Topic diversity in an ecosystem: Discover the marvels of diversity in an ecosystem, where intricate relationships and varied species form the foundation of life"s resilience and beauty on Earth.
Table of Content
- What does ecosystem diversity encompass and what are its benefits?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change Mitigation
- Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
- Global Initiatives and Policies on Ecosystem Diversity
- Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
What does ecosystem diversity encompass and what are its benefits?
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats and communities found in a geographic location. It includes both biotic properties (biodiversity) and abiotic properties (geodiversity). The benefits of ecosystem diversity are numerous. Here are some key ones:
- Increased resilience: Ecosystems with higher diversity are more resilient to disturbances such as natural disasters, invasive species, or climate change. This is because a diverse range of species allows for greater adaptability and ecosystem stability.
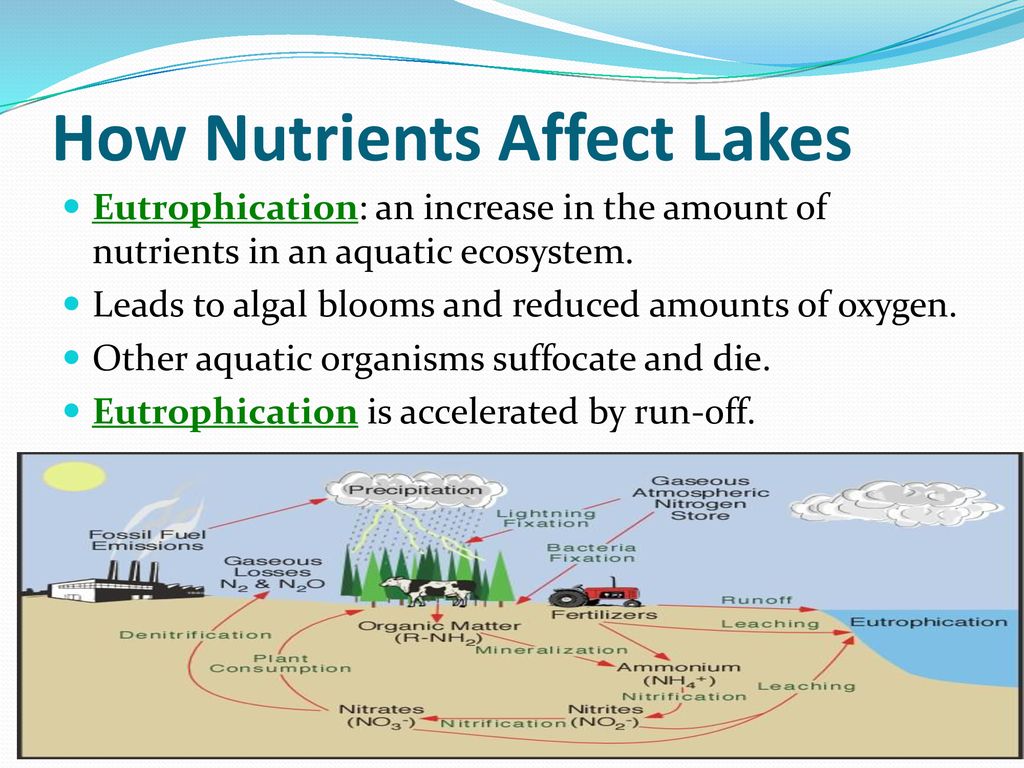
- Enhanced ecosystem services: Different habitats and communities within an ecosystem contribute to various ecosystem services, including nutrient cycling, water filtration, pollination, and carbon sequestration. Ecosystem diversity ensures the availability and effectiveness of these essential services.
- Promotion of genetic diversity: Ecosystem diversity supports a higher genetic diversity within species. This genetic diversity enables populations to respond and adapt to changing environmental conditions, reducing the risk of extinction.
- Economic value: Many economic activities rely on ecosystem services and resources. Ecosystem diversity allows for a wider range of opportunities, such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, and pharmaceutical discoveries.
