Topic biodiversity in an ecosystem refers to: Explore the essence of biodiversity in an ecosystem, where the intricate web of life forms a vibrant tapestry, underpinning the health and sustainability of our planet.
Table of Content
- What does the term biodiversity in an ecosystem refers to?
- Understanding Biodiversity
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Types of Biodiversity
- Factors Influencing Biodiversity
- Threats to Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Importance of Biodiversity to Ecosystems
- Conservation Strategies
- The Role of Ecosystems in Biodiversity
- Human Impact on Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Hotspots
- Future of Biodiversity
What does the term biodiversity in an ecosystem refers to?
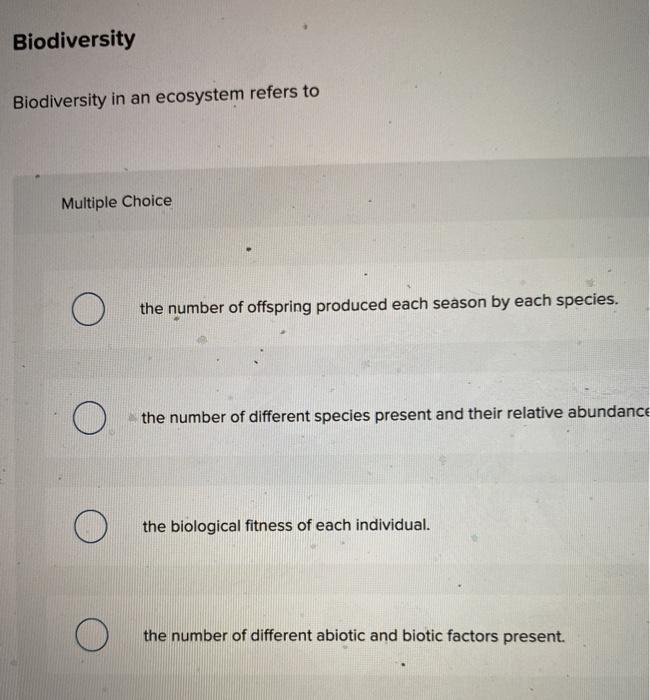
Biodiversity in an ecosystem refers to the variety of species present and their relative abundance. It encompasses both the number of different species and the distribution of individuals within each species. Biodiversity is a measure of the health and resilience of an ecosystem.
- Biodiversity includes the diversity of plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms present in an ecosystem.
- It takes into account the genetic diversity within each species, as well as the variety of species present.
- Biodiversity also considers the interactions and relationships between different species, including predator-prey relationships, symbiosis, and competition.
- It can be used to assess the overall ecosystem stability and functioning, as different species perform different ecological roles and contribute to the overall balance of the ecosystem.
In summary, biodiversity in an ecosystem refers to the range and variety of species, their abundance, genetic diversity, and the interactions between them. It is a crucial aspect of ecosystem health and resilience.
