Topic sahara desert interesting facts: Explore the fascinating realm of the Sahara Desert, a land of ancient mysteries, diverse wildlife, and extraordinary natural phenomena, revealing a world beyond the sand.
Table of Content
- What are some interesting facts about the Sahara Desert?
- Geographical Significance and Location
- Historical Importance and Trade Routes
- Unique Climatic Conditions
- Flora and Fauna Adaptations
- Remarkable Landscapes and Natural Features
- Economic and Resource Significance
- YOUTUBE: Incredible Facts About the Sahara Desert
- Cultural and Historic Sites
- Impact on Global Climate and Weather Patterns
- Travel and Exploration Tips
- Challenges and Future of the Sahara
What are some interesting facts about the Sahara Desert?
Here are some interesting facts about the Sahara Desert:
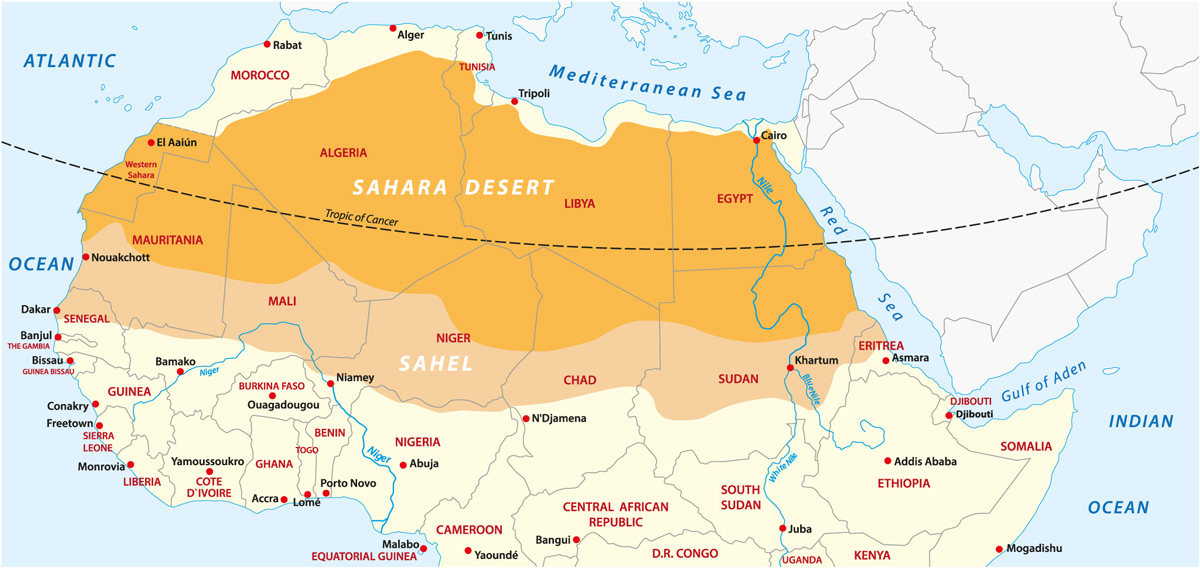
- The Sahara Desert is the largest desert in the world, spanning approximately 3,000 miles from east to west and covering most of northern Africa.
- Despite its name, the Sahara is not just a vast expanse of sand; in fact, sand dunes and sheets only cover around 25% of its actual surface.
- The Sahara is largely composed of rock, with sand being a minor part of the desert.
- The Sahara experiences extreme temperature variations, with daytime temperatures often exceeding 120°F (49°C) and dropping below freezing at night.
- While it appears barren, the Sahara is home to a surprising array of flora and fauna, including various species of desert-adapted plants, insects, reptiles, and mammals.
- The desert is known for its strong sandstorms, called \"haboobs,\" which carry dust and sand for hundreds of miles, reducing visibility and impacting air quality.
- The Sahara\'s sand dunes can reach impressive heights, with some towering over 600 feet (183 meters).
- The region experiences little rainfall, and certain parts of the Sahara have not seen rain for decades.
