Topic ecosystem diversity define: Ecosystem diversity encompasses the vast variety of habitats, biological communities, and ecological processes in the natural world, playing a crucial role in maintaining the planet"s health and resilience.
Table of Content
- What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
- Definition of Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Challenges to Ecosystem Diversity
- Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Diversity
- Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Regulation
- Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Successes in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
- Future Perspectives on Ecosystem Diversity
What is the definition of ecosystem diversity?
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of different ecosystems that exist within a specific region or on a global scale. It includes the range of habitats, communities, and ecological processes that are present in a particular geographic area.
Here are some key points that help explain the definition of ecosystem diversity:
- Ecosystem diversity encompasses both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
- It takes into account the variation in habitats, such as forests, grasslands, wetlands, coral reefs, and freshwater ecosystems.
- Each ecosystem has its own unique set of species, communities, and ecological interactions.
- Ecosystem diversity is influenced by factors such as climate, topography, soil composition, and human activities.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, as different ecosystems provide various ecological services and perform different functions.
- Ecosystem diversity is important for the overall health and resilience of the planet, as it enhances the ability of ecosystems to adapt to environmental changes.
- Conservation and preservation of ecosystem diversity are essential for the protection of biodiversity and the sustainability of ecosystems.
Overall, ecosystem diversity represents the incredible array of ecosystems that exist on Earth and the interconnections between them, highlighting the value of preserving and understanding these diverse habitats.
READ MORE:
Definition of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems within a particular region or across the globe. It encompasses the range of different habitats, including forests, deserts, grasslands, wetlands, and marine environments, each with distinct communities of plants, animals, microorganisms, and their non-living environments. This diversity includes the varied interactions among these organisms and their physical surroundings, which contribute to the planet"s overall biological diversity. Ecosystem diversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and supports the array of services ecosystems provide, such as air and water purification, soil fertility, pollination, and climate regulation.

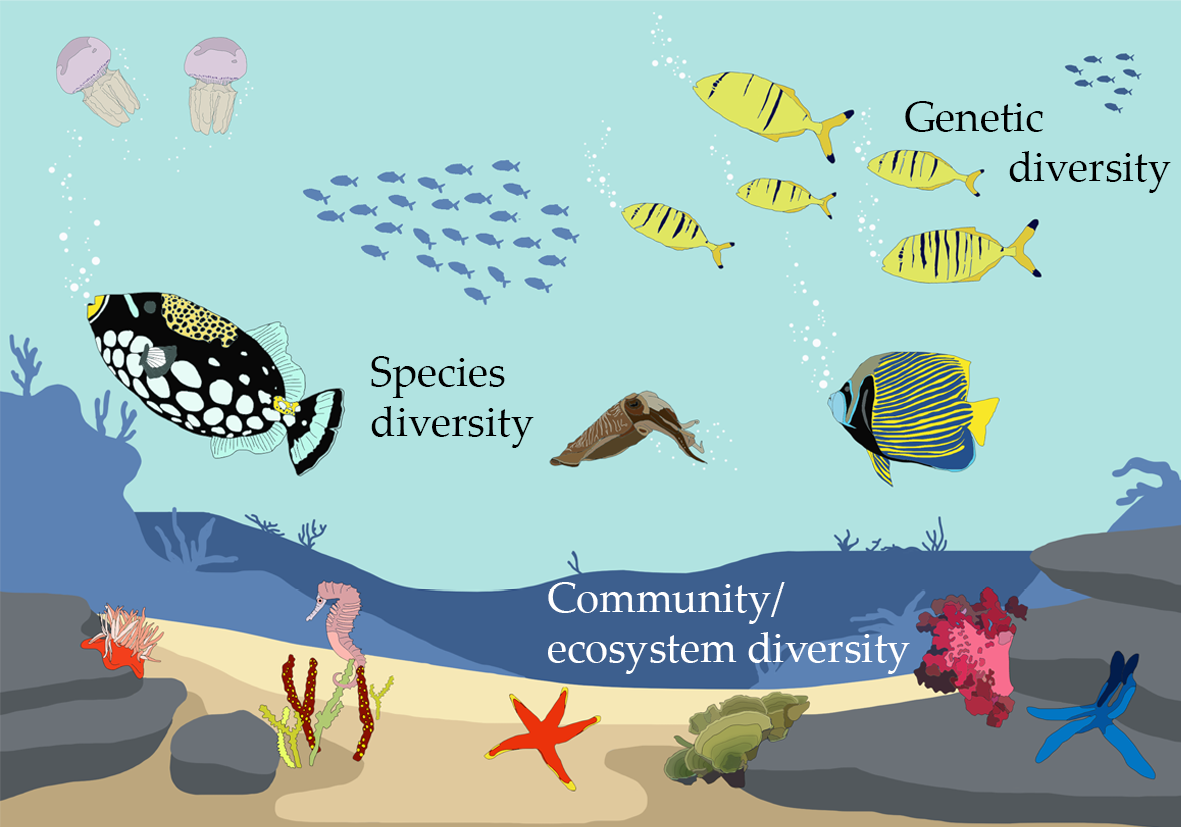
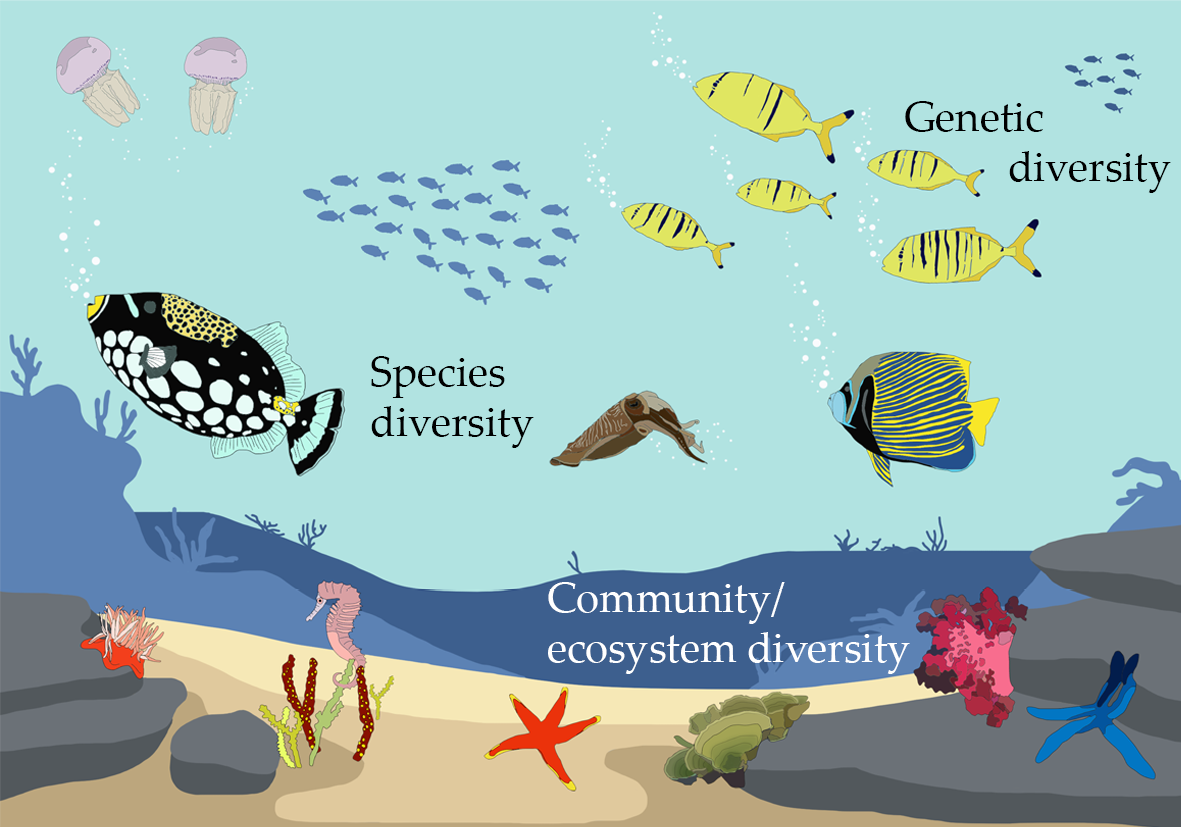
Types of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is broadly categorized into two main types: terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Each of these main categories is further divided into more specific ecosystems based on their unique characteristics and the organisms they support.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: These are land-based ecosystems and include:
- Forests (e.g., tropical rainforests, temperate deciduous forests, boreal forests)
- Grasslands (e.g., savannas, prairies, steppes)
- Deserts
- Tundras
- Mountain ecosystems
- Aquatic Ecosystems: These are water-based ecosystems and are categorized into:
- Freshwater ecosystems (e.g., lakes, rivers, wetlands)
- Marine ecosystems (e.g., oceans, coral reefs, estuaries)
Each ecosystem type supports a unique set of species and interactions, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the planet. Understanding these diverse ecosystems is crucial for their conservation and the sustainable management of natural resources.
