Topic lizards in the sahara desert: Embark on a captivating journey to explore the resilient and diverse lizards thriving in the Sahara Desert, a realm of mystery and natural wonder.
Table of Content
- What types of lizards can be found in the Sahara Desert?
- Adaptations of Sahara Desert Lizards
- Diversity of Lizard Species in the Sahara
- Historical Presence of Dinosaurs in the Sahara
- Impact of Climate on Lizard Habitats
- Geographical Features of the Sahara Affecting Lizard Populations
- Conservation Efforts for Lizards in the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Lizard Escapes Heat in Unusual Way
- Human Interaction and Its Effects on Lizards
- Lizards in Sahara Folklore and Culture
- Future of Lizards in the Sahara Amidst Climate Change
- Comparative Analysis of Sahara Lizards with Other Deserts
What types of lizards can be found in the Sahara Desert?
Several types of lizards can be found in the Sahara Desert, including:
- Monitor Lizards - These intelligent lizards are somewhat venomous and primarily feed on rodents, birds, or other small mammals.
- Acanthodactylus fringe-toed lizards - These lizards exhibit high diversity in the Sahara Desert and are similar to Podarcis spp. They hold potential for eco-evolutionary studies.
- Uma (fringe-toad) lizards - These lizards belong to the genus Uma in the family Phrynosomatidae. They have a brown and tan coloration, which helps them blend into their desert environment.
These are just a few examples of the lizards that inhabit the Sahara Desert. The desert ecosystem supports a variety of reptile species adapted to the arid conditions.
READ MORE:
Adaptations of Sahara Desert Lizards
Lizards in the Sahara Desert exhibit remarkable adaptations to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. These adaptations are key to their survival in extreme conditions of heat and aridity.
- Temperature Regulation: Being ectothermic, these lizards regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun for warmth and seeking shade or burrows to cool down.
- Water Conservation: Sahara lizards minimize water loss through efficient excretion methods and obtaining moisture from their food.
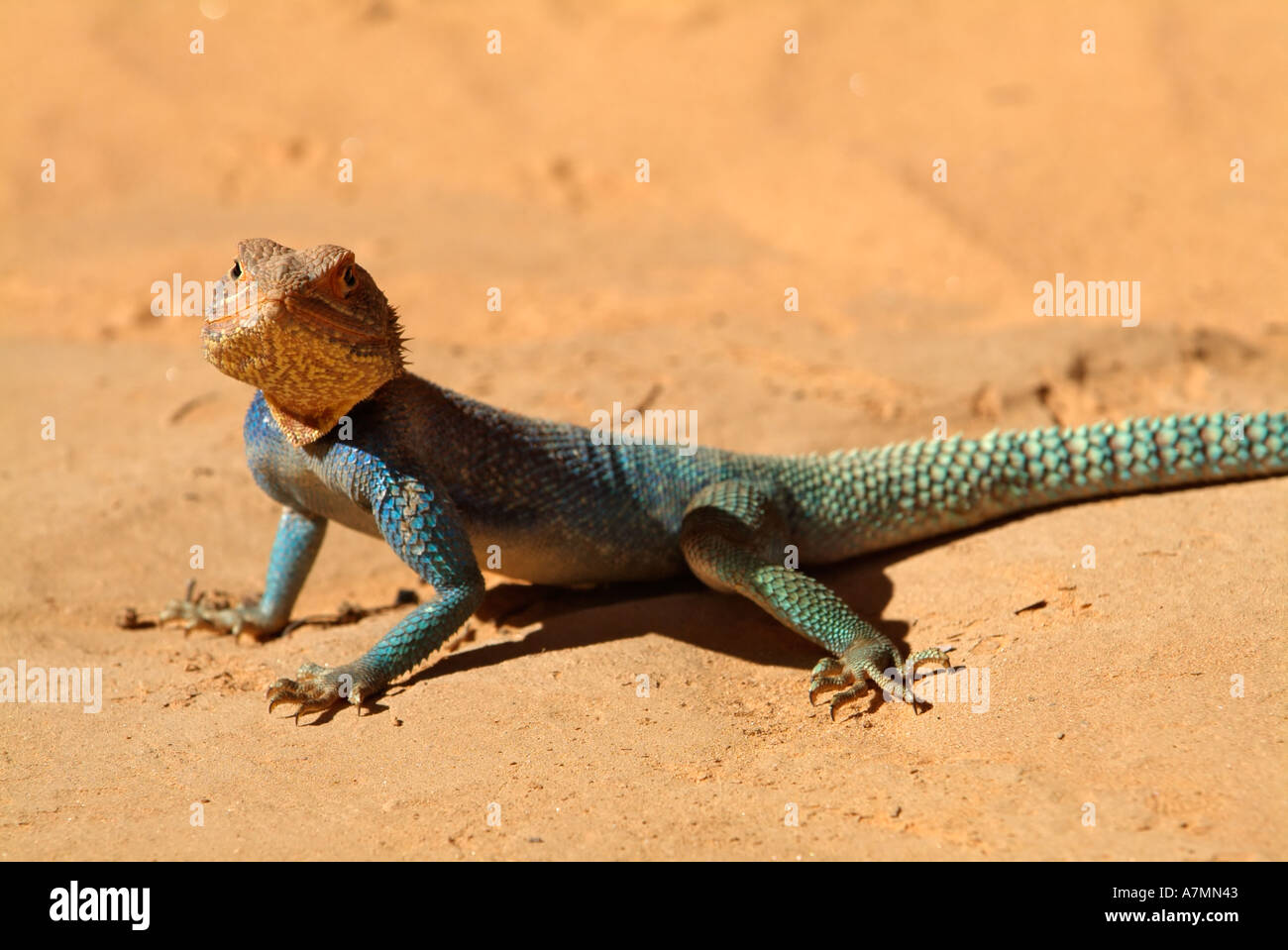
- Camouflage: Many lizards have skin colors that blend with the desert sands, providing camouflage against predators.
- Burrowing: Some species create or use existing burrows to escape the extreme desert heat and to maintain body temperature.
- Sand-Swimming: Certain species like the sandfish skink exhibit sand-swimming behavior, allowing them to navigate and escape predators quickly.
- Long Limbs and Padded Feet: These features aid in efficient movement across hot sand and rocky terrains.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Desert lizards often exhibit behaviors like limiting activity during peak heat and being more active during cooler parts of the day.
