Topic interesting facts about the sahara desert: Embark on a fascinating journey through the Sahara Desert, a land of extremes where the secrets of nature and history blend under the blazing sun. Uncover intriguing facts about the world"s largest hot desert and its captivating allure.
Table of Content
- What are some interesting facts about the Sahara desert?
- Geographic and Climatic Features
- Historical and Prehistoric Aspects
- Flora and Fauna of the Sahara
- Human Influence and Inhabitants
- YOUTUBE: Incredible Facts About the Sahara Desert
- Economic Significance and Resources
- Environmental and Global Impact
- Challenges and Opportunities for Exploration
- Cultural Significance and Local Traditions
- Future of the Sahara: Changes and Predictions
- Mysteries and Unresolved Questions of the Sahara
What are some interesting facts about the Sahara desert?
Here are some interesting facts about the Sahara desert:
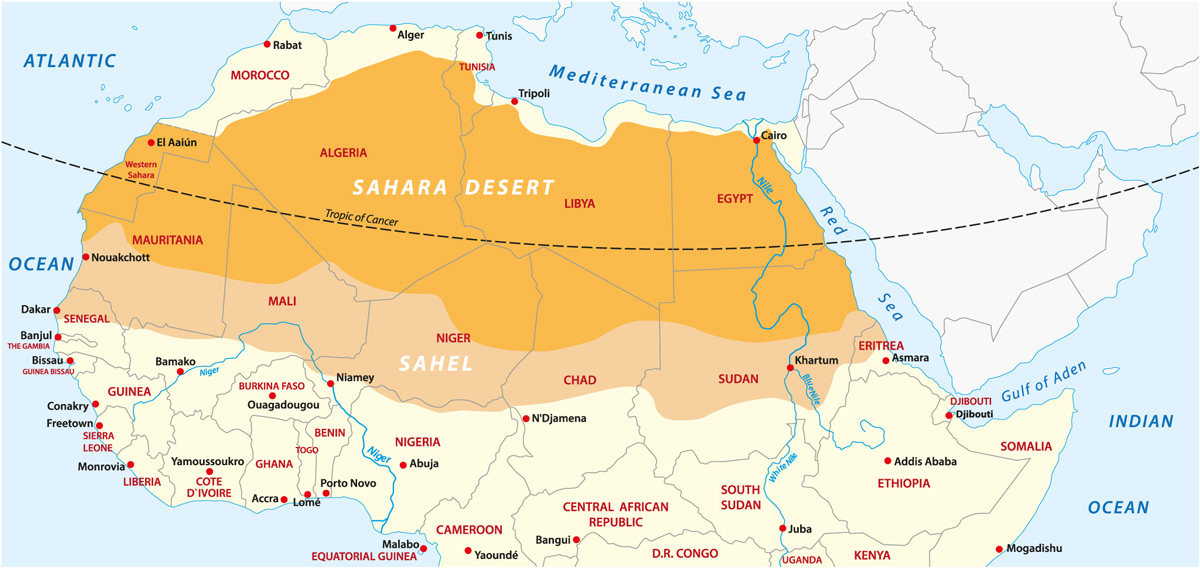
- The Sahara desert is the largest hot desert in the world, covering an area of more than 9 million square kilometers.
- It stretches across multiple countries in northern Africa, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- Despite its reputation for being a vast expanse of sand, only around 25% of the Sahara is covered by sand dunes and sheets. The majority of the desert is composed of rocky plains and gravel-covered plateaus.
