Topic diversity in ecosystems: Discover the unparalleled beauty and crucial importance of diversity in ecosystems, a testament to the Earth"s complex web of life and its vital role in sustaining our planet.
Table of Content
- How does diversity in ecosystems affect decomposition and standing stocks?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
- The Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystems
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- The Role of Keystone Species in Ecosystems
- Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Exploring Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest Diversity
- Conservation Efforts to Protect Ecosystem Diversity
- Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
- The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
How does diversity in ecosystems affect decomposition and standing stocks?
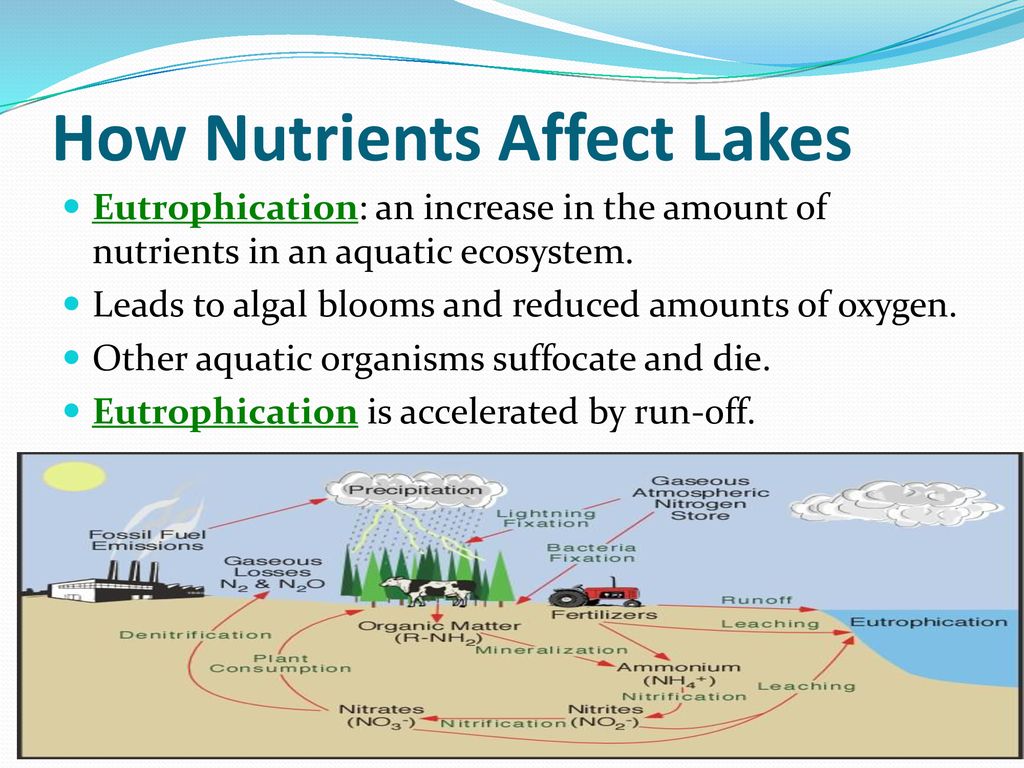
Diversity in ecosystems can have a significant impact on decomposition and standing stocks. Research has shown that increased diversity of producers, such as plants and algae, leads to enhanced decomposition rates and reduced standing stocks of organic matter.
Here are some key points that explain the relationship between diversity in ecosystems and decomposition:
- Increased producer diversity provides a wider range of resources for decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, to feed on. This abundance of resources helps to stimulate their activity and increase the rate of decomposition.
- Different species of decomposers have varying abilities to break down different types of organic matter. With higher diversity, there are more species with specialized abilities to decompose specific types of organic material, leading to more efficient decomposition overall.
- Greater producer diversity also results in increased plant productivity and biomass. This means that there is more organic matter available for decomposition, which can result in lower standing stocks as decomposers break down and recycle the organic material more quickly.
The relationship between diversity in ecosystems and decomposition is often studied in the context of the biodiversity and ecosystem functioning framework. This field of research aims to understand the impact of biodiversity on ecosystem processes and services, including decomposition.
