Topic biodiversity in an ecosystem: Discover the vital role of biodiversity in an ecosystem, a cornerstone of life on Earth, fostering resilience, sustainability, and unparalleled natural wealth.
Table of Content
- What is the role of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) in assessing the state of biodiversity in an ecosystem?
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Threats to Biodiversity
- Benefits of Biodiversity to Ecosystem Services
- Role of Invasive Species in Biodiversity
- Impact of Human Activities on Biodiversity
- Conservation Strategies for Enhancing Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystems
- Global and Local Biodiversity Initiatives
- Case Studies: Successful Biodiversity Conservation Efforts
- The Future of Biodiversity in Changing Climates
- How Individuals Can Contribute to Biodiversity Conservation
What is the role of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) in assessing the state of biodiversity in an ecosystem?
The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) plays a crucial role in assessing the state of biodiversity in an ecosystem. Here is a step-by-step explanation of its role:
- IPBES is an intergovernmental body that assesses the state of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- It performs regular and timely assessments of knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services at the global level.
- IPBES aims to provide policymakers with reliable scientific information and assessments related to biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- It helps in identifying key drivers of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation, as well as effective strategies for conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
- By assessing the state of biodiversity in an ecosystem, IPBES contributes to understanding the current status, threats, and potential consequences of changes in biodiversity.
- IPBES also highlights the importance of biodiversity for human well-being and sustainable development.
In summary, the main role of IPBES is to assess and provide policymakers with valuable information on biodiversity and ecosystem services, helping them make informed decisions for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
READ MORE:
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity, or biological diversity, plays a crucial role in the health and stability of ecosystems across the globe. It encompasses the variety of life forms, from the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals, including the diversity of species, genetics, and ecosystems. The importance of biodiversity in an ecosystem cannot be overstated, as it ensures natural sustainability for all life forms.
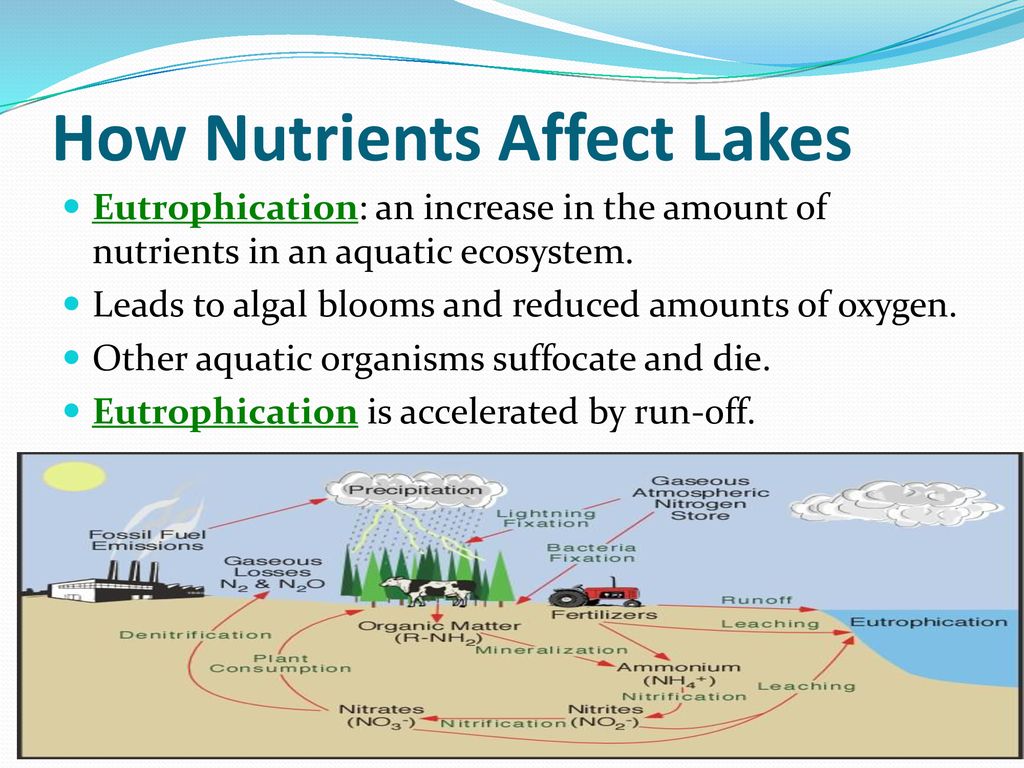
- Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity provides essential ecosystem services such as air and water purification, climate regulation, pollination of crops, and control of agricultural pests. These services are critical for human survival and well-being.
- Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances, such as climate change and natural disasters. A rich variety of species can adapt to changes, ensuring ecosystem stability and sustainability.
