Topic diversity of ecosystems: Discover the incredible diversity of ecosystems, where the intricate web of life showcases our planet"s unique habitats and the importance of preserving them for future generations.
Table of Content
- What is the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning?
- Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
- Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
- The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
- Importance of Ecosystem Diversity for Environmental Stability
- Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
- YOUTUBE: Tropical Rainforest Diversity | California Academy of Sciences
- Conservation Strategies for Protecting Ecosystem Diversity
- The Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Diversity
- Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
- The Future of Ecosystem Diversity: Predictions and Trends
What is the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning?
The relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning is a topic of research and study within the field of ecology. It explores how the diversity of species within an ecosystem affects the overall functioning and health of that ecosystem. There are several key points to consider when discussing this relationship:
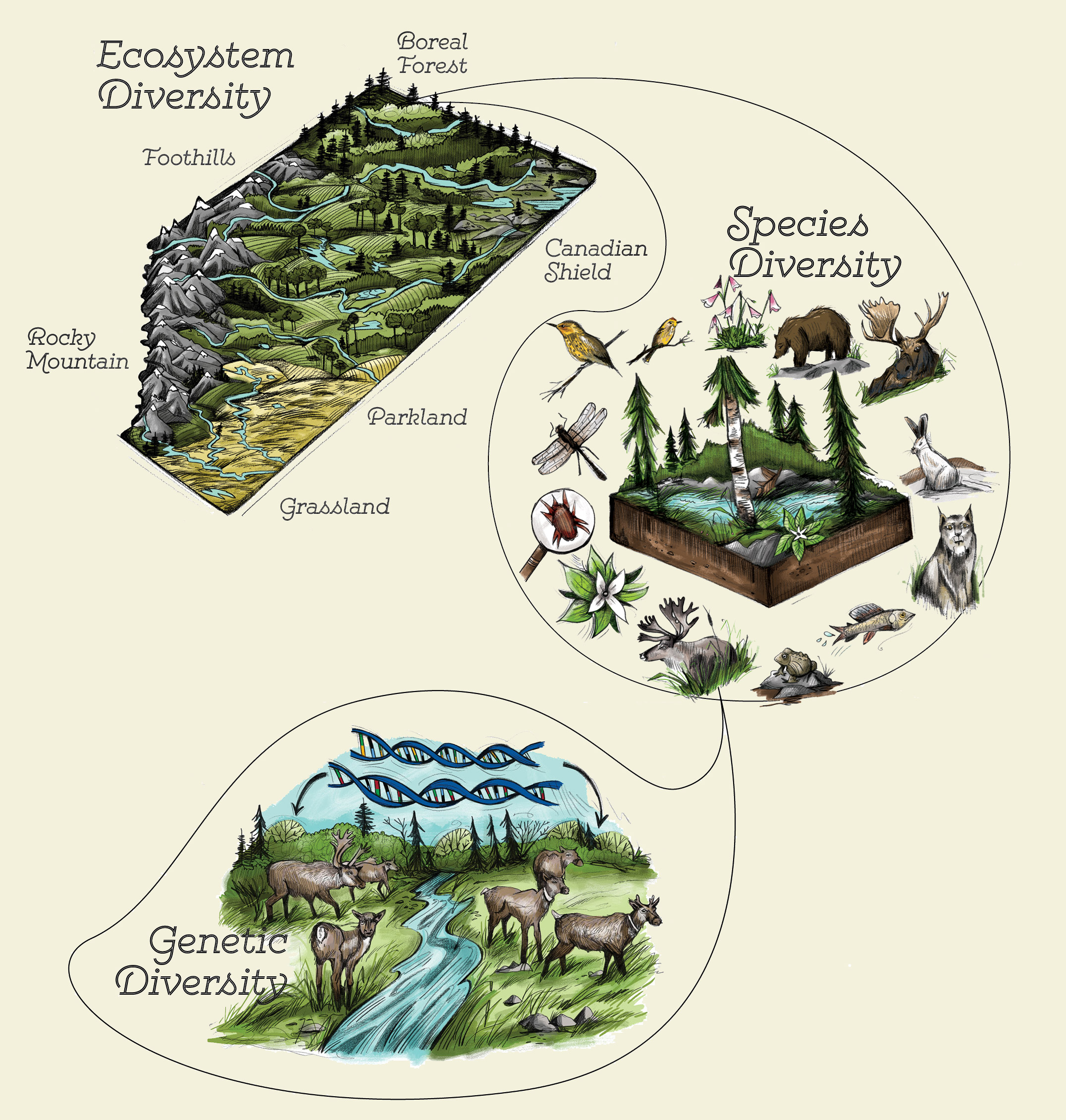
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species and genetic diversity within a particular ecosystem. It includes everything from plants and animals to microorganisms.
