Topic where is the sahara desert located: Explore the vast, enigmatic Sahara Desert, the world"s largest hot desert, spanning across North Africa"s intriguing landscape. Discover its secrets and the diverse life it sustains.
Table of Content
- Where is the Sahara desert located?
- Geographical Location and Size
- Countries Encompassing the Sahara
- Climatic Conditions of the Sahara
- Ecological Diversity and Adaptations
- Historical and Cultural Significance
- Topographical Features and Landscape
- YOUTUBE: How Big Is the Sahara Desert Actually?
- Human Habitation and Lifestyle
- Environmental Challenges and Changes
- Wildlife and Conservation Efforts
- Impact on Global Climate and Weather Patterns
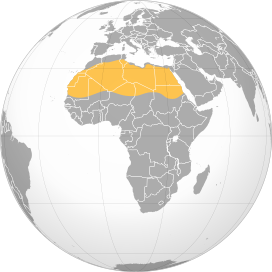
Where is the Sahara desert located?
The Sahara desert is located in
- Northern Africa
- It spans across several countries including: Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
With an area of approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 square miles), it is the largest hot desert in the world.
READ MORE:
Geographical Location and Size
The Sahara Desert, renowned as the world"s largest hot desert, spans across much of North Africa. It covers approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers, making it the third-largest desert globally, only smaller than the cold deserts of Antarctica and the Arctic.
- The desert extends from the Red Sea in the east, including parts of the Sinai Peninsula, to the Atlantic Ocean in the west.
- Its northern boundaries are marked by the Mediterranean Sea, encompassing coastal areas of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt.
- The southern edge of the Sahara borders the Sahel region, a semi-arid zone between the desert and more humid savannas of sub-Saharan Africa.
This vast desert not only includes iconic sandy dunes but also features diverse landscapes such as arid mountains, plateaus, and dry valleys. The Sahara"s climatic conditions vary, with different regions experiencing distinct weather patterns, rainfall levels, and temperatures.

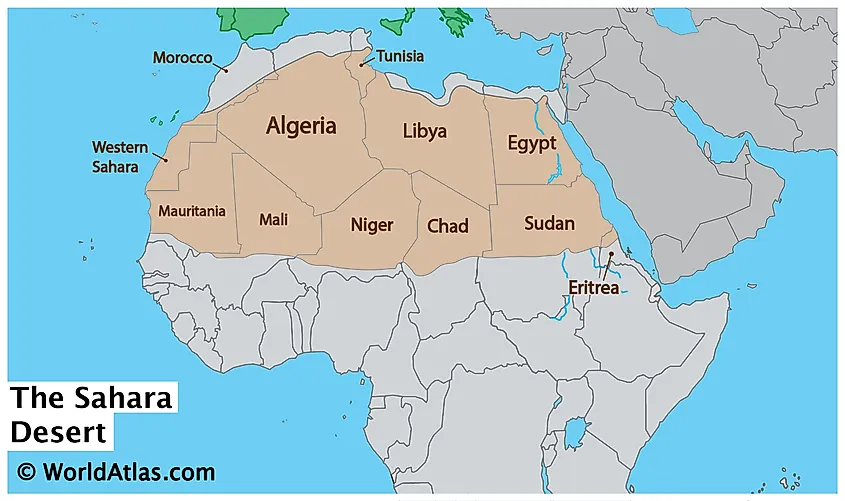
Countries Encompassing the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of arid terrain, stretches across several countries in North Africa, each contributing to the desert"s diverse cultural and geographical tapestry.
- Algeria: Home to a significant portion of the Sahara, including varied landscapes from dunes to mountains.
- Chad: Features the Sahara"s remarkable landscapes, including the Tibesti Mountains.
- Egypt: The Sahara covers the western part, including parts of the famous Nile Valley.
- Libya: A large part of this country is under the Sahara, showcasing prominent sand seas.
- Mali: Northern regions are dominated by the Sahara, affecting its climate and culture.
- Mauritania: The Sahara covers a significant area, contributing to its desert landscape.
- Morocco: The Sahara"s influence extends into southern regions, blending desert with mountainous areas.
- Niger: Encompasses eastern portions of the Sahara, including unique desert features.
- Sudan: The Sahara"s reach extends into the northern regions of the country.
- Tunisia: The Sahara"s northern dunes and arid landscapes are present here.
- Western Sahara: A disputed territory, largely consisting of desert landscapes.
These countries not only share the Sahara"s geographical features but also a rich blend of cultures and histories shaped by the desert environment.
Climatic Conditions of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, known for its extreme climate, exhibits a range of climatic variations influenced by geography and seasonal changes.
