Topic climate graph sahara desert: Explore the dynamic climate of the Sahara Desert through our detailed climate graphs, revealing a world of extreme temperatures and scarce rainfall in this vast and majestic landscape.
Table of Content
- What is the climate graph for the Sahara Desert?
- Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
- Temperature Variations in the Sahara Desert
- Precipitation Patterns in the Sahara Desert
- Seasonal Climate Differences Across the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
- Historical Climate Changes in the Sahara Desert
- Impact of Global Climate Change on Sahara Desert
- Future Projections of Sahara Desert Climate
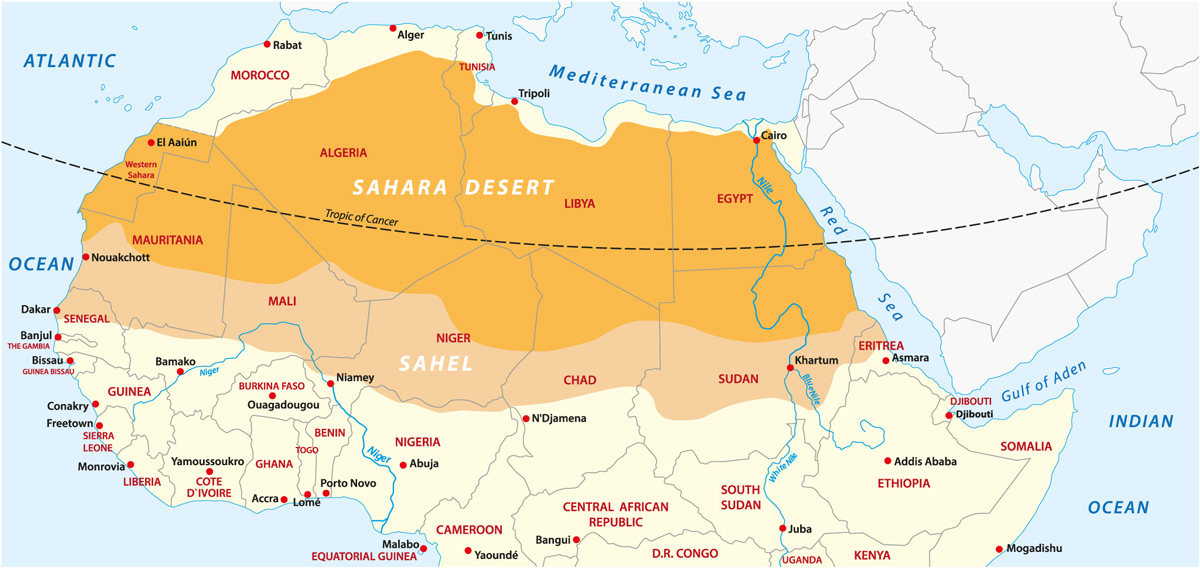
What is the climate graph for the Sahara Desert?
The Sahara Desert is known for its extreme climate, with hot and arid conditions prevailing throughout the year. The climate graph for the Sahara Desert would typically show the following characteristics:
- Hot Summers: The summer season in the Sahara Desert experiences scorching temperatures, with average highs around 40 °C (104 °F) and even reaching up to 47 °C (116.6 °F) for several months.
- Low Rainfall: Deserts are characterized by low average annual rainfall, usually totaling around 100 millimeters or less. The Sahara Desert is among the driest regions on Earth.
- Dry Winters: The winter season in the Sahara Desert remains dry, with little to no rainfall. However, temperatures can drop significantly during the nighttime.
- Extreme Temperature Variation: The climate graph would show a significant difference between day and night temperatures. Daytime temperatures can be extremely high, while nighttime temperatures can often plummet.
Overall, the climate of the Sahara Desert is characterized by its intense heat, limited precipitation, and extreme temperature fluctuations.
READ MORE:
Overview of Sahara Desert Climate
The Sahara Desert, known for its vast and arid landscapes, exhibits a climate that is as extreme as its geography. This region, which has evolved over millions of years, presents a fascinating study in climatic variability.
