Topic expansion of sahara desert: Discover the intriguing dynamics of the Sahara Desert"s expansion, a vital topic that impacts global climate, biodiversity, and human societies. Unearth the mysteries of this vast desert"s growth and its far-reaching implications in our comprehensive exploration.
Table of Content
- How much has the Sahara Desert expanded since 1920?
- Historical Transformation of the Sahara
- Climatic and Geographical Influences
- Ecological and Biodiversity Aspects
- Human History and Civilization Impact
- Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
- Global Environmental Influence
- YOUTUBE: The Green Sahara: A Moment in History
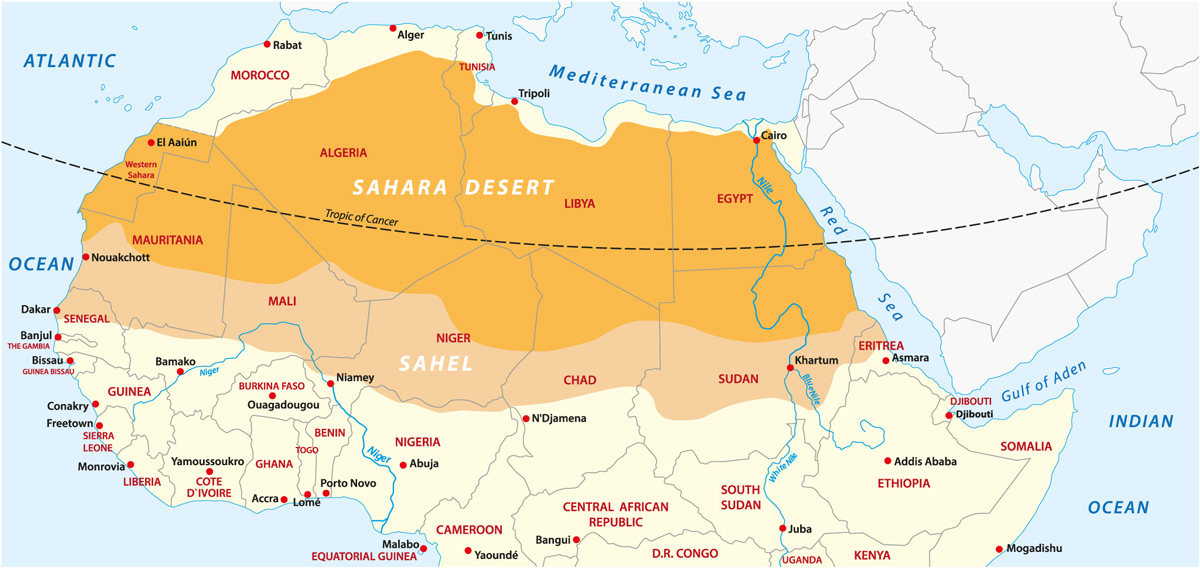
How much has the Sahara Desert expanded since 1920?
According to a study funded by the National Science Foundation, the Sahara Desert has expanded by approximately 10% since 1920.
- In 1920, the Sahara Desert covered a certain area.
- Over the years, the desert has expanded due to various factors such as climate change and human activities.
- The expansion of the Sahara is a cause for concern as it can exacerbate food insecurity and contribute to instability in affected regions.
- Recent observations suggest that the desert is growing at a rate of about 48km per year.
- This expansion has significant implications for the people living in and around the Sahara, as it can affect their livelihoods and access to resources.
READ MORE:
Historical Transformation of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, recognized as the world"s largest warm-weather desert, has undergone significant changes over the past century. A critical examination of its historical transformation reveals a complex interplay of natural and anthropogenic factors driving its expansion.
- Century-Scale Growth: Since the early 20th century, the Sahara has expanded by approximately 10%, with significant changes observed in the seasonal expansion patterns, particularly during the summer months.