In conclusion, diverse ecosystems tend to have higher rates of decomposition and lower standing stocks of organic matter. The increased availability of resources and specialization among decomposers contribute to this relationship. Understanding the importance of diversity in ecosystems can help inform conservation and management efforts to maintain healthy and balanced ecosystems.
READ MORE:
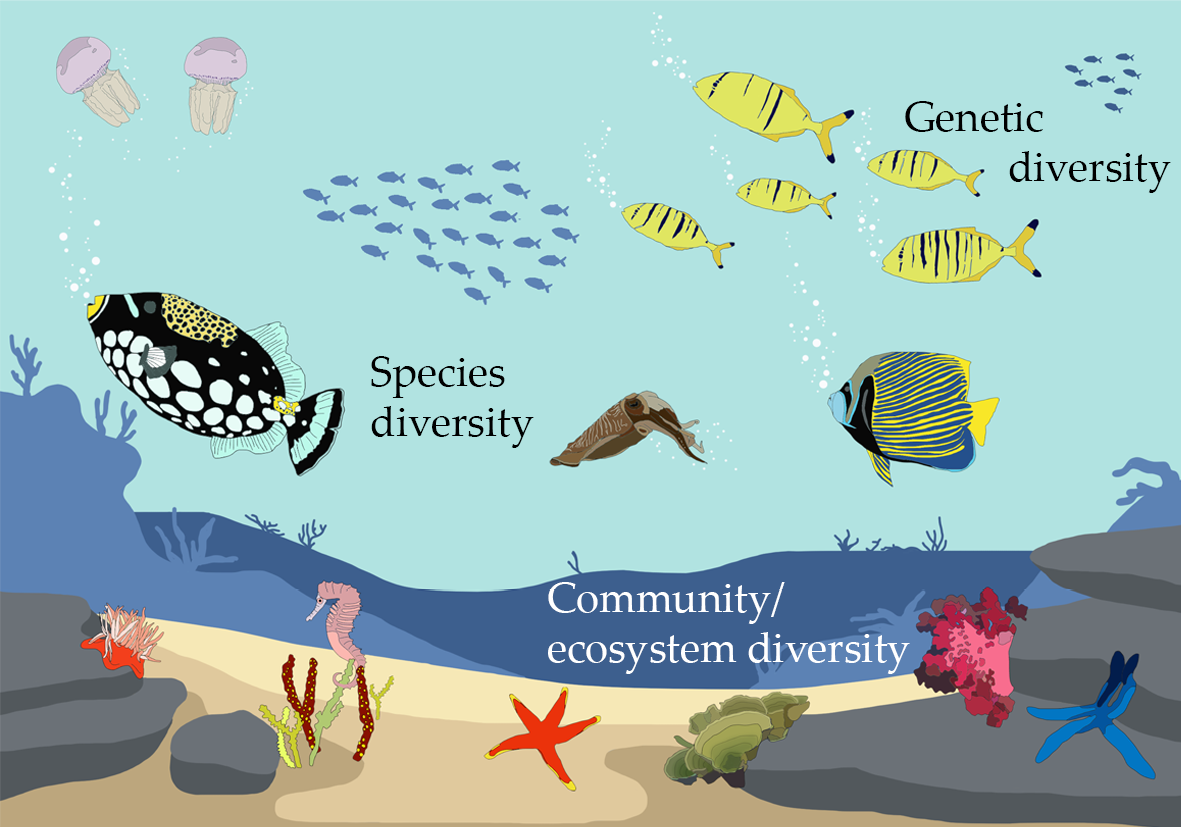
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats, biotic communities, and ecological processes in the natural world, as well as the genetic diversity within species. This diversity is crucial for the resilience and health of our planet.
- Habitat Diversity: Refers to the different places where organisms live, ranging from forests and deserts to oceans and rivers.
- Species Diversity: The variety of species within a habitat, ensuring ecological balance and resilience against environmental changes.