- Cultural and aesthetic value: Ecosystem diversity enriches our lives by providing cultural and aesthetic values. Diverse ecosystems offer opportunities for recreation, education, inspiration, and spiritual connection.
In conclusion, ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats and communities in a geographic location and brings numerous benefits ranging from resilience and enhanced ecosystem services to economic, cultural, and aesthetic values.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats, living organisms, and ecological processes in the natural world. It includes the diversity of species, the genetic variation within species, and the variety of ecosystems that house them.
- Types of Ecosystems: From forests and oceans to deserts and wetlands, each ecosystem has its own unique composition of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Role of Biodiversity: Biodiversity within ecosystems contributes to the resilience and adaptive capacity of habitats, supporting everything from food production to water purification and climate regulation.
- Ecological Niches: Diversity also includes the variety of ecological niches occupied by species, the interactions among species, and the processes that cycle nutrients and energy through the environment.
- Conservation Importance: Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is crucial for sustaining the planet’s health and the well-being of all species, including humans.
Recognizing the interconnectedness of all living things, ecosystem diversity is a testament to the complexity and beauty of our planet, necessitating efforts for its conservation and sustainable management.
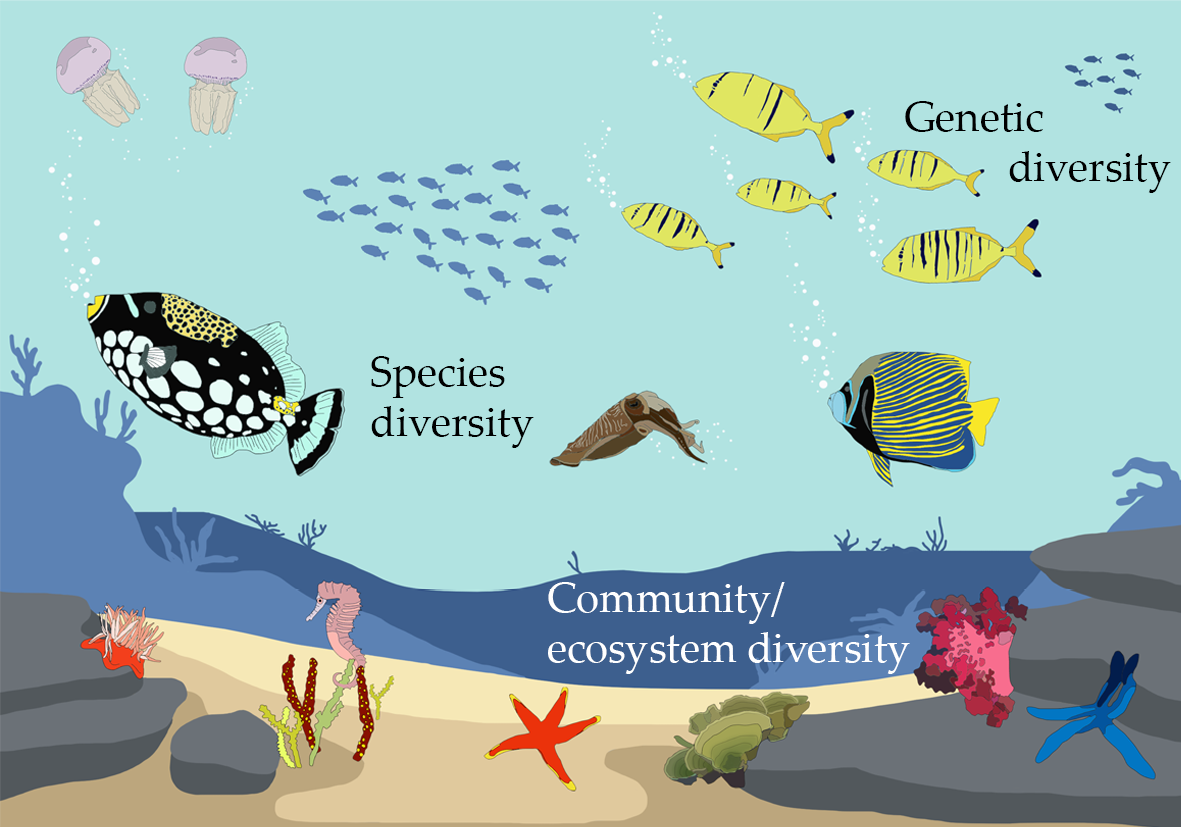
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is fundamental for the health and sustainability of our planet. It ensures natural sustainability for all life forms and provides a framework for understanding the complex interdependencies among organisms.
