Topic sahara desert coordinates: Discover the vastness of the Sahara Desert through its coordinates, unveiling the secrets of the world"s largest hot desert and its intriguing landscapes, cultures, and history.
Table of Content
- How can I find the coordinates of the Sahara Desert on a map using latitude and longitude?
- Geographical Coordinates of the Sahara Desert
- Population and Demographics of the Sahara
- Countries Encompassing the Sahara Desert
- Climatic Conditions and Environmental Features
- Recommended Clothing for Sahara Expeditions
- Essential Gear for Sahara Desert Camping
- Navigational Tools and Safety Measures
- Historical Significance and Cultural Aspects
- Conservation Efforts and Ecological Concerns
- Popular Tourist Attractions and Activities
How can I find the coordinates of the Sahara Desert on a map using latitude and longitude?
To find the coordinates of the Sahara Desert on a map using latitude and longitude, you can follow these steps:
- Open a map application or website that allows you to search for specific locations.
- Enter the name \"Sahara Desert\" or the specific country name where you want to find the Sahara Desert.
- Click on the search or enter button to initiate the search.
- The map should now show the location of the Sahara Desert.
- Look for the coordinates displayed on the map or in a sidebar.
- The coordinates will be displayed in both decimal degrees and DMS (degrees, minutes, seconds) format.
- Note down the latitude and longitude values for future reference or use.
By following these steps, you can easily find the coordinates of the Sahara Desert on a map using latitude and longitude.
READ MORE:
Geographical Coordinates of the Sahara Desert
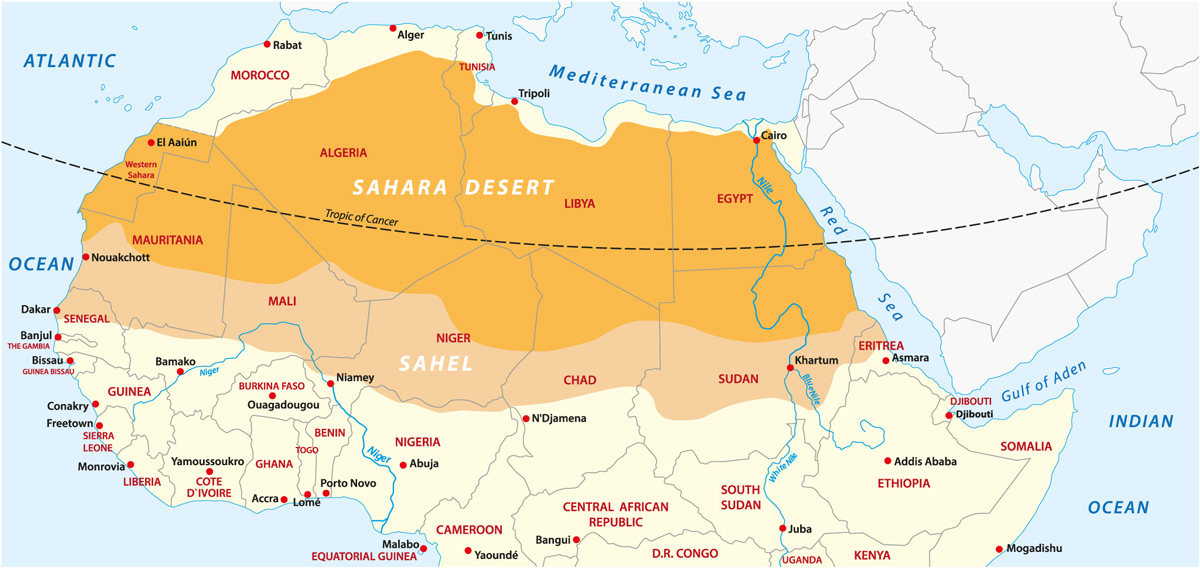
The Sahara Desert, the world"s largest hot desert, spans several degrees of latitude and longitude. Its vastness covers a significant portion of North Africa, extending from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Sahel in the south.
- Approximate Central Coordinates: Latitude 20° 37" 58.02" N, Longitude 11° 12" 21.80" E.
- Covering an area of about 9.2 million square kilometers, the Sahara"s coordinates vary widely due to its immense size.
- The desert"s eastern boundary near the Red Sea hovers around 25° E longitude, while its western edge near the Atlantic Ocean extends to about 15° W longitude.
- From north to south, the Sahara stretches from approximately 37° N latitude in Morocco and Algeria, down to about 16° N latitude in Mali and Niger.
- The desert encompasses parts of several countries, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan, and Tunisia.
These coordinates highlight the Sahara"s vast expanse, offering a glimpse into the diverse landscapes ranging from sandy dunes to rocky plateaus that define this iconic desert.