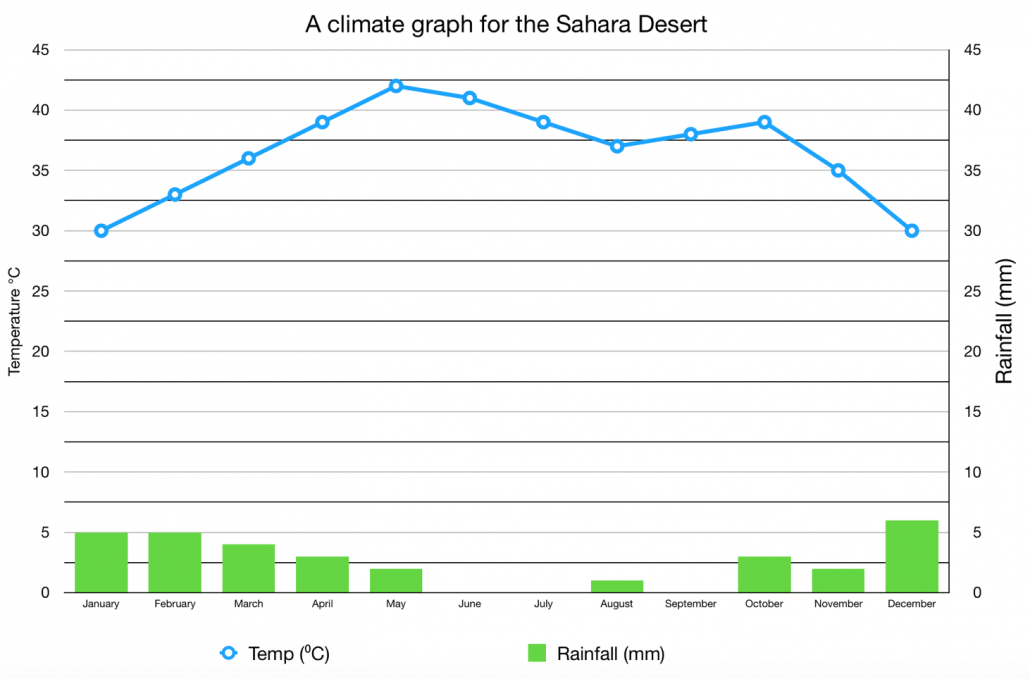
- The Sahara experiences extreme temperatures, with daytime temperatures often exceeding 50°C (122°F), while nighttime temperatures can drop below freezing.
- Annual precipitation in the Sahara is very low, ranging from almost none in some areas to around 100 millimeters in the northern regions.
- The desert is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species, some of which are specialized to survive in the harsh desert environment. This includes various species of desert-adapted mammals, reptiles, insects, and plants.
- The Sahara is known for its expansive sand dunes, which can reach heights of up to 180 meters (590 feet). These dunes are constantly reshaped by wind and can form unique patterns and shapes.
- Throughout history, the Sahara has been an important trade route, connecting Africa with the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Caravans used to travel across the desert, transporting goods such as gold, salt, and slaves.
- The desert has been inhabited by various indigenous cultures, such as the Tuareg people, who have developed unique ways of life and survival techniques in the harsh desert environment.
- The Sahara has also been the setting for several famous movies, including \"Lawrence of Arabia\" and \"The English Patient,\" due to its stunning and otherworldly landscapes.
READ MORE:
Geographic and Climatic Features
The Sahara Desert, spanning across North Africa, is the largest hot desert in the world, covering an area of approximately 9.2 million square kilometers. This vast region encompasses several countries including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara. The desert is characterized not just by its iconic sand dunes, which make up about 25% of its surface, but also by rocky hamadas, gravel plains, salt flats, and various mountain ranges.
The Sahara"s topography includes some of the world’s largest sand dunes, like the Isaouane-n-Tifernine Sand Sea in Algeria, with dunes as high as 450 meters, and the Erg Chigaga in Morocco. Additionally, it houses impressive mountain ranges such as the Air Mountains in Niger, the Hoggar Mountains in Algeria, and the Tibesti Mountains shared by Chad and Libya. The highest point in the Sahara is the Emi Koussi, a dormant volcano in Chad, reaching an elevation of 3,415 meters.
Climatically, the Sahara experiences extreme conditions with significant variability. Northern regions of the desert have arid subtropical climates with two rainy seasons, while the southern parts are more tropical but also arid with one rainy season. The desert"s edges transition to the Sahel, a semiarid region acting as a buffer zone. The Sahara is known for its high temperatures, sometimes exceeding 40°C, and minimal rainfall, especially in its central parts where some areas receive less than 20 millimeters annually. However, the Sahara has also experienced historical shifts in climate, transforming from lush green landscapes thousands of years ago to its current arid state.