- Genetic Resources: Biodiversity is a source of immense genetic material that has potential uses in agriculture, medicine, and biotechnology. Many medicines are derived from compounds found in plants and animals.
- Economic Benefits: Many industries, including agriculture, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and tourism, directly depend on biodiversity. Healthy ecosystems contribute to the economy by providing raw materials and supporting livelihoods.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Biodiversity enriches cultures and provides inspiration, recreational opportunities, and spiritual significance. Natural landscapes and wildlife are integral to human identity and enjoyment.
In summary, the importance of biodiversity in an ecosystem extends beyond the intrinsic value of nature; it is foundational to ecosystem health, human well-being, and economic prosperity. Protecting biodiversity is essential for maintaining the balance of life on Earth and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.

Threats to Biodiversity
The diversity of life on Earth is under constant threat from a variety of sources. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect biodiversity. Below are key factors contributing to the loss of biodiversity:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, agriculture expansion, and mining lead to the loss of natural habitats for many species, reducing biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Global warming and climate change affect weather patterns, sea levels, and habitats, posing a significant threat to species unable to adapt quickly.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources can degrade natural habitats and poison wildlife.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, logging, and harvesting at rates faster than species can replenish leads to a drastic decline in certain populations.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species introduced to new environments can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystems.
- Overpopulation: Human population growth increases consumption and land use pressure, exacerbating other threats to biodiversity.
Addressing these threats requires coordinated global and local efforts, including conservation, sustainable practices, and policies that protect natural habitats and species. By mitigating these threats, we can help preserve the rich biodiversity of our planet for future generations.
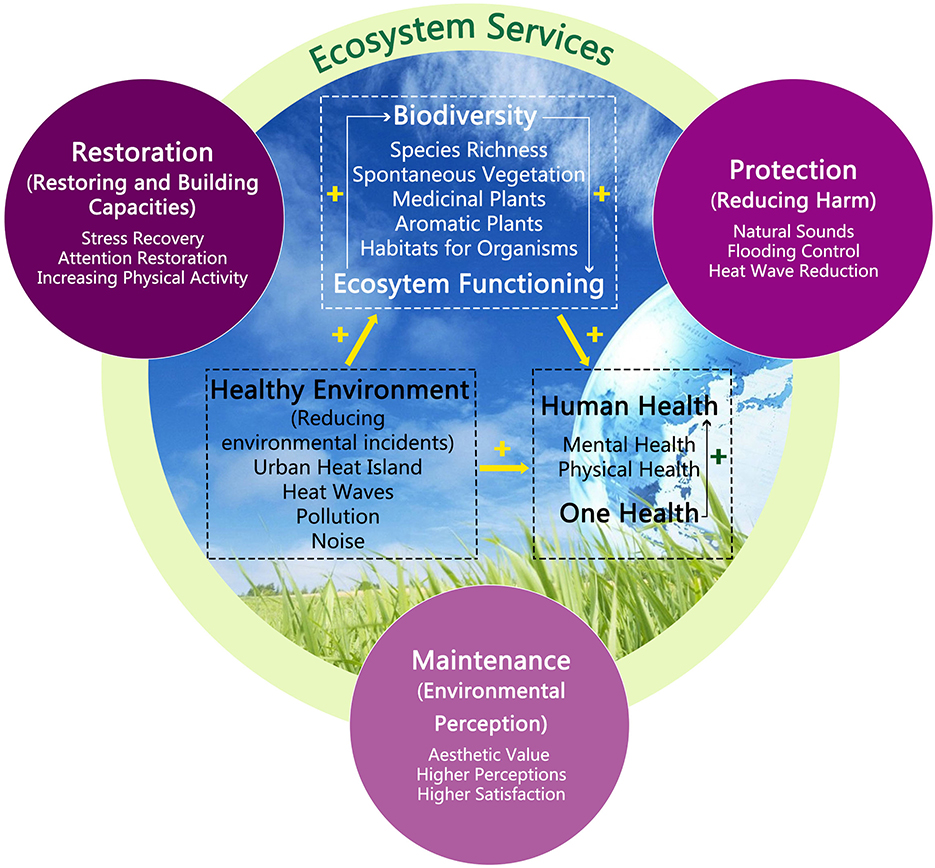
Benefits of Biodiversity to Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity underpins the health of our planet and has a direct impact on the services ecosystems provide. These services are essential for human survival and well-being. The following points highlight the key benefits of biodiversity to ecosystem services:
- Regulation of Climate: Forests and marine ecosystems play a crucial role in regulating the Earth"s climate by sequestering carbon dioxide, thus mitigating climate change.
- Pollination Services: Biodiversity includes a variety of pollinators that are essential for the reproduction of many plants, including crops vital for food security.
