Topic why is species diversity important in an ecosystem: Discover why species diversity is pivotal in ecosystems, enhancing stability, productivity, and resilience, ultimately securing our planet"s health and future.
Table of Content
- Why is species diversity important in an ecosystem?
- Key Roles of Species Diversity in Ecosystems
- Benefits of Species Diversity to Ecosystem Stability
- Impact of Species Diversity on Ecosystem Services
- Species Diversity and Ecosystem Productivity
- Species Diversity as a Buffer Against Environmental Changes
- Contribution of Diverse Species to Human Well-being
- YOUTUBE: Why is biodiversity so important?
- Challenges and Threats to Species Diversity
- Conservation Efforts and Their Importance for Species Diversity
- Future Perspectives on Maintaining Species Diversity
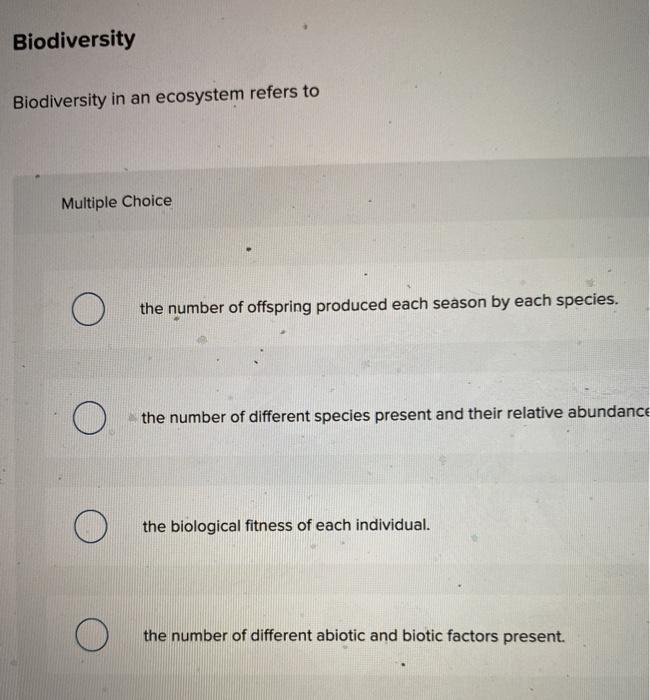
Why is species diversity important in an ecosystem?
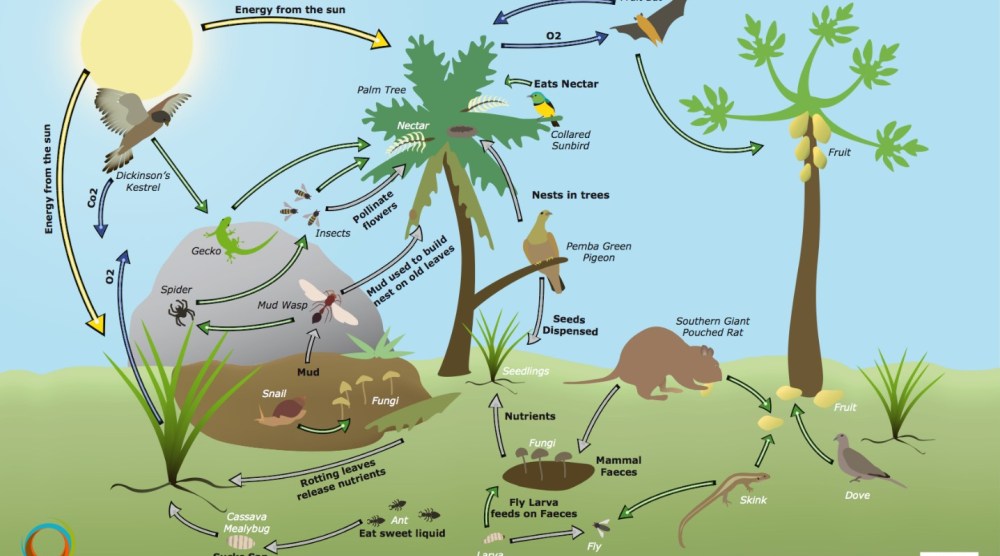
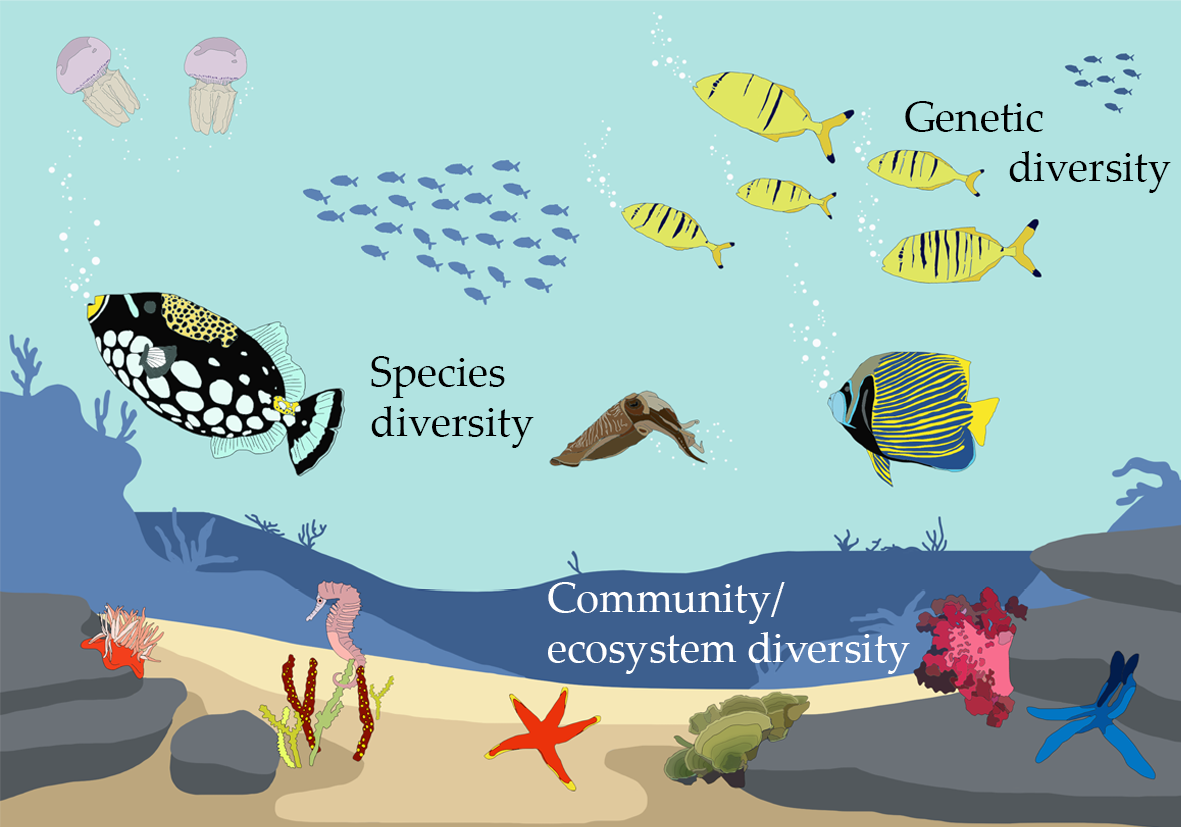
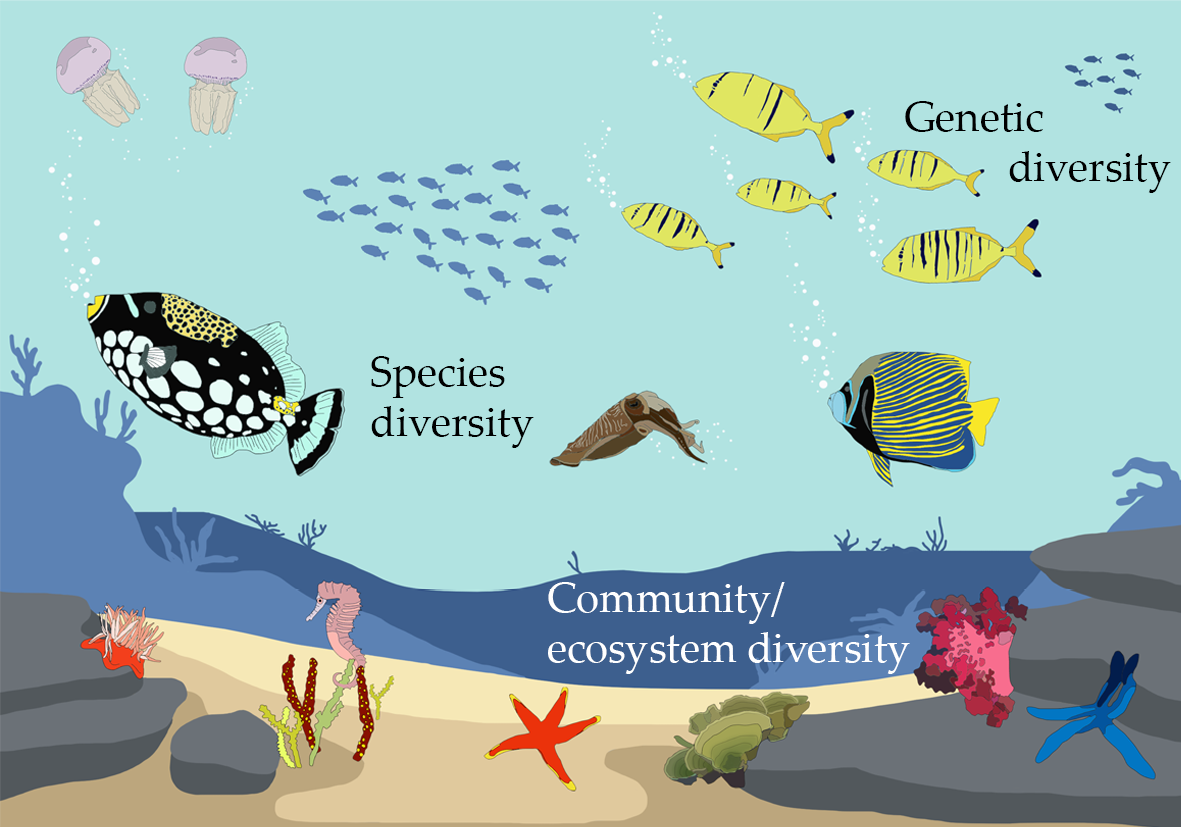
Species diversity refers to the variety of different species present in an ecosystem. It is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy and balanced ecosystem. Here are several reasons why species diversity is important:
1. Stability and Resilience:
