Topic diversity of ecosystem: Explore the "Diversity of Ecosystem" to unveil the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. From lush rainforests to arid deserts, discover how each unique ecosystem plays a critical role in global ecology.
Table of Content
- How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the variety of habitats and communities found in a specific geographic location?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
- Challenges Facing Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies of Ecosystem Recovery and Success
- Future Directions in Ecosystem Diversity Research
How does ecosystem diversity contribute to the variety of habitats and communities found in a specific geographic location?
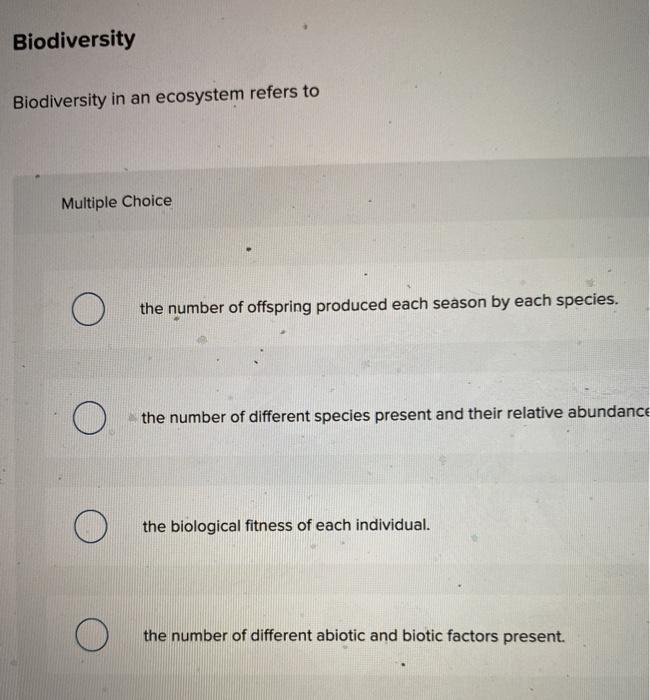
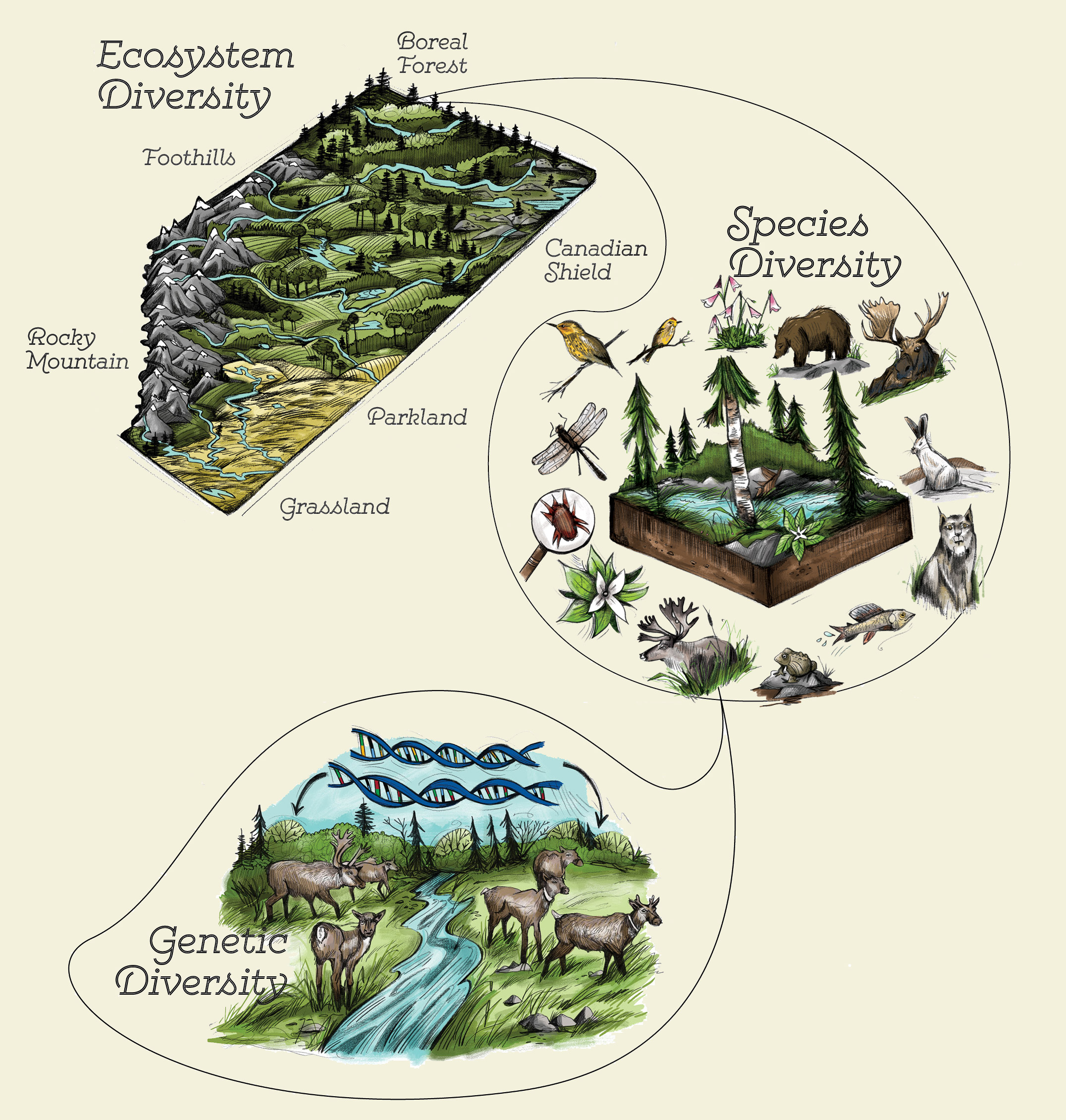
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems within a specific geographic location. It plays a crucial role in contributing to the variety of habitats and communities found in that area.
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how ecosystem diversity contributes to the variety of habitats and communities:
- Ecosystem differentiation: Ecosystem diversity leads to the differentiation of various habitats within a geographic location. Each ecosystem has its own unique characteristics, such as climate, soil type, topography, and vegetation. These differences create a range of habitats, providing diverse niches for different organisms to thrive.
- Species adaptation: The different habitats resulting from ecosystem diversity provide opportunities for species to adapt and specialize in specific conditions. Organisms evolve and adapt to their specific habitat requirements, such as temperature, moisture, and food availability. This adaptation leads to the creation of unique communities within each habitat.
- Species interactions: In diverse ecosystems, the variety of habitats and communities allow for a multitude of species interactions. Different species rely on each other for food, shelter, reproduction, and other ecological services. For example, a forest ecosystem may support interactions between tree species, birds, mammals, insects, and fungi, each playing their roles in a complex web of relationships.
- Increased resilience: Ecosystem diversity enhances the resilience of the overall ecosystem. If one habitat or community is negatively affected by a disturbance, such as a natural disaster or human intervention, other habitats and communities can potentially withstand the impact. This resilience helps maintain the overall stability and functioning of the ecosystem.
In summary, ecosystem diversity contributes to the variety of habitats and communities found in a specific geographic location through ecosystem differentiation, species adaptation, species interactions, and increased resilience. These factors work together to create a rich tapestry of life and support the conservation of biodiversity within ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the natural world. It includes the different kinds of ecosystems, such as forests, deserts, grasslands, wetlands, and marine environments. Each ecosystem supports its own unique set of species and interactions among those species, as well as between organisms and their physical environment.
- Types of Ecosystems: The planet hosts a multitude of ecosystem types, each with distinct climates, geographies, and life forms.
- Biological Interactions: Ecosystem diversity is driven by the myriad interactions between organisms, including predation, competition, and symbiosis.
