Topic where is sahara desert located on a map: Discover the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, the world"s largest hot desert, intriguingly situated in North Africa and spanning across multiple countries, a marvel to explore on any map.
Table of Content
- Where is the Sahara Desert located on a map?
- Geographic Overview of the Sahara Desert
- Countries Encompassing the Sahara
- Climate Variability Within the Sahara
- Physical Features and Topography
- Historical and Cultural Significance
- Economic Resources and Challenges
- YOUTUBE: Sahara Desert Location on Africa Map
- Flora and Fauna Adaptations
- Environmental and Conservation Efforts
Where is the Sahara Desert located on a map?
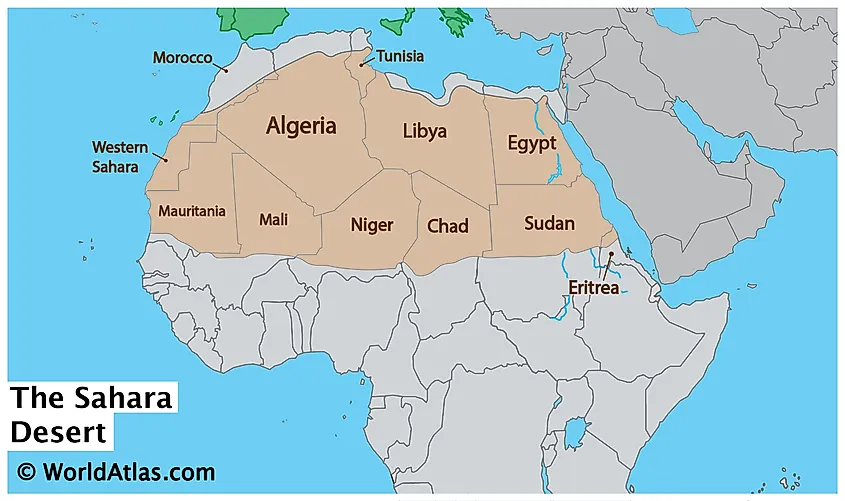
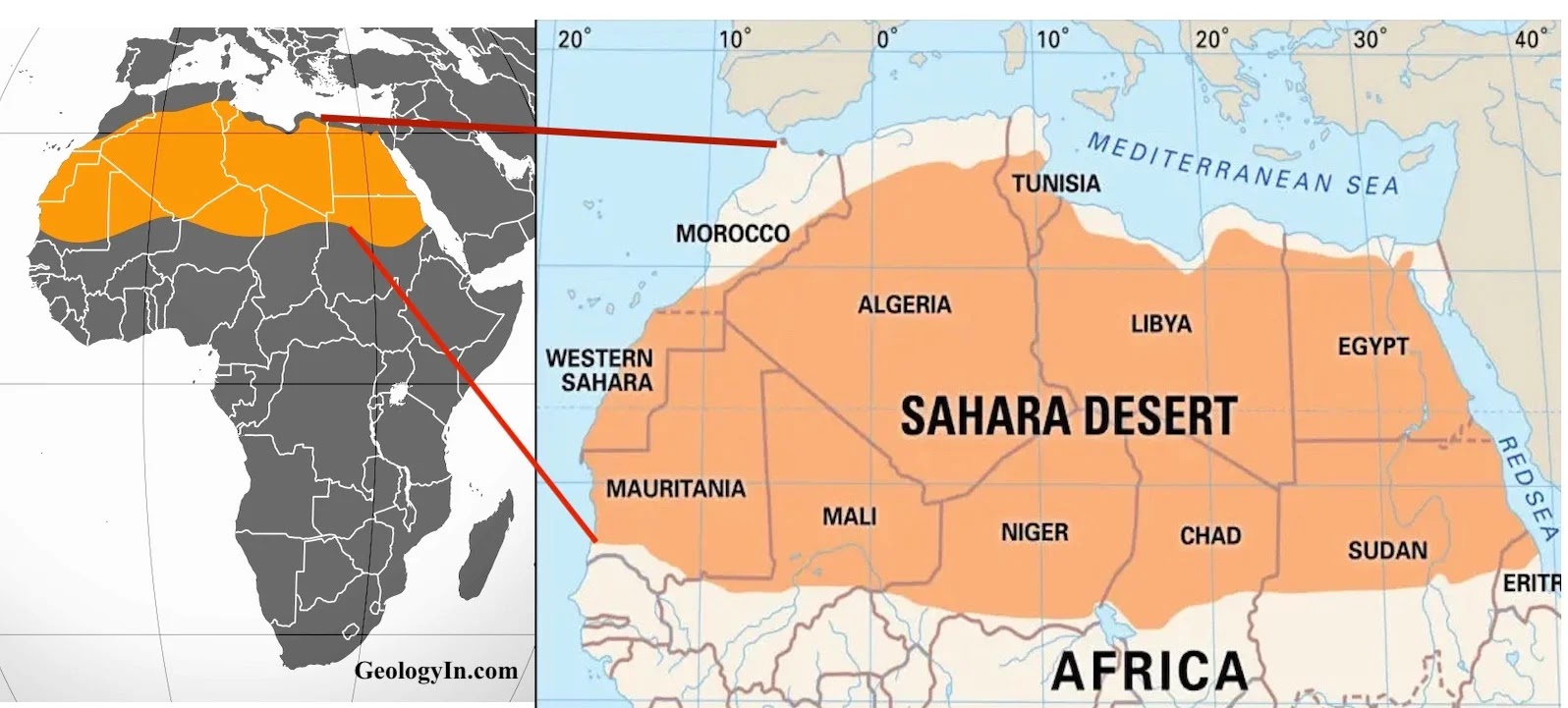
The Sahara Desert is located in northern Africa.