Population and Demographics of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, often perceived as an inhospitable expanse, is home to a diverse population adapting to its challenging environment. Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara supports a variety of cultures and lifestyles.
- Population Density: The Sahara is sparsely populated, with an estimated population of about 2.5 million people, which translates to less than one person per square mile.
- Indigenous Inhabitants: The Sahara is primarily inhabited by various nomadic groups, including the Tuareg, Berbers, Moors, and Toubou, each with unique cultural identities and traditions.
- Sedentary Communities: Along the edges of the desert, particularly near oases, sedentary communities thrive, engaging in agriculture and trading.
- Lifestyle and Adaptations: The inhabitants of the Sahara have adapted to the extreme conditions through nomadic lifestyles, traditional knowledge of water sources, and a diet primarily based on dates, grains, and animal products.
- Economic Activities: Economic activities in the Sahara include pastoralism, agriculture near oases, salt mining, and in some areas, tourism and oil exploration.
- Impact of Modernization: Modernization and climate change are impacting traditional lifestyles, with more inhabitants moving to urban areas or adopting settled ways of life.
- Cultural Heritage: The Sahara is rich in cultural heritage, including rock art, traditional music, and festivals, which are integral to the identity of its people.
Understanding the demographics of the Sahara provides insight into how human resilience and adaptability prevail in one of the world"s most challenging environments.
Countries Encompassing the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert in the world, spans across multiple countries in North Africa. Each of these countries shares a portion of the desert"s expansive and diverse landscape.
- Algeria: With over 80% of its land covered by the Sahara, Algeria has a significant portion of the desert, including its unique sand dunes and rock formations.
- Chad: The Sahara covers much of northern Chad, featuring the Tibesti Mountains, some of the highest in the desert.
- Egypt: The western part of Egypt falls within the Sahara, including parts of the Libyan Desert.
- Libya: Libya"s landscape is dominated by the Sahara, offering some of the most picturesque dunes and oases.
- Mali: Northern Mali is Sahara territory, characterized by its vast, arid landscapes.
- Mauritania: The Sahara in Mauritania is known for its extensive dune fields and the unique Richat Structure.
- Morocco: The Sahara stretches into southern Morocco, including the famous Erg Chebbi dunes.
- Niger: The Sahara covers the northern regions of Niger, including the Air Mountains.
- Sudan: Northern Sudan includes Sahara desert areas, extending into the Nubian Desert.
- Tunisia: The Sahara reaches into southern Tunisia, offering diverse ecosystems and landscapes.
- Western Sahara: This disputed territory is primarily Saharan desert, with a coastline along the Atlantic Ocean.
Each country contributes unique geographical features and cultural elements to the Sahara, making it a mosaic of ecosystems and human heritage.

Climatic Conditions and Environmental Features
The Sahara Desert, known for its extreme climate and unique environmental features, presents a range of geographical variations across its vast expanse.
- Climate: The Sahara is characterized by one of the harshest climates on Earth, predominantly hot and arid. Temperatures often exceed 50°C (122°F) in summer, while nights can be significantly cooler.
- Rainfall: It receives less than 75mm (3 inches) of rain annually, making it one of the driest regions in the world.
- Sand Dunes and Ergs: The Sahara is famous for its sand dunes (ergs), which can reach heights of up to 150 meters.
- Rocky Plateaus: Vast rocky plateaus (hamadas) cover large areas, providing a stark contrast to the sandy dunes.
- Mountain Ranges: The desert includes several mountain ranges, such as the Tibesti Mountains in Chad and the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria.
- Vegetation and Wildlife: Despite its aridity, the Sahara hosts various species of vegetation and wildlife, adapted to survive in the extreme conditions.
- Seasonal Wind Patterns: The region experiences seasonal wind patterns, including the hot, dry Sirocco and Harmattan winds.
- Temperature Variations: Diurnal temperature variation can be extreme, with hot days and significantly cooler nights.
- Oases: Scattered oases provide vital water sources and support small populations and diverse wildlife.
- Environmental Challenges: The Sahara faces environmental challenges like desertification and climate change impacts.
This diverse climatic and environmental landscape makes the Sahara a region of stark beauty and extreme conditions, offering a unique ecosystem on our planet.
Recommended Clothing for Sahara Expeditions
Proper attire is crucial for a safe and comfortable experience in the Sahara Desert. The extreme weather conditions demand specific types of clothing to protect against the elements.
- Lightweight and Breathable Fabrics: Opt for clothing made of natural fibers like cotton or linen, which allow for air circulation and help in managing body temperature.
- Loose-Fitting Garments: Choose loose clothing to promote airflow and facilitate movement, essential in the desert environment.
- Long-Sleeved Shirts and Pants: Despite the heat, cover as much skin as possible to protect from the sun"s rays and minimize the risk of sunburn.
