Topic define ecosystem diversity: Discover the vast tapestry of life on Earth through the lens of ecosystem diversity, a critical component for sustaining our planet"s health and vitality.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
- What is Ecosystem Diversity?
- Types of Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
- Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
- Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecological Diversity: Exploring the Depths of Biodiversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change
- Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
- Future of Ecosystem Diversity
What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
Ecosystem diversity can be defined as the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes that exist within a specific geographic location. It encompasses the range of different ecosystems, including terrestrial and aquatic systems, and the various species that inhabit them.
Key components of ecosystem diversity include:
- Habitats: Ecosystem diversity includes the different types of habitats found within a particular area, such as forests, grasslands, wetlands, coral reefs, and freshwater bodies.
- Communities: It also refers to the diverse communities of organisms that inhabit these habitats, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
- Interactions and Processes: Ecosystem diversity encompasses the ecological processes and interactions that occur within and between these habitats and communities. This includes nutrient cycling, energy flow, predator-prey relationships, and symbiotic associations.
Ecosystem diversity is important for maintaining the overall health and stability of the natural environment. It contributes to the resilience of ecosystems, their ability to adapt to environmental changes, and provides a wide range of ecological services, such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
READ MORE:
What is Ecosystem Diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety and variability of natural environments within a specific area or across the globe. It encompasses the different types of ecosystems, such as forests, deserts, grasslands, wetlands, and marine environments, highlighting the range of interactions between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components within each system. This diversity is a fundamental aspect of nature, contributing to the resilience and functionality of our planet by supporting a wide range of life forms, processes, and services essential for the survival and well-being of all organisms, including humans.
- Biotic Components: These include all living organisms within an ecosystem, from microorganisms and plants to animals and humans.
- Abiotic Components: These are the non-living elements that influence the living organisms, such as climate, soil, water, and sunlight.
- Interactions: The dynamic interactions between biotic and abiotic components, which drive the functioning of ecosystems, their productivity, and their capacity to adapt to changes.
Understanding ecosystem diversity is crucial for conservation efforts, as it highlights the importance of protecting varied habitats to maintain biodiversity, ecosystem services, and the overall health of our planet.

Types of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the vast range of environments found on Earth, each supporting unique life forms and ecological dynamics. This diversity can be broadly categorized into two main types: Terrestrial and Aquatic ecosystems, each with further subdivisions.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These are land-based ecosystems and include:
- Forests (Tropical, Temperate, and Boreal)
- Grasslands (Savannas, Prairies, and Steppes)
- Deserts (Hot and Cold)
- Tundra (Arctic and Alpine)
- Mountain Ecosystems
- Aquatic Ecosystems: These ecosystems are water-based and are divided into:
- Freshwater Ecosystems (Lakes, Rivers, and Wetlands)
- Marine Ecosystems (Oceans, Coral Reefs, and Estuaries)
Each ecosystem type supports distinct communities of organisms adapted to their specific environment. The variation in ecosystem types is crucial for biodiversity, providing different habitats that support a wide range of species and ecological processes.
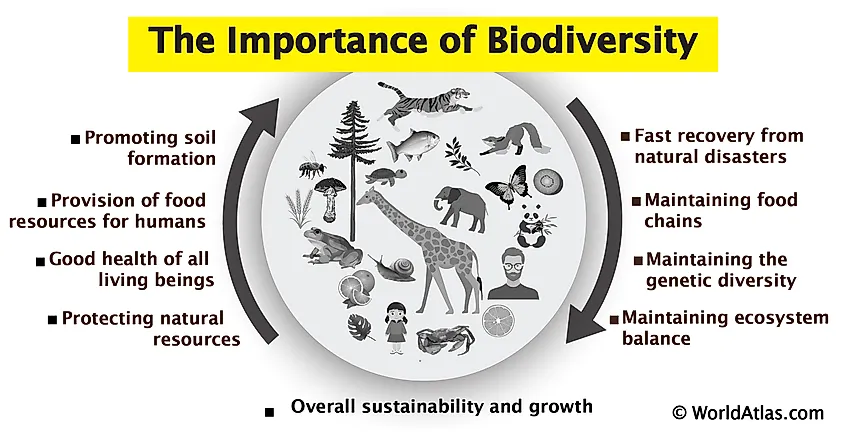
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is vital for the health and sustainability of our planet. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of natural processes, supporting a wide array of services that are essential for life. The importance of ecosystem diversity can be highlighted through several key aspects:
- Supports Biodiversity: Rich ecosystem diversity provides varied habitats, supporting an incredible range of species. This biodiversity is crucial for ecological stability and the resilience of communities.