- The Sahara has played a significant role in human history, serving as a trade route and home to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and Berbers.
- The Sahara\'s landscapes are diverse, encompassing not only sandy deserts but also rocky plateaus, mountain ranges, and oasis areas.
READ MORE:
Geographical Significance and Location
The Sahara Desert, renowned as the largest hot desert in the world, spans approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, encompassing much of North Africa. This vast landscape extends from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Sahel in the south.
- The Sahara"s diverse terrain includes not just iconic sand dunes, but also rocky plateaus (hamadas), gravel plains (regs), dried-up lakes and valleys, salt flats, and a variety of mountain ranges.
- Some of the prominent mountain ranges in the Sahara include the Air Mountains, Hoggar Mountains, Tibesti Mountains, and the Saharan Atlas. The desert also houses the Emi Koussi volcano, the highest peak in the Sahara.
- Despite its arid reputation, the Sahara experiences some climatic variations. Its northern part is arid subtropical with two rainy seasons, while the southern part is more tropical with one rainy season.
- The Sahara plays a pivotal role in global weather patterns, including contributing to the fertility of the Amazon rainforest through dust transport across the Atlantic.
- Historical significance is marked by archaeological finds like dinosaur fossils and ancient megalithic stone circles, indicating a rich past life.
- Interestingly, the Sahara wasn"t always a desert; it used to be fertile farmland, and it undergoes cyclical changes from arid to savannah grassland approximately every 20,000 years.
- While often perceived as an endless sea of sand, only about 30% of the Sahara is sandy, with the rest comprising of gravel and other landscapes.
The Sahara"s geographical diversity and historical richness make it a fascinating subject of study and exploration, offering insights into both past civilizations and present-day ecological dynamics.

Historical Importance and Trade Routes
The Sahara Desert has been a pivotal region throughout history, serving as a bridge between different civilizations and cultures. Its vast expanse was traversed by numerous trade routes, collectively known as the Trans-Saharan trade routes, which were instrumental in the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices across continents.
- The Trans-Saharan trade routes connected the Mediterranean coast to the West African savannah and the sub-Saharan region, facilitating the trade of gold, ivory, salt, and slaves. These routes also played a significant role in the spread of Islam and other religions, languages, and cultural traditions.
- The trade routes were used by various peoples and civilizations, including the ancient Romans, the Arab empires of the Middle Ages, and later the European colonial powers.
- Major trading centers like Timbuktu and Gao emerged along these routes, becoming hubs of learning, culture, and commerce.
- The introduction of camels around 300 BCE revolutionized trade across the Sahara, as these animals were ideally suited to the harsh desert conditions.
- Caravans, often comprising hundreds of camels, transported goods across the desert. These caravans were complex operations, with meticulous planning required for the long and perilous journey.
- The Kingdom of Mali, one of the most powerful and prosperous civilizations in the Sahara, flourished due to these trade routes. It was known for its wealth and cultural achievements, with cities like Timbuktu becoming centers of intellectual and religious activities.
- Despite modern advancements in transportation, the legacy of the Trans-Saharan trade routes continues to influence the economy and culture of the region.
The Sahara"s historical trade routes not only shaped the economic landscape of Africa but also left an indelible mark on the cultural and social fabric of the continent, influencing generations and continuing to fascinate historians and archaeologists.