- Light-Colored Clothing: Light colors reflect sunlight and help keep the body cooler compared to dark colors that absorb heat.
- Headgear: A wide-brimmed hat or a headscarf is essential to shield the face and neck from direct sunlight.
- Sunglasses: UV-protected sunglasses are important to protect your eyes from the intense glare of the desert.
- Quality Footwear: Closed-toe shoes with a good grip are necessary to navigate the uneven and often hot desert terrain.
- Thermal Wear for Evenings: Pack a lightweight jacket or thermal wear, as temperatures can drop significantly at night.
- Sunscreen: A high-SPF sunscreen is essential to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Insect Repellent: Although not abundant, insects in the Sahara can be a nuisance, so insect repellent is advisable.
Equipping yourself with the right clothing and accessories is key to enjoying the majestic beauty of the Sahara while staying protected from its harsh conditions.

Essential Gear for Sahara Desert Camping
When camping in the Sahara Desert, being well-prepared is key. The right gear can make the difference between a challenging and a rewarding experience in this extreme environment.
- Sturdy Tent: A high-quality, wind-resistant tent is crucial for protection against sandstorms and extreme weather conditions.
- Sleeping Bag and Pad: Choose a sleeping bag suitable for the desert"s fluctuating temperatures and a pad for insulation from the ground.
- Adequate Water Supply: Carry sufficient water for hydration, with additional reserves for emergencies. Consider a portable water filtration system for longer trips.
- Sun Protection: Pack sunscreen with high SPF, sunglasses, and a wide-brimmed hat to protect against the intense sun.
- Comfortable Footwear: Durable, closed-toe shoes are essential for navigating the desert terrain. Include lightweight sandals for relaxation at the campsite.
- Layered Clothing: Prepare for hot days and cold nights with a mix of lightweight, breathable clothing and warm layers for the evening.
- Navigation Tools: A compass, GPS device, and detailed maps are vital for navigation in the vast, featureless landscapes.
- First Aid Kit: Bring a comprehensive first aid kit equipped for minor injuries and emergencies.
- Portable Cooking Equipment: Compact and efficient cooking gear is necessary for preparing meals.
- Emergency Communication Device: A satellite phone or a similar device can be a lifeline in remote areas of the desert.
- Flashlights and Batteries: Reliable lighting is essential for nighttime activities and emergencies.
- Waste Disposal Supplies: Bring biodegradable bags for responsible waste management, preserving the desert"s natural beauty.
Equipping yourself with these essential items will ensure a safer and more enjoyable Sahara desert camping experience, letting you focus on the adventure and the stunning surroundings.
Navigational Tools and Safety Measures
When camping in the Sahara Desert, being well-prepared is key. The right gear can make the difference between a challenging and a rewarding experience in this extreme environment.
- Sturdy Tent: A high-quality, wind-resistant tent is crucial for protection against sandstorms and extreme weather conditions.
- Sleeping Bag and Pad: Choose a sleeping bag suitable for the desert"s fluctuating temperatures and a pad for insulation from the ground.
- Adequate Water Supply: Carry sufficient water for hydration, with additional reserves for emergencies. Consider a portable water filtration system for longer trips.
- Sun Protection: Pack sunscreen with high SPF, sunglasses, and a wide-brimmed hat to protect against the intense sun.
- Comfortable Footwear: Durable, closed-toe shoes are essential for navigating the desert terrain. Include lightweight sandals for relaxation at the campsite.
- Layered Clothing: Prepare for hot days and cold nights with a mix of lightweight, breathable clothing and warm layers for the evening.
- Navigation Tools: A compass, GPS device, and detailed maps are vital for navigation in the vast, featureless landscapes.
- First Aid Kit: Bring a comprehensive first aid kit equipped for minor injuries and emergencies.
- Portable Cooking Equipment: Compact and efficient cooking gear is necessary for preparing meals.
- Emergency Communication Device: A satellite phone or a similar device can be a lifeline in remote areas of the desert.
- Flashlights and Batteries: Reliable lighting is essential for nighttime activities and emergencies.
- Waste Disposal Supplies: Bring biodegradable bags for responsible waste management, preserving the desert"s natural beauty.
Equipping yourself with these essential items will ensure a safer and more enjoyable Sahara desert camping experience, letting you focus on the adventure and the stunning surroundings.

Historical Significance and Cultural Aspects
When camping in the Sahara Desert, being well-prepared is key. The right gear can make the difference between a challenging and a rewarding experience in this extreme environment.
- Sturdy Tent: A high-quality, wind-resistant tent is crucial for protection against sandstorms and extreme weather conditions.
- Sleeping Bag and Pad: Choose a sleeping bag suitable for the desert"s fluctuating temperatures and a pad for insulation from the ground.