- Genetic Diversity: The variation of genes within species, allowing for adaptation to changing environments and resistance to diseases.
Understanding ecosystem diversity helps us appreciate the complexity of interactions among different organisms and their environments, highlighting the importance of each species and habitat in maintaining ecological balance. It"s a foundation for conservation efforts, guiding us in protecting and preserving the Earth"s biodiversity for future generations.
Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
Ecosystems are classified into two main types: terrestrial and aquatic. Each type has distinct environments that support various forms of life with unique adaptations.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These include forests, deserts, grasslands, and tundras, each with specific climates, soil types, and biological diversity.
- Forests: Characterized by high rainfall and dense tree coverage, forests are home to a vast array of plant and animal species.
- Deserts: Known for their extreme dryness, deserts support life adapted to scarcity of water and extreme temperatures.
- Grasslands: Dominated by grasses, these areas support a variety of herbivores and predators, along with seasonal plant and animal life.
- Tundras: Cold, treeless regions with permafrost, tundras support hardy species adapted to extreme cold and short growing seasons.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: These are divided into freshwater (lakes, rivers, and ponds) and marine (oceans, seas, and coral reefs) environments.
- Freshwater: Characterized by a low salt concentration, these ecosystems support diverse species of fish, plants, and invertebrates.
- Marine: Covering most of the Earth"s surface, marine ecosystems have a high salt content and host a vast array of life, from microscopic plankton to the largest whales.
Each ecosystem type plays a vital role in the global ecology, contributing to the Earth"s biodiversity and the services it provides to humanity, such as air and water purification, climate regulation, and sources of food, medicine, and recreation.
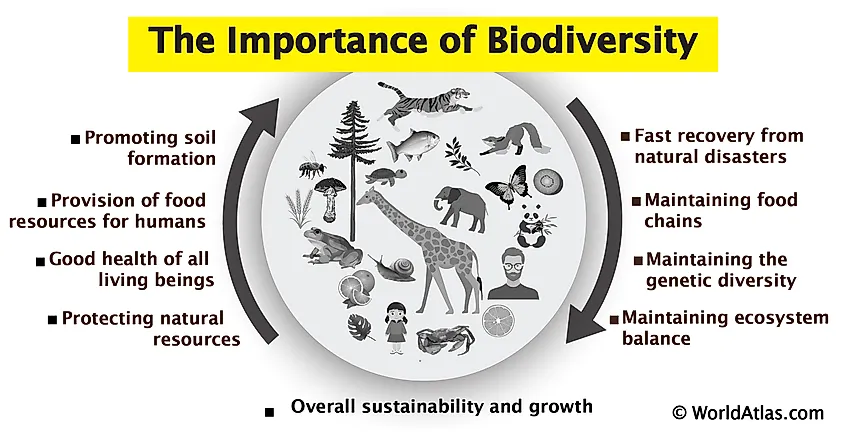
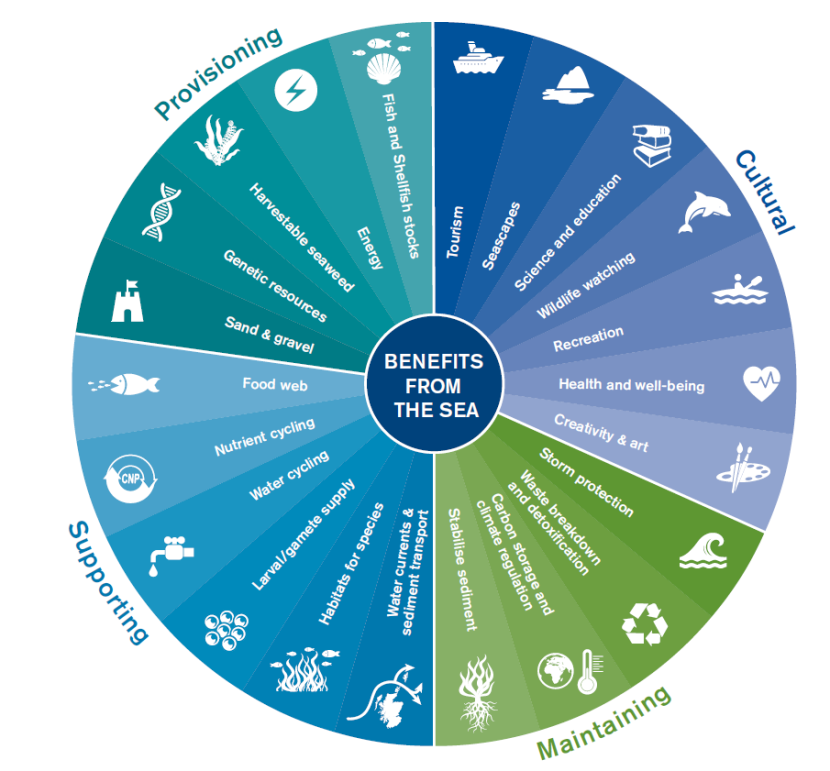
The Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystems
Biodiversity, the variety of life in all its forms, levels, and combinations, plays a critical role in maintaining the functionality and resilience of ecosystems. It is fundamental to ecosystem health, human well-being, and the Earth"s sustainability.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem services such as air and water purification, soil fertility, pollination of plants, and climate regulation.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances and changes. They can better withstand environmental stressors and recover more quickly from disasters.
- Provides Economic Benefits: Many industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, directly benefit from biodiversity through the provision of raw materials, medicines, and natural beauty.
- Contributes to Social and Cultural Values: Biodiversity enriches cultures and provides spiritual, recreational, and educational benefits. It inspires art, folklore, and national identity, while contributing to mental and physical health.