- Historical Climate Evolution: Geological studies suggest that the Sahara became a desert around 2-3 million years ago, transitioning through various humid and drier periods. Remarkably, evidence shows that about 7,000 years ago, the Sahara was lush with vegetation, supporting human and animal life.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is notorious for its extreme temperatures. During the summer, temperatures often soar above 38°C (100.4°F), with record highs reaching up to 58°C (136.4°F). Winters, in contrast, can be very cold, especially at night.
- Rainfall Patterns: Rainfall in the Sahara is minimal and highly inconsistent. The average annual rainfall barely reaches 3 inches. The northern and southern fringes of the desert experience slightly more rainfall due to geographical factors, but central Sahara receives almost no rain, dominated by anticyclonic weather patterns.
- Seasonal Variations: The climate of the Sahara varies between the north and south. The northern region experiences a dry subtropical climate with two rainy seasons, while the southern part has a dry tropical climate with one rainy season.
- Current Climate Trends: Recent studies indicate that the Sahara Desert is expanding, with significant changes in climate indices observed from 1950 to 2015. This expansion is linked to various factors, including land use changes and vegetation-climate interactions.
Understanding the Sahara"s climate is crucial not only for comprehending its past transformations but also for anticipating future changes in this vast and ecologically significant region.
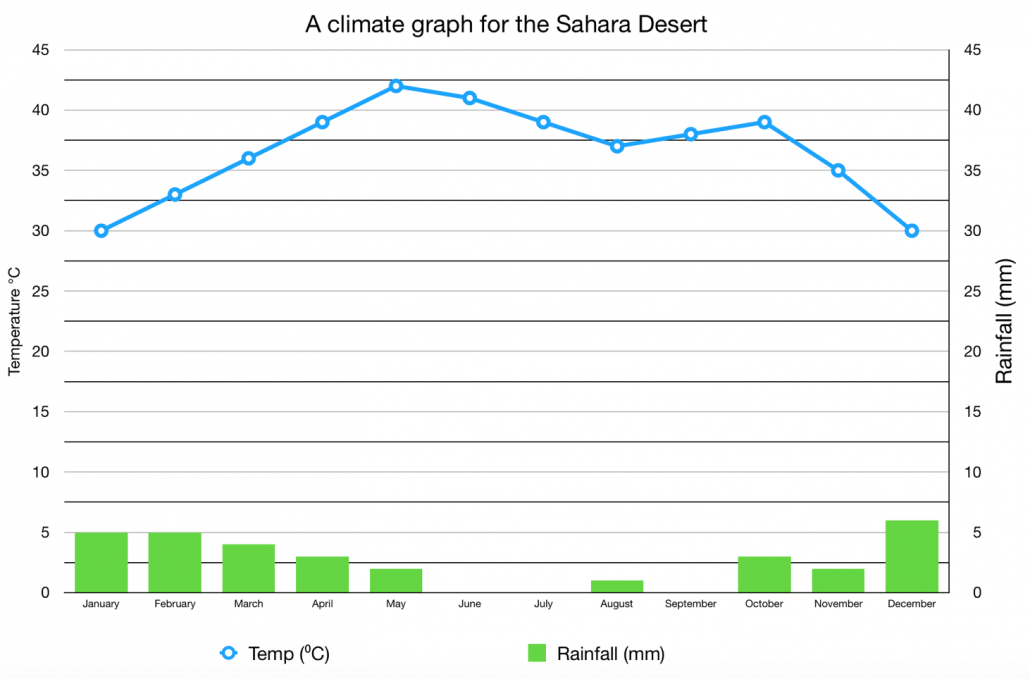
Temperature Variations in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, a region of stark beauty and extreme temperatures, exhibits significant temperature fluctuations across its vast expanse. Understanding these variations is crucial for comprehending the unique challenges and adaptations required for life in this harsh environment.
- Extreme Heat: The Sahara is characterized by some of the highest temperatures recorded on earth. Summer temperatures regularly exceed 40°C (104°F) and can soar up to 47°C (116.6°F), particularly over the central and eastern parts.