The Sahara is more than a desolate landscape; it supports diverse life forms and human settlements. Despite its harsh conditions, it is home to various plant species, over a thousand in some regions, and a range of animals including the critically endangered addax antelope, fennec foxes, and Saharan cheetahs. The desert"s human population, estimated at around 2.5 million, consists of groups like the nomadic Tuareg and Berber people, who have adapted to life in this challenging environment.

Historical and Prehistoric Aspects
The Sahara Desert, rich in both history and prehistoric significance, has been a cradle of human and natural history for millennia. Ancient trade routes once flourished across this vast desert, playing a vital role in the economies of Ancient Africa. Goods such as gold, copper, and salt were transported using camel caravans, some consisting of thousands of camels, highlighting the Sahara"s importance in historic trade networks.
Archaeological discoveries have unearthed fascinating insights into the Sahara"s past. The region was not always the arid landscape we see today. Evidence suggests that thousands of years ago, the Sahara was a lush, green environment, teeming with life. This dramatic environmental change is believed to be due to shifts in the Earth"s tilt, affecting climate patterns. The Sahara is expected to undergo further transformations over time, potentially reverting to a more verdant state in the future.
The Sahara"s historical richness is further evidenced by various archaeological and paleontological finds. Discoveries like the 6000-year-old megalithic stone circles, Saharan rock paintings, and the fossilized remains of dinosaurs such as the Mansourasaurus shahinae, paint a picture of a region that has been a center of life and activity for ages. The presence of these historical artifacts indicates a diverse and vibrant history, stretching back to prehistoric times.
Today, the Sahara is home to around 2.5 million people, many of whom have Arabic or Berber roots and maintain a blend of nomadic and settled lifestyles. This human presence adds a rich cultural layer to the Sahara"s historical tapestry, continuing the legacy of one of the world"s most fascinating and diverse regions.
Flora and Fauna of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, often perceived as a vast barren landscape, is actually a biodiverse region with a variety of flora and fauna adapted to its extreme conditions. Despite its harsh environment, the Sahara supports a range of life forms, from plants to large mammals and reptiles.
- Plants: The Sahara hosts over a thousand species of plants, including those in its oases and more arid regions. The presence of underground rivers and oases contributes to this diversity, supporting species adapted to arid conditions.
- Large Mammals: Among the large mammals, the critically endangered addax antelope, dorcas, rhim, and dama gazelles, and the Saharan cheetah stand out. These animals have evolved to thrive in the challenging desert conditions.
- Small Mammals: Smaller mammals like the fennec fox, jerboas, North African gerbil, and desert hedgehog are also found here. Many of these species exhibit nocturnal behavior to avoid the extreme daytime heat.
- Reptiles and Insects: The Sahara is home to a variety of reptiles and insects, including the desert monitor lizard, skinks, horned viper, Sahara sand viper, and the essential dung beetle, which plays a crucial role in the ecosystem.
- Birds: Bird species such as the Namaqua dove, African silverbill, lappet-faced vulture, and ostrich also inhabit the Sahara, showcasing the desert"s ability to support avian life.
- Adaptations: The fauna of the Sahara have developed unique adaptations to survive. For example, many animals are nocturnal, and plant species have evolved to maximize water retention and reduce transpiration.
Despite the Sahara"s reputation as a lifeless desert, it is a region brimming with life, each species uniquely adapted to its challenging environment.

Human Influence and Inhabitants
The Sahara Desert, covering a vast land area equivalent to the United States, is home to approximately 2.5 million people, a stark contrast to the dense population of the U.S. This low population density is a testament to the harsh living conditions and the nomadic lifestyle of many Sahara inhabitants.
Despite the challenging environment, human life in the Sahara is vibrant and diverse. The Sahara has been a cradle of various cultures and ethnic groups, each contributing to the unique human landscape of the desert.