- The northern Sahara experiences a subtropical arid climate, characterized by hot summers and mild winters, with minimal rainfall distributed unevenly through the year.
- The southern Sahara, closer to the Sahel, sees slightly more rainfall and exhibits more tropical arid conditions.
- Central parts of the Sahara are the driest, receiving almost negligible annual rainfall, creating one of the most arid environments on Earth.
- Temperature variations are extreme, with daytime temperatures often exceeding 50°C (122°F) in summer and dropping to freezing at night during winter.
- Seasonal winds, like the hot, dry Harmattan, significantly influence the climate, causing sandstorms and dust devils.
The Sahara also experiences unique climatic events, such as the rare occurrence of snow in some high-altitude regions. These diverse climatic conditions contribute to the desert"s challenging yet fascinating environment.

Ecological Diversity and Adaptations
Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara Desert is a biome rich in ecological diversity and unique adaptations.
- Flora: The Sahara hosts a variety of plants like acacia trees, succulents, and date palms. These species have adapted to survive in arid conditions through deep root systems and water-conserving structures.
- Fauna: The desert supports a range of resilient animals, including mammals like the fennec fox, reptiles like the horned viper, and various bird species. Many of these animals have evolved nocturnal habits to escape the extreme daytime heat.
- Adaptations: Both flora and fauna in the Sahara have developed unique adaptations to survive. Plants often have small, thick leaves to minimize water loss, while animals may have specialized features for heat tolerance and water conservation.
- Ecoregions: The Sahara contains several distinct ecoregions, each with its own set of species and environmental conditions. These include areas like the Saharan steppe, montane xeric woodlands, and various oases.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Certain areas in the Sahara, like the oases, are biodiversity hotspots, providing critical habitats for a variety of species.
These ecological aspects highlight the Sahara"s role as a unique and important ecosystem, despite its challenging environment.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Sahara Desert has been a cradle of historical and cultural evolution, influencing and shaping the civilizations around it.
- Ancient Civilizations: The Sahara was once a more fertile region, hosting early human settlements. Archaeological findings, such as rock paintings and artifacts, indicate a rich history of human activity dating back thousands of years.
- Trans-Saharan Trade Routes: For centuries, the Sahara was a nexus for trade routes connecting sub-Saharan Africa with the Mediterranean and the Middle East, facilitating the exchange of goods and cultural ideas.
- Nomadic Cultures: The desert has been home to various nomadic tribes like the Tuareg and Berbers, known for their rich traditions, art, and survival skills adapted to the desert environment.
- Colonial History: The Sahara has seen various phases of colonial influence, particularly during the 19th and 20th centuries, impacting its geopolitical landscape.
- Religious and Spiritual Significance: The region holds religious and spiritual importance for many, with historic trade routes also serving as conduits for the spread of religions like Islam.
- Modern Cultural Influence: Today, the Sahara continues to inspire artists, writers, and filmmakers, symbolizing both the beauty and the harshness of nature.
The Sahara"s historical and cultural legacy continues to be a subject of fascination, reflecting the resilience and adaptability of human cultures in one of the world"s most challenging environments.

Topographical Features and Landscape
The Sahara Desert is characterized by a diverse topography, ranging from vast sand dunes to rugged mountain ranges.
- Sand Dunes (Ergs): The Sahara is famous for its ergs, large seas of dunes that can reach up to 150 meters in height. These dunes are formed by the action of wind and can change shape over time.
- Rocky Plateaus (Hamadas): Large stretches of the Sahara consist of rocky, barren plateaus, offering a stark contrast to the sandy dunes.
- Mountain Ranges: The desert features several mountain ranges like the Tibesti Mountains in Chad and the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria, home to some of the highest peaks in the Sahara.
- Oases: Scattered across the desert, oases are fertile areas where water is available, supporting vegetation and wildlife, as well as human settlements.
- Dry Valleys and Depressions: The Sahara includes dry valleys and depressions, the largest being the Qattara Depression in Egypt.
- Salt Flats (Chotts): In some areas, salt flats or chotts form where water evaporates, leaving behind layers of salt and other minerals.
This varied landscape not only shapes the Sahara"s unique ecosystem but also tells a story of geological processes spanning millions of years.
How Big Is the Sahara Desert Actually?
Get ready for a mesmerizing journey through the breathtaking landscapes of the Sahara Desert! Immerse yourself in the golden sand dunes and witness the serene beauty of this majestic desert, as captured in this awe-inspiring video. Don\'t miss the chance to experience the allure of the Sahara Desert right from your screen!
Which Countries Does the Sahara Desert Cover?
