Topic meaning of ecosystem diversity: Discover the essence of ecosystem diversity, a vital component of our planet"s health, illustrating the variety of life and the complex interactions within natural habitats.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
- What is Ecosystem Diversity?
- Types of Ecosystems
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
- Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies on Ecosystem Diversity
- Future of Ecosystem Diversity
What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety and variation of ecosystems present in a given geographic area. It encompasses the range of different habitats, communities, and ecological processes found within an ecosystem. Ecosystem diversity takes into account both the biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living components) properties that contribute to the overall composition and functioning of an ecosystem.
Here are a few key points to understanding the definition of ecosystem diversity:
- Habitat Variety: Ecosystem diversity considers the different types of habitats found within a specific region. This includes terrestrial (land), aquatic (water-based), and even aerial (air-based) habitats.
- Community Composition: Ecosystem diversity encompasses the various communities of organisms that inhabit a given area. This includes plants, animals, microorganisms, and their interactions with each other and the environment.
- Ecological Functions: Ecosystem diversity takes into account the different processes and functions that occur within ecosystems. These functions can include nutrient cycling, energy flow, pollination, water purification, and many others.
By understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of our planet. It supports the overall stability and resilience of ecosystems, provides essential ecosystem services, and contributes to the overall well-being of both humans and biodiversity.
READ MORE:
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems within a specific geographical area, encompassing different habitats, communities, and ecological processes. It is a measure of the richness and complexity of the natural world, including forests, deserts, grasslands, wetlands, oceans, and all the living beings and physical environments within these contexts.
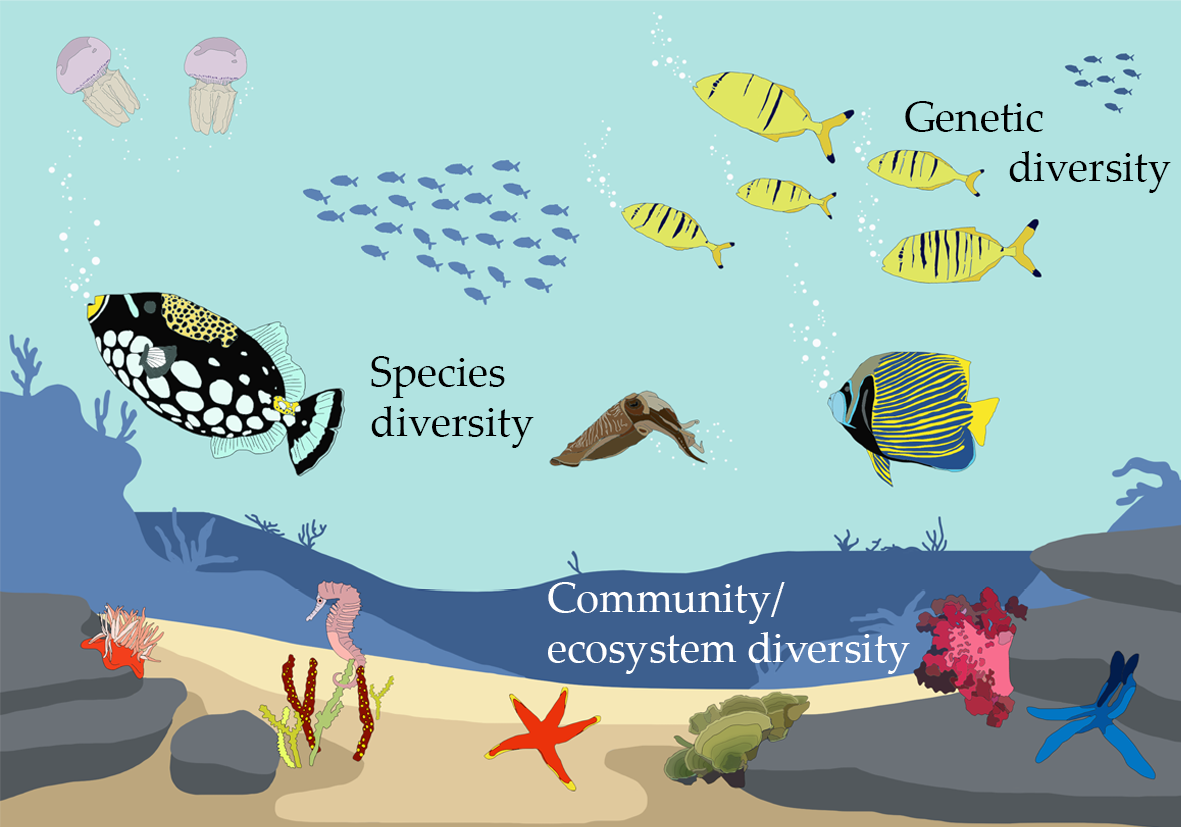
- Variety of Habitats: It includes the range of different places where life exists, from vast oceans to tiny creeks, each supporting unique species and ecological functions.
