Topic why is diversity important in an ecosystem: Discover the pivotal role of diversity in ecosystems, where varied life forms interconnect to forge resilience, enhance productivity, and sustain ecological balance for future generations.
Table of Content
- Why is diversity important in an ecosystem?
- Enhancing Ecosystem Productivity and Health
- Supporting Air Quality and Food Production
- Role of Keystone Species in Ecosystem Stability
- Contribution to Water Purification and Oxygen Availability
- Impact on Soil Fertility and Pollination Processes
- Mitigating Climate Change and Environmental Stresses
- YOUTUBE: Why is Biodiversity Important with Sir David Attenborough
- Supporting Biodiversity for Disease Resistance and Recovery
- Importance for Human Health and Medicinal Resources
- Ensuring Sustainability and Resilience of Ecosystems
- Role in Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
Why is diversity important in an ecosystem?
Diversity is important in an ecosystem for several reasons:
- Enhanced Stability: A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand and recover from disturbances. When an ecosystem has a variety of species with different characteristics and functions, it is more resilient to changes in environmental conditions. If one species is adversely affected by a disturbance, others can fill the void and maintain the balance.
- Increased Productivity: Different species in an ecosystem often have different roles and niches. Each species contributes in its own way, such as by providing food, breaking down organic matter, or pollinating plants. This division of labor enhances the overall productivity of the ecosystem as a whole.
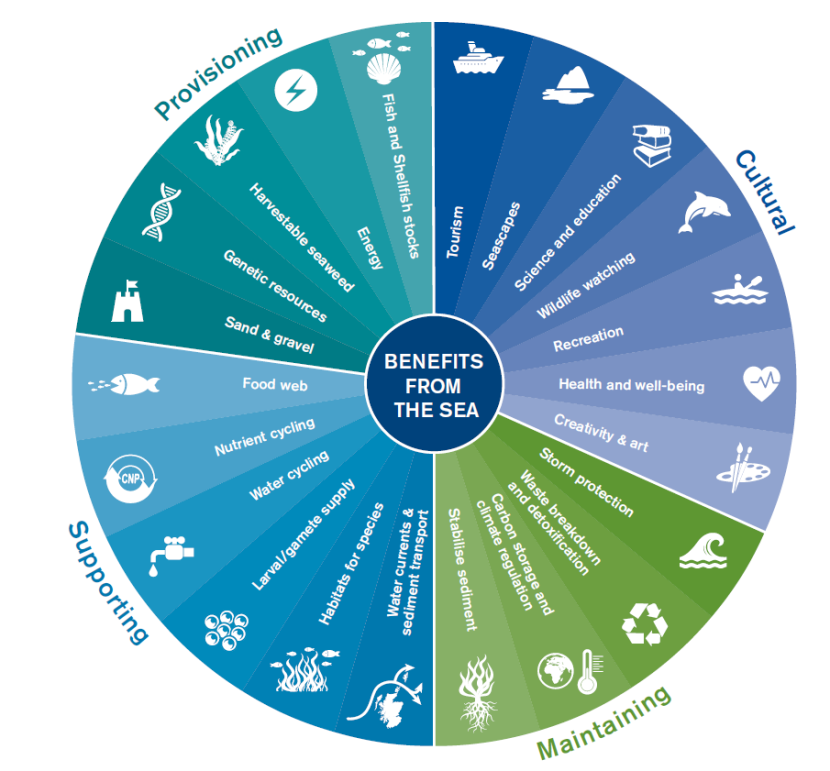
- Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity in an ecosystem provides a wide range of services that are vital for the environment and human well-being. For example, diverse ecosystems help regulate climate, purify water, control pests and diseases, and provide habitats for countless organisms.