Key Inhabitants
- Tuaregs: Known for their matriarchal society, the Tuaregs are a prominent nomadic group in the Sahara. In these communities, women play a central role in literacy and business ownership.
- Moors and Toubou: Other notable nomadic tribes in the Sahara include the Moors and Toubou, who, like the Tuaregs, traverse the desert, adapting to its extreme conditions.
- Berbers: The Berbers have a rich history as nomads, navigating the desert by the stars and maintaining a unique cultural identity, including distinctive blue robes and a strong sense of community and hospitality.
Adaptations to Desert Life
Life in the Sahara is characterized by adaptation to extreme conditions. Daytime temperatures can soar above 120°F (49°C), while night temperatures may plummet. Inhabitants wear loose-fitting clothes and head wraps to protect against heat and sand.
Oases play a crucial role in Sahara life, serving as hubs of vegetation, animal life, and human settlements. These oases, surrounded by strong palm trees to protect against winds, are centers of agriculture and community life.
Cultural and Economic Aspects
The Sahara has a rich history of trade, with ancient trade routes once bustling with caravans transporting goods like gold, copper, and salt. Today, this tradition continues, albeit on a smaller scale, preserving the economic and cultural heritage of the Sahara.
Despite modern challenges and environmental threats, the people of the Sahara continue to exhibit resilience and adaptability, preserving their unique way of life in one of the world"s most extreme environments.
Incredible Facts About the Sahara Desert
Explore the awe-inspiring beauty of the Sahara Desert in this captivating video. Immerse yourself in its vast landscapes, stunning dunes, and breathtaking sunsets. Witness the resilience of life in this arid paradise, as you embark on an unforgettable journey through one of Nature\'s true wonders.
Interesting Facts About the Sahara Desert
Prepare to be amazed as this video unravels mesmerizing and little-known facts from around the world. From mind-boggling natural phenomena to fascinating historical events, this compilation will leave you awe-inspired and hungry for knowledge. Join us on this exhilarating voyage of discovery and expand your horizons with intriguing facts that are bound to pique your curiosity.
Economic Significance and Resources
The Sahara Desert is not only the world"s largest hot desert but also a treasure trove of natural resources and a hub for economic activities, shaping the lives of its inhabitants and influencing the global economy.
Natural Resources
- Oil and Natural Gas: The Sahara boasts significant reserves of oil and natural gas, particularly in Algeria and Libya. These resources are a cornerstone of the regional economy, attracting international investment.
- Minerals: The desert is rich in minerals like iron ore, found in Algeria and Mauritania, and phosphates in Morocco and Western Sahara. Other minerals include copper, manganese, and uranium, crucial for various industries.
- Water Resources: Despite its arid nature, the Sahara has vital water reserves. Oases and underground aquifers provide essential water for nomadic tribes and fauna.
Economic Activities
- Trans-Saharan Trade: Historically, the Sahara was a conduit for extensive trade routes, particularly for gold from West Africa and salt from the desert. This trade was facilitated by the introduction of camels, making long-distance desert travel feasible.
- Agriculture: In regions where water is available, particularly around oases, agriculture flourishes, contributing to the local economies.
- Tourism: The unique landscape and cultural heritage of the Sahara attract tourists, contributing to the local economy through activities like sand-boarding and desert treks.
The Sahara Desert, while harsh and challenging, is a vital region with significant economic and resource potential, playing a key role in the livelihoods of its inhabitants and the economies of surrounding countries.

Environmental and Global Impact
The Sahara Desert, while often perceived as a vast and lifeless expanse, plays a significant role in global environmental processes and climate systems. Its size, geography, and unique characteristics contribute to various global impacts.
Climate Influence and Desert Expansion
One of the Sahara"s most notable impacts is its influence on climate. The desert is expanding, with studies showing a 10% increase in its land coverage since the early 20th century. This expansion is partly attributed to natural climate cycles, but human-driven climate change also plays a role. The growth of the Sahara affects regions such as the Sahel, leading to reduced agricultural productivity and increased food insecurity.