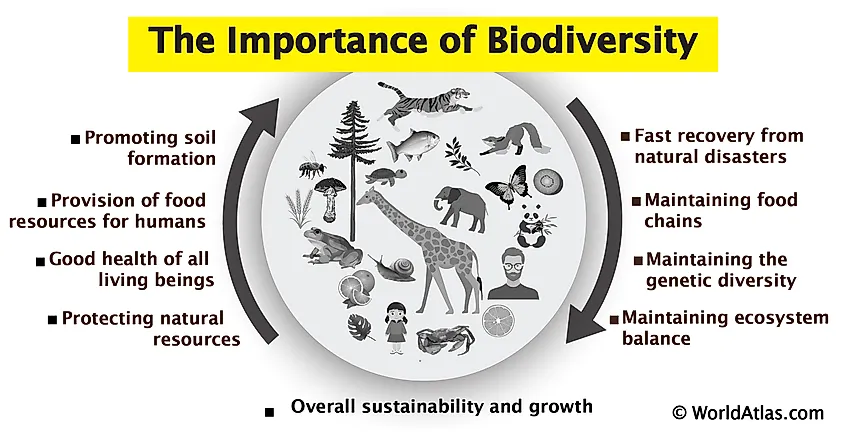
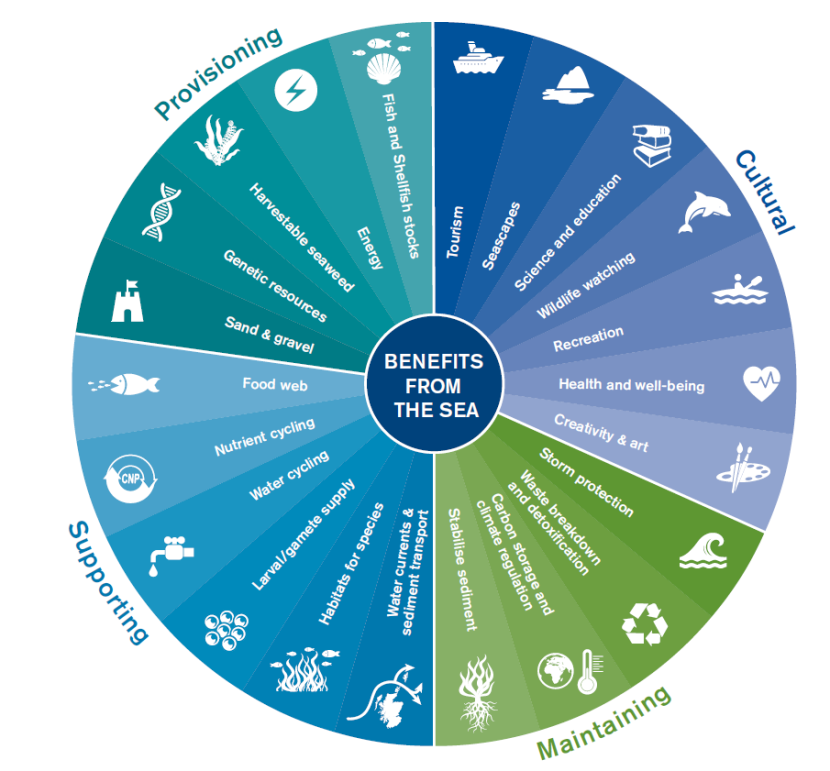
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is fundamental to Earth"s life support systems. It ensures natural sustainability for all living things and provides a suite of services essential for human well-being. Below are key points highlighting its importance:
- Supports Biodiversity: Diverse ecosystems are home to a wide range of species, contributing to global biodiversity. This diversity ensures resilience against environmental changes and disasters.
- Provision of Ecosystem Services: Ecosystems perform vital services such as air and water purification, soil stabilization, carbon sequestration, and nutrient cycling, which are crucial for human survival.
- Enhances Food Security: A variety of ecosystems means a diversity of crops and livestock, enhancing food security by reducing dependence on a single source of nutrition.
- Medical Discoveries: Many medicines are derived from plants and animals found in diverse ecosystems, highlighting the role of ecosystem diversity in health and medicine.