- A diverse ecosystem is more stable and resilient to changes in the environment. Different species have different roles and functions within an ecosystem, and their interactions contribute to the overall stability of the system.
- Higher species diversity can buffer against disturbances such as disease outbreaks, natural disasters, or climate change. If one species is affected, others may still thrive, preventing a complete collapse of the ecosystem.
2. Ecosystem Productivity:
- Species diversity is closely linked to ecosystem productivity. Each species plays a unique role in the food web and contributes to the overall energy flow within the ecosystem.
- Greater species diversity leads to more efficient resource utilization and nutrient cycling, resulting in increased productivity. This productivity is vital for supporting other organisms, including humans, who depend on the ecosystem for food, clean water, and other resources.
3. Ecological Services:
- Species diversity is crucial for the provision of important ecological services. Different species perform various functions such as pollination, seed dispersal, soil fertility, and pest control.
- For example, bees and other pollinators are critical for the reproduction of many plants, including major food crops. Loss of species diversity can disrupt these services, leading to reduced crop yields and ecological imbalances.
4. Medicinal and Genetic Resources:
- Species diversity is a source of valuable medicinal compounds and genetic resources. Many plants and animals provide essential compounds for developing medicines, including antibiotics, cancer treatments, and pain relievers.
- Furthermore, genetic diversity within species ensures their ability to adapt to changing conditions, enhancing their resilience and potential for future discoveries.
In summary, species diversity is important in an ecosystem for maintaining stability, supporting productivity, providing essential ecological services, and serving as a valuable source of medicinal and genetic resources. Preserving and promoting species diversity is crucial for the well-being of both the ecosystem and human society.
READ MORE:
Key Roles of Species Diversity in Ecosystems
Species diversity plays a fundamental role in ensuring the health and functionality of ecosystems worldwide. It is the cornerstone upon which the stability and productivity of ecosystems rest. Here"s a closer look at its key roles:
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Diverse ecosystems provide essential services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation, which are vital for human survival and well-being.
- Enhances Ecosystem Resilience: A variety of species ensures that ecosystems can withstand and recover from environmental stresses, disturbances, and changes, thereby maintaining ecosystem functions.