- Efficient Predation and Diet: They have adapted to be efficient predators or foragers, making the most of the scarce resources available.
These adaptations are not only crucial for their survival but also make them an integral part of the Sahara"s ecosystem, contributing to its unique biodiversity.

Diversity of Lizard Species in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, known for its harsh and arid conditions, is home to a surprisingly diverse range of lizard species. These lizards have adapted over time to thrive in the desert"s extreme environment.
- Spiny-footed Lizards (Acanthodactylus scutellatus complex): These are prominent inhabitants of the Sahara"s sandy fields, known for their ability to endure extreme dryness. Research indicates that these lizards have thrived for millions of years in the Sahara, showing remarkable resilience and adaptability to arid conditions.
- Desert Monitor (Varanus griseus): This carnivorous lizard, growing up to 1-2 meters in length, is a prominent species in the Sahara. It hibernates from September to April and feeds on a variety of prey including rodents, fish, and eggs.
- Long Fringe-fingered Lizard (Acanthodactylus longipes): Known for its conspicuous presence in the Saharan ergs, this species is another example of the desert"s rich lizard biodiversity.
These lizards are not only significant for their ecological roles but also for their contribution to the Sahara"s unique biodiversity. The Sahara"s lizard species, particularly the spiny-footed lizards, have shown a wide range of intraspecific divergence, indicating a complex and rich evolutionary history in the region. Despite the extreme conditions, the Sahara Desert supports a variety of species, each with its unique adaptations and ecological niches.
Historical Presence of Dinosaurs in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, now a vast expanse of arid sand dunes, was once a thriving habitat for an array of dinosaurs millions of years ago. This ancient ecosystem was home to a diverse group of dinosaurs, each uniquely adapted to the prehistoric environment.
- Ferocious Carnivores: The Sahara hosted a range of fearsome carnivorous dinosaurs, including large predators that dominated the food chain in this lush green landscape.
- Flying Reptiles: Pterosaurs, the flying reptiles of the dinosaur era, were also part of this diverse ecosystem, soaring above the prehistoric Sahara.
- Marine Dinosaurs: Evidence suggests the presence of aquatic dinosaurs in the Sahara, indicating that parts of this region were underwater or had significant water bodies.
- Remarkable Discoveries: Paleontologists have unearthed fossils in various parts of the Sahara, shedding light on the region"s rich prehistoric life.
- Significant Species: Among the discoveries are fossils of the Spinosaurus with a unique fin-like tail, suggesting its swimming capabilities, and remains of sauropod dinosaurs, known for their massive size.