- Economic Benefits: Ecosystem diversity supports industries such as agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and tourism, contributing significantly to global and local economies.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Many cultures derive their identity and values from their natural surroundings, and diverse ecosystems offer inspiration, recreation, and education.
- Climate Regulation: Different ecosystems play specific roles in the carbon cycle and in regulating the Earth"s climate, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Protecting and maintaining ecosystem diversity is thus crucial for ecological balance, human health, and economic development, highlighting the interconnectedness of all life on Earth.

Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems is influenced by a variety of both natural and anthropogenic factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for the conservation and sustainable management of ecosystems. Here are some of the key factors:
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and other climate conditions greatly influence the type of ecosystems that can thrive in a particular area.
- Geography: Geographic features such as mountains, rivers, and soil types play a significant role in shaping ecosystem diversity.
- Altitude: Changes in altitude affect climate conditions, leading to different ecosystems at various elevations.
- Human Activities: Urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution can drastically alter and reduce ecosystem diversity.
- Biotic Interactions: Interactions among species, including competition, predation, and symbiosis, influence the structure and composition of ecosystems.
- Evolutionary History: The evolutionary past of an area and its species can influence current ecosystem diversity.
- Disturbances: Natural disturbances such as fires, floods, and hurricanes can create opportunities for new ecosystems to develop.
These factors interact in complex ways, determining the distribution, structure, and function of ecosystems around the world. Addressing the impacts of negative influences, particularly human activities, is essential for preserving ecosystem diversity.
Challenges to Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity faces several challenges that threaten its integrity and sustainability. Addressing these challenges is vital for the preservation of biodiversity and the well-being of the planet. Key challenges include:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urban development, and agriculture expansion are leading causes of habitat loss, significantly reducing ecosystem diversity.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect the distribution and function of ecosystems, leading to the loss of species and habitats.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade ecosystems and diminish their diversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete native species, disrupt ecosystems, and lead to biodiversity loss.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable logging, fishing, and hunting pressure certain species and ecosystems, threatening their survival.
- Land Use Change: Converting natural landscapes into agricultural or urban areas alters ecosystems, reducing their diversity and functionality.
- Global Warming: Rising temperatures can shift or shrink habitats, impacting the species and ecosystems that depend on specific climate conditions.
Efforts to mitigate these challenges through conservation, sustainable practices, and policy interventions are crucial to protect and restore ecosystem diversity for future generations.

Conservation Strategies for Ecosystem Diversity
Conserving ecosystem diversity is essential for maintaining the balance of nature and ensuring the survival of species. Various strategies can be employed to protect and enhance ecosystem diversity:
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing protected areas like national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine sanctuaries to conserve natural habitats.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetlands restoration, and other habitat restoration efforts.
- Legislation and Policies: Implementing laws and policies that protect ecosystems and biodiversity, such as environmental impact assessments and conservation acts.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts through education, sustainable livelihood initiatives, and participatory management.
- Invasive Species Management: Controlling or eradicating invasive species that threaten native biodiversity.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Adopting practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sequestration to combat climate change and its impact on ecosystems.
- Sustainable Use Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to minimize habitat destruction and overexploitation.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: Conducting regular monitoring and research to track changes in biodiversity and the effectiveness of conservation strategies.
These strategies require coordinated efforts from governments, NGOs, the scientific community, and the general public to effectively conserve ecosystem diversity for future generations.
Ecosystem Diversity
Discover the true definition of happiness and how it can transform your life. This inspiring video will guide you through the many facets of happiness, helping you unlock its power and experience true joy.
Ecosystem Diversity - Nature World
Immerse yourself in the breathtaking beauty of nature with this captivating video. Journey through lush green forests, majestic mountains, and serene waterfalls, and be reminded of the incredible wonders that surround us. Let nature\'s tranquility rejuvenate your soul.
Role of Ecosystem Diversity in Climate Regulation
Ecosystem diversity plays a critical role in regulating the global climate, offering multiple benefits that help stabilize the Earth"s climate system. This regulation occurs through various mechanisms:
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests, wetlands, and oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. This process reduces the greenhouse effect and global warming.
- Temperature Regulation: Vegetation cover, such as forests and grasslands, can influence local temperatures by providing shade and releasing water vapor through transpiration, cooling the air.
- Water Cycle Regulation: Ecosystems like forests and wetlands play a key role in the water cycle by capturing, storing, and releasing water, affecting precipitation patterns and water availability.
- Protection Against Extreme Weather: Healthy ecosystems such as mangroves and coral reefs act as barriers against natural disasters, reducing the impact of storms and flooding and helping to protect coastlines.