- Chilly Winters: Contrary to popular belief, the Sahara also experiences very cold winters, especially during the night. In some regions, nighttime temperatures can drop significantly, contrasting sharply with the daytime heat.
- Seasonal Variability: The temperature contrast is least pronounced during spring and autumn, with hot days and slightly cool nights. Summers are intensely hot and dry, with a greater temperature difference between day and night. Winters are milder during the day but much colder at night.
- Monthly Temperature Trends: Statistical data from places like Merzouga-Erg Chebbi reveal clear skies throughout the year with varying average low and high temperatures each month. For instance, January sees average temperatures ranging from 3°C to 18°C, while July can have highs of 43°C and lows of 26°C.
- Geographical Impact: Temperature variations are also influenced by geographical factors. For example, the northern fringes of the Sahara, influenced by low-pressure systems from the Mediterranean, have different climatic conditions compared to the southern fringes bordering the Sahel.
These temperature variations play a significant role in shaping the life and landscape of the Sahara, making it a region of both extreme challenge and fascinating adaptability.
Precipitation Patterns in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert is known for its extremely low rainfall, which is a defining characteristic of its harsh climate. The annual precipitation in the Sahara typically does not exceed 130mm, emphasizing its arid nature. The desert experiences significant climatic variability, with different regions experiencing varying patterns of rainfall.
Regional Variability
In the northern latitudes of the Sahara, the climate is arid subtropical with two rainy seasons, whereas the southern latitudes, though also arid, are more tropical and have only one rainy season. The western margins of the desert are slightly cooler and more humid, influenced by ocean currents.
Seasonal Variations
- Summer: This season is hotter and drier with a greater temperature difference between day and night.
- Winter: The coldest and most humid season, with milder temperatures during the day but much colder at night.
- Spring and Autumn: These seasons experience the least temperature contrast, being somewhat hot during the day and slightly cool at night.
Historical and Future Trends
Historical evidence suggests that the Sahara became arid approximately two to three million years ago. However, there is some contention among scientists regarding the exact timeline. Looking towards the future, climate change could further affect precipitation patterns in the Sahara, although specific projections are complex due to the desert"s vast size and varying topography.
Travel Recommendations
For travelers to the Sahara, it is important to be prepared for the extreme conditions. Due to the minimal likelihood of rainfall, precautions against heat during the day and cold at night are more critical. Carrying appropriate clothing, sunglasses, sunscreen, and hydration is essential for a safe desert experience.

Seasonal Climate Differences Across the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, characterized by its vast and diverse landscape, exhibits significant climatic variations across seasons. This arid region"s climate is predominantly influenced by its geographical position and the time of the year, leading to distinct seasonal weather patterns.
Summer Season
During summer, the Sahara experiences its most extreme weather. Temperatures frequently soar above 40°C (100°F), creating a hot and dry environment. This season marks the highest temperature variations between day and night, with cooler temperatures at night.
Winter Season
The winter months bring milder daytime temperatures, but nights can be significantly colder. This season is also characterized by the most humidity, contrasting with the otherwise dry conditions of the desert.
Spring and Autumn
Spring and autumn in the Sahara are known for having the least contrast in temperature. Days are moderately hot, while nights are slightly cool, offering a more temperate climate compared to the extreme conditions of summer and winter.
Regional Climate Variations
- The northern Sahara experiences a dry subtropical climate with two rainy seasons, leading to slightly more varied weather conditions.
- The southern Sahara, while also arid, presents a more tropical climate with one rainy season.
- The western edge of the Sahara, influenced by ocean currents, tends to be cooler and more humid than the central desert areas.
Climate Influences
Several factors contribute to the Sahara"s climatic variability, including topography and ocean currents. Additionally, historical climatic oscillations have shaped the desert"s current weather patterns, with human activities also playing a role in its climatic stability.
Travel Considerations
Visitors to the Sahara should be prepared for the region"s unpredictable and extreme weather. Protective clothing, hydration, and shelter are essential, especially during the extreme heat of summer days and the cold of winter nights.