READ MORE:
Understanding Biodiversity
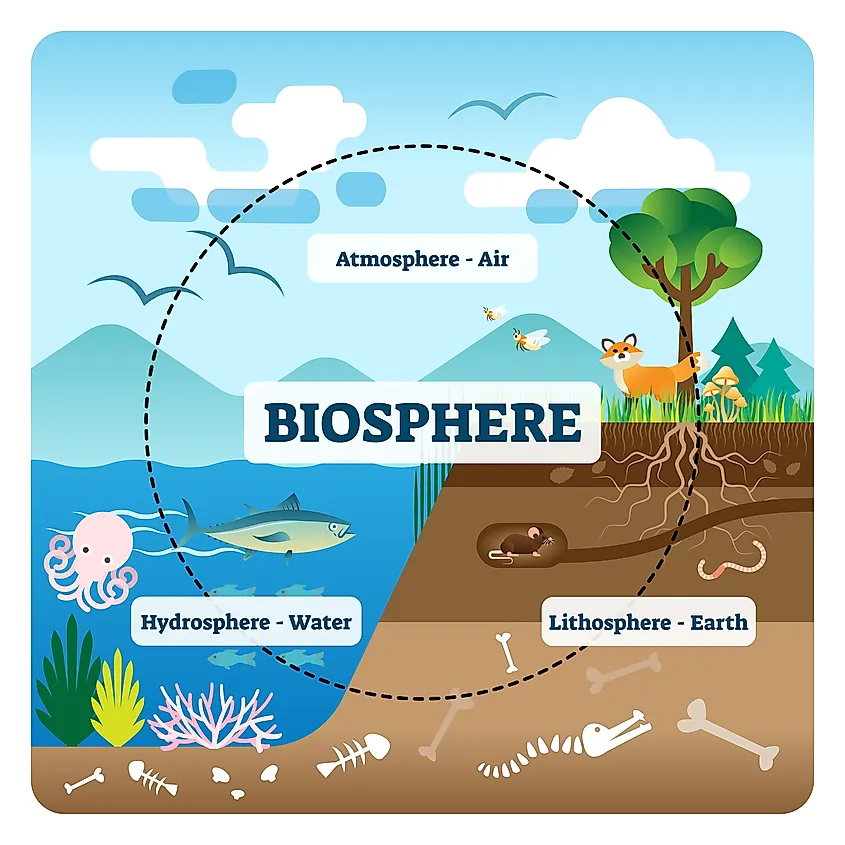
Biodiversity, or biological diversity, refers to the variety of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or for the entire Earth. It encompasses the diversity of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the genetic differences within these species and the complex ecosystems they form.
- Genetic Diversity: This includes the variety of genetic information contained in all of the individual plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- Species Diversity: This refers to the variety of species within a habitat or a region.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This covers the variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the living world, including terrestrial, marine, and desert ecosystems.
Biodiversity is not static; it is constantly changing. It is increased by genetic change and evolutionary processes and reduced by processes such as habitat degradation, climate change, and overexploitation of resources.
Understanding biodiversity is crucial for the sustainability of life on Earth, as it affects ecosystem productivity, resilience, and the ability of biological systems to respond to environmental changes and natural disasters.
Importance of Biodiversity
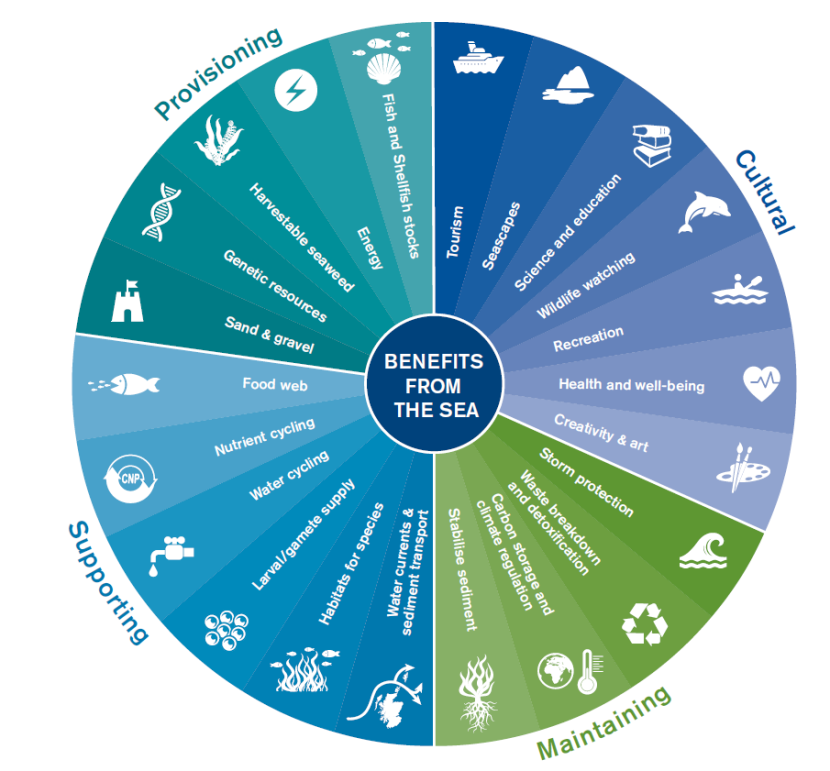
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems and provides a wide range of ecosystem services that are vital to human well-being and the planet"s health. Its importance spans across various dimensions:
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Essential services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, water filtration, and soil formation are sustained by biodiversity.