- Facilitates Adaptation and Evolution: Genetic diversity within and among species is crucial for adaptation to changing environmental conditions and for the evolutionary process itself.
Protecting biodiversity is therefore essential for sustaining the ecosystems upon which humans and all other life forms depend. It is a shared responsibility that requires global and local action to mitigate threats like habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution.

Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is influenced by a combination of natural and human factors that interact in complex ways to shape the variety and abundance of life in different environments.
- Climate: Temperature, rainfall, and seasonal patterns are critical in determining the types of ecosystems that can thrive in a given area.
- Geography: Landforms such as mountains, rivers, and valleys play a significant role in shaping ecosystems by influencing climate and habitat diversity.
- Soil Types: The composition and quality of soil affect the types of plants that can grow in an area, which in turn influences the diversity of animal species that can be supported.
- Altitude: Changes in altitude affect temperature and moisture levels, creating different living conditions and habitats as elevation increases.
- Human Activities: Agriculture, urban development, deforestation, and pollution significantly alter ecosystems, often reducing their diversity and resilience.
- Biological Interactions: The interactions among species, such as predation, competition, and symbiosis, also play a crucial role in shaping ecosystem diversity.
Understanding these factors is essential for the conservation and sustainable management of ecosystems, ensuring that they continue to provide the vital services and benefits on which all life depends.
The Role of Keystone Species in Ecosystems
Keystone species play a critical role in maintaining the structure and integrity of their ecosystems. Their presence and activities have a disproportionately large impact on the environment relative to their abundance.
- Predators: By controlling the population of other species, predators prevent any single species from dominating and thus maintain species diversity.
- Engineers: Species like beavers alter their environments in ways that create new habitats for other organisms. By building dams, they create wetlands that support a diverse range of life.
- Mutualists: Certain plants and animals have mutual relationships that are essential for ecosystem function. For example, bees pollinate flowers, which is crucial for the reproduction of many plants.
- Decomposers: Organisms like fungi and bacteria break down dead material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem and supporting plant growth.
Protecting keystone species is vital for conserving the biodiversity and resilience of ecosystems. Their loss can lead to significant changes in ecosystem structure, function, and the loss of biodiversity. Conservation efforts often focus on these species to ensure the health and stability of ecosystems.