These discoveries highlight the Sahara"s dynamic geological past and provide insights into the diverse and complex ecosystem that existed long before it became the desert we know today.

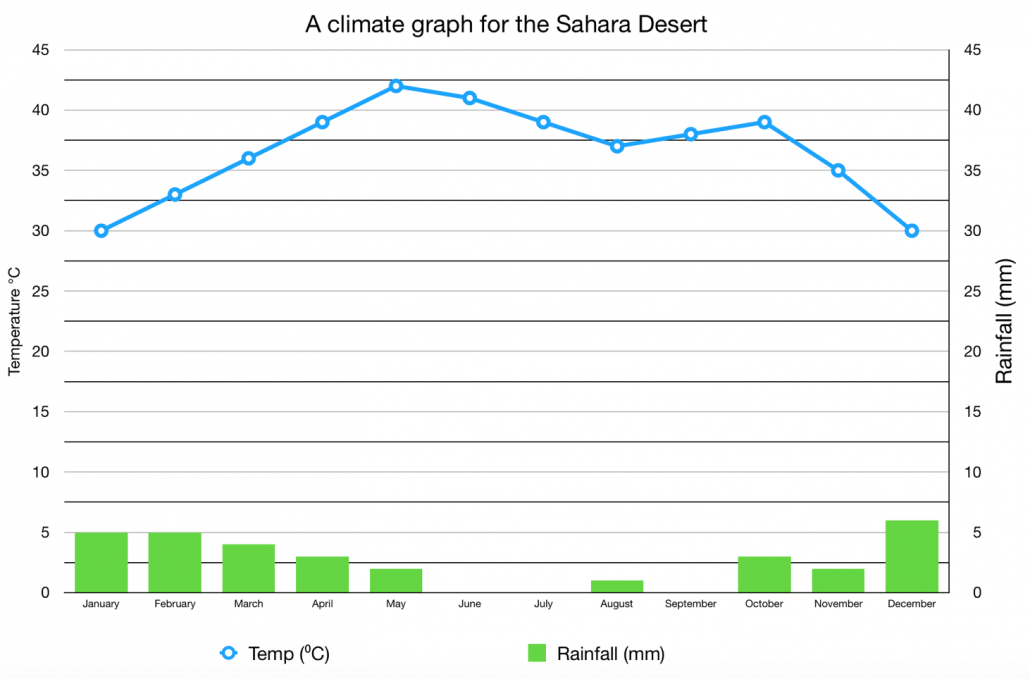
Impact of Climate on Lizard Habitats
The Sahara Desert"s lizard habitats are significantly influenced by the region"s climate, which shapes their existence and survival strategies.
- Temperature Extremes: Lizards in the Sahara experience extreme temperatures, which they must navigate through various behavioral and physiological adaptations.
- Shifting Sand Dunes: The movement and formation of sand dunes, driven by climate and wind patterns, constantly reshape the habitat, affecting lizard populations and their hunting grounds.
- Water Scarcity: The arid climate results in scarce water resources, making lizards rely heavily on moisture obtained from their prey and dew.
- Vegetation Changes: Climate variations affect the availability and type of vegetation, which in turn impacts the food chain and the habitat of insectivorous and herbivorous lizards.
- Climate Change Impact: Global warming and climate change are altering the Sahara"s ecosystem, potentially leading to habitat loss and challenging the survival of various lizard species.
The resilience of Sahara"s lizards is constantly tested by the dynamic and often harsh climate of the desert, necessitating ongoing adaptation and evolution.