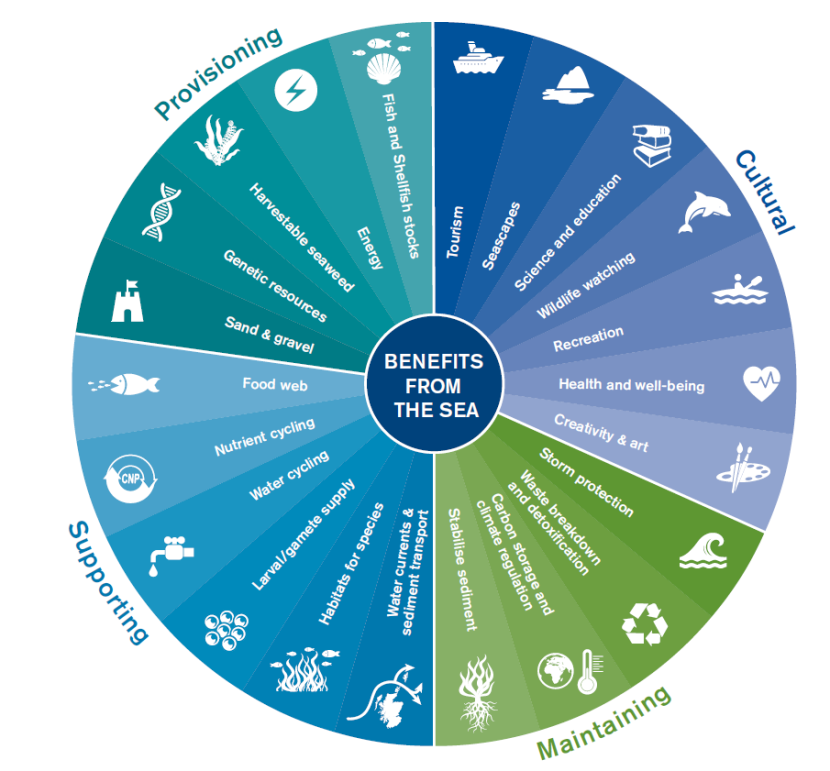
- Importance of Diversity: A diverse ecosystem is crucial for the resilience and stability of ecological processes, supporting everything from soil formation and nutrient cycling to water filtration and the production of oxygen.
Ecosystem diversity not only underpins the functioning of the biosphere but also provides essential services to human society, such as food, fresh water, and raw materials, along with recreational and cultural benefits.

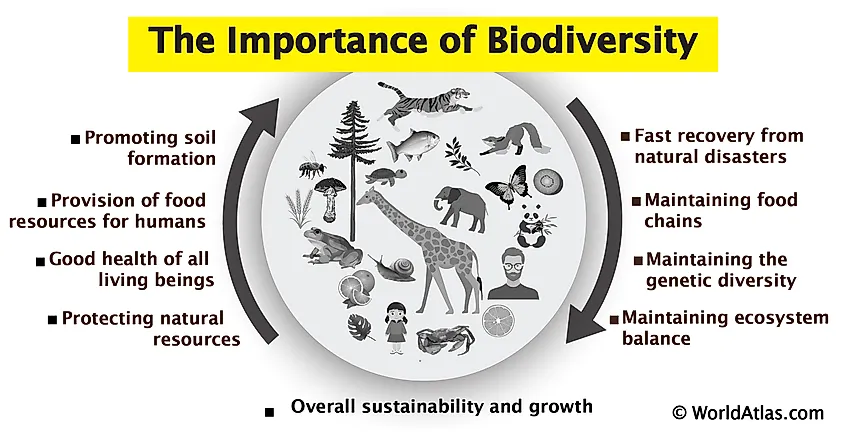
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is fundamental to the health and stability of our planet. It ensures natural sustainability for all life forms and provides the essential services upon which human civilization relies. The benefits of ecosystem diversity touch every aspect of our lives, from environmental to economic and beyond.
- Supports Biodiversity: Diverse ecosystems are critical habitats for a wide range of species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the planet.
- Regulates Climate: Different ecosystems play key roles in carbon sequestration and regulating global climate patterns.
- Provides Resources: Ecosystems supply a wealth of resources including food, fiber, medicinal plants, and the raw materials for products.
- Ensures Resilience: A variety of ecosystems means greater resilience against environmental disturbances, helping to maintain ecological balance and recovery from disasters.
- Supports Human Well-being: Beyond physical resources, ecosystems contribute to mental and physical health through recreational and spiritual benefits.