- Water Purification: Wetlands, forests, and other ecosystems filter pollutants and sediment from water, improving its quality for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
- Disease Regulation: Healthy ecosystems can help control diseases by regulating populations of organisms that carry disease to humans and other species.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse ecosystems contribute to the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients, enhancing soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
- Recreational and Cultural Benefits: Biodiversity supports activities such as ecotourism, hiking, and birdwatching, which have cultural, educational, and recreational value.
These ecosystem services underscore the intrinsic link between biodiversity and human well-being. Protecting biodiversity is not only a matter of conserving nature but also safeguarding the ecosystem services that sustain human societies and economies.
Role of Invasive Species in Biodiversity
Invasive species play a significant and often detrimental role in biodiversity, impacting ecosystems worldwide. While native to one region, these species become invasive when introduced to new environments, where they can outcompete, displace, or eradicate native species. The following points elucidate the role of invasive species in biodiversity:
- Competition: Invasive species often have competitive advantages over native species, such as rapid reproduction or growth, leading to the displacement of native species.
- Predation: Some invasive species prey on native species that have not evolved defenses against these new predators, leading to declines or extinctions of native populations.
- Disease Transmission: Invasive species can introduce diseases to which native species have no immunity, causing widespread illness or death among native populations.
- Ecosystem Alteration: Certain invasive species can dramatically alter ecosystem functions, such as water flow or fire regimes, making environments less hospitable for native species.
- Hybridization: Invasive species can breed with native species, leading to hybrid species that may lack the survival traits of either parent species, diluting genetic diversity.
Managing and controlling invasive species is crucial for protecting biodiversity. Strategies include prevention, early detection, eradication, and public education. By understanding the significant impact of invasive species, we can take steps to preserve the balance and health of ecosystems around the world.
Impact of Human Activities on Biodiversity
Human activities have a profound impact on biodiversity, influencing ecosystem health and species survival worldwide. The complex interplay between human development and biodiversity conservation presents significant challenges and opportunities for sustainable management. Here"s how human actions affect biodiversity:
- Land Use Change: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation alter habitats, reducing the space and resources available for wildlife, leading to biodiversity loss.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial processes, agriculture, and waste disposal introduce harmful substances into ecosystems, affecting both plant and animal life.
- Climate Change: The burning of fossil fuels and deforestation contribute to climate change, altering habitats and threatening species adapted to specific climate conditions.
- Overexploitation: Hunting, fishing, and harvesting at unsustainable rates deplete populations faster than they can recover, leading to a decrease in species diversity.
- Introduction of Invasive Species: Transporting species across natural barriers, intentionally or accidentally, can lead to the establishment of invasive species that threaten native biodiversity.
Addressing the impact of human activities on biodiversity requires coordinated global efforts, including conservation, sustainable practices, and policies aimed at reducing harmful impacts while promoting biodiversity-friendly development. By understanding and mitigating these impacts, we can work towards a more sustainable coexistence with the natural world.

Conservation Strategies for Enhancing Biodiversity
Effective conservation strategies are essential to enhance biodiversity and ensure the resilience and sustainability of ecosystems. These strategies aim to protect species, preserve habitats, and maintain ecological processes. Below are key approaches to biodiversity conservation:
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to conserve critical habitats and species.
- Restoration Projects: Rehabilitating degraded ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and coral reefs to restore their ecological functionality and biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policy: Implementing laws and policies that protect endangered species and habitats, regulate hunting and fishing, and control pollution and land use.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts through education, sustainable livelihood initiatives, and participatory management of natural resources.
- Conservation Corridors: Creating corridors to connect fragmented habitats, allowing for wildlife movement and genetic exchange between populations.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices that conserve biodiversity while meeting human needs.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change impacts to protect biodiversity.
By integrating these strategies, we can work towards a future where biodiversity thrives, supporting ecosystems and human societies alike. Conservation requires a collective effort from governments, organizations, communities, and individuals to ensure the preservation of our planet"s invaluable biodiversity.
Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystems
Importance: Discover the significance of this topic and why it holds such value in our lives. Watch this video to gain a deeper understanding of its importance and uncover how it can positively impact your journey.
Understanding Biodiversity
Understanding: Dive into the depths of this subject and develop a comprehensive understanding through this enlightening video. Uncover key insights and broaden your knowledge to grasp the intricate aspects of this captivating topic.
Global and Local Biodiversity Initiatives
Efforts to conserve biodiversity are being implemented at both global and local levels, aiming to protect ecosystems, species, and genetic diversity. These initiatives play a crucial role in combating biodiversity loss and fostering sustainable development. Here are some of the key initiatives:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): A global agreement adopted by 196 countries, focusing on the conservation of biodiversity, the sustainable use of its components, and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources.
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Provides comprehensive information on the global conservation status of animal, fungi, and plant species, guiding conservation actions and policies.