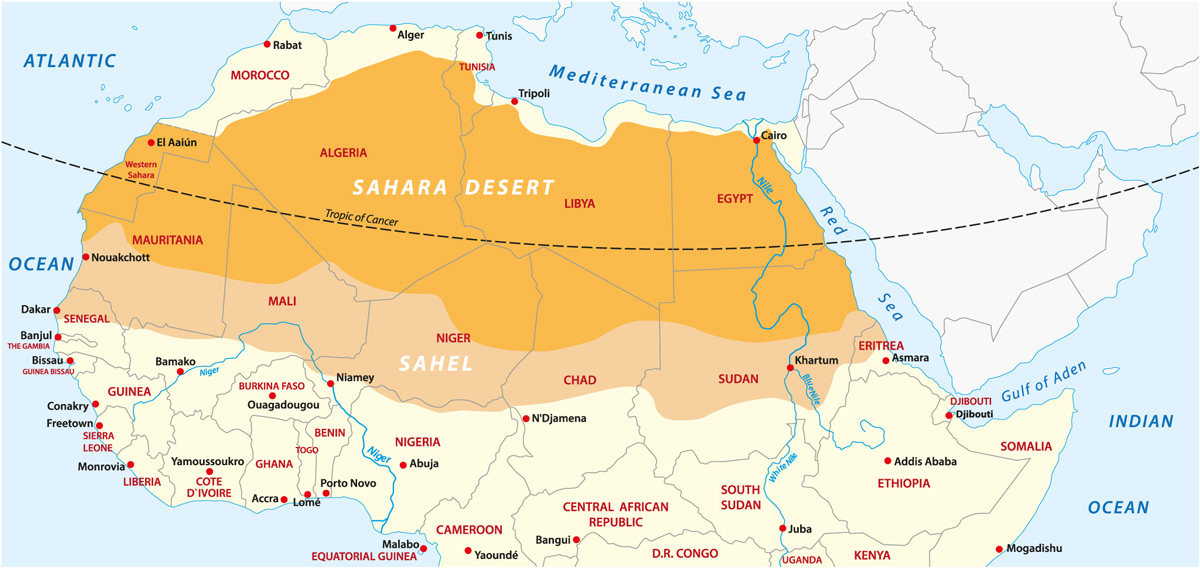
Geographical Features of the Sahara Affecting Lizard Populations
The Sahara Desert"s unique geographical features play a crucial role in shaping the habitats and survival of its lizard populations.
- Vast Sand Dunes: The ever-shifting sand dunes create dynamic habitats, influencing the distribution and movement patterns of lizards.
- Rocky Outcrops and Plateaus: These areas provide shelter and basking spots, crucial for thermoregulation in lizards.
- Mountain Ranges: Mountains in the Sahara, like the Tibesti and Ahaggar, offer varied microhabitats and can act as refuges for diverse lizard species.
- Oases: These isolated patches of vegetation and water are vital for supporting lizard populations, offering food and hydration sources.
- Desert Valleys: Valleys can create unique ecological niches, influencing lizard diversity and distribution.
- Salt Flats: Although challenging environments, some lizard species have adapted to survive in these harsh conditions.
- Extreme Climatic Conditions: The harsh climate of the Sahara, with its extreme temperatures and scarce water, heavily influences lizard survival strategies.
Understanding how these geographical features impact lizard populations is essential for conservation efforts and ecological studies in the Sahara Desert.

Conservation Efforts for Lizards in the Sahara
Conservation of lizards in the Sahara Desert is crucial due to the unique adaptations and ecological roles these species play. Efforts are underway to preserve these reptiles and their habitats.
- Habitat Protection: Preserving the natural habitats of lizards in the Sahara, including sand dunes, rocky outcrops, and oases, is a primary focus of conservation efforts.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research to understand the biology, behavior, and ecological needs of Sahara lizards is essential for effective conservation strategies.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing the impacts of climate change, which significantly affects desert environments and lizard populations, is a key aspect of conservation.
- Public Awareness: Educating local communities and the broader public about the importance of lizard species and the threats they face is crucial for gaining support for conservation measures.
- Collaboration with Local Communities: Involving local communities in conservation efforts helps ensure sustainable practices and protection of lizard habitats.
- Legal Protection: Implementing and enforcing laws to protect lizards from overexploitation and habitat destruction is an important conservation tool.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among countries within the Sahara region is essential for transboundary conservation efforts, given the wide-ranging habitats of many lizard species.
Through these efforts, conservationists aim to safeguard the diverse lizard species of the Sahara, ensuring their survival for future generations.
Lizard Escapes Heat in Unusual Way
Experience the exhilarating power of heat in this captivating video! Witness scorching flames and intense temperatures that will leave you in awe. Don\'t miss out on this sizzling adventure - watch now!
Tiny Lizard Dives Through Hot Desert Sand
Embark on a breathtaking journey through the majestic desert in this mesmerizing video. Marvel at vast landscapes, golden sand dunes, and the tranquility of this mysterious and enchanting place. Immerse yourself in the beauty of the desert - click play and be transported.
Human Interaction and Its Effects on Lizards
Human activities in the Sahara Desert significantly impact the lizard populations residing there. These interactions range from habitat alteration to direct effects on lizard species.
- Habitat Destruction: Development, mining, and other land alterations by humans lead to habitat loss for many lizard species.
