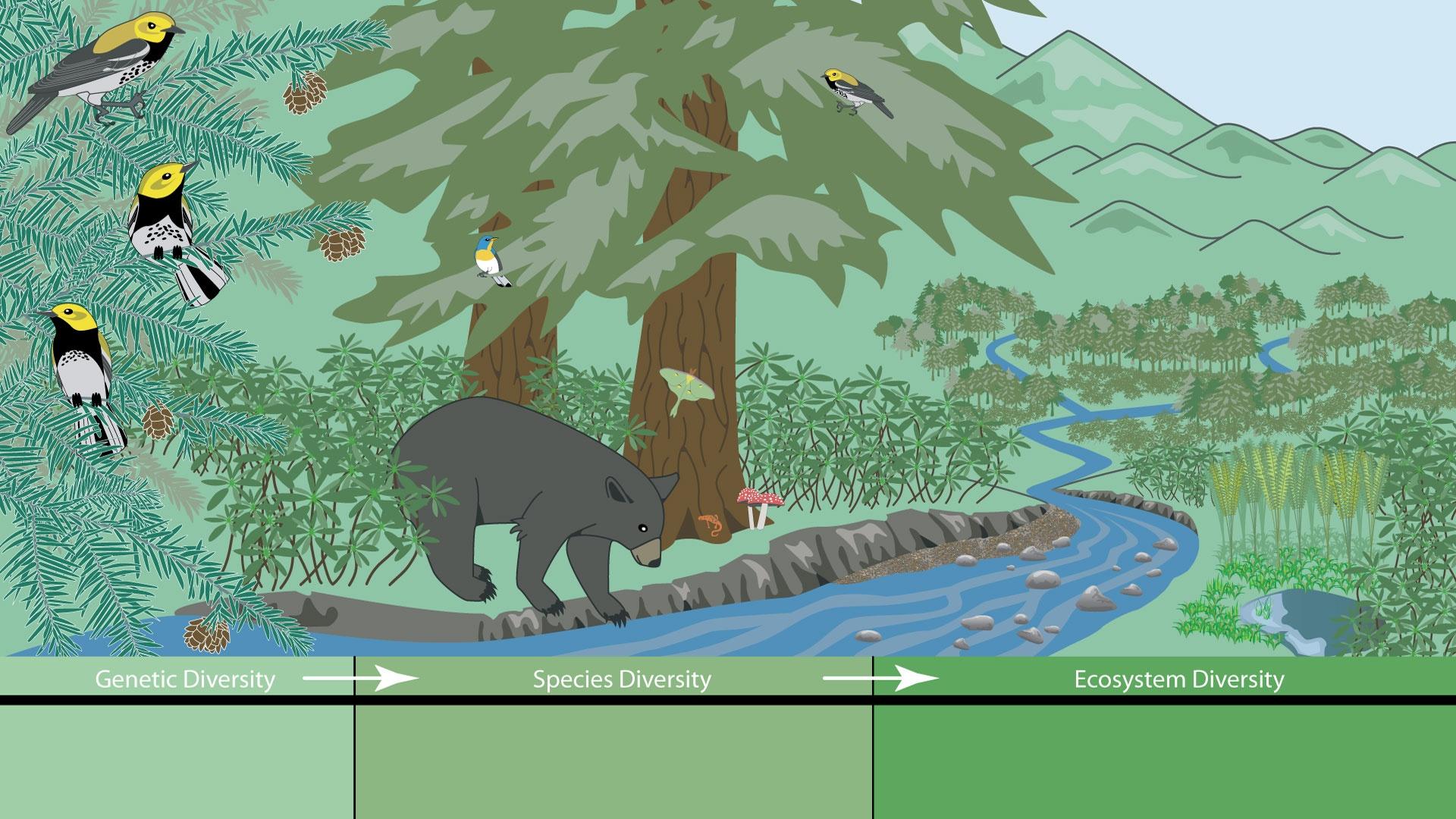
- Biomes: Large community of plants and animals that occupy a major habitat.
- Genetic Diversity: The variety of genes within a species.
- Species Diversity: The number of different species within an ecosystem.
- Functional Diversity: The range of different functions performed by organisms within an ecosystem.
This diversity ensures natural sustainability for all life forms and provides the foundation for the ecosystems" services humans rely on for survival, including air and water purification, pollination of crops, and climate regulation.

Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining the balance and sustainability of our planet. It plays a significant role in providing essential services and benefits that support life on Earth, including humans.
- Supports Biodiversity: Rich ecosystems support a wider range of species, contributing to greater biodiversity which is key for resilience and adaptation.
- Climate Regulation: Diverse ecosystems like forests and oceans act as carbon sinks, helping to regulate the Earth"s climate by absorbing CO2.
- Food Security: Ecosystem diversity ensures a variety of crops and wild food sources, enhancing food security and nutritional health.
- Medicinal Resources: Many medicines are derived from plants and animals in diverse ecosystems, highlighting the importance of conserving these natural pharmacies.
- Water Regulation and Purification: Wetlands and forests play critical roles in water purification and the regulation of water cycles, ensuring clean water supply.
- Economic Benefits: Ecosystems contribute to economies through tourism, fishing, and agriculture, providing livelihoods for billions of people.
- Cultural and Recreational Value: Natural landscapes offer cultural significance and recreational opportunities, enhancing human well-being and community.
Ultimately, ecosystem diversity is a cornerstone for ecological stability, human health, and economic prosperity, underscoring the need for urgent conservation and sustainable management efforts.
Types of Ecosystems and Their Unique Characteristics
Ecosystems are diverse and vary widely across the globe, each with unique characteristics and life forms. Understanding the different types of ecosystems is crucial for appreciating the diversity of life on Earth.
- Forest Ecosystems: Characterized by dense tree populations, these ecosystems are crucial for carbon storage, oxygen production, and biodiversity. They are subdivided into tropical, temperate, and boreal forests.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Including both freshwater (lakes, rivers, wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs) environments, aquatic ecosystems are vital for water regulation, habitat provision, and supporting diverse marine life.
- Desert Ecosystems: Defined by low precipitation, deserts are home to uniquely adapted plants and animals that can withstand harsh, dry conditions.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Dominated by grasses, these areas support a variety of fauna and are important for agriculture and livestock. Grasslands include savannas and temperate grasslands.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Characterized by cold temperatures and short growing seasons, tundras support a limited range of plants and animals adapted to extreme conditions.
- Mountain Ecosystems: Varied climates and altitudes create diverse habitats within mountain ecosystems, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
Each ecosystem type plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of our planet"s environmental systems, contributing to the overall health and diversity of life on Earth.
Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity, or the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem, is fundamental to the stability and resilience of ecosystems. It ensures the sustainability of complex ecological processes and services.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand environmental changes and recover from disturbances, such as natural disasters and climate change impacts.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity contributes to the provision of essential ecosystem services, including air and water purification, soil fertility, pollination, and disease regulation.
- Promotes Productivity: A greater variety of species in an ecosystem can lead to higher productivity, ensuring that ecosystems can maintain and support more life.
- Genetic Diversity: Genetic variation within and across species ensures adaptability and survival under changing environmental conditions, contributing to ecosystem stability.
- Ecological Balance: Biodiversity maintains a balance among species, preventing any single species from dominating and destabilizing the ecosystem.
The role of biodiversity in stabilizing ecosystems is irreplaceable, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to protect diverse habitats and species for the health of our planet.
Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have significantly impacted ecosystem diversity across the globe, often leading to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change, among other effects. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate damage and preserve biodiversity.
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, critically endangering numerous species and ecosystems.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal disrupts ecosystems and harms wildlife.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and altered weather patterns affect the distribution and viability of many species, impacting ecosystem diversity and functionality.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at unsustainable rates diminish species populations and genetic diversity, reducing ecosystem resilience.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balances.
- Resource Depletion: Unsustainable resource extraction, such as mining, logging, and water use, degrades ecosystems and reduces their capacity to support diverse life forms.
Addressing these impacts through sustainable practices, conservation efforts, and global cooperation is essential for the preservation and restoration of ecosystem diversity for future generations.

Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of our planet"s environments and ensuring the survival of countless species. Various strategies and efforts are being implemented worldwide to protect and restore diverse ecosystems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats from human encroachment and exploitation.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and the reintroduction of native species to restore ecological balance.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and conserve resources.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing environmental laws and policies that regulate emissions, limit deforestation, and protect endangered species and habitats.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their role and knowledge in managing and protecting ecosystems.