Here are the step-by-step instructions to locate the Sahara Desert on a map:
- Open a map of Africa.
- Identify the northern part of the continent.
- Look for the region that spans across several countries, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- This vast region is the Sahara Desert.
You can also refer to a Sahara Desert map to get a visual representation of its location.
READ MORE:
Geographic Overview of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, renowned as the largest hot desert in the world, is strategically located in North Africa. Stretching over approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers, it covers a significant portion of the continent.
- The Sahara spans several countries, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
- Geographically, it is bounded by the Red Sea to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Sahel region to the south.
- The desert"s coordinates are roughly 23°N and 13°E, placing it squarely across the Tropic of Cancer.
- Its landscape is diverse, featuring everything from vast sand dunes (ergs) and gravel plains (regs) to large plateaus and some of the world’s highest sand dunes.
- The Sahara is also home to several mountain ranges, like the Tibesti Mountains in Chad and the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria.
- Despite its arid reputation, the Sahara contains several oases, providing crucial water sources and supporting life in this harsh environment.
This immense desert not only shapes the geography of North Africa but also plays a critical role in the climate and culture of the region.

Countries Encompassing the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of arid land, extends across several countries in North Africa, each contributing unique geographic and cultural elements to this grand desert.
- Egypt: Featuring the Western Desert, the Sahara in Egypt includes striking landscapes like the Gilf Kebir plateau and numerous oases like Siwa and El Faiyum.
- Libya: The Libyan Desert portion is known for its extreme dryness and varying landscapes, including mountains and oases. It experiences high temperatures, sometimes reaching record levels.
- Mali: Covering about 65% of Mali, the Sahara here is characterized by high temperatures and features like the Niger River Valley and shifting dune formations.
- Chad: The Sahara covers most of Northern Chad, with minimal rainfall and features like oases and sporadic wells that support some agriculture.
- Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Niger, Sudan: Each of these countries also hosts a portion of the Sahara, contributing to its diverse ecology and cultural significance.
These regions collectively form the Sahara, making it not just a geographical marvel, but also a tapestry of different cultures and ecosystems.
Climate Variability Within the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, known for its extreme weather conditions, exhibits significant climatic variability across its vast expanse.
- The desert primarily experiences a hot desert climate, with clear skies allowing for high sunshine exposure, contributing to its status as one of the world"s hottest regions.
- Temperature variations are extreme, with average high temperatures during the hottest months ranging between 38° to 40°C, and record temperatures reaching around 58°C in certain locations like Aziziyah, Libya.
- Nighttime temperatures can vary significantly, dropping below freezing in the winter.
- Precipitation in the Sahara is extremely low and erratic, with some central areas receiving almost no rainfall, influenced by anticyclonic weather patterns.
- The northern fringes of the Sahara receive minimal annual rainfall due to low-pressure systems from the Mediterranean, while the southern fringes, bordering the Sahel, receive summer rainfall influenced by the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
- Historically, the Sahara has undergone cycles of arid desert conditions and lush greenery, driven by slight changes in Earth’s axial tilt, affecting monsoon activity and regional climate.
- Powerful and capricious winds from the northeast contribute to severe dust storms, impacting local visibility and carrying dust across vast distances.
This climatic diversity contributes to the unique and challenging environment of the Sahara, affecting both its ecology and the human activities within the region.
Physical Features and Topography
The Sahara Desert"s landscape is a blend of diverse physical features that add to its stunning and rugged beauty.
- The Sahara is characterized by several prominent geological features including mountains, sand dunes (ergs), rocky plateaus (hamadas), and oases.
- Mountain ranges such as the Ahaggar and Tibesti mountains are significant landforms within the Sahara, with the latter being home to the highest point in the desert.
- The desert"s varied terrain includes vast sand seas, known as ergs, which are massive areas covered with wind-swept sand.
- The Sahara is also known for its hamadas or stony plateaus that offer a stark contrast to the sandy dunes.
- Oases in the Sahara, such as Umm al-Ma Lake, provide vital water sources and are key ecological regions within the harsh desert environment.
- The desert"s topography is further marked by dry valleys and depressions, some of which are below sea level and contain salt lakes.
- Additionally, the Sahara"s landscape has been shaped by wind over time, contributing to its unique and varied topography.