- Climate Change: Human-induced climate change affects desert environments, altering the habitats and survival conditions for lizards.
- Overexploitation: Lizards face threats from overexploitation for pet trade, traditional medicine, and as food sources in some local communities.
- Pollution: Pollution from various human activities can degrade lizard habitats and affect their health and reproduction.
- Introducing Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native species by humans can disrupt the ecological balance, often leading to competition for resources and predation.
- Research and Education: On a positive note, human interaction through research and educational initiatives helps in understanding and conserving lizard species in the Sahara.
Effective management and conservation strategies are crucial to mitigate these human impacts and ensure the survival of lizard species in the Sahara Desert.

Lizards in Sahara Folklore and Culture
The Sahara Desert, rich in cultural heritage and folklore, has a unique relationship with lizards that extends beyond their ecological significance. Lizards in the Sahara are often intertwined with local beliefs, practices, and traditions.
- Symbology in Berber Culture: In the Berber culture, prevalent in regions like the Rif mountains, lizards and other fauna hold significant symbolic value. These animals are often associated with various ethnozoological practices, which may include their use in traditional human and veterinary medicine or in rituals and magic.
- Traditional Beliefs: The Saharan communities harbor a range of beliefs about lizards, viewing them with a mix of reverence and superstition. In some cases, lizards are seen as symbols or omens, featuring prominently in local stories and folklore.
- Impact on Conservation: The cultural significance of lizards in Saharan societies can have implications for their conservation. Understanding and respecting these cultural connections is essential for effective conservation strategies.
- Cultural Preservation: As modernization impacts traditional practices, there"s a growing need to preserve the cultural heritage associated with lizards and other wildlife in the Sahara. This includes maintaining the rich tapestry of folklore and traditional knowledge that has been passed down through generations.
The relationship between lizards and Saharan folklore is a testament to the deep connection between the region’s people and their natural environment. It underscores the importance of integrating cultural perspectives into wildlife conservation and ecological studies.
Future of Lizards in the Sahara Amidst Climate Change
Climate change poses significant challenges to the future of lizard populations in the Sahara Desert. These changes are expected to have profound impacts on their habitats and survival.
- Temperature Increases: Rising temperatures due to climate change can lead to thermal stress for lizards. Lizards rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature, but excessive heat can exceed their tolerance limits.
- Changes in Habitat: Climate change is altering the Sahara"s landscape, affecting the availability and quality of lizard habitats. This includes changes in vegetation, availability of prey, and the physical environment.
- Species Extinction Risks: Some lizard species, especially those adapted to colder environments, may face the risk of local extinction due to their inability to cope with rapid climate changes.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Lizards may exhibit adaptive responses to climate change, but the extent and effectiveness of these adaptations are uncertain. The ability of lizards to adapt will play a crucial role in their future survival.
- Conservation Efforts: Conservation strategies, including habitat protection and climate change mitigation efforts, are essential to safeguard the future of lizard populations in the Sahara.
The impact of climate change on Sahara"s lizards highlights the need for comprehensive studies to understand their adaptation strategies and to develop effective conservation measures in the face of environmental changes.

READ MORE:
Comparative Analysis of Sahara Lizards with Other Deserts
Lizards in the Sahara Desert exhibit distinct ecological characteristics compared to their counterparts in other deserts around the world.
- Diversity and Abundance: The Sahara Desert has a unique lizard fauna, but it is not as species-rich as some other desert regions, such as Australia"s arid zones, which boast exceptional lizard diversity.
- Adaptation to Extreme Conditions: Sahara lizards are well-adapted to extreme heat and aridity, whereas lizards in other deserts, like the Sonoran or Mojave, may face different environmental challenges.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Sahara lizards have evolved unique behaviors to cope with the desert environment, which may differ from those of lizards in deserts with varying climates and terrains.
- Impact of Climate Change: The effects of climate change on lizard populations may vary between deserts. Sahara lizards may face different challenges compared to lizards in cooler or more temperate deserts.
- Species Specialization: Lizards in the Sahara tend to be highly specialized for desert living, whereas lizards in other deserts might have a broader range of adaptations due to more varied microhabitats.
This comparative analysis underscores the importance of considering regional and environmental differences when studying desert lizards and formulating conservation strategies.
Exploring the vibrant world of Sahara"s lizards unveils a fascinating tale of resilience and adaptation, underscoring the intricate tapestry of life in one of the Earth"s most extreme environments.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)