- Boosts Ecosystem Productivity: The presence of a wide range of species leads to more efficient utilization of resources, resulting in higher overall productivity and enabling ecosystems to support more life.
- Promotes Nutrient Cycling: Diverse organisms play specialized roles in the decomposition of organic matter and the cycling of nutrients, which is essential for ecosystem health.
- Facilitates Adaptation: Genetic diversity within and among species fosters adaptation to environmental changes, ensuring long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
Understanding and preserving species diversity is crucial for maintaining the balance and vitality of the Earth"s ecosystems, highlighting the intrinsic value of biodiversity for current and future generations.
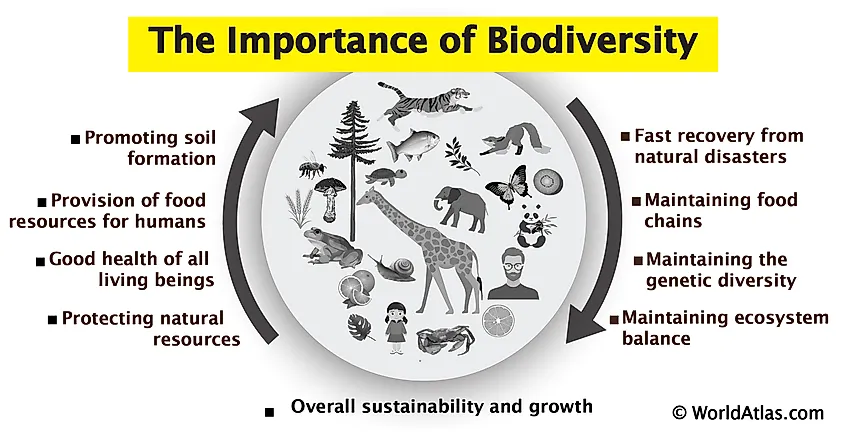
Benefits of Species Diversity to Ecosystem Stability
The stability of ecosystems is intricately linked to the diversity of species they contain. This diversity acts as a foundation for ecological balance and the sustained delivery of ecosystem services. Here are the key benefits:
- Enhanced Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to cope with environmental changes and disturbances, such as droughts, floods, and pest outbreaks, thereby maintaining their functionality over time.
- Reduced Vulnerability to Invasions: Ecosystems with high species diversity are less susceptible to invasive species, which can disrupt ecosystem balance and lead to the loss of native species.
- Stabilized Ecosystem Processes: A variety of species ensures more consistent and reliable ecosystem processes, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and decomposition, even in the face of external pressures.
- Better Adaptation Capabilities: The genetic diversity within and across species in diverse ecosystems fosters better adaptation to changing environmental conditions, promoting ecosystem stability.
- Buffer Against Extinction: Species diversity provides a buffer against extinction. The presence of multiple species performing similar ecological roles ensures that the loss of one does not drastically impact ecosystem functions.
Collectively, these benefits highlight the critical importance of conserving species diversity to ensure the long-term stability and health of ecosystems globally.
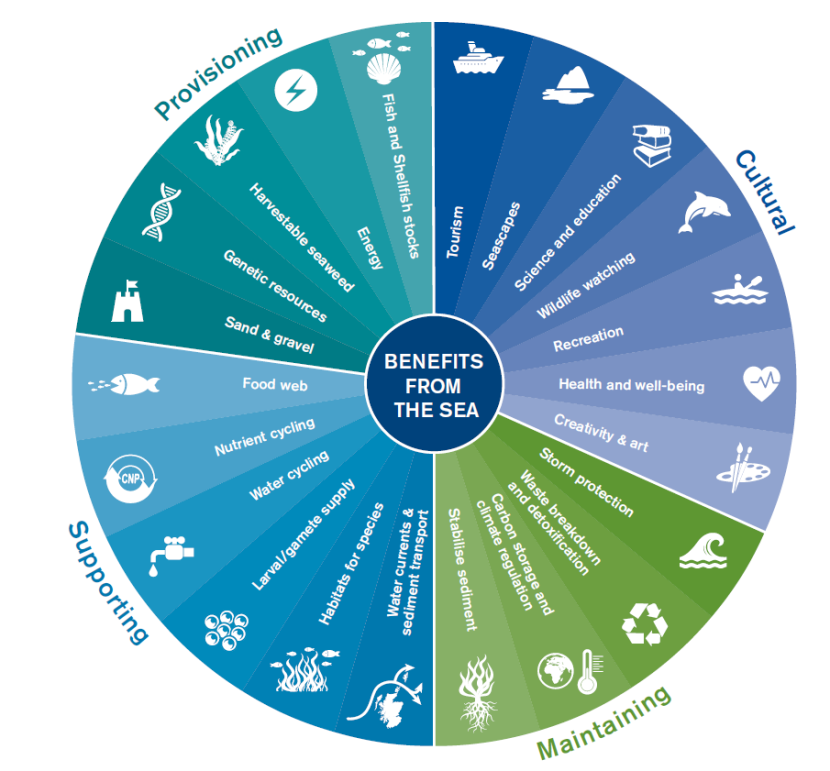
Impact of Species Diversity on Ecosystem Services
Species diversity significantly influences the quality and quantity of services ecosystems can provide, which are essential for human survival and economic well-being. The intricate relationships between species facilitate numerous ecosystem services, including:
- Pollination: A diverse range of pollinators enhances crop yields and quality, supporting agriculture and food production.