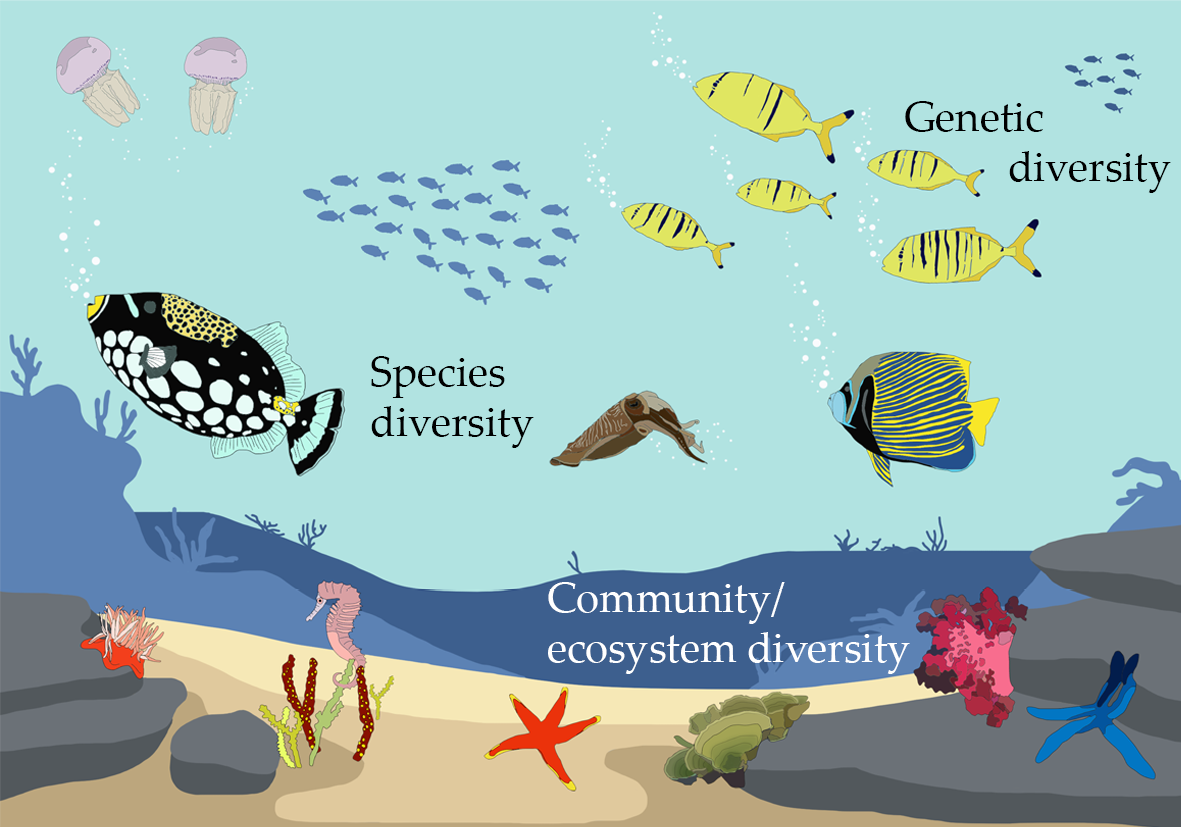
- Genetic Diversity: Within a species, genetic diversity is essential for adaptation and evolution. A diverse gene pool allows a population to adapt to changing environmental conditions, resist diseases, and recover from population declines.
- Ecological Balance: Some species in an ecosystem depend on others for their survival. For example, predator-prey relationships help regulate populations and maintain balance in the ecosystem. Without these interactions, the ecosystem can become imbalanced, leading to negative consequences.
Overall, diversity in an ecosystem is crucial for its functioning, stability, and the provision of essential ecosystem services that benefit both the environment and human society.
READ MORE:
Enhancing Ecosystem Productivity and Health
Ecosystem diversity is the foundation of our planet"s health, ensuring robust, productive environments that support a wide range of life forms. By fostering a rich tapestry of species, ecosystems can perform essential functions more effectively, leading to enhanced productivity and overall health.
- Boosts Nutrient Recycling: Diverse ecosystems facilitate the efficient recycling of nutrients, crucial for plant growth and soil health.
- Improves Pollination: A variety of pollinators increases the chances of successful plant reproduction, contributing to food security.
- Enhances Disease Resistance: Biodiversity acts as a buffer against pathogens, reducing the likelihood of disease outbreaks.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Clean air, fresh water, and fertile soil are all products of diverse and healthy ecosystems.
- Promotes Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand and recover from environmental stresses and disturbances.
Through these mechanisms, biodiversity not only sustains the ecosystems on which human life depends but also ensures their resilience in the face of climate change and other challenges.