This intricate interplay of physical features makes the Sahara not just a desert, but a region of fascinating geological diversity.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Sahara Desert is not just a geographical wonder but also a place of rich historical and cultural significance.
- The Sahara"s history is marked by various civilizations that have thrived in its challenging environment. Archaeological discoveries, such as prehistoric cave and rock paintings, provide evidence of human life dating back thousands of years.
- Studies indicate that the Sahara was once a lush, green oasis, alternating between arid and fertile periods due to changes in Earth’s axial tilt, influencing monsoon activity and climate.
- Ancient trade routes crossed the Sahara, facilitating the exchange of goods and culture between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa.
- The desert has been home to nomadic pastoralists, sedentary agriculturalists in oases, and various cultural groups like the Berbers, who have adapted to the challenging conditions of the Sahara.
- The Sahara has also been a source of inspiration for various forms of art, literature, and folklore, capturing the imagination of people worldwide.
- Its vast expanse and harsh conditions have often symbolized mystery and endurance in human history.
The Sahara Desert"s historical depth and cultural richness make it much more than just the largest hot desert; it is a testament to human resilience and cultural diversity.

Economic Resources and Challenges
The Sahara Desert, while harsh and unforgiving, holds significant economic resources alongside its environmental challenges.
- The Sahara is rich in natural resources, including potential reserves of oil and natural gas, particularly in Algeria and Libya, which are vital to the economies of these countries.
- Other minerals found in the Sahara include phosphates, iron ore, and uranium, contributing to the mining sector in various Saharan countries.
- Agriculture in the Sahara is limited due to the arid climate but is possible in oases where date palms and other crops are cultivated.
- Tourism is another economic resource, with many visitors attracted to the desert"s unique landscape and cultural heritage, including prehistoric sites and traditional nomadic lifestyles.
- However, the Sahara faces several environmental challenges, such as desertification, which threatens the livelihoods of those who depend on the land.
- Climate change poses a significant risk, impacting weather patterns and potentially reducing the already scarce water resources.
The Sahara"s economic resources offer opportunities for development, but these must be balanced with the need to address environmental challenges and ensure sustainable management of the desert"s resources.
Sahara Desert Location on Africa Map
Discover the mystifying beauty of the Sahara Desert located in North Africa. Immerse yourself in the stunning landscapes, endless sand dunes, and breathtaking sunsets that make this desert a must-visit destination. Watch the video to explore this enchanting location like never before.
Physical Geography of Africa / African Continent Physical Map / Africa Geographic Map
Journey through the diverse physical geography of Africa by watching this captivating video. Learn about the different natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and savannas, that shape the African continent. Get a deeper understanding of Africa\'s magnificent physical landscape and its rich biodiversity by delving into this informative video.
Flora and Fauna Adaptations
The Sahara Desert, with its extreme climate, is home to unique flora and fauna that have adapted to survive in its harsh environment.
- Flora in the Sahara includes a variety of plants that have evolved to withstand the arid conditions. These include acacia trees, succulents, Saharan cypress, grasses, date palms, tamarisk, spiny shrubs, and desert thyme. These plants typically grow shorter to reduce water loss, store water in thick stems, and have long roots to seek surface moisture.
- Many plants are ephemerals, completing most of their life cycle soon after a heavy rain. They have small thick leaves to minimize water loss through evapotranspiration.
- The Sahara"s fauna is equally adapted to the desert climate. Animal species include desert foxes, addax antelopes, gazelles, Saharan cheetah, African wild dog, hyrax, and various reptiles like the horned viper and monitor lizards.
- Some animals, like the desert snail, use estivation to survive extreme environmental stress. Many species are adapted for a Mediterranean or tropical climate and are found in the Sahara"s highlands and oases.
- Notable avian species include the red-necked ostrich, African silverbill, and the black-faced firefinch.
The adaptability of flora and fauna in the Sahara highlights the resilience of life even in the most challenging climates.
READ MORE:
Environmental and Conservation Efforts
Environmental preservation and conservation efforts in the Sahara Desert are crucial due to its unique ecosystem and the challenges it faces.
- Efforts are focused on combating desertification, a significant threat to the Sahara, caused by climate change and human activities like overgrazing and deforestation.
- Conservation projects aim to protect the unique flora and fauna of the Sahara, many of which are endemic and have adapted to the extreme desert conditions.
- Initiatives include the establishment of protected areas and national parks to safeguard biodiversity and promote sustainable land use practices.
- Research into the Sahara"s changing climate and ecological dynamics is ongoing to inform conservation strategies and adapt to environmental changes.
- International collaborations and partnerships are essential in these efforts, considering the vast expanse of the Sahara across several countries.
- Local communities play a vital role in conservation efforts, leveraging traditional knowledge and practices to sustainably manage the desert"s resources.
These environmental and conservation efforts are critical to preserving the Sahara"s unique landscape and ensuring its resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
The Sahara Desert, a marvel of nature"s extremities and cultural richness, stretches across North Africa, offering a world to be discovered, both in its vast, sandy expanses and in the resilient life it harbors.