- International Agreements: Participating in global treaties and collaborations, such as the Convention on Biological Diversity, to address environmental challenges collectively.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research to understand ecosystems better and monitoring biodiversity to inform conservation strategies.
These efforts, combined with increased public awareness and education, are crucial for the conservation of ecosystem diversity, ensuring a healthy and resilient planet for future generations.
Ecosystem Biodiversity
\"Discover the wonders of biodiversity in our captivating video! Immerse yourself in the vibrant colors, unique species, and intricate connections that make our planet so special. Join us and become a guardian of biodiversity!\"
What Is an Ecosystem?
\"Explore the remarkable balance and beauty of ecosystems in our enlightening video. From lush rainforests to sprawling coral reefs, witness the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. Step into this captivating world and discover the hidden secrets of ecosystems!\"
Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
While efforts to preserve ecosystem diversity are ongoing, several challenges complicate these endeavors. Addressing these issues is crucial for effective conservation strategies.
- Climate Change: Rapid climate shifts challenge ecosystems" ability to adapt, threatening species with extinction and altering habitat viability.
- Habitat Loss: Expanding urbanization, agriculture, and industrial activities consume natural habitats, fragmenting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity.
- Pollution: Contamination of air, water, and soil from industrial and agricultural activities harms species and disrupts ecological processes.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can dominate ecosystems, displacing native species and disrupting ecological balance.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable harvesting of resources, including logging, fishing, and hunting, depletes populations and degrades ecosystems.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient public understanding and appreciation of ecosystem diversity limits support for conservation efforts.
- Political and Economic Priorities: Conservation often competes with economic development goals, leading to policies that favor exploitation over preservation.
Overcoming these challenges requires integrated approaches that combine scientific research, policy innovation, public engagement, and international cooperation to ensure the preservation of ecosystem diversity for the benefit of all life on Earth.

Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
Across the globe, numerous ecosystem restoration projects have demonstrated the potential for human intervention to positively impact and restore biodiversity and ecological balance. Here are some notable examples:
- The Loess Plateau in China: Once one of the most eroded regions in the world, extensive reforestation and sustainable agricultural practices have transformed it into fertile land, significantly improving local livelihoods.
- Yellowstone National Park in the USA: The reintroduction of wolves in 1995 has led to remarkable ecological changes, demonstrating the importance of top predators in ecosystem health.
- The Great Green Wall in Africa: An ambitious initiative to combat desertification across the Sahel region by planting a belt of trees across Africa, improving biodiversity and supporting local communities.
- New Zealand’s Predator-Free 2050: Aiming to eradicate invasive predator species to protect native wildlife, showcasing the critical role of removing invasive species for ecosystem recovery.
- The Danube River Restoration in Europe: Efforts to restore floodplains and wetlands have improved water quality, increased biodiversity, and restored natural river dynamics.
These case studies highlight the positive outcomes that can be achieved with committed restoration efforts, offering valuable lessons and inspiration for future projects aimed at preserving ecosystem diversity.
READ MORE:
The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on our actions today. With concerted global efforts, innovative conservation strategies, and sustainable practices, we can ensure the preservation and flourishing of diverse ecosystems around the world.
- Increased Conservation Initiatives: Expanding protected areas and implementing more ambitious global conservation targets to safeguard critical habitats.
- Restoration and Rehabilitation: Investing in large-scale restoration projects to revive degraded ecosystems and enhance biodiversity.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating biodiversity considerations into urban planning, agriculture, and industry to minimize environmental impacts.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Adopting aggressive measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change, protecting ecosystems from its adverse effects.
- Community Engagement and Education: Fostering a deeper connection between people and nature through education and participatory conservation projects, encouraging stewardship of the natural world.
- Technological Innovation: Leveraging technology for better monitoring, managing, and restoring ecosystems, including the use of satellite imagery and bioengineering.
- International Cooperation: Strengthening global collaboration to address transboundary environmental challenges and share successful conservation practices.
By embracing these approaches, we can work towards a future where ecosystem diversity is not only preserved but thrives, supporting a healthy planet for generations to come.
Embracing ecosystem diversity is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Through conservation and awareness, we can foster a resilient and vibrant planet for future generations, ensuring a harmonious balance between humans and nature.