- Supports Species Diversity: Varied ecosystems support a wide range of habitats that nurture diverse species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the planet.
- Enhances Resilience: Ecosystems with greater diversity are better equipped to withstand and recover from environmental stresses, disturbances, and changes, ensuring ecological stability.
- Drives Ecological Services: Diverse ecosystems provide essential services such as air and water purification, pollination of crops, pest control, and climate regulation that are vital for human survival.
- Promotes Economic Benefits: Many industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, directly benefit from the resources and services provided by diverse ecosystems.
- Facilitates Research and Education: The variety of ecosystems offers vast opportunities for scientific research, education, and the discovery of new knowledge, enriching our understanding of the natural world.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Ecosystem diversity contributes to the cultural identity of communities, offering inspiration, recreation, and spiritual significance.
Ultimately, the importance of ecosystem diversity cannot be overstated; it is crucial for maintaining the balance and health of the earth, supporting socio-economic development, and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
Several factors play a critical role in shaping the diversity of ecosystems. Understanding these factors is essential for the conservation and sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight are key climate factors that influence the types of species and ecosystems that can thrive in an area.
- Geography: Geographic features such as mountains, rivers, and soil types determine the distribution of ecosystems and the species they support.
- Human Activities: Land use change, pollution, deforestation, and climate change induced by human activities significantly impact ecosystem diversity.
- Biological Factors: Interactions between species, such as competition, predation, and symbiosis, affect the composition and functioning of ecosystems.
- Evolutionary Processes: Evolution through natural selection and genetic variation over time leads to the emergence of new species and ecosystems.