The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
Ecosystems: Explore the mesmerizing beauty and diverse wildlife of different ecosystems in this captivating video. Discover the delicate balance of nature and the wonders of our planet waiting to be explored! Farmland: Step into the world of lush green fields and bustling farm life in this heartwarming video. Experience the serenity of the countryside and learn about the hard work that goes into producing our food.
How the Sahara Desert is Turning into a Farmland Oasis - GREENING THE DESERT PROJECT
In the African Sahel a country called Niger bordering the Sahara Desert, the largest desert in the world, is stopping desertification ...
Historical Climate Changes in the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert has undergone significant climatic changes throughout its history. The formation of the Sahara as a climatic desert is estimated to have occurred approximately 2-3 million years ago, during the transition from the late Pliocene to the early Pleistocene Epoch. However, some studies, such as the discovery of 7-million-year-old dune deposits in northern Chad, suggest that the region may have become arid even earlier, during the Miocene Epoch (23 million to 5.3 million years ago).
Climate Oscillations
Since its formation, the Sahara has experienced short- and medium-term oscillations between drier and more humid conditions. These climatic variations have been influenced by a variety of factors including topography, ocean currents, and human activity.
Human Impact
Human activities, particularly over the past 7,000 years, have contributed to the desert"s climatic stability. Practices such as cattle-based animal husbandry have influenced the Sahara"s climate, aiding in maintaining the arid conditions prevalent today.
The Little Ice Age
A notable departure from the Sahara"s typical climate occurred during the period known as the Little Ice Age (16th to 18th century). This period saw an increase in precipitation along the tropical margin of the Sahara, within the desert itself, and possibly along the northern margin as well. However, by the 19th century, a climate similar to present-day conditions was reestablished.
Current Climatic Regimes
Today, the Sahara is characterized by two major climatic regimes: a dry subtropical climate in the northern latitudes, with two rainy seasons, and a dry tropical climate in the southern latitudes, with one rainy season. The Sahel, a semiarid buffer zone, marks the transition from the Sahara to more temperate savanna biomes.
Impact of Global Climate Change on Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, one of the most iconic arid regions on Earth, is experiencing significant impacts due to global climate change. This desert is characterized by its diverse climatic regimes, ranging from arid subtropical in the north, which experiences two rainy seasons, to the more tropical climate in the south with one rainy season. The Sahel region, a semiarid zone, marks the transition from the Sahara to more temperate savanna biomes.
Climatic Variability and Change
The Sahara"s climate has historically shown considerable variability. Factors such as topography and ocean currents have played a significant role in shaping its climate. These natural phenomena are now intersecting with global climate change, leading to noticeable impacts on the desert"s environment.
Recent Trends and Observations
- Increased aridity and expanding desert area have been noted in recent decades.
- Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns are evident, influencing both the natural ecosystem and human activities in the region.
- Changes in atmospheric conditions have been observed, which could have broader implications for regional weather patterns.
Future Projections
While the exact future impact of climate change on the Sahara is complex and involves various factors, current trends suggest continued changes in its climatic conditions. This could include further desert expansion and alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns, with potential implications for both the desert"s ecology and the surrounding regions.
Human Influence
Human activities, particularly in the realm of agriculture and land use, have also contributed to the changing landscape of the Sahara. These activities, combined with global climate change, are reshaping this vast desert in profound ways.
READ MORE:
Future Projections of Sahara Desert Climate
The Sahara Desert"s climate has historically shown significant variability, characterized by a mix of arid subtropical and tropical climates. Future projections suggest continuing changes due to global and regional factors. Key aspects include:
- Increased aridity and potential expansion of desert areas.
- Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns, influencing ecosystems and human activities.
- Greater climatic variability within the desert"s borders, influenced by topography and ocean currents.
These changes could have far-reaching impacts on the Sahara"s environment and the surrounding regions, affecting both natural ecosystems and human communities.
Explore the fascinating climate dynamics of the Sahara Desert, a region of extreme contrasts and surprising variability. From historical shifts to future projections, understand how this vast desert"s climate shapes its unique ecosystem and affects global weather patterns.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)