- Enhances Food Security: A diverse genetic pool ensures resilient food systems with a variety of crops and livestock that can withstand pests, diseases, and climate change.
- Promotes Medical Discoveries: Many medicines, including cancer treatments and antibiotics, have been derived from the genetic material of plants and animals found in diverse ecosystems.
- Regulates Climate: Diverse ecosystems like forests and oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and helping to mitigate climate change.
- Supports Cultural and Recreational Values: Many cultures derive their identity and values from biodiversity, which also supports tourism and recreational activities.
The conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity are therefore essential for ecological stability, human health, and economic development. By protecting biodiversity, we ensure that future generations can enjoy and benefit from the rich natural world.
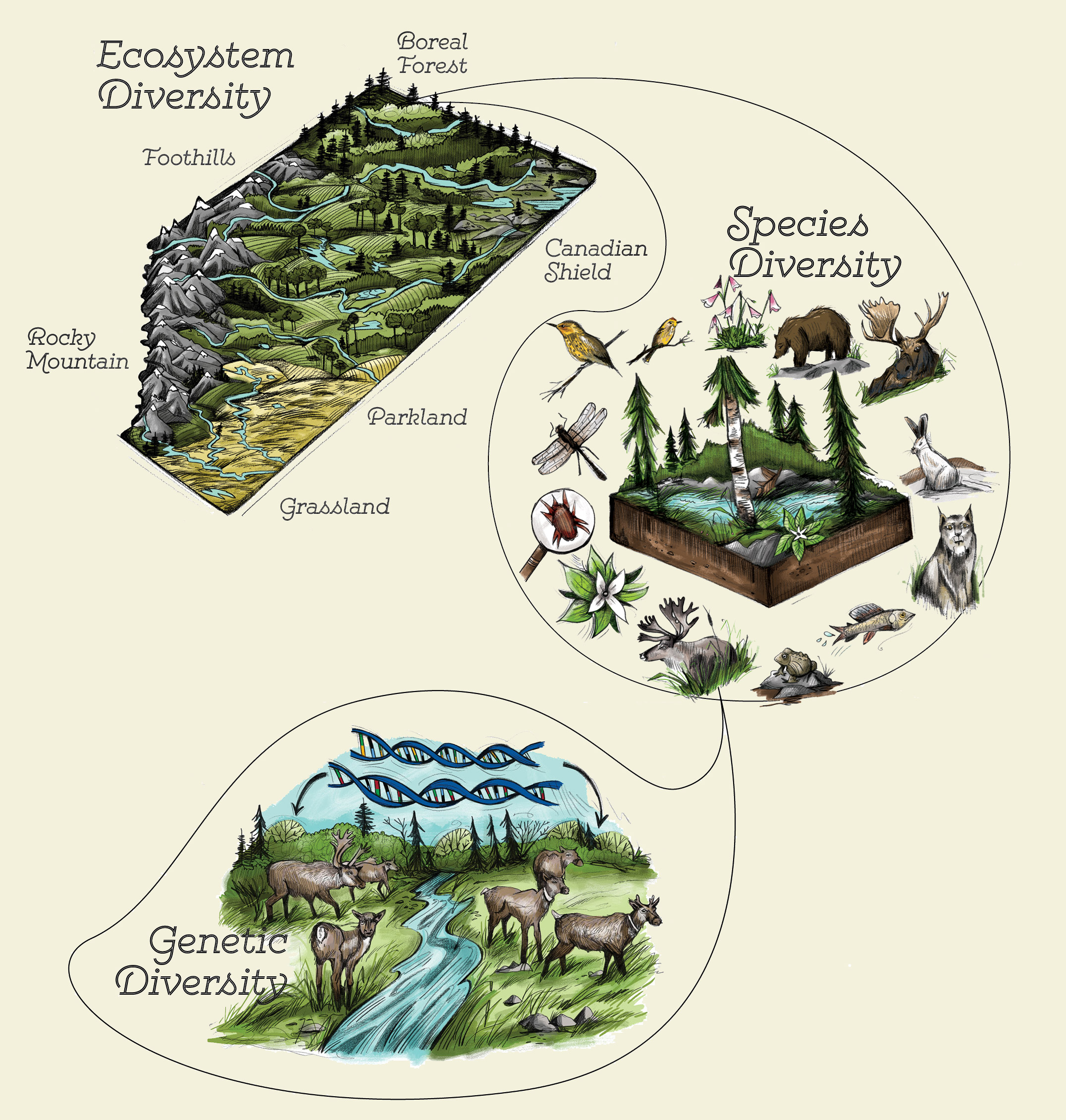
Types of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is not a monolithic concept but rather is classified into three primary types, each of which plays a significant role in the overall diversity of life on Earth. Understanding these types helps in appreciating the complexity and interdependence of life forms.