Ecosystem functioning refers to the processes and interactions that occur within an ecosystem, such as nutrient cycling, energy flow, and the maintenance of ecological balance.
Research has shown that there is a positive relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. In other words, higher levels of biodiversity tend to lead to more efficient and resilient ecosystem processes and functions.
Species within an ecosystem often have specific roles or functions, known as ecological niches, which contribute to the overall functioning of the ecosystem. As the number and diversity of species increase, there are more unique niches filled, leading to a greater range of functions being performed.
Increased biodiversity can enhance ecosystem resilience and stability. A diverse ecosystem is better able to withstand disturbances, such as natural disasters or human-induced changes, as different species may respond differently to these disturbances.
Functional redundancy is another important concept in the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. It refers to the idea that multiple species within an ecosystem may perform similar functions, providing a backup system in case one species is lost.
In conclusion, a higher level of biodiversity is generally associated with more efficient and resilient ecosystem functioning. Understanding and preserving biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the health and stability of ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Diversity
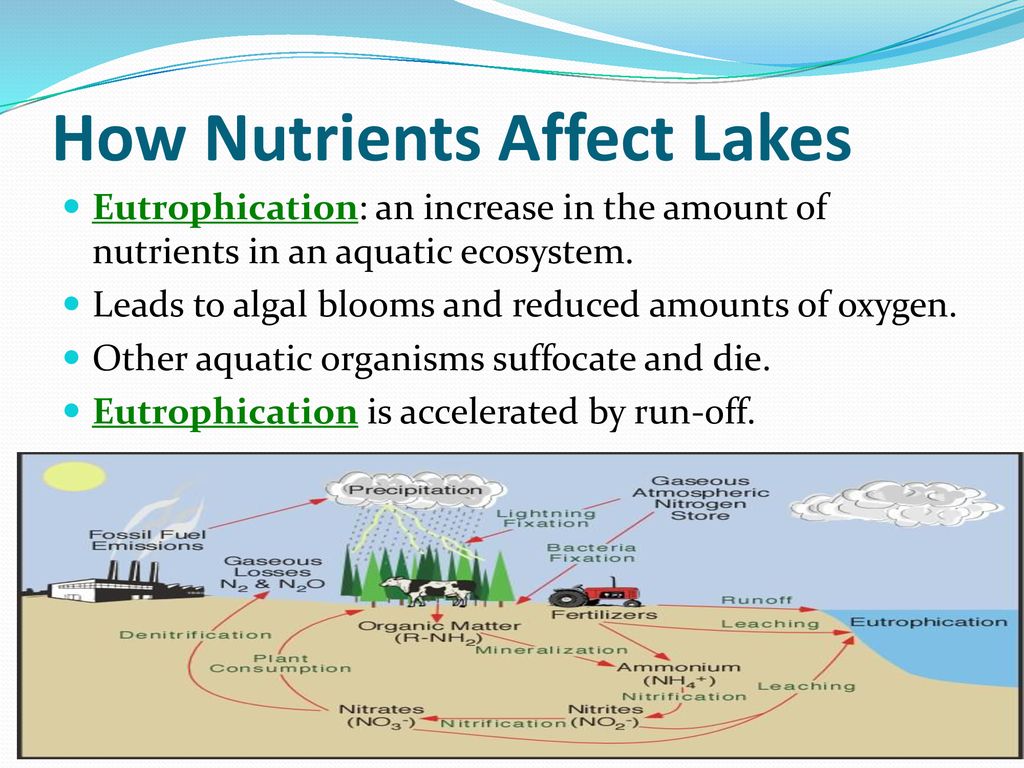
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats, natural communities, and ecological processes in the natural environment. It includes the diversity of species and the complex interactions among them, which form different ecosystems such as forests, deserts, coral reefs, and wetlands.
- Types of Ecosystems: From aquatic to terrestrial, ecosystems vary widely in their characteristics, species composition, and functions.
- Ecological Processes: These processes, including energy flow and nutrient cycling, are crucial for the sustainability of ecosystems.
- Importance for Biodiversity: Ecosystem diversity is a key component of biodiversity, providing essential services like clean air and water, pollination of plants, and climate regulation.
- Human Impact: Human activities have a significant impact on ecosystems, affecting their diversity and functionality.
Understanding the diversity of ecosystems is essential for conservation efforts, enabling us to protect and preserve the natural world for future generations.