Dust Transport and Its Effects
- Nutrient Transport: Sahara dust storms transport significant amounts of mineral-rich dust across vast distances. This dust is a source of nutrients for distant ecosystems like the Amazon rainforest, providing essential minerals that contribute to the forest"s fertility.
- Climate Regulation: The dust also impacts global climate patterns. The particles in the atmosphere can influence cloud formation, rainfall distribution, and temperature regulation.
- Marine Ecosystems: When Saharan dust falls into oceans, it can stimulate the growth of phytoplankton, which are crucial for marine food chains and play a role in carbon sequestration.
Future Projections
With ongoing climate change, the role of the Sahara in global environmental systems may evolve. Some predictions suggest a reduction in Saharan dust transport in the future, which could have cascading effects on distant ecosystems and climate regulation. However, the precise implications of these changes remain an active area of research and discussion among scientists.
The Sahara Desert is more than just a vast sandy expanse; it is an integral part of our planet"s environmental and climate systems, affecting life far beyond its borders.
Challenges and Opportunities for Exploration
The Sahara Desert, a vast and formidable landscape, presents unique challenges and opportunities for exploration. Its harsh environment, coupled with its rich history and abundant natural resources, makes it a fascinating subject for researchers and adventurers alike.
Historical Explorations
Exploration of the Sahara has a long history, dating back to classical times. Early accounts by Herodotus and Roman expeditions reveal a growing interest in the desert. Medieval travelers, such as Arab writers al-Yaʿqūbī, ash-Sharīf al-Idrīsī, and Ibn Baṭṭūṭah, contributed further to the understanding of the Sahara and its peoples. European exploration in the Sahara intensified during the 19th century, with notable explorers like Alexander Gordon Laing, René Caillié, Heinrich Barth, and others undertaking significant expeditions.
Modern Challenges
- Environmental Conditions: The extreme temperatures, vast sand dunes, and limited water sources make the Sahara one of the harshest environments for exploration.
- Logistical Challenges: Navigating the vast, featureless landscape requires advanced planning, reliable transportation, and expert knowledge of the terrain.
Opportunities for Research and Discovery
Despite these challenges, the Sahara Desert remains a rich field for scientific research and discovery.
- Archaeological Treasures: The Sahara is home to numerous archaeological sites, offering insights into ancient civilizations and human history in the region.
- Natural Resources: The desert is rich in minerals like phosphate, iron ore, and uranium, presenting opportunities for geological and environmental studies.
- Climate Change Studies: As a sensitive ecological zone, the Sahara is an important area for studying the impacts of climate change.
The Sahara Desert, with its combination of historical significance, natural beauty, and scientific value, continues to attract explorers, scientists, and adventurers from around the world.

Cultural Significance and Local Traditions
The Sahara Desert is a region of profound cultural richness, influenced by the diverse communities that inhabit this vast landscape. The cultural heritage of the Sahara is as multifaceted as its environment, characterized by unique traditions, clothing, music, dance, and rituals.
Traditional Clothing and Jewelry
The use of natural materials like animal hide, cotton, wool, and camel leather is prevalent in Saharan clothing, tailored to suit the harsh desert conditions. For example, the Tuareg tribe is known for their indigo-dyed robes called tagelmusts, symbolizing social status. Women in the Sahara often wear brightly colored dresses with intricate embroidery and beading, serving as symbols of beauty and femininity. Jewelry, such as silver necklaces and bracelets, is also significant in Saharan culture, often symbolizing wealth and prestige.
Music and Dance in Rituals
Music and dance play pivotal roles in Sahara rituals, reflecting the community"s beliefs and history. Instruments like drums, flutes, and stringed instruments are commonly used, creating a joyful atmosphere in celebrations. Different music styles like Gnawa, Tuareg Blues, and Takamba are prevalent, each with unique characteristics and historical significance.
Feasts and Ceremonies
Traditional foods hold a special place in Sahara celebrations. Dishes like couscous, tajine, dates, and honey are not just sustenance but also embody the region"s history and geography. These celebrations often emphasize values like hospitality, sharing, gratitude, and respect for elders, playing a key role in maintaining community cohesion and cultural heritage.