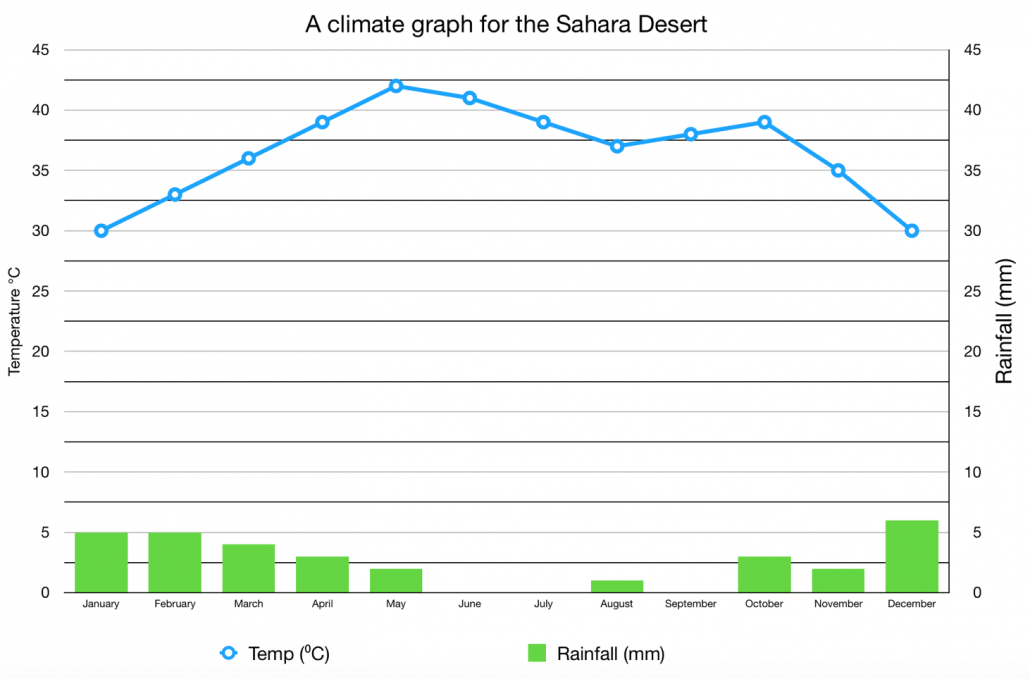
Unique Climatic Conditions
The Sahara Desert is characterized by its unique and extreme climatic conditions, which have evolved over millions of years. It"s known for being one of the driest and hottest regions on the planet.
- Historical Climate Shifts: Geological studies suggest that the Sahara became a climatic desert approximately 2-3 million years ago. However, there is evidence of the desert"s arid conditions dating back to the Miocene Epoch (23 to 5.3 million years ago).
- Rainfall Patterns: The central parts of the Sahara receive almost no rain, often less than 0.04 inches annually. The desert experiences minimal rainfall due to the influence of anticyclonic weather patterns.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is known for its extreme temperatures, with scorching hot days and significantly cooler nights. This large diurnal temperature range is a defining characteristic of the desert"s climate.
- Climatic Oscillations: The Sahara undergoes cycles of dry and more humid conditions. Every 20,000 years, the desert alternates between dry and lush green landscapes, influenced by the Earth"s axial tilt and resulting changes in monsoon activity.
- Human Impact: Human activities, such as animal husbandry, have contributed to the stability of the desert"s arid conditions by influencing surface reflectivity and reducing evapotranspiration.
These climatic features not only define the ecological character of the Sahara but also significantly impact the surrounding regions, contributing to its status as one of the most fascinating natural wonders of the world.

Flora and Fauna Adaptations
The Sahara Desert, despite its harsh climate, is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, each uniquely adapted to the extreme conditions of the desert.
- Flora: Vegetation in the Sahara includes plants such as the date palm, acacia, doum palm, desert gourd, tamarisk, and Ephedra alata. These plants have developed adaptations like deep root systems, water storage in stems, and rapid lifecycle completion after rains. The colocynth, for example, has a milky sap used as an antidote to scorpion bites.
- Fauna: The Sahara hosts a variety of wildlife, including mammals like the dromedary camel, Barbary sheep, oryx, addax antelope, and gazelles (Dorcas, Rhim, Dama). Reptiles include horned vipers, cobras, and skinks. Birds such as ostriches and Nubian bustards are also common.
- Adaptations: Animals in the Sahara have evolved unique adaptations. For instance, the fennec fox has large ears for heat dissipation and sensitive hearing. The addax antelope has flat feet for easy movement on sand and a pale coat to reflect sunlight.
- Role in Ecosystem: Each plant and animal plays a crucial role in the Sahara ecosystem, contributing as pollinators, seed dispersers, and predators.