Types of Ecosystems and Their Characteristics
Ecosystems are diverse and can be classified into two main categories: terrestrial and aquatic. Each type hosts unique habitats and species, contributing to the planet"s biodiversity.
- Forest Ecosystems: Characterized by dense tree cover, they are crucial for carbon storage, climate regulation, and providing habitat for a vast array of species.
- Desert Ecosystems: Defined by low precipitation, deserts are home to specially adapted plants and animals thriving in harsh conditions.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Split into freshwater (lakes, rivers, wetlands) and marine (oceans, coral reefs) systems, supporting diverse life forms adapted to water environments.
- Grassland Ecosystems: Dominated by grasses, these areas support a variety of fauna, including many herbivores, and are important for agriculture and grazing.
- Tundra Ecosystems: Characterized by cold temperatures and short growing seasons, tundras host a limited range of plants and animals adapted to extreme conditions.
Each ecosystem type plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance and supports a unique set of organisms adapted to its specific environment.
The Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity, the variety of life in all its forms and interactions, is a critical component that underpins the functioning of ecosystems. It ensures the resilience and stability of ecosystems, enabling them to provide essential services.
- Supports Ecosystem Services: Biodiversity contributes to the provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural services that ecosystems provide, such as clean water, pollination, and climate regulation.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to disturbances like climate change and natural disasters, as they can adapt and recover more quickly.
- Promotes Productivity: High biodiversity levels lead to increased productivity in ecosystems, as a wider range of species can utilize resources more efficiently.
- Nutrient Cycling: The interaction between various organisms facilitates nutrient cycling, which is essential for ecosystem health.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiverse ecosystems can better regulate diseases, reducing the spread of pathogens among species.
Understanding the role of biodiversity in ecosystem functioning is crucial for conservation efforts, as it highlights the need to protect diverse habitats and species for the overall health of the planet.
Factors Influencing Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity is influenced by a variety of natural and anthropogenic factors that determine the distribution, structure, and function of ecosystems across the globe.
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight directly affect the types of ecosystems that can thrive in a particular area.
- Geography: The geographical location and features (mountains, rivers, islands) influence the isolation and development of unique ecosystems.
- Soil Types: Soil composition and quality can determine the variety of plant species that can grow, influencing the overall biodiversity of an area.
- Human Activities: Urbanization, agriculture, deforestation, and pollution significantly alter and often reduce ecosystem diversity.
- Evolutionary History: The evolutionary past of an area, including speciation and extinction events, shapes its current ecosystem diversity.
- Ecological Interactions: Predator-prey relationships, competition, and symbiosis among species affect ecosystem structure and complexity.
Understanding these factors is essential for effective conservation strategies that aim to protect and enhance ecosystem diversity.
Importance of Ecosystem Diversity for Environmental Stability
Ecosystem diversity plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and resilience of the environment, ensuring the sustainability of resources for all life forms.
- Enhances Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are better equipped to withstand and recover from environmental stresses and disturbances, such as natural disasters and climate change.
- Supports Species Diversity: Varied habitats support a wide range of species, promoting genetic diversity and reducing the risk of extinction.
- Regulates Climate: Ecosystems like forests and oceans act as carbon sinks, playing a key role in climate regulation and mitigating global warming.
- Improves Soil Health: Different ecosystems contribute to soil formation and fertility, affecting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Water Regulation: Ecosystems regulate the water cycle, ensuring clean water supply and reducing the risk of floods and droughts.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Biodiverse ecosystems support the processes necessary for plant reproduction, which is vital for food security and biodiversity.
The conservation of ecosystem diversity is thus essential for environmental stability, human well-being, and the planet"s future.

Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Diversity
The diversity of ecosystems faces numerous challenges and threats, many of which are exacerbated by human activities and global environmental changes.
- Habitat Destruction: Urban expansion, deforestation, and agricultural development lead to the fragmentation and loss of habitats, critically endangering ecosystem diversity.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt the balance of ecosystems, affecting their ability to support diverse life forms.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal harm ecosystems and reduce biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, displace, or predate native species, significantly altering ecosystem dynamics.
- Overexploitation: The unsustainable extraction of natural resources, including overfishing and logging, depletes ecosystems and leads to biodiversity loss.
- Policy and Enforcement Gaps: Insufficient environmental protection policies and the lack of effective enforcement mechanisms hinder the conservation of ecosystem diversity.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable practices, and strong conservation policies to ensure the preservation of ecosystem diversity for future generations.