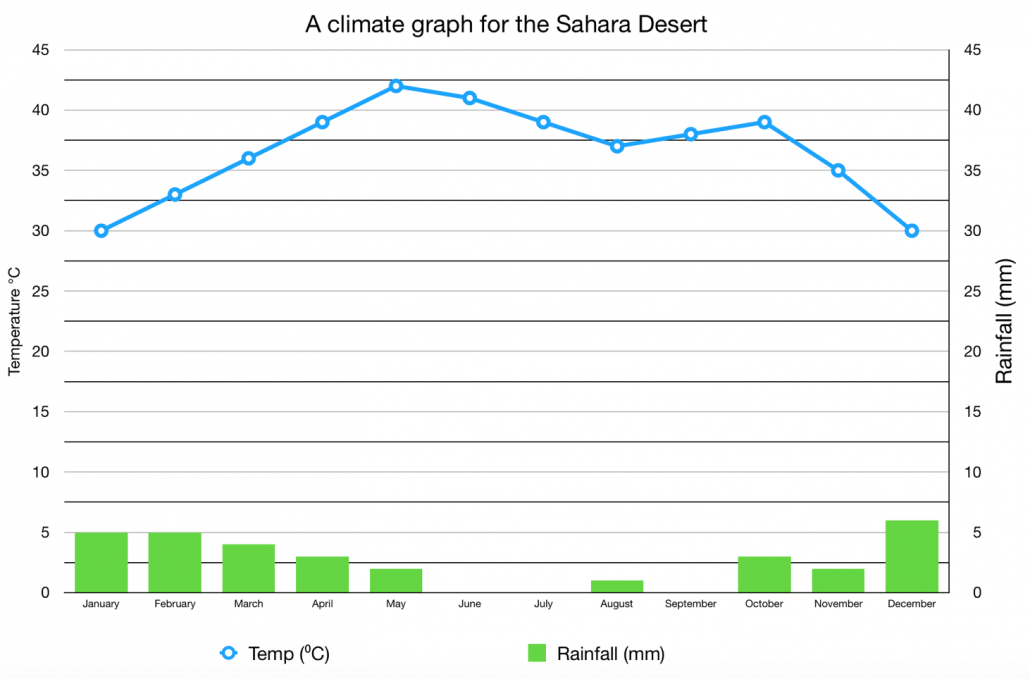
- Climate Variability and Rainfall Patterns: The desert"s growth has been influenced by various climatic cycles, including the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), which affect rainfall distribution in the Sahara and the adjoining Sahel region.
- Human Impact: Alongside natural climate cycles, human-induced climate change has played a substantial role in the Sahara"s expansion, accounting for about one-third of the observed increase. This highlights the intricate relationship between human activities and environmental changes.
- Impact on the Sahel and Lake Chad: As the Sahara expands, the Sahel region, a semi-arid transition zone, retreats. This has led to the disruption of ecosystems and human societies, with Lake Chad serving as a prominent indicator of the changing climatic conditions in the Sahel.
- Global Implications: The expansion of the Sahara holds broader implications for other subtropical deserts around the world. It emphasizes the need to understand and mitigate the effects of desertification in the face of increasing global temperatures and changing rainfall patterns.
- Future Research Directions: Ongoing research aims to deepen the understanding of the mechanisms behind desert expansion, not only in the Sahara but also in other regions, emphasizing the importance of addressing global climate challenges.
Climatic and Geographical Influences
The expansion of the Sahara Desert, a phenomenon with significant climatic and geographical implications, has been extensively studied. Understanding these factors is crucial in comprehending the broader impact of this desertification process.
- Role of Climate Change: Research suggests that a notable portion of the Sahara"s expansion is attributed to human-caused climate change. This influence is seen in the changing rainfall patterns and temperature dynamics in the region.
- Natural Climate Cycles: Natural climatic phenomena, such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), play a significant role in determining the rainfall and, consequently, the desertification processes in the Sahara.
- Hadley Circulation Effects: The Hadley circulation, a fundamental aspect of global climate, contributes to the formation of deserts in the subtropics. Changes in this circulation due to global warming are believed to influence the expansion of subtropical deserts, including the Sahara.
- Impact on the Sahel Region: The Sahara"s expansion impacts the adjoining Sahel region, a semi-arid transition zone. This shift disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems and affects human societies, notably through the drying of Lake Chad, a vital water resource in the region.
- Geographical Variations: The Sahara exhibits significant geographical variability, with different climatic regimes in its northern and southern latitudes. The interaction between these climatic zones plays a critical role in the desert"s expansion.
Ecological and Biodiversity Aspects
The ecological and biodiversity aspects of the Sahara"s expansion reveal a complex interplay between climate, habitat, and species. This section delves into how the desertification of the Sahara is influencing ecological dynamics and biodiversity in the region.
- Impact on Flora and Fauna: The expanding desert conditions are altering the composition of plant and animal life. Some species are adapting to the arid conditions, while others are facing increased risk of extinction.
- Changes in Habitat: As the desert expands, habitats are shifting. This includes a decrease in savanna ecosystems, which are crucial for various wildlife species, leading to alterations in their distribution and population dynamics.
- Effects on the Sahel Region: The encroachment of the Sahara into the Sahel region is disrupting this crucial transition zone, impacting both its ecology and the societies that depend on its resources.
- Adaptation and Survival Strategies: Species in the Sahara and Sahel regions are exhibiting remarkable adaptations to cope with the harsh desert environment and changing climatic conditions.
- Role of Climate Cycles: Natural climate cycles, such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, influence rainfall patterns, which in turn affect vegetation growth and wildlife in these regions.