In conclusion, the Sahara is a region where traditional customs and modernity blend, creating a unique cultural tapestry that continues to evolve while preserving its rich heritage.
Future of the Sahara: Changes and Predictions
The future of the Sahara Desert is a subject of great interest and concern, especially in the context of climate change and environmental shifts. Several studies have highlighted key changes and predictions for this vast and dynamic region.
Expansion of the Sahara
Recent research indicates that the Sahara Desert has expanded by about 10% since the early 20th century. This expansion is largely attributed to a combination of natural climate cycles and human-driven climate changes. One significant impact of this expansion is the desertification of areas like the Sahel, a semi-arid region just south of the Sahara, which is experiencing a receding grassland ecosystem and the drying of Lake Chad, affecting millions who depend on these resources.
Climate Change Impacts
- Increased Rainfall: Predictions suggest that the Sahara and Sahel regions may experience increased rainfall due to climate change, potentially leading to periods of greening similar to the African humid periods witnessed in the past.
- Desertification: The expansion of the Sahara poses a threat to the livelihoods of people living in the Sahel region, impacting agriculture, livestock, and fisheries.
- Dust Transport: Climate change is expected to result in reduced Saharan dust transport in the future. This could have profound effects on a variety of phenomena, such as air quality, climate, and storm formation.
Environmental and Societal Challenges
The growing Sahara Desert presents both environmental and societal challenges. The reduction of arable land and changes in rainfall patterns due to the expansion of the desert could lead to food scarcity affecting millions. Additionally, the changes in the Sahara"s environment and the associated impacts on neighboring regions highlight the need for robust strategies to manage these challenges, emphasizing the importance of global cooperation in addressing climate change.
In conclusion, the Sahara Desert"s future is intertwined with global environmental trends and human activities. Understanding and addressing the changes occurring in the Sahara is crucial for the sustainable development and preservation of this unique and vital region.

READ MORE:
Mysteries and Unresolved Questions of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert is not only a vast expanse of sand and heat but also a place of deep mysteries and unresolved questions that have puzzled scientists and historians for decades. Here are some of the most intriguing enigmas of this desert.
Fairy Circles
In the Namibian part of the Sahara, millions of evenly spaced circles, known as fairy circles, dot the landscape. These circles are characterized by barren centers with rings of abundant grass around them. Despite various theories, including termite activity and competition between grasses, the exact cause of these circles remains a mystery. They are a fascinating feature, stretching over 1,100 miles and never overlapping, which suggests some level of systematic organization.
Iram of the Pillars: The Atlantis of the Sands
The story of Iram of the Pillars, also known as the Atlantis of the Sands, is a tale of a city buried by a sandstorm as a divine punishment. Its existence, once thought to be mythical, was given credence when the site of Shisr in Oman was discovered. This site, featuring ruins over 5,000 years old, is believed to be the fabled Iram, with its collapse into a sinkhole possibly explaining its disappearance.
The Richat Structure
The Richat Structure in Mauritania, also known as the Eye of the Sahara, is a prominent geological formation visible from space. It consists of concentric circles spread over 28 miles. The structure is neither a meteor crater nor the remains of a volcano, challenging the usual explanations for such formations. The current theory suggests it"s an eroded domed anticline, a dome-shaped uplift of rock strata.
Niya: A Lost Kingdom
The ancient city of Niya, once a cosmopolitan hub on the Silk Road, vanished without clear explanation. Excavations suggest a sudden abandonment, possibly due to a changing river course or drought conditions. The city, with its rich blend of cultures and extensive written records, offers an intriguing glimpse into the past.
These mysteries of the Sahara reflect the desert"s vast history and the many secrets still buried beneath its sands. From ancient civilizations to natural phenomena, the Sahara continues to be a source of fascination and intrigue.
Discover the Sahara Desert"s captivating blend of history, mystery, and natural wonders. From ancient civilizations to enigmatic phenomena, each fact unveils a story, inviting you to explore the vast, mystical allure of this legendary desert.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SaharaDesert-58c1a5603df78c353c3d525d.jpg)