Tropical Rainforest Diversity | California Academy of Sciences
Step into the mesmerizing world of tropical rainforest diversity and uncover the breathtaking beauty hidden within the dense foliage. Immerse yourself in vibrant colors, captivating sounds, and a wide array of unique species that call this lush ecosystem their home. Prepare to embark on an unforgettable journey through the rainforest, where every corner holds a remarkable surprise waiting to be discovered. Don\'t miss the chance to witness nature\'s intricate masterpiece unfold before your very eyes in this enchanting video.
Diversity of Ecosystems: A Geographic Perspective
Experience the awe-inspiring diversity of ecosystems through a captivating geographic perspective. Journey across the globe as we delve into the intricate web of interconnected habitats, witnessing how different landscapes shape life on Earth. Get ready to explore stunning landscapes, from remote deserts to lush rainforests, and discover the astonishing variety of plants, animals, and climates that make our planet so unique. Gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that exists within each ecosystem and marvel at the wonders that Mother Nature has to offer in this illuminating video.
Conservation Strategies for Protecting Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity encompasses the variety of habitats, natural communities, and ecological processes in the natural world, as well as the incredible variety of species that inhabit them. Protecting this diversity is crucial for maintaining environmental stability, supporting life, and ensuring the well-being of the planet. The following conservation strategies are vital in safeguarding ecosystem diversity:
- Establishment of Protected Areas: Designating specific areas as protected parks, reserves, or wildlife sanctuaries helps to preserve critical habitats, protect endangered species, and maintain natural ecological processes.
- Restoration of Degraded Ecosystems: Activities such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and rehabilitation of degraded lands help to restore ecosystem health and functionality, enhancing biodiversity and resilience.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing sustainable practices in forestry, agriculture, and fishing ensures that natural resources are used in a way that preserves ecosystem balance and biodiversity.
- Combating Invasive Species: Managing or eradicating invasive species that threaten native biodiversity helps to maintain ecosystem integrity and protect native flora and fauna.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and strategies to adapt to climate change impacts are essential to protect ecosystems from the adverse effects of climate change.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem diversity can foster a culture of conservation and encourage sustainable practices.
- Legislation and Policy Development: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that protect endangered species, prohibit habitat destruction, and regulate land use helps to safeguard ecosystems against anthropogenic threats.
- International Cooperation: Biodiversity conservation is a global issue that requires cross-border collaboration through international agreements and partnerships to address challenges such as wildlife trafficking, habitat loss, and climate change.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research and monitoring ecosystems helps to understand ecological processes, assess the status of biodiversity, and inform conservation decisions.
- Financial Mechanisms: Funding conservation projects through environmental taxes, green bonds, and conservation financing initiatives supports the implementation of effective conservation strategies.
Implementing these strategies requires a coordinated effort among governments, non-governmental organizations, the private sector, and individuals. By working together, we can protect the rich diversity of ecosystems that sustain life on Earth.

The Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Diversity
Climate change is having profound impacts on ecosystem diversity across the globe, altering habitats, species distributions, and ecological processes. The consequences of these changes not only affect biodiversity but also the services ecosystems provide, which are vital for human survival and well-being. Understanding the impacts of climate change on ecosystem diversity is crucial for developing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. Here are some of the key ways in which climate change affects ecosystem diversity:
- Shifts in Species Distribution: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are causing many species to move to cooler or more suitable habitats, altering community compositions and potentially leading to the loss of species in some areas while introducing species to others.
- Alteration of Habitat: Climate change is leading to the degradation, fragmentation, and loss of habitats through phenomena such as melting ice caps, rising sea levels, increased desertification, and more frequent and severe wildfires, which in turn threaten the diversity of species that rely on these habitats.
- Changes in Phenology: The timing of biological events, such as flowering, breeding, and migration, is shifting in response to climate change. These changes can disrupt ecological interactions, such as pollination and food web dynamics, potentially destabilizing ecosystems.
- Increased Extinction Risk: Climate change, along with habitat loss and fragmentation, invasive species, and pollution, increases the risk of extinction for many vulnerable and endangered species, leading to a reduction in biodiversity.
- Changes in Ecosystem Services: The impacts of climate change on ecosystem diversity can affect the provision of vital ecosystem services, including water purification, pollination of crops, carbon sequestration, and protection from natural disasters, with significant implications for human societies.
- Altered Ecological Processes: Climate change affects key ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, soil formation, and water cycling, which can further impact ecosystem health and biodiversity.
- Increased Pressure on Marine Ecosystems: Ocean acidification, warming waters, and changing ocean currents are affecting marine biodiversity, coral reefs, fish stocks, and the livelihoods of people who depend on marine ecosystems.