- Water Purification: Different species contribute to natural filtration systems, improving water quality by breaking down pollutants and regulating water cycles.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiversity in ecosystems can help control pathogens and reduce the incidence of certain diseases.
- Climate Regulation: Various species play a role in carbon sequestration and storage, contributing to climate mitigation efforts by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Soil Fertility: The diversity of soil organisms contributes to nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the maintenance of soil structure, which are critical for productive land use and agriculture.
By safeguarding species diversity, we ensure the resilience and continuity of these vital services, highlighting the interconnectedness of all life forms and their collective importance to human well-being and planetary health.
Species Diversity and Ecosystem Productivity
Ecosystem productivity, a measure of how much energy or biomass is produced in a given area and time, is deeply influenced by species diversity. The variety of life forms in an ecosystem contributes to its overall productivity and sustainability through several mechanisms:
- Niche Complementarity: Different species utilize resources in slightly different ways, leading to more efficient resource use overall, which enhances productivity.
- Facilitation: Some species may improve the conditions for other species, such as legumes fixing nitrogen in the soil for the benefit of other plants, thereby boosting ecosystem productivity.
- Insurance Hypothesis: Species diversity provides a form of insurance for ecosystems by ensuring that some species can maintain function in the face of environmental change, thus sustaining productivity.
- Increased Resistance to Pests and Diseases: A diverse ecosystem is less likely to be decimated by pests or diseases, as the presence of many species acts as a natural control mechanism, preserving productivity.
- Enhanced Recovery from Disturbances: Diverse ecosystems can recover more quickly from disturbances (like fires or storms), due to the presence of species that can quickly repopulate and rebuild the productivity of the area.
Therefore, preserving species diversity is not just about protecting wildlife; it"s about ensuring our ecosystems remain productive and capable of supporting life in all its forms, including human life.
Species Diversity as a Buffer Against Environmental Changes
Species diversity plays a critical role in buffering ecosystems against environmental changes, ensuring their stability and resilience in the face of challenges. This protective function is facilitated through various mechanisms:
- Redundancy Role: Multiple species performing similar ecological roles can compensate for the loss or decline of a particular species, ensuring continued ecosystem function.
- Adaptation and Evolution: A diverse gene pool allows species to adapt to changing environmental conditions, promoting ecosystem adaptability over time.
- Resistance to Stress and Disturbances: Ecosystems with high species diversity are better able to resist and recover from stressors such as climate extremes, pollution, and habitat destruction.
- Mitigation of Environmental Fluctuations: The presence of diverse species can help stabilize ecosystem processes and mitigate the impacts of environmental fluctuations.
- Support for Complex Food Webs: Biodiversity supports more complex and stable food webs, which enhances ecosystem resilience against changes that could otherwise lead to collapse.
By acting as a natural buffer, species diversity ensures that ecosystems can withstand and adapt to environmental changes, highlighting the importance of biodiversity conservation for ecosystem health and sustainability.

