Topic sahara desert growing: Explore the intriguing dynamics of the Sahara Desert"s growth, a landscape transforming through nature"s rhythm, revealing secrets of ecological resilience and human history in its expanding sands and occasional greening.
Table of Content
- Is the Sahara Desert growing in size?
- The Phenomenon of Sahara Desert Expansion
- Historical Greening of the Sahara
- Climate Modeling and the African Humid Periods
- Challenges and Strategies in Desert Reforestation
- Impact of Climate Change on Sahara"s Future
- Edible Plants and Survival in the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: The Green Sahara: A Look into its Past
- The Role of the Sahara in Early Human Evolution
- Implications for Global Climate and Ecology
Is the Sahara Desert growing in size?
According to a study conducted in 2018, the Sahara Desert, which is already the world\'s largest desert, has grown by 10 percent since 1920. This expansion is believed to be a result of various factors, including climate change and human activities.
One major contributing factor to the expansion of the Sahara Desert is climate change. The region has been experiencing increasing drought and desertification, leading to the growth of the desert. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and deforestation all play a role in this process.
Additionally, human activities such as overgrazing, agriculture, and urbanization have also contributed to the expansion of the desert. These activities have led to the degradation of land and the loss of vegetation, making the area more susceptible to desertification.
It\'s important to note that, while the Sahara Desert is growing in size, it is not expanding into the rest of Africa. The growth is happening within the existing boundaries of the desert. However, the expansion of the Sahara has significant implications for the region, including the displacement of local populations, increased food insecurity, and the loss of biodiversity.
READ MORE:
The Phenomenon of Sahara Desert Expansion
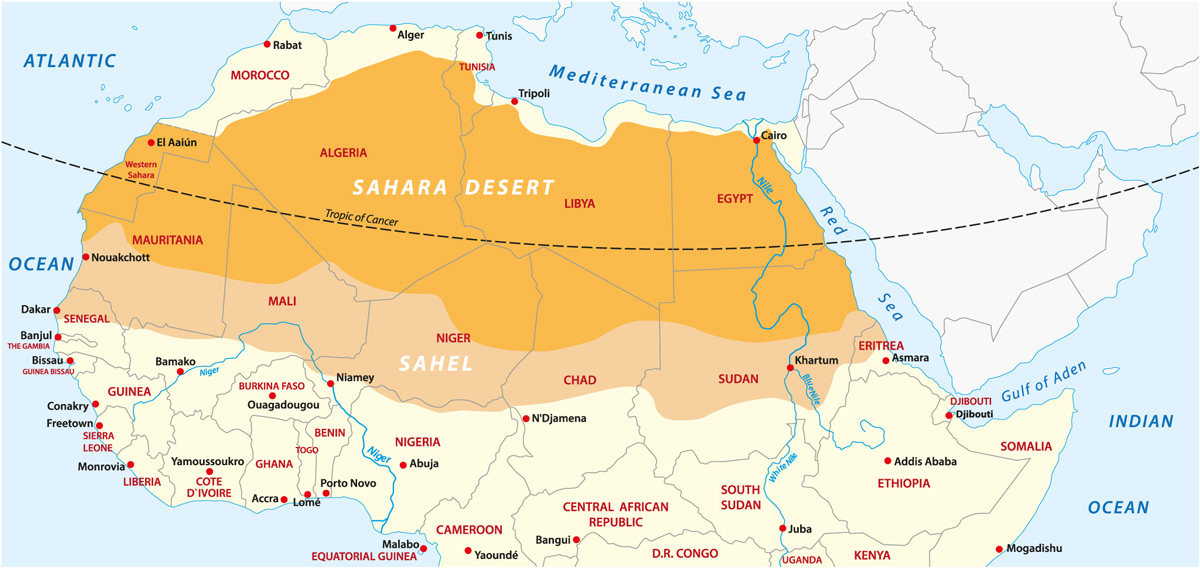
The Sahara, the world"s largest hot desert, has undergone significant expansion since the early 20th century. Studies reveal a growth of approximately 10% since 1920, with the expansion being more pronounced during summer months, sometimes reaching up to 16%. This change is partly attributed to natural climate cycles such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, and partly to human-induced climate change. The widening of the Hadley circulation, a key atmospheric phenomenon, is also contributing to the northward advance of subtropical deserts. This expansion poses challenges for the adjacent Sahel region, where the semi-arid grasslands are retreating against the encroaching desert, affecting millions who depend on the land for agriculture, livestock, and fisheries.