Protecting and preserving ecosystem diversity is thus not only an environmental imperative but a necessity for sustaining human life and economic development.
Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
Ecosystems vary widely across the globe, each with unique characteristics and life forms. Understanding the main types of ecosystems and their features helps us appreciate the diversity of life on Earth.
- Forest Ecosystems: Characterized by dense trees and rich biodiversity, including various species of plants, animals, and microorganisms. They are critical for carbon storage and oxygen production.
- Desert Ecosystems: Defined by low rainfall, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation. Adaptations in this ecosystem include drought-tolerant flora and fauna specialized for survival in harsh conditions.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Dominated by grasses, these ecosystems are found in regions with moderate to low rainfall. They are important for supporting herbivores and are often used for agriculture.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Includes freshwater (lakes, rivers, and ponds) and marine (oceans, estuaries, and coral reefs) environments. They are vital for water cycling, climate regulation, and supporting a wide range of aquatic life.
- Wetland Ecosystems: Areas where water covers the soil for part of the year. They are crucial for water purification, flood protection, and providing habitat for diverse species.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Characterized by cold temperatures, low biodiversity, and a short growing season. The tundra is home to specialized species adapted to extreme cold.
Each type of ecosystem plays a unique role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life. By protecting these ecosystems, we ensure the survival of the intricate networks of life they support.

Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is affected by a combination of natural and human-induced factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for the conservation and management of biodiversity.
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight are primary drivers of ecosystem diversity, influencing habitat conditions and species survival.
- Geography: Geographic features such as mountains, rivers, and soil types play a significant role in shaping ecosystems by creating diverse habitats.
- Altitude: Changes in altitude affect climate conditions, leading to different ecosystems at various heights, from lowland forests to alpine meadows.
- Human Activities: Agriculture, urbanization, deforestation, and pollution significantly impact ecosystem diversity by altering habitats and reducing species populations.
- Biological Factors: Interactions among species, such as competition, predation, and symbiosis, also influence ecosystem diversity.
- Conservation Efforts: Protection, restoration, and sustainable management practices can enhance or restore ecosystem diversity.
These factors interact in complex ways to determine the richness and composition of ecosystems. Addressing the challenges of ecosystem diversity requires a holistic approach that considers all underlying factors.
Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and resilience of ecosystems. The variety of life forms within a given ecosystem contributes to the complexity and functionality of ecological networks, enhancing ecosystem health and productivity.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse species contribute to the efficient cycling of nutrients, ensuring essential elements are available to different organisms within the ecosystem.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Biodiversity supports processes like pollination and seed dispersal, crucial for the reproduction of many plant species and the continuation of food webs.
- Pest and Disease Control: A variety of predators and parasites helps regulate populations of potential pests and reduces the incidence of disease, protecting ecosystem health.
- Climate Regulation: Biodiverse ecosystems play a key role in regulating the climate, with plants and trees acting as carbon sinks and influencing local and global climate patterns.
- Resilience to Environmental Changes: High biodiversity increases an ecosystem"s ability to withstand and recover from environmental stresses and disturbances, promoting long-term stability.
Thus, the conservation of biodiversity is essential not only for the intrinsic value of ecosystems but also for the sustainability of the services they provide to humanity.
Challenges Facing Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems across the globe is under threat from various challenges, many of which are exacerbated by human activities. Addressing these threats is critical for the preservation of our planet"s biodiversity and the well-being of future generations.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, directly reducing ecosystem diversity.
- Climate Change: Alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns affect ecosystem functioning and species distribution, putting stress on biodiversity.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade ecosystems and harm wildlife.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced to new areas can outcompete, predatize, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balances.
- Overexploitation: Excessive hunting, fishing, and resource extraction can deplete species and degrade ecosystems.
- Policy and Management: Insufficient environmental policies and poor natural resource management practices contribute to the degradation of ecosystem diversity.
Combating these challenges requires global cooperation and the implementation of sustainable practices to ensure the protection and restoration of ecosystem diversity.
Ecosystem Diversity
Explore the fascinating world of ecosystems in this captivating video. Discover the intricate balance of nature and witness the diverse species that call these enchanting environments home. Journey through lush forests, vibrant coral reefs, and sprawling grasslands, and gain a deep appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things.