- Adequate Water Supply: Carry sufficient water for hydration, with additional reserves for emergencies. Consider a portable water filtration system for longer trips.
- Sun Protection: Pack sunscreen with high SPF, sunglasses, and a wide-brimmed hat to protect against the intense sun.
- Comfortable Footwear: Durable, closed-toe shoes are essential for navigating the desert terrain. Include lightweight sandals for relaxation at the campsite.
- Layered Clothing: Prepare for hot days and cold nights with a mix of lightweight, breathable clothing and warm layers for the evening.
- Navigation Tools: A compass, GPS device, and detailed maps are vital for navigation in the vast, featureless landscapes.
- First Aid Kit: Bring a comprehensive first aid kit equipped for minor injuries and emergencies.
- Portable Cooking Equipment: Compact and efficient cooking gear is necessary for preparing meals.
- Emergency Communication Device: A satellite phone or a similar device can be a lifeline in remote areas of the desert.
- Flashlights and Batteries: Reliable lighting is essential for nighttime activities and emergencies.
- Waste Disposal Supplies: Bring biodegradable bags for responsible waste management, preserving the desert"s natural beauty.
Equipping yourself with these essential items will ensure a safer and more enjoyable Sahara desert camping experience, letting you focus on the adventure and the stunning surroundings.
Conservation Efforts and Ecological Concerns
The Sahara Desert, while seemingly inhospitable, is an ecologically sensitive area facing various environmental challenges. Conservation efforts are key to preserving its unique ecosystem.
- Desertification: One of the major concerns is the advancing desertification, which threatens the livelihoods of millions of people living in and around the desert.
- Climate Change: The impacts of climate change, including temperature increases and erratic rainfall patterns, are altering the Sahara"s ecosystem.
- Biodiversity Loss: The Sahara is home to numerous species adapted to its harsh conditions. However, habitat loss and changing climate conditions are leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity is a significant issue in this arid region, exacerbated by overuse and pollution of scarce water resources.
- Conservation Initiatives: Several initiatives, including reforestation projects and the establishment of protected areas, are underway to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Renewable Energy Projects: The Sahara"s vast open land and sunlight are ideal for renewable energy projects, like solar power, but these need to be balanced with environmental conservation.
- Eco-Tourism: Responsible eco-tourism is being promoted as a way to raise awareness and generate funds for conservation while respecting the desert’s fragile ecosystem.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring are crucial to understand the ecological changes and to inform conservation strategies.
- International Cooperation: Given the Sahara spans multiple countries, international cooperation is essential for effective environmental management and conservation.
- Local Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is key, as they are directly affected by and knowledgeable about the Sahara’s environment.
Addressing these ecological concerns through concerted conservation efforts is vital for the sustainability of the Sahara Desert"s unique environment.
READ MORE:
Popular Tourist Attractions and Activities
The Sahara Desert offers a wealth of attractions and activities for visitors seeking adventure, culture, and unparalleled natural beauty.
- Erg Chebbi and Erg Chigaga Dunes: These spectacular sand dunes in Morocco are popular for camel treks and overnight desert camping.
- Timbuktu, Mali: Once a thriving trade city, Timbuktu is now a UNESCO World Heritage site, known for its historic mosques and manuscripts.
- Tassili n"Ajjer, Algeria: This UNESCO World Heritage site is famous for its prehistoric rock art and unique sandstone formations.
- Nile River Cruises, Egypt: Cruises along the Nile River offer a glimpse into ancient Egyptian civilization on the desert’s eastern edge.
- Tuareg Cultural Tours: Experience the culture of the Tuareg people, known for their distinctive blue clothing and silver jewelry.
- Siwa Oasis, Egypt: This remote oasis is known for its Berber culture, hot springs, and the Oracle of Amun temple ruins.
- 4x4 Desert Safaris: Exciting off-road adventures through the desert landscapes offer a thrilling way to explore the Sahara.
- Star Gazing: The Sahara"s clear skies make it an ideal location for astronomical observation and stargazing.
- Sahara Marathon: An annual marathon event held in Western Sahara to raise awareness of the Sahrawi cause.
- Atlas Mountains Hiking: The Atlas Mountains on the Sahara’s northern fringe offer spectacular hiking and mountaineering experiences.
- Fossil Hunting: The Sahara’s prehistoric lakes and seas have left a rich deposit of fossils for enthusiasts to explore.
Whether it"s adventure, relaxation, or cultural exploration, the Sahara Desert provides an unforgettable experience for every traveler.
The Sahara Desert, with its unique coordinates, unveils a world of mysteries, adventures, and cultural richness, offering an unparalleled journey into one of the Earth"s most majestic natural wonders.