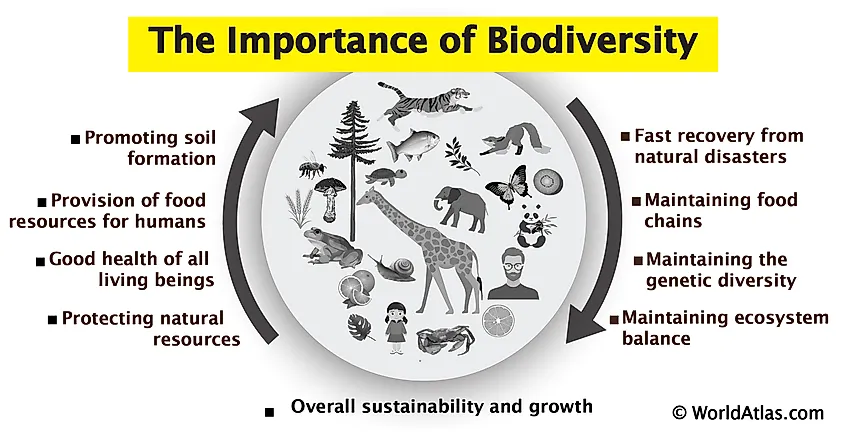
Supporting Air Quality and Food Production
Diverse ecosystems play a critical role in maintaining the air we breathe and the food we consume. Through a variety of processes, biodiversity directly influences air quality and aids in the production of food, making it an essential component for environmental health and human survival.
- Enhances Air Quality: Plants in diverse ecosystems contribute to air purification by absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis, thus improving air quality and supporting life.
- Boosts Food Production: Biodiversity ensures the availability of a wide range of crops and livestock, promoting genetic diversity that is crucial for agriculture and food security.
- Supports Pollination: A variety of insects and birds in biodiverse ecosystems facilitate pollination, essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and seeds.
- Improves Soil Health: Diverse organisms contribute to soil formation and fertility, crucial for plant growth and agriculture.
- Promotes Sustainable Farming: Agricultural diversity can lead to more resilient and sustainable farming practices, reducing dependence on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
By supporting these vital functions, biodiversity in ecosystems not only sustains the natural world but also underpins agricultural systems and food production, showcasing the indispensable link between ecological diversity and human well-being.
Role of Keystone Species in Ecosystem Stability
Keystone species hold a pivotal role in maintaining the stability and integrity of ecosystems. Their presence and activities have disproportionate effects on the environmental structure and the diversity of life within their habitat.
- Regulators of Population Balance: Keystone species help regulate the populations of other species, preventing any single species from dominating and thus maintaining biodiversity.
- Creators of Habitats: Certain keystone species, like beavers, alter their environment in ways that create new habitats for other species, thereby increasing ecosystem diversity.
- Supporters of Niche Diversity: By performing unique roles, keystone species support a wider range of niches, allowing for more species to coexist and thrive.
- Enhancers of Ecosystem Productivity: Through their activities, keystone species can enhance nutrient cycling and energy flow, leading to more productive ecosystems.
- Facilitators of Recovery: In the aftermath of disturbances, keystone species can be crucial in facilitating the recovery and rebuilding of ecosystem structures.
The loss of a keystone species can lead to significant changes in ecosystem composition and function, highlighting their critical role in maintaining ecological stability and diversity.

Contribution to Water Purification and Oxygen Availability
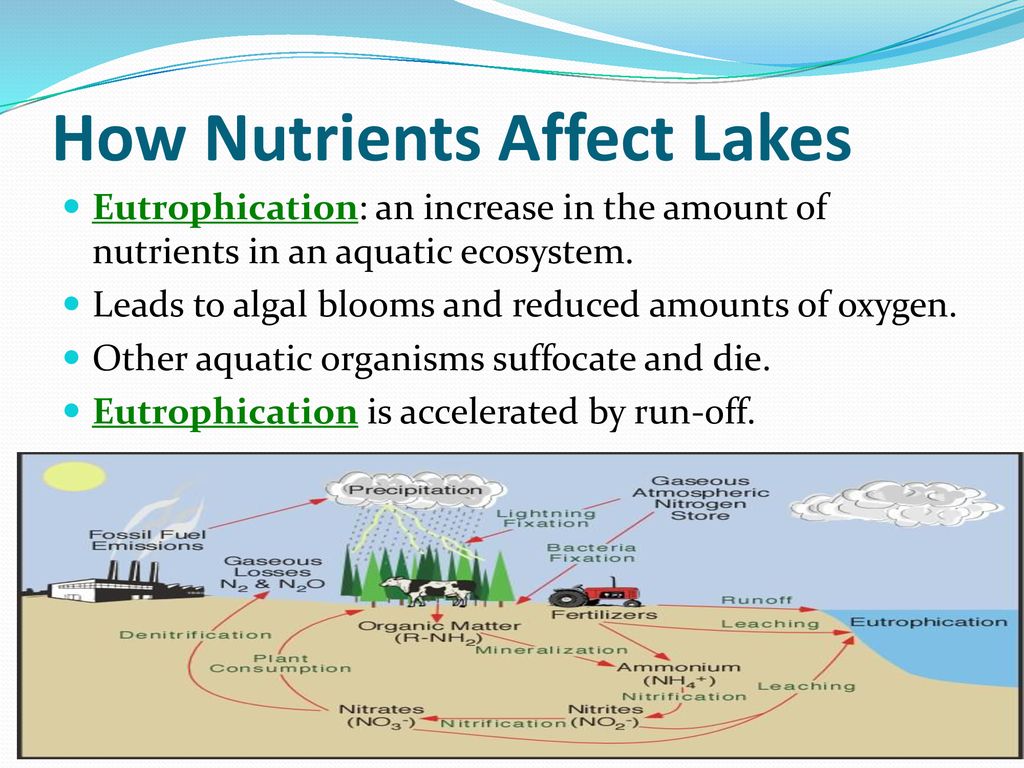
Diverse ecosystems significantly contribute to the purification of water and the availability of oxygen, fundamental for sustaining life on Earth. These natural processes are enhanced by the varied organisms within an ecosystem, each playing a unique role.
- Water Filtration: Aquatic plants and soil microorganisms filter pollutants, reducing the need for artificial purification and ensuring cleaner waterways.
- Oxygen Production: Through photosynthesis, plants and phytoplankton release oxygen into the atmosphere, essential for respiratory life forms.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse ecosystems facilitate the breakdown and redistribution of nutrients, including those vital for water purification processes.