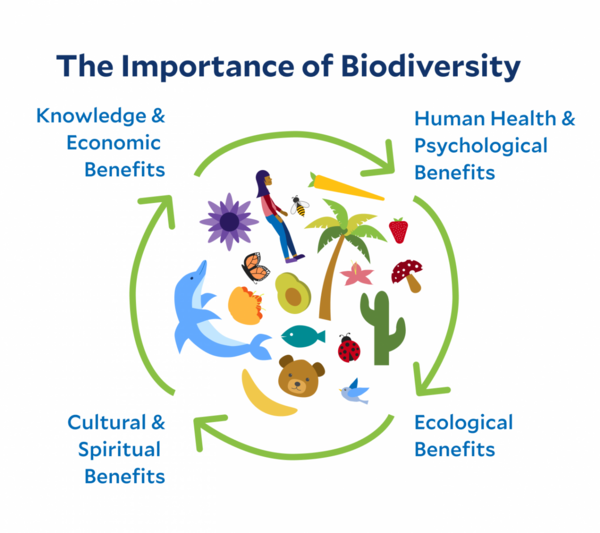
Contribution of Diverse Species to Human Well-being
The contribution of diverse species to human well-being is immense and multifaceted, touching every aspect of our lives from health to economic stability. Here"s how biodiversity enriches our world:
- Food Security: Diversity among crop species and their wild relatives provides genetic materials crucial for breeding programs, enhancing resilience to pests, diseases, and climate change.
- Medicinal Resources: Many pharmaceuticals are derived from chemical compounds found in plants, animals, and microorganisms, with biodiversity offering a vast library of potential medicines.
- Economic Benefits: Ecosystems services such as pollination, water purification, and soil fertility underpin industries like agriculture, fishing, and forestry, driving economic growth and supporting livelihoods.
- Cultural and Recreational Value: Natural environments enriched by species diversity provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits, contributing to mental and physical health.
- Ecosystem Services: Beyond tangible resources, diverse ecosystems regulate climate, filter air and water, and mitigate natural disasters, safeguarding human habitats.
Protecting species diversity is not just an environmental imperative but a necessity for human health, prosperity, and future generations" well-being.
Why is biodiversity so important?
Discover the wonders of our planet\'s biodiversity! Explore the importance of protecting and preserving our Earth\'s diverse ecosystems in this captivating video. Join us on an educational journey to better understand the vital role biodiversity plays in sustaining life on our beautiful planet.
Why is biodiversity important with Sir David Attenborough
Dive into the extraordinary career and passion of the legendary Sir David Attenborough! Get inspired by his unparalleled dedication to wildlife conservation and his incredible storytelling abilities. This captivating video offers an exclusive look into the life and work of the world\'s most beloved naturalist and broadcaster.
Challenges and Threats to Species Diversity
Despite its crucial importance, species diversity faces numerous challenges and threats that jeopardize ecosystem health and functionality. Understanding these threats is essential for effective conservation efforts:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, critically impacting species survival.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect habitat suitability, species distribution, and ecosystem dynamics, posing a significant threat to biodiversity.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect species health and ecosystems" balance.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, and harvesting pressure species populations, leading to declines or extinction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predation, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem balance.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: The reduction in genetic diversity within species populations increases their vulnerability to diseases and environmental changes.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and strong conservation policies to safeguard species diversity for future generations.

Conservation Efforts and Their Importance for Species Diversity
Despite its crucial importance, species diversity faces numerous challenges and threats that jeopardize ecosystem health and functionality. Understanding these threats is essential for effective conservation efforts:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, critically impacting species survival.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect habitat suitability, species distribution, and ecosystem dynamics, posing a significant threat to biodiversity.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect species health and ecosystems" balance.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, and harvesting pressure species populations, leading to declines or extinction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predation, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem balance.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: The reduction in genetic diversity within species populations increases their vulnerability to diseases and environmental changes.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and strong conservation policies to safeguard species diversity for future generations.
READ MORE:
Future Perspectives on Maintaining Species Diversity
Despite its crucial importance, species diversity faces numerous challenges and threats that jeopardize ecosystem health and functionality. Understanding these threats is essential for effective conservation efforts:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, critically impacting species survival.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect habitat suitability, species distribution, and ecosystem dynamics, posing a significant threat to biodiversity.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect species health and ecosystems" balance.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, and harvesting pressure species populations, leading to declines or extinction.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predation, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem balance.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: The reduction in genetic diversity within species populations increases their vulnerability to diseases and environmental changes.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and strong conservation policies to safeguard species diversity for future generations.
Embracing species diversity is crucial for a resilient and productive planet. By conserving biodiversity, we ensure a sustainable future, highlighting our interconnectedness with the natural world and its indispensable benefits to humanity.