- Human-Induced Changes: Activities such as overgrazing, deforestation, and land management practices are exacerbating the desertification process, impacting ecological balance.
Human History and Civilization Impact
The expansion of the Sahara Desert has profound implications on human history and civilizations. As the desert landscape changes, so too does the way of life for the people who inhabit these regions.
- Agricultural Changes: The expansion of the Sahara has led to significant changes in agricultural practices. Areas that were once fertile are increasingly becoming arid, affecting food production and leading to food insecurity.
- Impact on Water Resources: Key water sources such as Lake Chad have been drastically affected. The reduction in water availability has dire consequences for millions of people who rely on these resources for their livelihood.
- Migration and Conflict: As resources become scarce, communities are forced to migrate, often leading to conflict over the remaining resources. This has been particularly evident in regions like Mali, where desertification has been a contributing factor to ongoing conflicts.
- Cultural Impacts: Traditional ways of life are being upended as people adapt to the changing landscape. Nomadic lifestyles, for example, are becoming increasingly challenging with the expansion of the desert.
- Economic Challenges: Economies that rely heavily on agriculture and livestock are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of desertification, which can lead to economic instability and increased poverty rates.
- Historical and Archaeological Impacts: As the desert landscape changes, historical sites and archaeological treasures are also at risk, potentially leading to a loss of cultural heritage and knowledge about past civilizations.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
The expansion of the Sahara Desert presents both challenges and opportunities in the contemporary world. Understanding these aspects is vital for developing strategies to mitigate negative impacts and harness potential benefits.
- Environmental Challenges: The Sahara"s growth has intensified environmental issues such as reduced rainfall and droughts. These climatic changes are affecting ecosystems and leading to problems like water scarcity and reduced agricultural productivity, particularly in areas around Lake Chad.
- Socioeconomic Impact: The desert"s expansion is causing socioeconomic challenges, especially for those who depend on agriculture, livestock, and fisheries. Regions like Mali and Libya are experiencing increased food insecurity and conflict as a result of these changes.
- Opportunities for Climate Research: The Sahara"s expansion provides a unique opportunity for climate research, helping scientists understand the effects of natural climate cycles and human-induced climate change on desert environments.
- Global Implications: While the Sahara"s changes are specific to North Africa, they have broader implications for other desert regions globally. This highlights the need for international cooperation in climate and environmental research.
- Innovative Solutions: The challenges posed by the Sahara"s expansion are also driving the development of innovative solutions, like the Great Green Wall initiative, aimed at combating desertification and promoting sustainable land use.
- Adaptation Strategies: Communities affected by the Sahara"s growth are adapting through new agricultural practices and water conservation methods, demonstrating resilience in the face of environmental change.

Global Environmental Influence
The expansion of the Sahara Desert has significant global environmental implications. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing strategies to address climate change and environmental degradation on a global scale.
- Climatic Effects: The Sahara"s expansion is influenced by and contributes to global climate patterns, including the Hadley circulation. This affects the distribution of rainfalls and arid regions, potentially influencing other desert areas worldwide.
- Impact on Biodiversity: Changes in the Sahara"s size and the encroachment into the Sahel region affect ecosystems, leading to shifts in biodiversity and the potential loss of habitats and species.
- Hydrological Changes: The desert"s growth affects major water bodies like Lake Chad, which has implications for water availability not just locally, but in the broader region. This can influence agricultural patterns and food security.
- Soil and Air Quality: Expanding desert areas can lead to increased dust in the atmosphere, affecting air quality and contributing to global atmospheric changes.
- Global Warming and Climate Change: The Sahara"s expansion is both a result of and a contributor to global warming and climate change, underlining the interconnectedness of global environmental systems.
- Policy Implications: Understanding the Sahara"s expansion helps inform global environmental policies, highlighting the need for international cooperation in addressing climate change and desertification.
The expansion of the Sahara Desert, a phenomenon with profound global implications, underscores the urgent need for sustainable environmental practices and international cooperation to address the challenges of climate change and desertification.
The Green Sahara: A Moment in History
Discover the secrets behind the battle against desertification in this enlightening video! Learn how innovative approaches and grassroots efforts are reclaiming land and transforming arid landscapes into flourishing ecosystems. Don\'t miss out on witnessing nature\'s resilience unfold before your eyes!
READ MORE:
Africa\'s Remarkable Reforestation Efforts: The Great Green Wall
Dive into the captivating world of reforestation and witness the miraculous revival of once barren forests. Join us on this awe-inspiring journey as we explore the immense power of trees to combat climate change, restore biodiversity, and create sustainable communities. Prepare to be amazed by the extraordinary transformation happening around the globe!




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)