These adaptations allow the flora and fauna of the Sahara to not only survive but thrive in one of the most challenging environments on Earth.
Remarkable Landscapes and Natural Features
The Sahara Desert, covering large parts of Northern Africa, is renowned for its diverse and dramatic landscapes, ranging from vast sand dunes to rocky plateaus, mountains, and oases.
- Sand Dunes and Ergs: The Sahara is famous for its iconic sand dunes, known as ergs, which cover only about 15% of the desert. These dunes can be as high as 180 meters and take various shapes, including crescent, linear, star, and dome forms.
- Rocky Plateaus (Hamadas): Contrary to popular belief, most of the Sahara consists of rocky plateaus called hamadas. These landscapes are characterized by barren, rocky surfaces, offering a stark contrast to the sandy dunes.
- Mountains and High Points: The Sahara boasts several mountain ranges, like the Atlas Mountains and Tibesti Mountains. Its highest point is Chad"s Mount Koussi, an extinct volcanic crater.
- Oases: Scattered across the Sahara are numerous oases, providing lush vegetation amidst the arid desert. These include famous spots like the Siwa Oasis in Egypt and Tafilalt in Morocco.
- Unique Geological Features: The desert is also home to fascinating geological formations such as salt flats, dry valleys, and the Qattara Depression, which is below sea level.
- Climatic Variability: The Sahara experiences climatic variability with regions that have almost no rainfall and others influenced by the North African Monsoon, bringing about periodic green landscapes.
This vast desert is not only a place of extreme conditions but also of profound beauty and natural wonder, captivating the imagination of explorers and travelers for centuries.

Economic and Resource Significance
The Sahara Desert, while often perceived as an uninhabitable and barren expanse, has significant economic and resource value, shaping the livelihoods and economies of the surrounding regions and countries.
- Historical Trade: Historically, the Sahara served as a vital trade route, facilitating the movement of gold, salt, slaves, cloth, and ivory across Ancient Africa, significantly contributing to regional economies.
- Mineral Resources: The Sahara is rich in mineral resources. It houses substantial deposits of phosphates in Morocco and Western Sahara, iron ore in Algeria, and uranium in Niger. These resources have played a crucial role in local and global economies.
- Fuel Resources: Post World War II discoveries revealed significant reserves of oil, natural gas, and coal across the Sahara, particularly in Egypt, Libya, and Algeria. These resources have attracted international investment and introduced high-wage jobs, though they have also led to displacement and environmental concerns.
- Water Resources: Geological prospecting has uncovered vast underground reserves of water in sedimentary basins, offering potential for agriculture and industry development.
- Challenges in Economic Development: Despite its resources, the Sahara presents enormous challenges in development. The exploitation of resources has provided limited local employment opportunities and has often prioritized coastal regions over desert development.
- Impact on Indigenous Peoples: The economic activities in the Sahara, especially in the oil and mineral sectors, have significantly impacted the traditional lifestyles of desert peoples, contributing to a drift towards oases and towns and an increase in poverty and overcrowding in developed areas.
The Sahara"s economic and resource significance is thus a complex blend of opportunities and challenges, deeply intertwined with the region"s environmental and socio-cultural dynamics.
Incredible Facts About the Sahara Desert
Embark on an awe-inspiring journey through the remarkable Sahara Desert, where the golden sand dunes stretch as far as the eye can see. Experience the breathtaking beauty and untamed wilderness in this captivating video that will transport you to a world like no other.
Interesting Facts About the Sahara Desert
Prepare to be amazed by these mind-blowing and lesser-known facts that will leave you craving for more knowledge. This intriguing video will take you on an exciting expedition of fascinating tidbits that will make you see the world in a whole new light.
Cultural and Historic Sites
The Sahara Desert is not just a vast expanse of sand; it"s a treasure trove of cultural and historical sites, each telling a unique story about the region"s past civilizations and cultures.