Efforts to understand and mitigate the Sahara"s expansion include research on the drivers of these climatic changes and large-scale projects like the Great Green Wall. This initiative aims to create a stretch of vegetation across the continent to combat desertification. Innovative methods such as seawater greenhouses are also being explored to facilitate agriculture in arid regions by using seawater for crop growth. These approaches reflect the growing concern over the Sahara"s expansion and the search for sustainable solutions to preserve and restore the ecosystems and livelihoods affected by this phenomenon.

Historical Greening of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, currently an arid expanse, has experienced periods of lush vegetation and abundant wildlife. These greening phases, known as the African Humid Periods, occurred cyclically, driven by Earth"s orbital changes and monsoon intensification. Approximately every 20,000 years, warmer summers and increased rainfall transformed the Sahara, supporting rivers, lakes, and diverse ecosystems.
- During these green phases, the Sahara supported hunter-gatherers and pastoral communities, indicating a drastically different environment from its current state.
- Evidence suggests that these periods played a critical role in human evolution and migration, providing corridors for dispersal across Africa and beyond.
- Advanced climate modeling studies have shed light on the dynamics of these humid periods, enhancing our understanding of past climatic shifts and their global implications.
Understanding the Sahara"s historical greening offers valuable insights into the desert"s ecological past and potential future transformations. It also underscores the significant impact of natural climate cycles on terrestrial environments.
Climate Modeling and the African Humid Periods
Climate modeling has played a pivotal role in understanding the Sahara"s ecological past, particularly the African Humid Periods. These periods, characterized by increased rainfall and vegetation, are a result of Earth"s orbital changes affecting solar radiation and consequently, the monsoon patterns. Advanced climate models have enabled scientists to simulate these humid periods with greater accuracy, shedding light on the Sahara"s green past and providing insights into future climatic shifts.
- Periodic humidity and aridity in the Sahara are linked to slight wobbles in the Earth’s orbital axis, which alters solar radiation angles.
- Detailed studies, such as sediment core analysis and pollen records, have shown a correlation between human activities, like pastoralism, and environmental changes, suggesting a possible influence on the rate of desertification.
- Recent research highlights the importance of understanding vegetation feedbacks and dust changes in the Sahara"s transition from a green oasis to a desert.
These findings emphasize the complex interplay between natural orbital cycles, human influence, and environmental feedback mechanisms in shaping the Sahara"s climate history. Continued research and climate modeling are crucial for predicting future changes in arid and semi-arid regions globally.
Challenges and Strategies in Desert Reforestation
Reforesting deserts, particularly vast areas like the Sahara, presents unique challenges and requires innovative strategies. The primary challenges include extreme aridity, high temperatures, and soil conditions that are often unsuitable for traditional forestry practices. To address these, a combination of modern technology and traditional knowledge is being employed.
- Water Management: Critical to desert reforestation, strategies include rainwater harvesting, use of dew and fog, and efficient irrigation systems to maximize limited water resources.
- Selection of Plant Species: Using native and drought-resistant plant species that are adapted to the harsh desert environment is essential. These plants are more likely to thrive and support local biodiversity.
- Soil Improvement: Techniques such as the use of organic matter, sand dune stabilization, and soil conditioning are used to improve soil fertility and structure.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops and livestock farming can create sustainable land-use systems that benefit both the environment and local communities.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in reforestation efforts ensures sustainability and provides economic benefits through activities like agroforestry and ecotourism.
Projects like the Great Green Wall in Africa exemplify these strategies in action, aiming to combat desertification and improve livelihoods through a mosaic of green and productive landscapes across the Sahara and the Sahel. Such initiatives demonstrate that, while challenging, desert reforestation is a feasible and vital endeavor for ecological and socio-economic sustainability.
Impact of Climate Change on Sahara"s Future
The future of the Sahara Desert is closely intertwined with the ongoing effects of climate change. The Sahara is experiencing significant environmental transformations due to factors like rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns. These changes are expected to have profound impacts on the desert"s ecology, local communities, and even global climate systems.
- Rising Temperatures and Expanding Deserts: As global temperatures rise, desert areas like the Sahara are expected to expand. This expansion could further exacerbate water scarcity and reduce habitable land.
- Altered Rainfall Patterns: Climate change may lead to altered rainfall patterns in the Sahara, potentially affecting the delicate balance of ecosystems and impacting local agriculture and biodiversity.
- Influence on Global Climate: Changes in the Sahara"s climate and landscape can have far-reaching effects, influencing atmospheric circulation patterns and potentially impacting weather systems beyond Africa.
- Socio-Economic Impacts: The expansion of the Sahara and the associated environmental changes could lead to increased food insecurity, displacement of communities, and heightened conflict over scarce resources.
- Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies: Efforts are being made to adapt to and mitigate these changes, including projects like the Great Green Wall, aimed at halting desertification and promoting sustainable land management practices.
The Sahara"s future will largely depend on global efforts to address climate change, along with region-specific strategies to adapt to and mitigate its impacts. Understanding and preparing for these changes are crucial for the resilience of ecosystems and communities in and around the Sahara Desert.
Edible Plants and Survival in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, despite its harsh environment, hosts a variety of edible plants that have adapted to its extreme conditions. These plants are not only crucial for the survival of wildlife but also offer sustenance to humans living in or traversing this vast desert.
- Date Palms: One of the most iconic and vital plants in the Sahara. Dates provide essential nutrients and are a staple food for many desert communities.
- Desert Truffles: These fungi grow underground and are a delicacy in the region. They are a good source of protein and carbohydrates.
- Acacia Trees: The gum from these trees is edible and the leaves are used as fodder for animals. Acacia seeds are also consumed by local communities.
- Cacti: Species like the prickly pear are found in the Sahara. Their fruits are edible and can provide hydration and nutrition.
- Desert Melons: These melons can store water and are consumed by both humans and animals during times of scarcity.
In addition to these natural resources, modern efforts to transform parts of the Sahara into arable land have led to the introduction of more conventional crops through innovative agricultural practices. However, such initiatives must be sustainable to prevent further degradation of this delicate ecosystem.
The Green Sahara: A Look into its Past
Explore the captivating world of the past through this intriguing video. Dive into historical events, unravel ancient mysteries, and gain a deeper understanding of our roots. Discover how the past shapes our present and empowers us for the future.
Africa\'s Strategy to Combat the Spread of the Sahara
Brace yourself for an adrenaline-fueled combat experience like no other! Witness breathtaking displays of skill, strategy, and determination as warriors from across time and cultures engage in awe-inspiring battles. Prepare to be captivated by the sheer intensity and excitement of combat in this thrilling video.
The Role of the Sahara in Early Human Evolution
The Sahara Desert has played a significant role in early human evolution, a relationship deeply influenced by its environmental changes. The Sahara has experienced cyclical shifts between being a lush, green habitat and a vast, arid desert, largely due to changes in Earth"s orbit affecting solar radiation and monsoon patterns. These shifts have had profound effects on human populations and their ways of life.
- Human Settlement and Migration: During humid periods, the Sahara supported a variety of flora and fauna, creating favorable conditions for human habitation. These green periods may have facilitated human migration across and out of Africa.
- Adaptation to Changing Environments: The transition between green and desert phases required humans and their ancestors to adapt to rapidly changing environments, potentially influencing evolutionary paths.
- Impact of Human Activity: There is evidence suggesting that human activities, such as overgrazing by domesticated animals, may have influenced the Sahara"s environmental changes. These activities possibly contributed to the hastening of desertification processes.
- Archaeological Significance: The Sahara holds key archaeological and paleoenvironmental records that provide insights into human history and the interplay between climate change and human evolution.
The Sahara"s dramatic environmental shifts underscore its importance in understanding human history and evolution. Ongoing research continues to reveal the complexities of this relationship and the Sahara"s role as a significant factor in the story of humanity.

READ MORE:
Implications for Global Climate and Ecology
The expansion of the Sahara Desert has significant implications for global climate and ecological systems. As one of the largest deserts in the world, changes in the Sahara"s size and characteristics can influence weather patterns, wildlife habitats, and even carbon cycling processes on a global scale.
- Alteration of Weather Patterns: The growth of the Sahara could affect the global atmospheric circulation patterns, potentially altering weather systems far beyond the African continent.
- Impact on Biodiversity: Expanding desert landscapes can lead to loss of habitats, affecting biodiversity both within and around the desert regions.
- Carbon Cycling: Changes in desert areas can impact the global carbon cycle, especially considering the role of vegetation in carbon sequestration.
- Human Impact: Expanding deserts can lead to challenges for populations living at the desert margins, including impacts on agriculture, water resources, and livelihoods.
- Influence on Global Climate Change: Desertification processes contribute to global climate change dynamics, making understanding and managing desert expansion critical in the broader context of climate change mitigation.
Thus, the growing Sahara is not just a regional issue but a global concern, necessitating international cooperation and interdisciplinary research to understand and mitigate its impacts.
The Sahara"s growth is a vivid reminder of our planet"s dynamic nature, intertwining ancient rhythms with modern challenges. Its expansion raises critical questions about climate, ecology, and human adaptability, inviting us to rethink our relationship with Earth"s extraordinary landscapes.