- Habitat for Purifiers: Wetlands, often rich in biodiversity, serve as natural filters that trap and break down pollutants, improving water quality.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests and oceanic algae absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, thereby contributing to oxygen availability and climate regulation.
These mechanisms underline the critical role of biodiversity in maintaining the natural infrastructure that supports water purification and oxygen production, showcasing the interconnectedness of all life forms.
Impact on Soil Fertility and Pollination Processes
The intricate interplay between biodiversity and soil fertility, alongside the critical role of diverse species in pollination processes, underscores the importance of ecosystem diversity. This symbiotic relationship enhances agricultural productivity and ecological balance.
- Enhances Soil Fertility: A variety of organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and invertebrates, contribute to soil health by decomposing organic matter, which enriches the soil and makes nutrients available to plants.
- Improves Pollination Efficiency: Diverse ecosystems support a wide range of pollinators, ensuring the reproduction of many plant species, which is vital for food crops and natural vegetation.
- Supports Natural Pest Control: Biodiversity encourages the presence of natural predators, reducing the need for chemical pesticides that can harm the soil and ecosystem health.
- Promotes Resistance to Erosion: Plant diversity helps to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and loss of fertile land to wind or water.
- Facilitates Nutrient Cycling: The interaction between different species ensures efficient cycling of nutrients, crucial for maintaining soil fertility and ecosystem productivity.
Through these processes, biodiversity plays an essential role in sustaining the fertility of the soil and the effectiveness of pollination, both of which are foundational to the health and productivity of ecosystems worldwide.

Mitigating Climate Change and Environmental Stresses
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and buffering environmental stresses, showcasing the interconnectedness of ecosystems and their resilience against global changes.
- Carbon Sequestration: Diverse forests and marine ecosystems act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and reducing the impact of greenhouse gases.
- Regulation of Climate Patterns: Ecosystems like wetlands and forests influence local and global climate patterns, contributing to temperature regulation and precipitation.
- Enhancing Resilience to Climate Change: Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient to climate change effects, such as extreme weather events, helping to stabilize environments.
- Reducing Erosion and Degradation: Vegetation diversity helps to prevent soil erosion and land degradation, maintaining land fertility and water quality.
- Supporting Adaptive Responses: Genetic diversity within species enables adaptive responses to environmental changes, ensuring survival and continuity.
Through these mechanisms, biodiversity acts as a natural buffer against climate change and environmental stresses, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts for future sustainability.