- United Nations Decade on Biodiversity: Aims to promote the implementation of a strategic plan for biodiversity and its overall vision of living in harmony with nature by 2050.
- National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs): Developed by countries as part of their commitment to the CBD, these plans outline strategies and actions for conserving biodiversity at the national level.
- Local Conservation Efforts: Community-based conservation projects, habitat restoration, and local wildlife protection initiatives that involve indigenous peoples and local communities in biodiversity conservation.
- Corporate Biodiversity Initiatives: Efforts by businesses to integrate biodiversity conservation into their operations through sustainable practices, biodiversity offsets, and green infrastructure development.
These initiatives highlight the collaborative efforts required to preserve biodiversity. By supporting global strategies and participating in local conservation actions, we can contribute to the sustainability of our planet"s ecosystems.
Case Studies: Successful Biodiversity Conservation Efforts
Across the globe, numerous conservation efforts have successfully protected and restored biodiversity in various ecosystems. These case studies illustrate the positive impact of concerted conservation actions. Here are some notable examples:
- The Restoration of the American Bison: Once on the brink of extinction, conservation programs have successfully increased bison populations in North America through protected areas and sustainable management practices.
- Reforestation in Costa Rica: Costa Rica has reversed its deforestation rates through national forestry incentives, protected areas expansion, and eco-tourism, significantly increasing forest cover and biodiversity.
- Marine Protected Areas in the Coral Triangle: The establishment of marine protected areas in the Coral Triangle has helped preserve one of the most diverse marine habitats, safeguarding numerous species of fish, corals, and marine mammals.
- Community-led Conservation in Kenya: The Northern Rangelands Trust in Kenya demonstrates how community-led conservation efforts can protect wildlife, restore habitats, and improve local livelihoods through eco-tourism and sustainable resource management.
- Protection of the Iberian Lynx in Spain: Conservation actions, including habitat restoration, rabbit population management (the lynx"s main prey), and breeding programs, have helped recover the Iberian lynx population from the edge of extinction.
These case studies showcase the effectiveness of various conservation strategies, from legal protection and habitat restoration to community engagement and species recovery programs. They highlight the potential for positive change when efforts are targeted towards preserving and enhancing biodiversity.
The Future of Biodiversity in Changing Climates
The impact of climate change on biodiversity is a pressing concern, with shifting climates posing significant challenges to ecosystems worldwide. The future of biodiversity in these changing conditions depends on our actions today. Here’s a look into what the future may hold and the steps being taken to mitigate risks:
- Adaptation Strategies: Ecosystems and species will need to adapt to changing temperatures, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. Conservation efforts are focusing on enhancing the resilience of ecosystems to support this adaptation.
- Migration Corridors: Creating and maintaining migration corridors can facilitate species movement to more suitable habitats, a critical adaptation mechanism for many species facing climate change.
- Genetic Diversity Conservation: Preserving the genetic diversity within species is crucial for their ability to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Mitigating climate change itself by reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential to limit the extent of climate impacts on biodiversity.
- International Cooperation: Climate change and biodiversity loss are global issues that require coordinated international efforts to address through agreements like the Paris Agreement and the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The future of biodiversity in changing climates is uncertain, but with concerted global action to combat climate change and protect natural habitats, there is hope for preserving the planet"s biological diversity. Innovative conservation strategies and policies can help safeguard ecosystems and species, ensuring a rich and vibrant natural world for future generations.

READ MORE:
How Individuals Can Contribute to Biodiversity Conservation
Every individual has the power to make a difference in conserving biodiversity. From simple daily actions to more significant commitments, there are many ways people can help protect the planet"s biological diversity. Here are some practical steps individuals can take:
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donating to or volunteering with organizations dedicated to protecting wildlife and habitats can make a big impact.
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Reducing waste, recycling, using eco-friendly products, and conserving water and energy contribute to lessening the pressure on natural resources.
- Plant Native Species: Growing native plants in your garden supports local wildlife, including pollinators like bees and butterflies.
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Minimizing consumption and properly recycling can significantly reduce your ecological footprint.
- Stay Informed and Educate Others: Learning about local and global biodiversity issues and raising awareness within your community can inspire others to take action.
- Participate in Citizen Science Projects: Joining biodiversity monitoring programs can provide valuable data to help scientists understand and protect ecosystems.
- Advocate for Conservation Policies: Supporting policies that protect natural habitats and wildlife helps ensure the preservation of biodiversity at the governmental level.
Individual actions, when multiplied by millions, can lead to significant positive impacts on biodiversity conservation. By making conscious choices to protect the environment, we can all contribute to the health and sustainability of our planet.
Embracing the richness of biodiversity in our ecosystems is essential for a sustainable future. By understanding its importance, addressing threats, and implementing conservation strategies, we can all contribute to a vibrant, resilient planet for generations to come.