- Disturbance: Natural disturbances like wildfires, floods, and hurricanes can create opportunities for new species to thrive, influencing ecosystem diversity.
These factors interconnect to shape the complex mosaic of life on Earth, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to understanding and conserving ecosystem diversity.
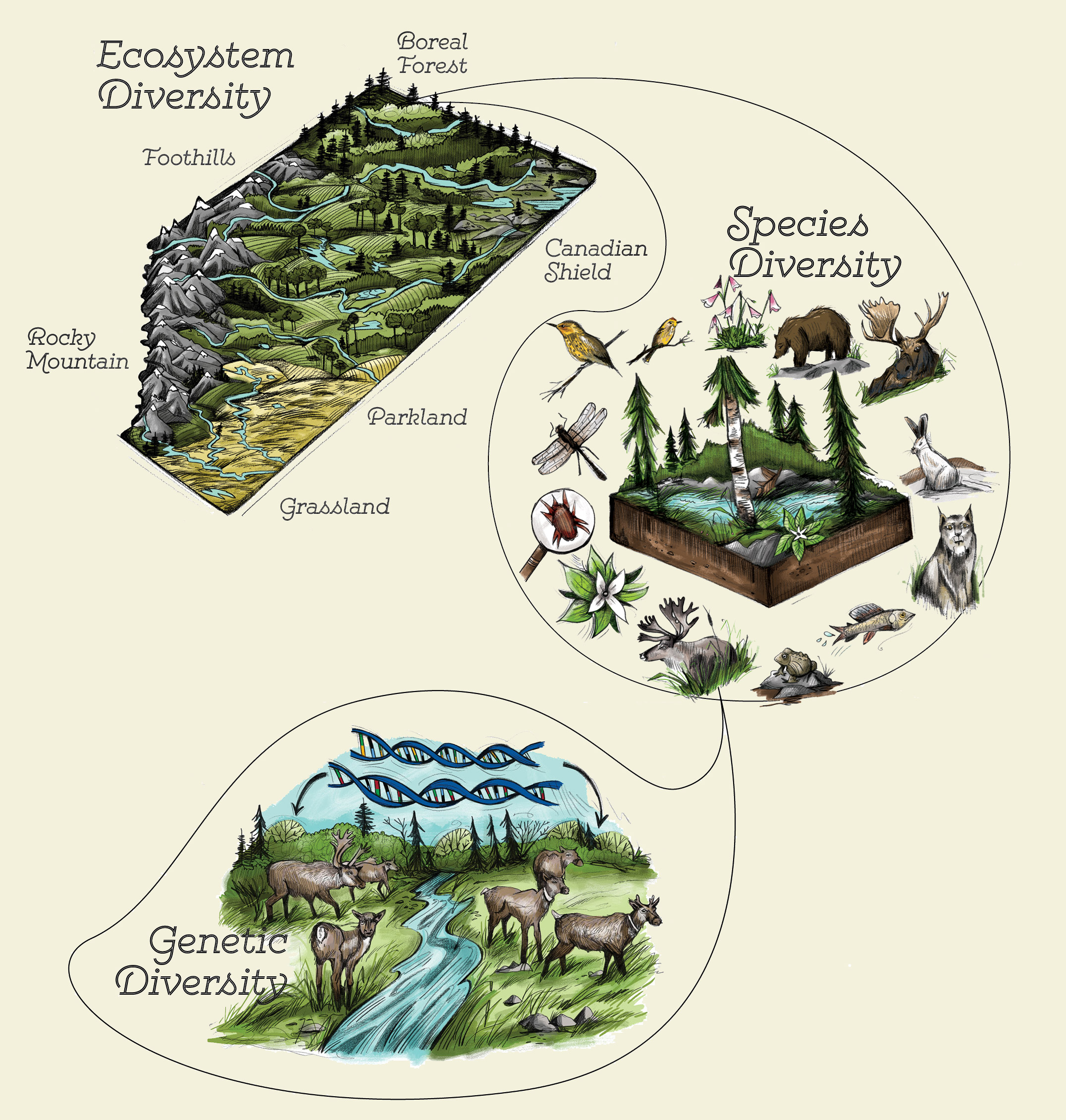
Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
The variety of ecosystems around the globe illustrates the vastness of ecosystem diversity. Each type of ecosystem supports unique species and processes, contributing to the planet"s overall biodiversity.
- Tropical Rainforests: Known for their high biodiversity, tropical rainforests are home to a multitude of species, including a wide array of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Coral Reefs: Often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," coral reefs provide habitat for an impressive variety of marine life, contributing significantly to oceanic biodiversity.
- Deserts: Despite harsh conditions, deserts host a unique set of flora and fauna adapted to survive with minimal water, showcasing nature"s adaptability.
- Grasslands: Grasslands, including savannas and prairies, support vast herds of grazing animals and play a key role in the biodiversity of landscapes.
- Wetlands: Wetlands, such as swamps, marshes, and bogs, are critical for water purification, flood protection, and as breeding grounds for many species.
- Tundra: The tundra ecosystem, characterized by cold temperatures and short growing seasons, supports species adapted to extreme conditions.
- Temperate Forests: These forests undergo seasonal changes and house a diverse range of plant and animal species, demonstrating seasonal variations in biodiversity.
These examples highlight the incredible variety of ecosystems that exist on our planet, each playing a vital role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life.
Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity faces numerous threats that can lead to loss of species, habitats, and ecological functions. Addressing these threats is crucial for the preservation of biodiversity and the health of our planet.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion result in the direct loss of habitats for many species.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal can degrade ecosystems and harm wildlife.