Why is Biodiversity Important with Sir David Attenborough
\"Discover the incredible wonders of biodiversity in this captivating video! Immerse yourself in the beauty and diversity of nature as you learn about the importance of preserving and protecting our planet\'s unique creatures and ecosystems.\"
Ecosystem Diversity
\"Explore the intricate web of life in our vast and fragile ecosystem through this fascinating video. Uncover the interdependence of flora and fauna, and gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that sustains our planet\'s biodiversity.\"
Supporting Biodiversity for Disease Resistance and Recovery
Biodiversity significantly enhances ecosystem resilience to diseases and their ability to recover from outbreaks. This natural defense mechanism is vital for the health of both natural ecosystems and human populations.
- Reduces Pathogen Spread: A diverse ecosystem can limit the spread of pathogens by breaking the chain of transmission, thereby reducing the risk of disease outbreaks.
- Enhances Genetic Diversity: Genetic variation within species makes them less susceptible to diseases, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Supports Natural Predators: Biodiversity ensures the presence of natural predators that can control the populations of potential disease vectors, such as mosquitoes.
- Facilitates Ecosystem Recovery: Diverse ecosystems are more adaptable and can recover more quickly from disease outbreaks, ensuring sustainability and continuity.
- Promotes Human Health: By reducing the incidence of zoonotic diseases, biodiversity protects human health and reduces the burden on healthcare systems.
Thus, supporting biodiversity is not just about preserving the natural world; it"s also about building a natural defense against diseases and ensuring the recovery and sustainability of ecosystems in the face of biological threats.

Importance for Human Health and Medicinal Resources
The importance of biodiversity for human health and the provision of medicinal resources is profound and multifaceted. Ecosystem diversity is a critical source of new and traditional medicines and plays a vital role in disease regulation.
- Source of Medicinal Compounds: Many pharmaceuticals are derived from chemical compounds found in plants, animals, and fungi, highlighting the need for conserving biodiversity to support medical research and drug development.
- Natural Health Solutions: Traditional medicines, relied upon by billions globally, come from the natural environment, underscoring the importance of diverse species for healthcare.
- Disease Regulation: Ecosystems with high biodiversity tend to have better functioning natural disease control mechanisms, reducing the prevalence of certain diseases.
- Psychological Well-being: Access to diverse natural environments has been linked to improved mental health, including reduced stress and enhanced mood.
- Research and Development: Biodiversity fuels scientific research and innovation, offering potential breakthroughs in healthcare and disease treatment.
Protecting biodiversity is thus not only about conserving nature but also about preserving the well-being of humanity and ensuring a reservoir of resources for future medical advancements.
Ensuring Sustainability and Resilience of Ecosystems
Ecosystem diversity is essential for the sustainability and resilience of our planet. Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand environmental changes and stresses, ensuring the long-term health and stability of our natural world.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Diverse ecosystems provide essential services such as air and water purification, pollination of crops, and climate regulation, which are vital for human survival.
- Increases Resilience: Biodiverse ecosystems can recover more quickly from disturbances like fires, floods, and climate change, maintaining ecological balance.
- Promotes Adaptability: Genetic diversity within species increases their adaptability to environmental changes, enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Ensures Food Security: Agricultural diversity is crucial for food security, offering a variety of crops that can withstand different conditions and pests.
- Protects Against Erosion: Plant diversity helps to stabilize soils and prevent erosion, preserving land and water resources.
By fostering biodiversity, we ensure the sustainability and resilience of ecosystems, protecting our planet for future generations.

READ MORE:
Role in Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
The role of biodiversity in ecosystem services and human well-being is indispensable, supporting critical functions that sustain life on Earth. These services are vital for the health of our planet and the prosperity of human societies.
- Provisioning Services: Biodiversity provides food, fresh water, medicinal resources, and raw materials, contributing to human survival and economic activities.
- Regulating Services: Ecosystems regulate climate, floods, diseases, and water quality, mitigating natural disasters and environmental hazards.
- Cultural Services: Natural environments are a source of inspiration, recreation, and spiritual enrichment, enhancing human well-being and cultural identities.
- Supporting Services: Biodiversity underpins ecosystem functions such as soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production, which are essential for life on Earth.
By preserving ecosystem diversity, we ensure the continuity of these services, safeguarding human well-being and promoting the resilience of our communities against environmental changes.
In conclusion, biodiversity is the cornerstone of ecosystem health, resilience, and productivity, underpinning vital services that sustain and enrich our lives. Preserving it is imperative for our future and the planet"s well-being.