Ecosystem Biodiversity
Immerse yourself in the wonders of biodiversity through this awe-inspiring video. Marvel at the incredible array of life forms that inhabit our planet, from tiny microorganisms to majestic elephants. Learn about the importance of preserving and protecting this richness of species, ensuring a harmonious coexistence for generations to come. Witness the beauty and resilience of nature\'s masterpiece - biodiversity.
Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Preserving the diversity of ecosystems is essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth. Various conservation strategies can be employed to protect and restore these vital natural systems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard habitats from human activities.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and the reintroduction of native species.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to minimize environmental impact and protect biodiversity.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance ecosystem resilience to climate change.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their role in managing and protecting natural resources.
- Legislation and Policies: Enforcing environmental laws and policies that promote the conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating on global initiatives and agreements to address transboundary conservation challenges and share best practices.
Through these strategies, we can work towards a sustainable future that values and preserves the diversity of ecosystems for generations to come.

Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have profound impacts on ecosystem diversity, often leading to its degradation. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative effects and promote biodiversity conservation.
- Land Use Changes: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation alter landscapes, reducing natural habitats and biodiversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial and agricultural processes can harm ecosystems and the species that depend on them.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects temperature, precipitation patterns, and sea levels, disrupting ecosystems worldwide.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at unsustainable rates lead to species decline and loss of biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompeting or preying on native species.
- Resource Extraction: Mining, logging, and drilling for oil and gas can result in habitat destruction and pollution.
Addressing human impacts on ecosystem diversity requires concerted efforts towards sustainable living, environmental protection, and the adoption of conservation practices.
Case Studies of Ecosystem Recovery and Success
Ecosystem recovery projects around the world showcase the resilience of nature and the positive outcomes of conservation efforts. These case studies highlight the success of various strategies in restoring ecosystem diversity and functionality.
- The Everglades, USA: Comprehensive restoration efforts including water flow restoration and invasive species management have led to significant improvements in water quality and habitat recovery.
- The Loess Plateau, China: Large-scale land restoration projects have transformed degraded agricultural land into a vibrant ecosystem, increasing biodiversity and improving local livelihoods.
- Chernobyl, Ukraine: Following the nuclear disaster, the unintentional rewilding created a refuge for wildlife, demonstrating nature"s ability to recover from severe human-induced disturbances.
- Yellowstone National Park, USA: The reintroduction of wolves in 1995 has led to cascading positive effects on ecosystem structure and species populations, exemplifying trophic rewilding success.
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Efforts to reduce water pollution and control crown-of-thorns starfish populations are crucial in protecting and recovering coral ecosystems.
These examples underscore the potential for ecosystem recovery through dedicated conservation initiatives, sustainable management practices, and international cooperation.

READ MORE:
Future Directions in Ecosystem Diversity Research
Advancing our understanding of ecosystem diversity and developing strategies for its conservation are critical challenges for the future. Research in this area is evolving, with new directions offering promise for deeper insights and more effective conservation efforts.
- Integrative Approaches: Combining traditional ecological studies with advancements in genomics, remote sensing, and data analysis to gain comprehensive insights into ecosystem dynamics.
- Climate Change Impacts: Focusing on understanding how changing climates affect ecosystem diversity and developing adaptation strategies for vulnerable ecosystems.
- Human-Nature Interactions: Examining the complex relationships between human activities and ecosystem health to guide sustainable development and conservation policies.
- Restoration Ecology: Enhancing methods for restoring degraded ecosystems, including rewilding and the use of native species to improve biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Global Biodiversity Monitoring: Developing global networks for monitoring biodiversity and ecosystems to track changes, identify threats, and inform conservation actions.
- Policy and Governance: Researching effective governance models and policy frameworks that support biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
Future research in ecosystem diversity is poised to play a pivotal role in addressing environmental challenges and guiding global conservation efforts towards sustainability and resilience.
In the journey to understand and protect the diversity of ecosystems, each step reveals the interconnectedness of life on Earth, highlighting our role in nurturing this precious diversity for future generations.