- Climate Change: Global warming and climate variability affect ecosystems by altering habitats, species distributions, and ecological processes.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predation on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balance.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and logging at unsustainable levels can lead to species extinction and loss of ecosystem services.
- Land Use Change: Converting natural landscapes into urban or agricultural areas reduces the natural diversity and resilience of ecosystems.
Combating these threats requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and conservation efforts to ensure the protection and resilience of ecosystem diversity.

Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Protecting the diversity of ecosystems is essential for the health of the planet and the survival of many species. Implementing effective conservation strategies can help mitigate threats and ensure the resilience of ecosystems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries to safeguard habitats and species from human exploitation.
- Restoration Projects: Restoring degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and the reintroduction of native species to their natural habitats.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and maintain biodiversity.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance the ability of ecosystems to adapt to climate change.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts through education and sustainable development initiatives to foster stewardship of natural resources.
- Legislation and Policies: Enforcing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate pollutants, and manage land use.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders to address global environmental challenges such as climate change, invasive species, and pollution.
By employing a combination of these strategies, we can preserve ecosystem diversity and ensure the sustainability of our natural world for future generations.
Ecosystem Diversity
Explore the incredible world of variation as this captivating video takes you on a journey through the mesmerizing colors, forms, and patterns found in nature. Witness the endless possibilities and appreciate the beauty that arises from each unique variation.
Importance of Biodiversity
Embark on a journey to discover the art of preservation in this eye-opening video. Learn about the innovative techniques and ancient traditions used to safeguard our natural and cultural heritage, ensuring a lasting legacy for future generations. Join us as we celebrate the importance of preserving our world\'s wonders.
Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change Mitigation
Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change, offering natural solutions to reduce atmospheric carbon levels and enhance resilience against climate impacts.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests, wetlands, and oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in plants and soil, reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
- Climate Regulation: Diverse ecosystems regulate local and global climates, influencing rainfall patterns, temperatures, and wind systems, which can help buffer against climate change effects.
- Resilience and Adaptation: Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient to climate change, providing species with better chances to adapt to changing conditions through natural processes.
- Protection Against Natural Disasters: Healthy ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs act as barriers against storms and flooding, reducing the impact of climate-related disasters on human communities.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Ecosystem diversity supports sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, contributing to reduced carbon footprints and enhanced food security.
By protecting and restoring ecosystem diversity, we can leverage nature"s own mechanisms to combat climate change, ensuring a more stable and sustainable environment for all living beings.

Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
Ecosystem services are the many and varied benefits that ecosystems provide to humanity, playing a vital role in ensuring our well-being and survival. The richness of ecosystem diversity directly enhances these services.
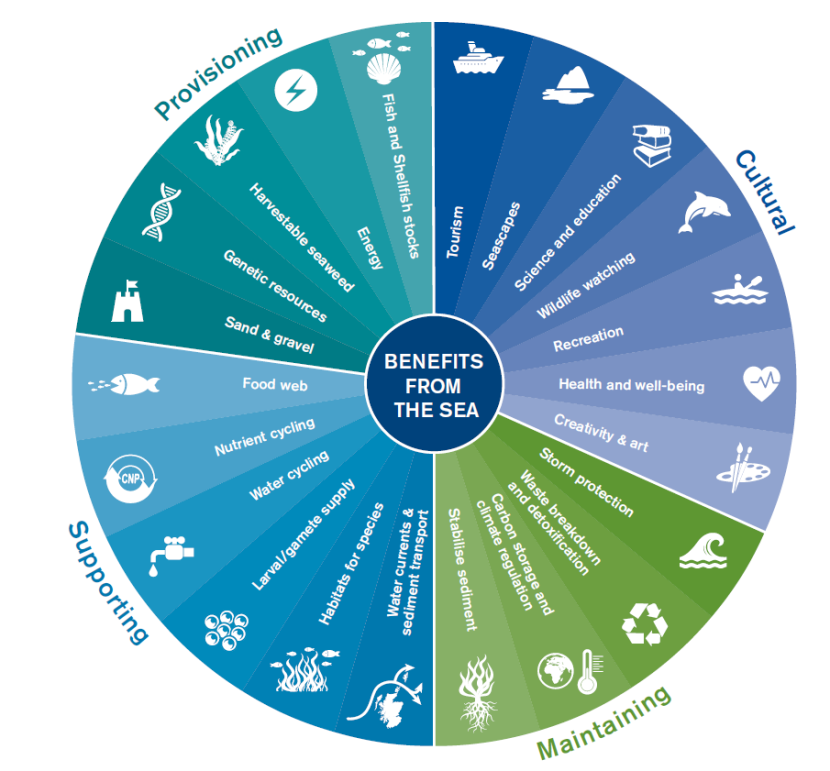
- Provisioning Services: These include the provision of food, fresh water, wood, fiber, and genetic resources, all crucial for human survival and economic activities.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality. For example, forests help regulate the climate, while wetlands filter water by removing pollutants.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, such as soil formation, photosynthesis, and nutrient cycling, supporting agriculture and forestry.