- Species Diversity: This component highlights the number of species within ecosystems, contributing to its overall diversity.
- Genetic Diversity: Within each species, genetic diversity plays a critical role in ecosystem resilience and adaptability.
Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and providing services essential for human survival, such as clean air and water, pollination of crops, and climate regulation. It also offers cultural, educational, and recreational values, enriching our lives in countless ways.

Types of Ecosystems
The planet Earth is home to a wide array of ecosystems, each with unique characteristics and life forms. Ecosystems are categorized based on their environments and the interactions between the organisms that inhabit them. Here are the primary types of ecosystems:
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These include forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundra, each supporting distinct flora and fauna adapted to their specific conditions.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater (rivers, lakes, and ponds) and marine (oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries) systems, each hosting diverse species adapted to water environments.
- Forest Ecosystems: Forests are crucial for biodiversity, providing habitat for a vast number of species. They are subdivided into tropical, temperate, and boreal forests.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Grasslands, including savannas and prairies, are dominated by grasses and have a wide range of herbivores and predators.
- Desert Ecosystems: Deserts are characterized by low precipitation and extreme temperatures, with specialized plants and animals adapted to these harsh conditions.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Tundra regions, found in the Arctic and Antarctic, feature cold, dry climates with permafrost, supporting limited vegetation and animal life.
- Urban Ecosystems: Urban areas, while heavily influenced by human activities, form unique ecosystems integrating both natural and artificial elements.
Each ecosystem type plays a vital role in the global ecology, contributing to the planet"s overall biodiversity and ecological balance.
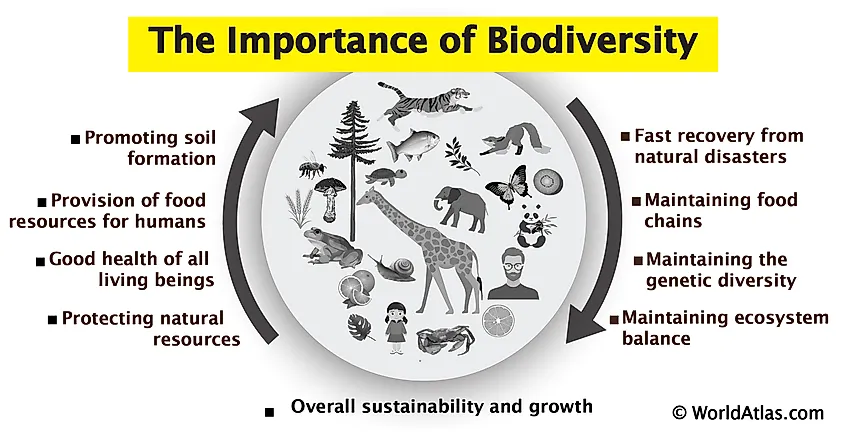
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is a cornerstone of ecological health and sustainability, underpinning the resilience and functionality of the biosphere. It is critical for the following reasons:
- Supports Biodiversity: Diverse ecosystems provide habitats for a wide range of species, supporting genetic, species, and habitat diversity which are essential for evolutionary processes and biological diversity.