Human Impact on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have a profound impact on ecosystem diversity, often leading to habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and the introduction of invasive species. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate damage and preserve biodiversity.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urban expansion, agriculture, and mining disrupt natural habitats, leading to the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal can degrade ecosystems and harm wildlife.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affect species distribution, migration patterns, and the timing of biological cycles, threatening ecosystem balance.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and harvesting at unsustainable rates deplete populations and can lead to the extinction of species.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecological balance.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation and sustainable practices to reduce our ecological footprint and ensure the preservation of ecosystem diversity for future generations.
Exploring Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest Diversity
Immerse yourself in the enchanting beauty of the tropical rainforest as you embark on a visual journey like no other. Discover the vibrant colors, exotic wildlife, and lush greenery that make this extraordinary ecosystem so captivating. Watch the video now and let nature\'s wonders transport you to a world of tranquility and awe-inspiring beauty.
Rainforests: Most Complex and Diverse Ecosystems on Earth
Prepare to be captivated by the intricate tapestry of life in this complex and diverse world. From the vast array of unique species to the interconnectedness of ecosystems, this video offers a mesmerizing glimpse into the complexity of nature. Brace yourself for a visual feast that will leave you in awe of the sheer diversity and wonder of our planet. Don\'t miss out on this captivating exploration of life\'s intricacies!
Conservation Efforts to Protect Ecosystem Diversity
Conservation efforts are crucial in safeguarding ecosystem diversity against the backdrop of increasing human impact. These efforts aim to preserve the natural balance and ensure the survival of species and habitats for future generations.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve habitats and species in their natural state.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems, such as reforestation of cleared lands and restoration of wetlands, to revive biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and regulations to protect endangered species, regulate hunting and fishing, and control pollution and land use.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their role in stewardship and benefitting from sustainable practices.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research to understand ecosystems and monitoring changes to adapt conservation strategies accordingly.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation initiatives, addressing global challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
These efforts, combined with education and awareness-raising about the importance of biodiversity, are vital to the health of our planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
Challenges in Preserving Ecosystem Diversity
Preserving ecosystem diversity faces several challenges, exacerbated by human activities and natural processes. Addressing these challenges is critical for the sustainability of ecosystems and the services they provide.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns threaten ecosystems by shifting species distributions, altering habitats, and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture reduce and isolate habitats, limiting species migration and genetic exchange.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources degrade ecosystems and affect species health and reproduction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can dominate ecosystems, displacing native species and altering food webs and ecosystem functions.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable harvesting of resources, overfishing, and hunting lead to population declines and loss of biodiversity.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient understanding and appreciation of ecosystem services and biodiversity value among the public and policymakers hinder conservation efforts.
- Insufficient Funding: Conservation projects often struggle with inadequate funding, limiting the scope and impact of preservation initiatives.
Overcoming these challenges requires integrated approaches that combine conservation with sustainable development, along with global cooperation and strong political will.
READ MORE:
The Future of Ecosystem Diversity
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on our actions today. With concerted efforts from individuals, communities, governments, and international bodies, we can foster a sustainable future that values and preserves biodiversity.
- Adaptive Management: Implementing flexible conservation strategies that can adjust to new challenges and scientific insights.
- Innovative Technologies: Utilizing technology for monitoring biodiversity, restoring ecosystems, and reducing human impact on the environment.
- Global Cooperation: Strengthening international partnerships to address global environmental challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Community Engagement: Empowering local communities to manage natural resources sustainably and participate in conservation efforts.
- Educational Initiatives: Enhancing public awareness and understanding of the importance of biodiversity through education and outreach programs.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, fishing, and urban development to reduce environmental impact and preserve ecosystems.
- Policy and Legislation: Enacting and enforcing laws and policies that protect biodiversity, regulate resource use, and mitigate climate change.
By embracing these approaches, we can secure a resilient and vibrant natural world for future generations, ensuring the continuation of ecosystem services essential for human survival and well-being.
Embracing the richness of ecosystem diversity illuminates the path to a sustainable future, highlighting our shared responsibility to preserve the intricate tapestry of life that sustains and enriches our planet.