- Genetic Diversity: This type refers to the variation of genes within species. This diversity allows species to adapt to changing environments, resist diseases, and contribute to biodiversity through the evolution of new species.
- Species Diversity: Species diversity measures the number of different species that are present in a specific ecosystem, region, or the entire planet. This includes all species, from the most common to the rarest.
- Ecosystem Diversity: This encompasses the variety of habitats, natural communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere. It includes the diversity of ecosystems such as forests, deserts, wetlands, mountains, lakes, rivers, and agricultural landscapes.
Each type of biodiversity is critical for the resilience and productivity of ecosystems. Genetic diversity ensures that species can adapt to changes, species diversity contributes to ecosystem functions, and ecosystem diversity supports the complex interactions between species and their physical environment.

Factors Influencing Biodiversity
The richness and variety of life on Earth are influenced by several key factors, both natural and human-induced. Understanding these factors is crucial for the conservation and sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Climate: Temperature, rainfall, and other climatic conditions play a significant role in determining the distribution and types of species and ecosystems found in an area.
- Altitude: Changes in altitude affect environmental conditions, which in turn influence the types of species that can survive in those conditions.
- Geography: Geographic barriers such as mountains and oceans can limit the movement and distribution of species, leading to the development of unique biodiversity in isolated areas.
- Soil Types: The composition and quality of soil affect the types of plants that can grow in an area, which in turn influences the animals that can inhabit those areas.
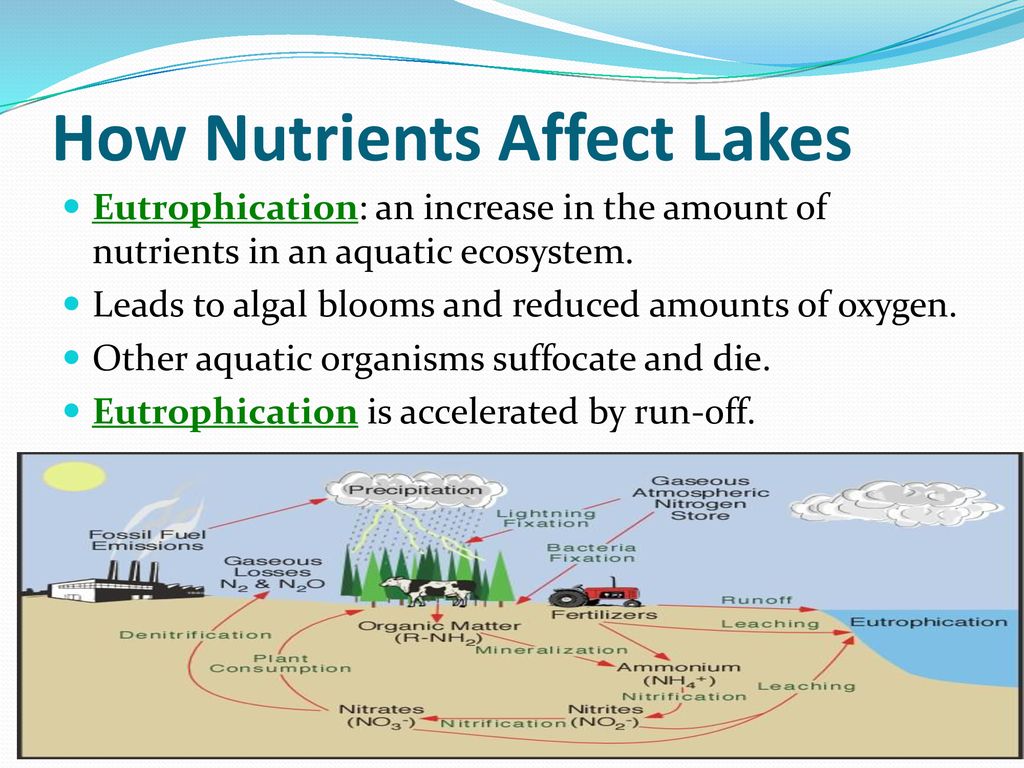
- Human Activities: Urbanization, deforestation, pollution, and climate change due to human activities have significant impacts on biodiversity. These activities can lead to habitat loss, species extinction, and reduced genetic diversity.
- Ecological Interactions: The relationships between species, such as predation, competition, and symbiosis, also shape the complexity of biodiversity.
These factors interact in complex ways to shape the unique biodiversity of each ecosystem. Recognizing and understanding these influences is essential for effective biodiversity conservation efforts.
Threats to Biodiversity
Biodiversity is under threat from various sources, many of which are exacerbated by human activities. Recognizing these threats is the first step towards mitigating their impact on ecosystems worldwide.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture expansion are leading causes of natural habitat loss, severely impacting species populations and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns affect ecosystems and species" ability to survive, leading to shifts in biodiversity and increased vulnerability of certain species.