- Enhances Ecosystem Services: Diverse ecosystems offer essential services like water purification, pollination of plants, climate regulation, and carbon sequestration. These services are critical for human survival and well-being.
- Promotes Resilience: Ecosystem diversity allows natural systems to be more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances, such as climate change, natural disasters, and human impacts.
- Drives Economic Benefits: Many economies rely on the goods and services provided by diverse ecosystems, including food, medicines, and tourism opportunities.
- Supports Cultural and Recreational Values: Diverse ecosystems contribute to cultural identity and offer recreational opportunities, enhancing human health and happiness.
Protecting ecosystem diversity is therefore not just about conserving nature, but about safeguarding the future of human societies as well. It underscores the interconnectedness of all life forms and the dependence of humanity on the health of our planet"s ecosystems.

Factors Affecting Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is influenced by a complex interplay of various factors that determine the nature and variety of ecosystems within a geographical area. These factors not only shape the current state of ecosystems but also have a profound impact on their future development and sustainability. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective conservation and management strategies:
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations significantly influence ecosystem types and distribution.
- Geography: Geographic features such as mountains, rivers, and soil types play a pivotal role in shaping ecosystems by creating diverse habitats.
- Altitude: Variations in altitude affect climate and vegetation types, leading to different ecosystems at different heights.
- Human Activities: Urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution drastically alter and often reduce ecosystem diversity.
- Natural Disasters: Events like wildfires, floods, and volcanic eruptions can change landscapes and create new ecosystems.
- Biological Factors: Interactions among species, including competition, predation, and symbiosis, affect ecosystem structure and diversity.
- Evolutionary Processes: Evolutionary changes over time can lead to the emergence of new species and ecosystems.
These factors highlight the dynamic nature of ecosystem diversity, underscoring the importance of adopting adaptive management and conservation approaches to safeguard this diversity for future generations.
Examples of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is a testament to the varied and rich environments that exist across our planet. Each ecosystem offers unique conditions that support distinct forms of life. Here are examples that illustrate the range of ecosystems and their inherent diversity:
- Tropical Rainforests: Rich in biodiversity, these ecosystems are characterized by high rainfall and a wide variety of plants and animals.
- Deserts: Despite harsh conditions, deserts host a range of specially adapted species, showcasing biodiversity resilience.
- Coral Reefs: Often referred to as the "rainforests of the sea," coral reefs support a vast array of marine life.
- Grasslands: These areas, including savannas and prairies, are vital for many species of plants, herbivores, and predators.
- Wetlands: Acting as natural water filters, wetlands are crucial for bird species, fish, and numerous aquatic plants.
- Arctic Tundra: Characterized by cold, dry conditions, the tundra supports unique flora and fauna adapted to extreme conditions.
- Temperate Forests: These forests experience distinct seasons and support a diverse range of plant and animal life.
- Mountain Ecosystems: Varying climates and altitudes on mountains create diverse habitats for a wide range of species.
These examples underscore the importance of preserving ecosystem diversity to maintain the balance and health of our planet.

Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity faces numerous threats that can significantly alter the structure, function, and health of these vital systems. Recognizing and addressing these threats is essential for conservation efforts and ensuring the sustainability of ecosystems worldwide. Here are some of the major threats to ecosystem diversity:
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Caused by deforestation, urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development, leading to the fragmentation and destruction of natural habitats.
- Climate Change: Alters temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting species distribution and ecosystem dynamics.
- Pollution: Chemicals, plastics, and waste released into the environment degrade ecosystems and harm wildlife.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable logging, fishing, and hunting pressure species populations and ecosystem balance.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced by human activities outcompete, predation, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem functions.
- Land Use Change: Conversion of natural areas for agriculture, forestry, and urban development reduces biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
These threats underscore the urgent need for global cooperation and action to protect and restore ecosystem diversity, thereby ensuring the health and well-being of our planet for future generations.
Ecological Diversity: Exploring the Depths of Biodiversity
Biodiversity: Dive into the enchanting world of biodiversity and witness the wonders of nature like never before. This mesmerizing video captures the vibrant harmony of various species, showcasing the intricate balance that sustains life on our planet. Prepare to be amazed by the diverse beauty that awaits you.