Embark on an incredible visual exploration of countries around the world! From the vibrant streets of bustling cities to the tranquil beauty of remote villages, this captivating video showcases the diverse cultures, rich heritage, and stunning landmarks of different countries. Pack your virtual bags and join this global adventure today!
Human Habitation and Lifestyle
The Sahara Desert, despite its harsh environment, is home to diverse communities that have adapted to the desert lifestyle over centuries.
- Nomadic Tribes: The Sahara is known for its nomadic tribes like the Tuareg and Berbers. These groups have historically moved across the desert, living in temporary settlements.
- Settled Communities: There are also settled communities in the Sahara, often located around oases where agriculture is possible. These settlements are centers of culture and trade.
- Lifestyle and Survival: Life in the Sahara requires adaptation to extreme conditions. Inhabitants often rely on livestock such as goats and camels, and have developed unique architectural styles to cope with the climate.
- Cultural Practices: The people of the Sahara have rich cultural traditions, including music, art, and festivals, that reflect their history and environment.
- Modern Changes: In recent times, some Sahara inhabitants have shifted to a more sedentary lifestyle due to factors like climate change, economic opportunities, and political borders.
- Economic Activities: Aside from agriculture, economic activities in the Sahara include mining, trade, and increasingly, tourism.
This human aspect of the Sahara reflects the resilience and ingenuity of its inhabitants in adapting to one of the world"s most challenging environments.
Environmental Challenges and Changes
The Sahara Desert faces several environmental challenges and is undergoing significant changes impacting both the local and global environment.
- Desertification: The expansion of desert landscapes, often due to human activities like overgrazing and deforestation, is a major concern. This process reduces arable land and leads to the loss of biodiversity.
- Climate Change: Changes in global climate patterns are affecting the Sahara, leading to variations in rainfall and temperature, which can further exacerbate desertification and impact local ecosystems.
- Water Scarcity: Limited and unpredictable rainfall, coupled with increasing demand for water resources, poses a significant challenge for inhabitants and wildlife in the Sahara.
- Biodiversity Loss: The harsh conditions and environmental changes are threatening the survival of various species, leading to a reduction in biodiversity.
- Human Impact: Increasing human activities, such as mining and urbanization, are altering the natural landscape and putting pressure on the fragile desert ecosystem.
- Air and Sand Pollution: Dust storms, common in the Sahara, contribute to air pollution and carry sand particles over long distances, affecting air quality and ecosystems far beyond the desert.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts and sustainable practices to preserve this unique and vital ecosystem for future generations.
Wildlife and Conservation Efforts
The Sahara Desert, despite its harsh conditions, hosts a unique array of wildlife, and there are ongoing efforts to conserve this fragile ecosystem.
- Diverse Fauna: The Sahara is home to various species adapted to the desert environment, including mammals like the fennec fox, reptiles such as the horned viper, and numerous bird species.
- Endangered Species: Some Sahara wildlife, like the Saharan cheetah and the addax antelope, are critically endangered due to factors like habitat loss and hunting.
- Adaptation to Desert Life: Animals in the Sahara have developed unique adaptations to survive in the extreme conditions, such as nocturnal habits to avoid daytime heat.
- Conservation Initiatives: Efforts are being made to protect endangered species and habitats, including the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves.
- Research and Monitoring: Scientific research and monitoring are crucial for understanding the desert"s ecosystem and the impact of environmental changes.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for sustainable wildlife protection and habitat preservation.
These conservation efforts are critical to maintaining the Sahara"s ecological balance and ensuring the survival of its unique wildlife.
READ MORE:
Impact on Global Climate and Weather Patterns
The Sahara Desert plays a significant role in influencing global climate and weather patterns.
- Heat Generation: The Sahara acts as a major heat source, especially in the summer, affecting atmospheric conditions and contributing to the formation of weather systems.
- Dust Transport: The Sahara is a major source of mineral dust, which is carried by winds across the globe. This dust can impact weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and even air quality in distant regions.
- Influence on Monsoons: The desert"s heat impacts the African Monsoon system, which is crucial for rainfall in the Sahel region and other parts of Africa.
- Impact on Atlantic Hurricanes: Dust and hot air from the Sahara can influence the development of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Global Climate Interaction: The desert interacts with various global climate systems, impacting phenomena such as El Niño and the North Atlantic Oscillation.
The Sahara"s impact on weather and climate extends well beyond its borders, highlighting the interconnectedness of global environmental systems.
The Sahara Desert, a marvel of nature and a testament to Earth"s diversity, stands as a symbol of endurance and mystery, inviting us to explore and appreciate the wonders of our planet.