- Pollution: Water, air, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources can degrade ecosystems and poison species, impacting their health and survival.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable harvesting of resources, such as overfishing and hunting, depletes populations faster than they can recover, leading to significant declines in biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced into new environments can outcompete, prey upon, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystems.
- Pesticides and Chemicals: The widespread use of pesticides and other chemicals in agriculture can harm non-target species, reducing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Addressing these threats requires concerted global efforts towards sustainable practices, conservation, and restoration projects to protect and enhance biodiversity for future generations.
Importance of Biodiversity to Ecosystems
Explore the wonders of ecosystems in this captivating video! Dive into lush rainforests, intricate coral reefs, and vibrant savannas, and discover the immense beauty and interconnectedness of nature\'s most enchanting habitats.
Conservation Strategies
Conservation of biodiversity is critical for maintaining the health and resilience of ecosystems. Various strategies can be employed to protect and sustain biodiversity:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve natural habitats and provide sanctuaries for species.
- Legislative Measures: Implementing laws and regulations to protect endangered species, regulate hunting, fishing, and logging, and control pollution and land use.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems through reforestation, wetland restoration, and the reintroduction of native species to restore ecological balance.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices to reduce environmental impact and conserve resources.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their traditional knowledge and vested interest in preserving biodiversity.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sinks to combat climate change and its impacts on biodiversity.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders on conservation projects and initiatives, sharing knowledge, and resources to address global biodiversity challenges.
Effective conservation requires a holistic approach that combines these strategies with ongoing research and monitoring to adapt to changing environmental conditions and threats to biodiversity.
The Significance of Biodiversity
Uncover the significance of small actions in this thought-provoking video. Learn how even the smallest choices we make can have a profound impact on the world around us. Join us on this inspiring journey to understand the true power of our individual actions.