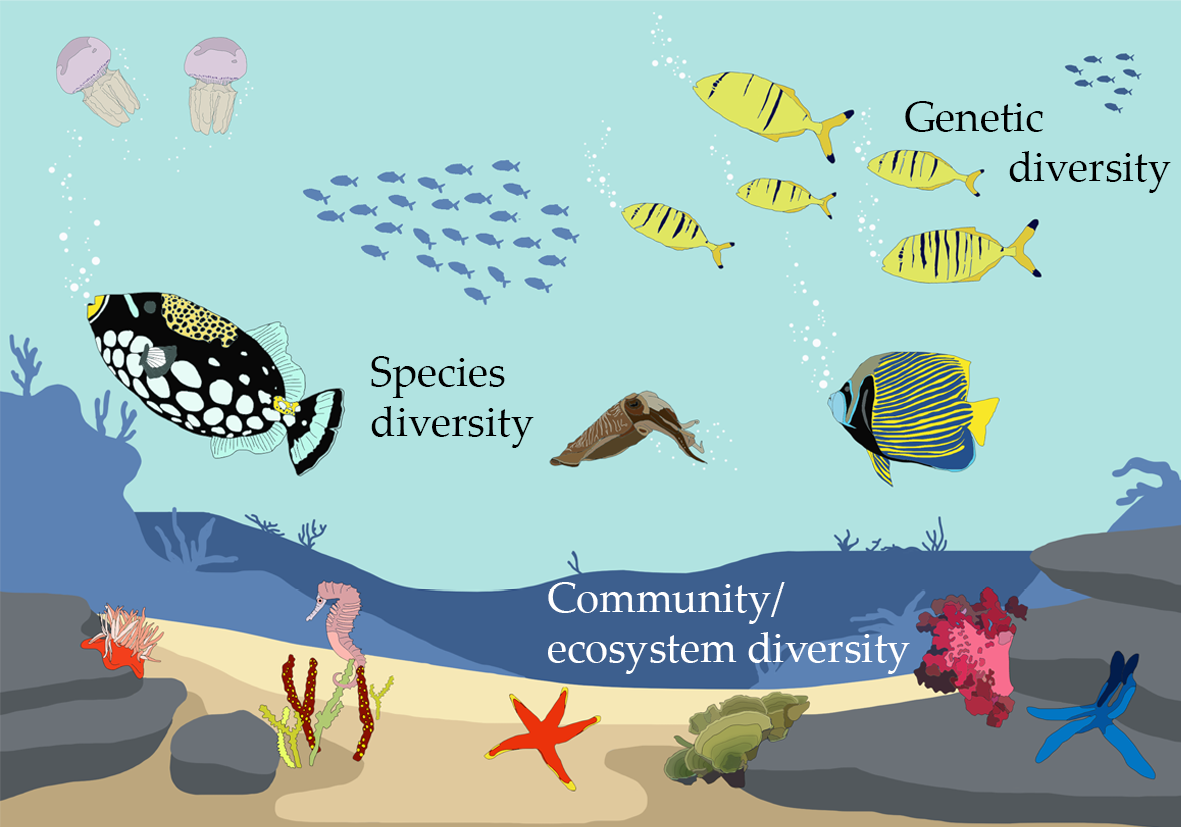
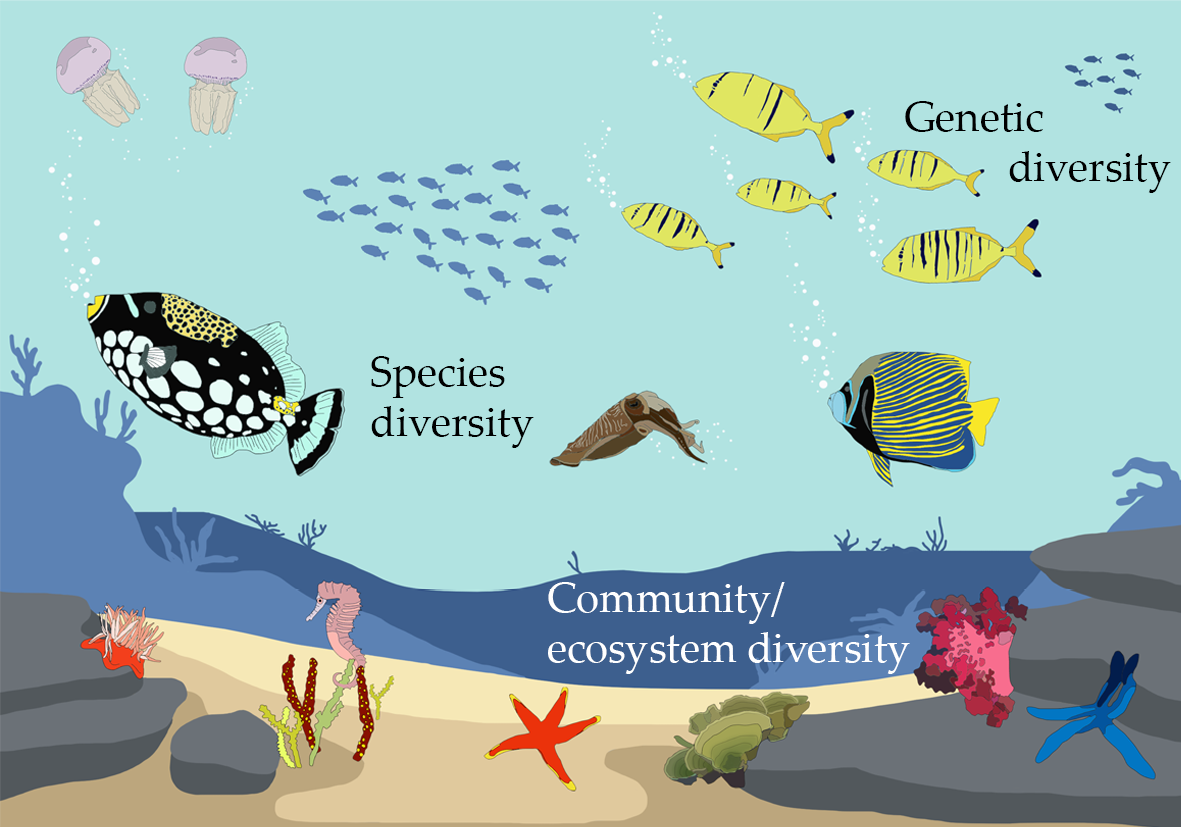
Biodiversity: Unveiling the Interconnectedness of Genetic, Species, and Ecosystem Diversity in Environmental Ecology
Interconnectedness: Unveil the hidden threads that bind our planet in a captivating dance of interconnectedness. Journey through this eye-opening video and unravel the fascinating web of relationships that shape our existence. Discover how every living being is intricately linked, and gain a profound understanding of the profound impact of these connections. Prepare to be inspired by the unity that lies beneath the surface.
Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Preserving ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth. Various conservation strategies have been developed and implemented worldwide to protect and restore diverse ecosystems. These strategies aim to mitigate threats and ensure the sustainable management of natural resources. Key conservation strategies include:
- In-Situ Conservation: Protecting natural habitats, establishing protected areas such as national parks and wildlife reserves, and conserving ecosystems in their natural state.
- Ex-Situ Conservation: Conserving species outside their natural habitats through botanical gardens, zoos, and seed banks.
- Restoration Ecology: Restoring degraded ecosystems to their original state by replanting native vegetation and reintroducing species.
- Sustainable Use of Resources: Implementing practices that allow for the sustainable use of natural resources to prevent overexploitation.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sinks to combat climate change, which is a significant threat to ecosystem diversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that protect ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Community Involvement and Education: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders to address global environmental issues that affect ecosystem diversity.
These strategies represent a multifaceted approach to conserving ecosystem diversity, each playing a vital role in the global effort to protect our planet"s natural heritage.

Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Change
The relationship between ecosystem diversity and climate change is complex and bidirectional. Ecosystem diversity plays a crucial role in both mitigating and adapting to climate change impacts. Here are key points illustrating this role:
- Carbon Sequestration: Diverse ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and oceans, act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and reducing the effects of climate change.
- Climate Regulation: Varied ecosystems help regulate climate conditions locally and globally by influencing water cycles and atmospheric conditions.
- Resilience to Climate Effects: High biodiversity within ecosystems enhances resilience to climate change, enabling better recovery from climate-related disturbances.
- Supporting Adaptation: Diverse ecosystems provide species with a range of habitats and conditions, supporting their ability to adapt to changing climates.
- Mitigating Extreme Weather: Ecosystems like forests and wetlands can act as natural barriers, reducing the impact of climate-induced disasters such as floods and hurricanes.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem diversity is therefore essential in the global effort to combat climate change, highlighting the need for integrated conservation and climate policies.
Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have profound impacts on ecosystem diversity, affecting the balance and health of ecosystems worldwide. These activities alter natural habitats, introduce pollutants, and lead to a loss of biodiversity. Here"s how human actions impact ecosystem diversity:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urban expansion, and agricultural development destroy and fragment habitats, reducing the space available for wildlife and plants.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources introduce toxins that harm organisms and disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects temperature, precipitation patterns, and sea levels, impacting ecosystems and species distributions.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting exceed natural reproduction rates, depleting species and altering ecological balances.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can outcompete, prey upon, or introduce diseases to native species, altering ecosystem dynamics.
- Resource Extraction: Mining, logging, and drilling disrupt the physical environment and can lead to significant habitat loss and degradation.
- Land Use Changes: Converting natural landscapes into urban or agricultural areas significantly reduces ecosystem diversity and resilience.
Addressing the impact of human activities on ecosystem diversity requires concerted global efforts towards sustainable practices, habitat restoration, and the protection of natural areas to ensure the health and sustainability of our planet"s ecosystems.
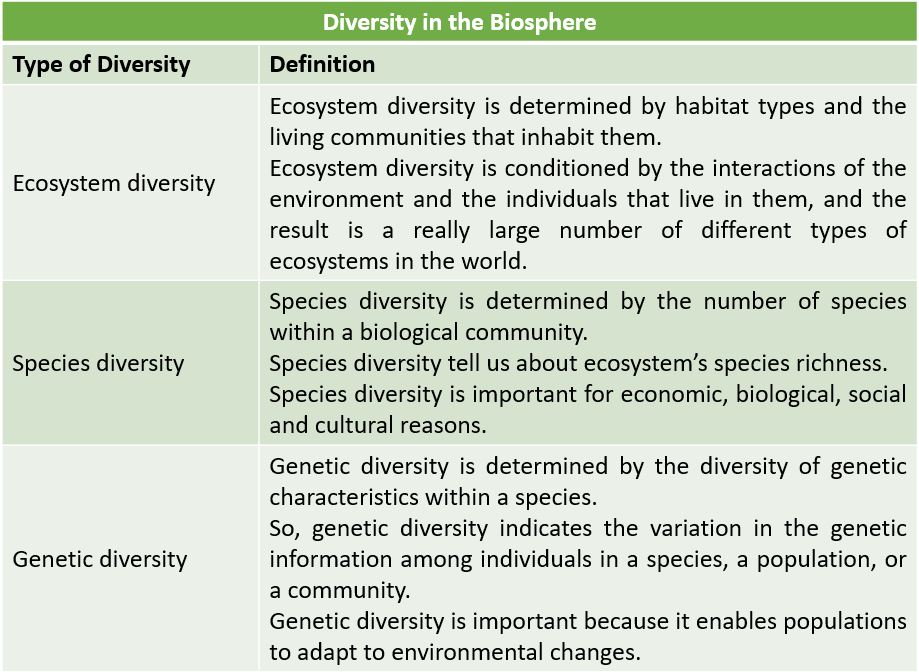
READ MORE:
Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on our current actions and the global commitment to conservation and sustainable practices. With the growing recognition of the importance of biodiversity for our planet"s health and human well-being, there is a positive momentum towards preserving and enhancing ecosystem diversity. Here are key factors that will shape the future of ecosystem diversity:
- Conservation Efforts: Strengthened global and local conservation initiatives aimed at protecting habitats and species are critical for maintaining ecosystem diversity.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and global warming are vital for preserving ecosystem diversity and preventing the loss of vulnerable habitats.
- Sustainable Development: Incorporating biodiversity considerations into development planning and industry practices can mitigate negative impacts on ecosystems.
- Technological Advancements: Innovative technologies and data analysis tools offer new ways to monitor biodiversity and implement effective conservation strategies.
- Public Awareness and Education: Increasing public awareness and education about the importance of ecosystem diversity can foster greater support for conservation actions.
- International Collaboration: Global challenges require international cooperation to ensure the conservation of ecosystem diversity across borders.
The future of ecosystem diversity is not predetermined; it will be shaped by the decisions we make today. By prioritizing biodiversity and ecosystem health, we can ensure a resilient and vibrant planet for future generations.
In our journey through understanding ecosystem diversity, we"ve seen its vastness and importance. Embracing conservation and sustainable practices ensures a vibrant planet, rich in life and opportunities for future generations.