- Albedo Effect Modification: Different land surfaces have varying abilities to reflect sunlight. Snow-covered areas and dense forests influence the Earth"s albedo, affecting global temperatures.
These natural processes highlight the importance of conserving and restoring ecosystem diversity as a strategy to mitigate climate change and ensure climate stability. The interconnection between diverse ecosystems and the climate underscores the need for integrated approaches to environmental conservation and climate action.

Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystem Diversity
Human activities have significantly impacted ecosystem diversity worldwide, often leading to negative consequences for the environment and biodiversity. Here are some key impacts:
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural expansion destroy habitats, leading to the loss of species and ecosystems.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial processes, agriculture, and waste disposal harm organisms and degrade ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Emissions of greenhouse gases from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes contribute to climate change, affecting ecosystems and species distributions.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and logging exceed the natural capacity of ecosystems to regenerate, leading to diminished biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can disrupt local ecosystems, outcompete native species, and lead to loss of native biodiversity.
- Land Use Change: Converting natural landscapes into urban or agricultural areas alters and fragments ecosystems, reducing their diversity and functionality.
- Water Use: Excessive water extraction for agriculture and urban use alters watercourses and can lead to habitat loss for aquatic and riparian species.
These activities not only reduce ecosystem diversity but also compromise the ability of ecosystems to provide essential services, such as climate regulation, water purification, and pollination, upon which all life depends. Addressing these impacts through sustainable practices and conservation efforts is critical for preserving ecosystem diversity and ensuring a stable environment for future generations.
Case Studies: Successes in Ecosystem Diversity Conservation
Conservation efforts worldwide have demonstrated significant successes in preserving and enhancing ecosystem diversity. Here are a few notable case studies:
- Restoration of the Loess Plateau, China: Through large-scale land management and restoration projects, this region has seen a dramatic transformation from degraded land to a vibrant ecosystem, significantly improving local livelihoods and biodiversity.
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) Expansion: The global increase in MPAs has helped protect marine biodiversity, supporting fish stocks recovery, coral reef preservation, and marine habitat protection.
- Reforestation Efforts in Costa Rica: Costa Rica has doubled its forest cover in the last 30 years through national reforestation efforts, contributing to biodiversity conservation and carbon sequestration.
- Community-Based Conservation in Namibia: Namibia"s community conservancy program empowers local communities to manage wildlife, leading to the recovery of several species and increased ecosystem diversity.
- Project Tiger, India: Launched in 1973, this conservation initiative has been instrumental in the significant increase in the tiger population through habitat restoration and anti-poaching efforts.
These case studies illustrate the positive impact of concerted conservation efforts on ecosystem diversity. They highlight the importance of multi-faceted approaches that include legal protection, community engagement, restoration activities, and sustainable management practices.

READ MORE:
Future Perspectives on Ecosystem Diversity
Looking towards the future, the conservation and enhancement of ecosystem diversity are pivotal for the sustainability of our planet. Here are several perspectives and approaches that could shape the future of ecosystem diversity:
- Integrative Conservation Strategies: Combining traditional conservation methods with innovative technologies and interdisciplinary research to address complex environmental challenges effectively.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Developing ecosystems that are resilient to the impacts of climate change through adaptive management practices and restoration efforts.
- Urban Biodiversity: Promoting green infrastructure in urban areas to support ecosystem diversity, including parks, green roofs, and urban gardens that provide habitats for various species.
- Policy and Governance: Strengthening international and national policies that protect ecosystem diversity, including the implementation of global agreements and local conservation initiatives.
- Community Engagement and Education: Enhancing awareness and involvement of local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing the value of traditional knowledge in ecosystem management.
- Sustainable Use of Resources: Encouraging practices that ensure the sustainable use of natural resources, reducing pressure on ecosystems and promoting biodiversity.
- Technological Advancements: Utilizing technology for better monitoring and management of ecosystems, including remote sensing, bioinformatics, and ecological modeling.
The future of ecosystem diversity depends on concerted efforts from all sectors of society to mitigate negative impacts and promote a sustainable coexistence with nature. These future perspectives highlight the importance of innovation, collaboration, and proactive measures in conserving the planet"s invaluable ecosystem diversity.
Embracing ecosystem diversity is pivotal for our planet"s health and future. By understanding, conserving, and enhancing our ecosystems, we can ensure a resilient and vibrant world for generations to come.