- Ensures Natural Sustainability: The variety of ecosystems contributes to natural processes such as water purification, soil formation and protection, nutrient recycling, and pollination, all of which are essential for life on Earth.
- Enhances Resilience: Ecosystem diversity enhances the resilience of the environment to withstand and recover from natural disasters and human-induced impacts, including climate change.
- Provides Ecosystem Services: Diverse ecosystems offer invaluable services that contribute to human well-being, including food, medicines, and raw materials, along with recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits.
- Promotes Economic Benefits: Many industries, such as agriculture, forestry, and tourism, directly rely on the sustainable management of diverse ecosystems.
- Climate Regulation: Ecosystems play a key role in regulating the climate, including carbon sequestration by forests and oceans, influencing local and global climate patterns.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is therefore imperative for maintaining the planet’s health, ensuring sustainable development, and securing a livable environment for future generations.

Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity faces numerous threats that can significantly impact the health and stability of the planet"s various habitats. Addressing these threats is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the continuation of ecosystem services. Major threats include:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urban expansion, agriculture, and mining lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, posing one of the most significant threats to ecosystem diversity.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt ecosystems, affecting species distribution and ecosystem functionality.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources degrade ecosystems, affecting both wildlife and human health.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balances and leading to biodiversity loss.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, and logging deplete resources faster than they can regenerate, leading to species extinction and loss of ecosystem services.
- Climate Change: Alters habitats and conditions, forcing species migration, which can lead to ecosystem imbalance and loss of biodiversity.
Combating these threats requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and policies that prioritize the protection of natural habitats and the biodiversity they support.
Conservation Efforts for Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth. Various strategies and initiatives have been developed to protect and restore ecosystems. Key conservation efforts include:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and sanctuaries to protect habitats and provide safe havens for species.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, to restore ecological balance and biodiversity.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to minimize environmental impact and ensure the long-term viability of resources.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate pollution, and manage natural resources sustainably.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in the preservation of ecosystems.
- International Agreements: Participating in global treaties and collaborations, such as the Convention on Biological Diversity, to address environmental challenges collectively.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research to understand ecosystems better and monitoring changes to assess conservation strategies" effectiveness.
Through these concerted efforts, it is possible to mitigate the threats to ecosystem diversity and ensure a resilient and vibrant natural world for future generations.

Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides to humans, essential for survival, economic activity, and our overall quality of life. These services are directly linked to the diversity and health of ecosystems. Understanding and valuing these services is critical for sustainable development and human well-being. Key ecosystem services include:
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood, fiber, and genetic resources. Healthy ecosystems ensure a stable supply of these resources.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality. Forests, for example, sequester carbon, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Cultural Services: Natural landscapes and ecosystems provide cultural, aesthetic, spiritual, and educational benefits, enriching human experience and fostering well-being.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and the water cycle.
The protection and restoration of ecosystem diversity are thus not only a matter of conserving nature but also of safeguarding and enhancing human health, livelihoods, and happiness. By investing in ecosystem conservation, we invest in our future.
Ecosystem Diversity
Discover the mesmerizing beauty and astounding balance of our planet\'s ecosystem in this captivating video. Dive into the rich biodiversity and witness the interconnectedness of life that makes our world thrive. Get ready to be inspired and awestruck by the wonders of nature!
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
Join us on a remarkable journey through the incredible tapestry of diversity that exists in our world. This thought-provoking video celebrates the uniqueness of every living being, showcasing the power of diversity to foster understanding and harmony. Prepare to be amazed by the multitude of colors, shapes, and cultures that make our planet a truly extraordinary place.