Addressing the impact of climate change on ecosystem diversity requires urgent global action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect and restore habitats, and develop adaptive management strategies that can help ecosystems and species cope with changing conditions. By doing so, we can safeguard the planet"s biodiversity for future generations.
Case Studies: Successful Ecosystem Restoration Projects
Ecosystem restoration projects play a crucial role in enhancing biodiversity, recovering endangered species, and improving ecological services. These projects often involve the rehabilitation of natural habitats, reforestation, wetlands restoration, and the reintroduction of native species. Below are examples of successful ecosystem restoration projects from around the world, demonstrating the positive impact of concerted conservation efforts.
- The Loess Plateau in China: Once one of the most eroded regions in the world, the Loess Plateau underwent an extensive restoration project that transformed it into fertile land. By implementing sustainable agricultural practices, terracing slopes, and planting vegetation, the project significantly improved soil quality, increased biodiversity, and enhanced local livelihoods.
- The Everglades in the United States: Recognized as one of the most significant wetland restoration efforts globally, the Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan aims to restore the natural flow of water, recover habitats, and preserve the region"s biodiversity. Efforts include removing invasive species, replanting native vegetation, and constructing water management structures.
- Kissama National Park in Angola: After decades of civil war, the Kissama Foundation initiated a project to repopulate the park with wildlife. Known as "Operation Noah"s Ark," the project successfully reintroduced various species, such as elephants, giraffes, and zebras, revitalizing the park"s biodiversity and attracting ecotourism.
- The Great Green Wall in Africa: An ambitious initiative to combat desertification across the Sahel region, the Great Green Wall aims to plant a belt of trees across Africa. This project not only helps in restoring degraded land but also in enhancing food security, creating jobs, and contributing to climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon dioxide.
- Project Tiger in India: Launched in 1973 to protect the endangered Bengal tiger, Project Tiger has led to the establishment of over 50 tiger reserves throughout India. Through habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, and community engagement, the project has played a significant role in increasing the tiger population and preserving biodiverse forests.
These case studies exemplify the positive outcomes that can be achieved through dedicated ecosystem restoration efforts. By prioritizing ecological health and biodiversity, these projects have not only conserved natural landscapes but also provided substantial benefits to human communities, showcasing a harmonious balance between conservation and sustainable development.
READ MORE:
The Future of Ecosystem Diversity: Predictions and Trends
The future of ecosystem diversity is a subject of immense importance, shaped by both natural processes and human activities. With the ongoing challenges of climate change, habitat loss, and biodiversity decline, understanding the potential directions in which our ecosystems may evolve is crucial for developing strategies to protect and sustain them. Here are some predictions and trends that could define the future of ecosystem diversity:
- Increased Conservation Efforts: Recognizing the critical role of biodiversity in sustaining life, it is expected that global and local conservation efforts will intensify. This includes expanding protected areas, enhancing habitat connectivity, and implementing more effective wildlife conservation strategies.
- Restoration of Degraded Ecosystems: Ecosystem restoration will become a more prominent trend, with large-scale projects aiming to rehabilitate lands affected by deforestation, pollution, and desertification. Success stories will inspire further restoration initiatives worldwide.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Ecosystem management strategies will increasingly incorporate climate adaptation measures, focusing on increasing the resilience of ecosystems to climate impacts. This includes supporting species migration, conserving genetic diversity, and safeguarding keystone species.
- Integration of Technology in Conservation: Technological advancements, such as remote sensing, AI, and genomics, will play a pivotal role in monitoring biodiversity, predicting ecosystem changes, and identifying conservation priorities more effectively.
- Greater Community Involvement: The involvement of local communities in conservation and restoration efforts will grow, recognizing their knowledge and the importance of sustainable livelihoods in biodiversity conservation. This includes participatory conservation projects and eco-tourism initiatives.
- Policy and Legislation Advances: It is anticipated that there will be stronger policy frameworks and legislation to protect ecosystems, driven by a better understanding of the economic, social, and environmental value of biodiversity.
- Global Collaboration for Biodiversity: International collaboration and agreements will be crucial in addressing transboundary conservation challenges, combating illegal wildlife trade, and coordinating responses to climate change.
The future of ecosystem diversity hinges on our actions today. By embracing sustainable development, investing in conservation, and fostering global cooperation, we can ensure that ecosystems continue to thrive, providing essential services and supporting biodiversity for generations to come.
Embracing the diversity of ecosystems is key to our planet"s health and prosperity. By understanding, conserving, and restoring these vital systems, we can secure a sustainable future for all forms of life on Earth.