- Agadez: Known as the gateway to the desert, Agadez, located on the southeastern edge of the Sahara, is a historic city dating back to the 15th and 16th centuries. It features a unique street pattern based on ancient tribal camps and includes a well-preserved religious and palatial complex, with a 27-meter-high mudbrick minaret, the tallest of its kind.
- Carthage: Once the center of the Carthaginian Empire, historic Carthage in Tunisia is an important archaeological site, reflecting the city"s evolution over a millennium and its ultimate downfall in the Punic Wars.
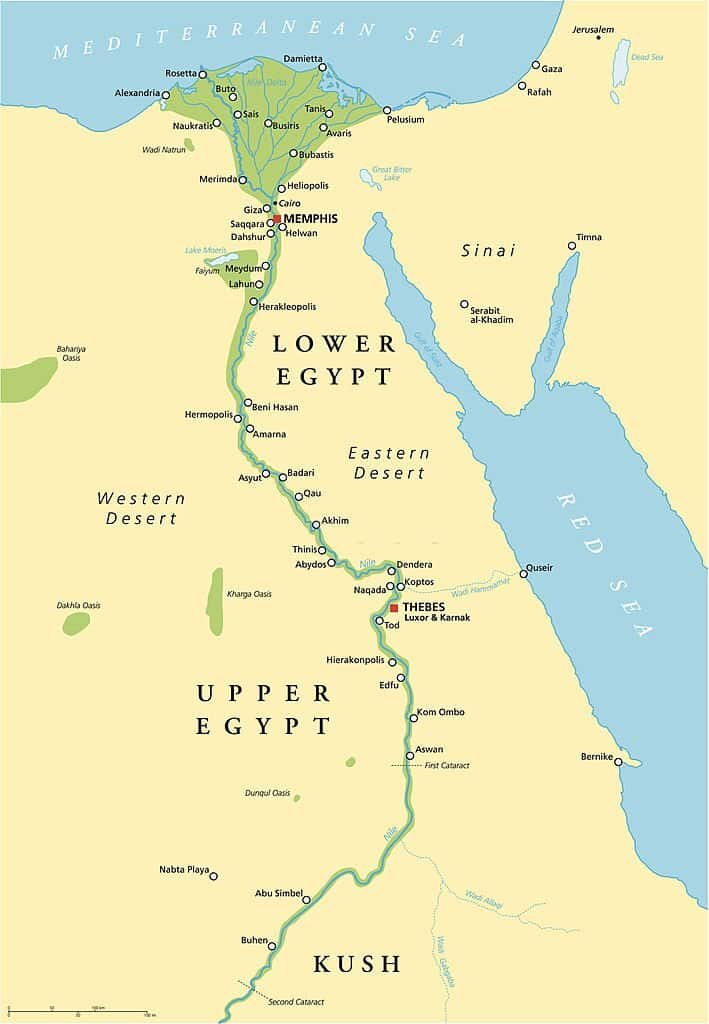
- Abu Simbel: This Egyptian site features the Great Temple of Ramses II and other structures, all of which were relocated to avoid being submerged during the creation of Lake Nasser. The relocation itself is a marvel of modern engineering.
- Meroë: Located in the desert of northern Sudan, the Pyramids of Meroë are a testament to the Nubian Kings of the Kingdom of Kush, with over 100 pyramids and structures rising out of the sands.
- Leptis Magna: In northwestern Libya, the ruins of Leptis Magna are some of the best-preserved Roman ruins in the world, offering a glimpse into the city"s grandeur before it was abandoned in the 7th century.
- Matmata: A small Tunisian village famous for its troglodyte (cave) dwellings, Matmata gained fame as a filming location for the original Star Wars series.
- Valley of the Kings: Located in Luxor, Egypt, this site is the burial place for many of Egypt’s pharaohs during the New Kingdom and includes the Tomb of Tutankhamun among many others.
These sites, among others in the Sahara, offer a window into the region"s rich history, from ancient civilizations to more recent cultural developments, showcasing a diversity that belies the desert"s barren reputation.

Impact on Global Climate and Weather Patterns
The Sahara Desert significantly influences global climate and weather patterns, contributing to environmental changes both regionally and globally.