Case Studies on Ecosystem Diversity
Exploring case studies on ecosystem diversity provides valuable insights into the importance of preserving varied ecosystems and the impact of human activities on them. These studies highlight successful conservation efforts and the challenges faced in maintaining ecosystem diversity. Notable examples include:
- The Amazon Rainforest: Home to an incredible variety of species, the Amazon showcases the critical importance of tropical forests in biodiversity conservation and carbon storage. Efforts to combat deforestation and promote sustainable use are ongoing.
- The Great Barrier Reef: This marine ecosystem off the coast of Australia is known for its vast biodiversity, including numerous species of coral, fish, and birds. Conservation initiatives focus on mitigating the effects of climate change, pollution, and overfishing.
- The Serengeti Plains: An example of grassland ecosystems, the Serengeti supports a wide range of wildlife and is known for its annual wildebeest migration. Conservation challenges include human-wildlife conflict and habitat fragmentation.
- The Arctic Tundra: Characterized by its cold climate and unique flora and fauna, the Arctic tundra is affected by climate change, which threatens its species and traditional ways of life of indigenous peoples.
- Madagascar’s Spiny Forests: These unique ecosystems are home to many endemic species. They face threats from deforestation and land conversion for agriculture. Conservation efforts aim to protect habitat while supporting local communities.
These case studies demonstrate the interconnectedness of human well-being and ecosystem diversity, emphasizing the need for sustainable management and conservation strategies.
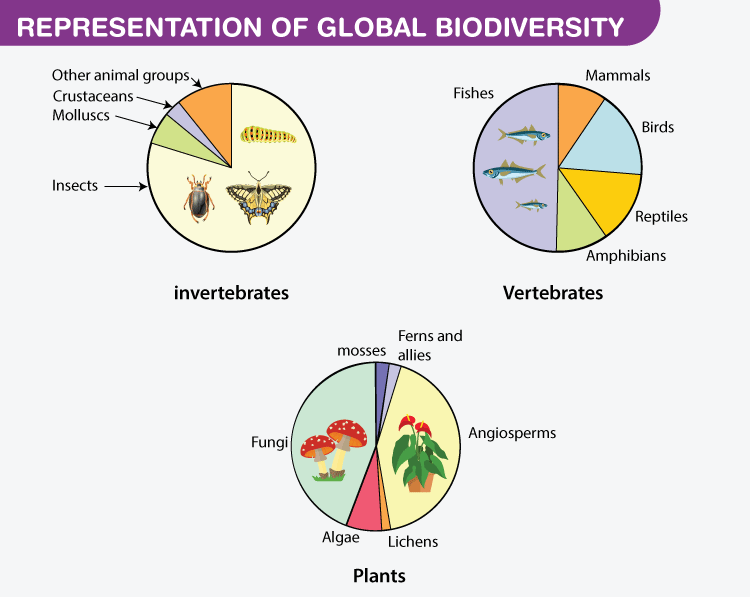
READ MORE:
Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on the actions taken today to mitigate threats and promote sustainable practices. With increasing awareness and global initiatives, there is hope for the preservation and enhancement of the world"s diverse ecosystems. Key factors influencing the future include:
- Global Conservation Efforts: Enhanced international cooperation and stronger conservation policies are essential for protecting diverse habitats and species.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing adaptation strategies are crucial to safeguard ecosystems from the adverse effects of climate change.
- Technological Advancements: Innovative technologies can aid in monitoring biodiversity, restoring ecosystems, and promoting sustainable resource use.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and increasing public awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity are vital for fostering stewardship of the natural world.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating ecosystem conservation into economic development plans ensures that progress does not come at the expense of environmental health.
Optimism for the future of ecosystem diversity is warranted, provided that concerted efforts continue to address the challenges facing the natural world. By valuing and protecting the diversity of ecosystems, humanity can ensure a resilient and vibrant planet for future generations.
Embracing ecosystem diversity is pivotal for sustaining life on Earth. Together, through conservation and sustainable practices, we can preserve the planet"s rich tapestry of life for future generations to cherish and enjoy.