The Role of Ecosystems in Biodiversity
Ecosystems play a fundamental role in supporting and enhancing biodiversity through their complex interactions and processes. They provide the essential services and conditions for different forms of life to thrive:
- Habitats and Niches: Ecosystems offer a variety of habitats and niches that accommodate a wide range of organisms, supporting species diversity.
- Nutrient Cycling: Ecosystem processes like decomposition and photosynthesis ensure the recycling of nutrients, which sustains plant and animal life.
- Water Regulation: Ecosystems regulate the water cycle through processes such as evapotranspiration and precipitation, supporting life and maintaining habitat conditions.
- Climate Regulation: Forests, oceans, and wetlands play crucial roles in regulating the Earth"s climate by acting as carbon sinks and influencing local weather patterns.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Many ecosystems depend on animals and insects for pollination and seed dispersal, essential for plant reproduction and genetic diversity.
By sustaining ecosystems, we support the intricate web of life that forms biodiversity. The health and resilience of our planet depend on the careful management and protection of these vital systems.
Human Impact on Biodiversity
The impact of human activities on biodiversity is profound and far-reaching, affecting ecosystems around the world in various ways:
- Habitat Destruction: Urban expansion, agriculture, mining, and infrastructure development lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, one of the primary causes of biodiversity loss.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources introduces toxins into ecosystems, harming wildlife and degrading habitats.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change, through the emission of greenhouse gases, alters habitats and conditions necessary for many species to survive, leading to shifts in biodiversity patterns.
- Overexploitation: The overharvesting of resources, including fishing, hunting, and logging, depletes populations of species and disrupts ecological balances.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species to new environments can outcompete, prey upon, or bring diseases to native species, significantly altering ecosystems.
- Resource Depletion: Unsustainable use of natural resources leads to depletion of soil, water, and other resources critical to biodiversity and human well-being.
Addressing human impacts on biodiversity requires a concerted effort to adopt sustainable practices, enforce protective regulations, and raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity for our survival and quality of life.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots are regions with exceptionally high levels of species diversity and endemism, yet facing significant threats from human activities. These areas are critical for conservation efforts as they represent a high priority for biodiversity conservation worldwide:
- Definition and Criteria: A biodiversity hotspot is an area that has at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics and has lost at least 70% of its original habitat.
- Global Importance: Hotspots hold a significant proportion of the world"s plant and animal species, many of which are endemic and cannot be found anywhere else on Earth.
- Examples of Hotspots: The Amazon rainforest, Madagascar, the Cape Floristic Region in South Africa, and the islands of Southeast Asia are among the most well-known biodiversity hotspots.
- Threats: These areas are under threat from habitat destruction, climate change, invasive species, overexploitation, and pollution.
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting biodiversity hotspots is a focus of international conservation organizations, aiming to preserve unique ecosystems, species, and genetic diversity.
Conserving biodiversity hotspots is crucial for maintaining global biodiversity, supporting ecosystems services, and sustaining human livelihoods that depend on these ecosystems.

READ MORE:
Future of Biodiversity
The future of biodiversity hinges on the actions taken today to conserve and restore natural habitats and ecosystems. Despite facing significant challenges, there is hope for preserving biodiversity through concerted global efforts:
- Conservation Initiatives: Expanding protected areas, restoring degraded ecosystems, and implementing sustainable management practices are crucial for the future health of our planet.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing natural carbon sinks are essential to mitigate the impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
- Technological Advances: Technology can play a role in monitoring biodiversity, tracking species populations, and restoring ecosystems.
- International Cooperation: Global collaboration is necessary to address the transboundary nature of biodiversity conservation and to share resources, knowledge, and best practices.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and recognizing their traditional knowledge and rights can enhance the effectiveness of biodiversity conservation.
- Policy and Legislation: Strong environmental policies and legislation are needed to protect endangered species, regulate land use, and control pollution.
The future of biodiversity is not predetermined and depends on the choices made by governments, communities, and individuals to value, protect, and restore the natural world.
Embracing the richness of biodiversity is vital for the health of our planet. By understanding, valuing, and actively protecting biodiversity, we ensure a resilient and vibrant world for future generations.