- Cultural Services: Ecosystems provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits that contribute to human well-being. This includes areas of cultural significance, recreational spots, and the inspiration derived from nature.
Protecting ecosystem diversity is not just about conserving nature; it"s about preserving the foundation of human health, culture, and livelihoods. As such, the conservation of ecosystem diversity is integral to maintaining and enhancing these vital services for future generations.
Global Initiatives and Policies on Ecosystem Diversity
International efforts and policies play a crucial role in the conservation and sustainable management of ecosystem diversity. These initiatives aim to protect biodiversity at a global scale, addressing challenges that transcend national borders.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): An international treaty with objectives to conserve biological diversity, promote sustainable use of its components, and ensure fair sharing of benefits from genetic resources.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Specifically, SDG 15 aims to protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, manage forests sustainably, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, and halt biodiversity loss.
- Paris Agreement on Climate Change: Though focused on climate change, this agreement recognizes the critical role of ensuring ecosystem integrity in mitigating climate change and its impacts.
- Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES): Provides assessments on biodiversity and ecosystem services for policymakers to make informed decisions.
- World Heritage Convention: Protects natural sites of outstanding universal value, including those significant for biodiversity conservation.
- Global Environment Facility (GEF): Provides funding to developing countries for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, the ozone layer, and persistent organic pollutants.
These and other initiatives demonstrate the global commitment to preserving ecosystem diversity, highlighting the importance of international cooperation and policy-making in safeguarding our planet"s biodiversity for future generations.
READ MORE:
Future Challenges and Opportunities in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
As the world evolves, the conservation of ecosystem diversity faces both new challenges and opportunities. Addressing these effectively is crucial for the sustainability of our planet"s natural resources and biodiversity.
- Climate Change: One of the greatest challenges, climate change requires adaptive management strategies to protect ecosystems and the services they provide.
- Urbanization and Land Use Change: Balancing development needs with conservation is essential, as urban expansion continues to threaten natural habitats.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies offer opportunities for better monitoring, understanding, and conserving biodiversity, such as through remote sensing and genetic research.
- Policy and Governance: Strengthening and enforcing environmental laws and policies, both nationally and internationally, are critical for effective conservation efforts.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation activities promotes stewardship of natural resources and supports sustainable livelihoods.
- Financial Mechanisms: Developing innovative financing solutions to support conservation projects can help address funding gaps.
- Global Cooperation: International collaboration is essential to address transboundary conservation issues and share best practices.
The path ahead for ecosystem diversity conservation is complex, yet filled with opportunities to foster a sustainable relationship between humanity and the natural world. Embracing these challenges and opportunities with innovative solutions and collaborative efforts is key to ensuring a resilient and biodiverse planet.
In embracing ecosystem diversity, we unlock the key to sustaining our planet’s health, enriching our lives, and securing a vibrant future for generations to come. The time to act is now, for diversity is life.