- Expansion and Climate Shifts: Studies suggest that under various climate change scenarios, the Sahara is expected to expand, particularly in the Maghreb region and over Senegal and Mauritania. These expansions are more pronounced under high-emission scenarios. Conversely, the Sahel region, which borders the Sahara to the south, may experience an increase in precipitation, causing the desert"s southern edge to retreat.
- Intertropical Convergence Zone Movement: The northward shift of the intertropical convergence zone is a key factor driving these changes, affecting water availability and agriculture in the surrounding regions.
- Sand and Climate Interaction: The Sahara"s sand plays a critical role in the Earth"s climate system. Dust storms in the Sahara can release up to a million tons of minute dust particles into the air, which are then transported over vast distances. This dust contributes significantly to atmospheric composition and can influence cloud formation and precipitation cycles in distant locations.
- Temperature Anomalies: The Sahara has been experiencing temperature anomalies, with the annual warming trend exceeding the global and tropical warming rates. This warming can have profound impacts on weather patterns and precipitation in the region and beyond.
- Impact on Rainfall: Research indicates that airborne Sahara desert sand might contribute to cloud formation, potentially affecting rainfall patterns. The interaction between sand particles and atmospheric conditions could be a factor in rain generation, though this area requires further investigation.
These factors highlight the Sahara"s complex and significant role in shaping global climate and environmental patterns, impacting ecosystems, weather phenomena, and human activities across the world.
Travel and Exploration Tips
Embarking on an adventure in the Sahara Desert is an experience of a lifetime. Here are essential tips to ensure a safe and memorable journey.
- Choose the Right Time: The best time to visit the Sahara is from October to May, to avoid the extreme summer heat.
- Guide and Tour Planning: Hiring a knowledgeable guide is crucial for navigating the vast desert. Consider booking guided tours for a comprehensive experience.
- Appropriate Clothing: Wear light, breathable, and protective clothing to shield yourself from the sun. A hat, sunglasses, and a light scarf are also essential.
- Footwear: Closed-toed shoes are necessary to protect your feet from the hot sand, especially during the afternoon. Sandals or bare feet are suitable for cooler times of the day.
- Hydration: Carry sufficient water to stay hydrated. The dry desert climate can lead to dehydration quickly.
- Sun Protection: Sunscreen is a must to protect your skin from harsh UV rays.
- Photography Gear: Bring a camera to capture the breathtaking landscapes. Protect your equipment from sand.
- Respect Local Cultures: Engage respectfully with local communities and be mindful of cultural sensitivities.
- Emergency Kit: Carry a basic first aid kit, a map, and a GPS device for safety.
- Enjoy the Quiet: Embrace the silence and vastness of the desert for a truly unique experience.
- Star Gazing: The clear desert sky offers an excellent opportunity for stargazing.
By following these tips, you can enjoy the Sahara"s majestic beauty safely and respectfully.

READ MORE:
Challenges and Future of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert faces significant environmental and socio-economic challenges, impacting both the region and the world.
- Desert Expansion: The Sahara is expanding, with a noticeable increase in land coverage over recent decades, affecting surrounding ecosystems and communities.
- Climate Change Effects: Climate change is accelerating desertification, with significant impacts on local weather patterns, water availability, and agriculture.
- Socio-Economic Impact: The expansion of the Sahara threatens local livelihoods, exacerbating food insecurity and potentially fueling conflict in the region.
- Global Environmental Impact: The Sahara"s changes have global implications, including the potential spread of desertification to other regions.
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies: Efforts to combat desertification involve erosion control, sustainable land management, and international cooperation for environmental conservation.
The Sahara"s future depends on effectively addressing these challenges through global and regional environmental policies and sustainable development practices.
The Sahara, a land of enigmatic beauty and timeless wonders, beckons the curious and the adventurous. Its profound mysteries, ancient legacies, and evolving challenges offer a captivating journey, inviting us to explore and appreciate our world"s natural marvels.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)