Topic location of sahara desert in africa: Discover the vast and enigmatic Sahara Desert, a majestic expanse in Africa that captivates with its rich history, diverse ecology, and stunning landscapes. Unearth the secrets of this unparalleled desert"s location and allure.
Table of Content
- What is the location of the Sahara Desert in Africa?
- Overview of the Sahara Desert
- Geographical Location and Size
- Countries Encompassing the Sahara
- Physical Features and Topography
- Climatic Conditions
- Ecological Regions and Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
- Historical and Cultural Significance
- Modern Day Sahara
- Travel and Exploration in the Sahara
What is the location of the Sahara Desert in Africa?
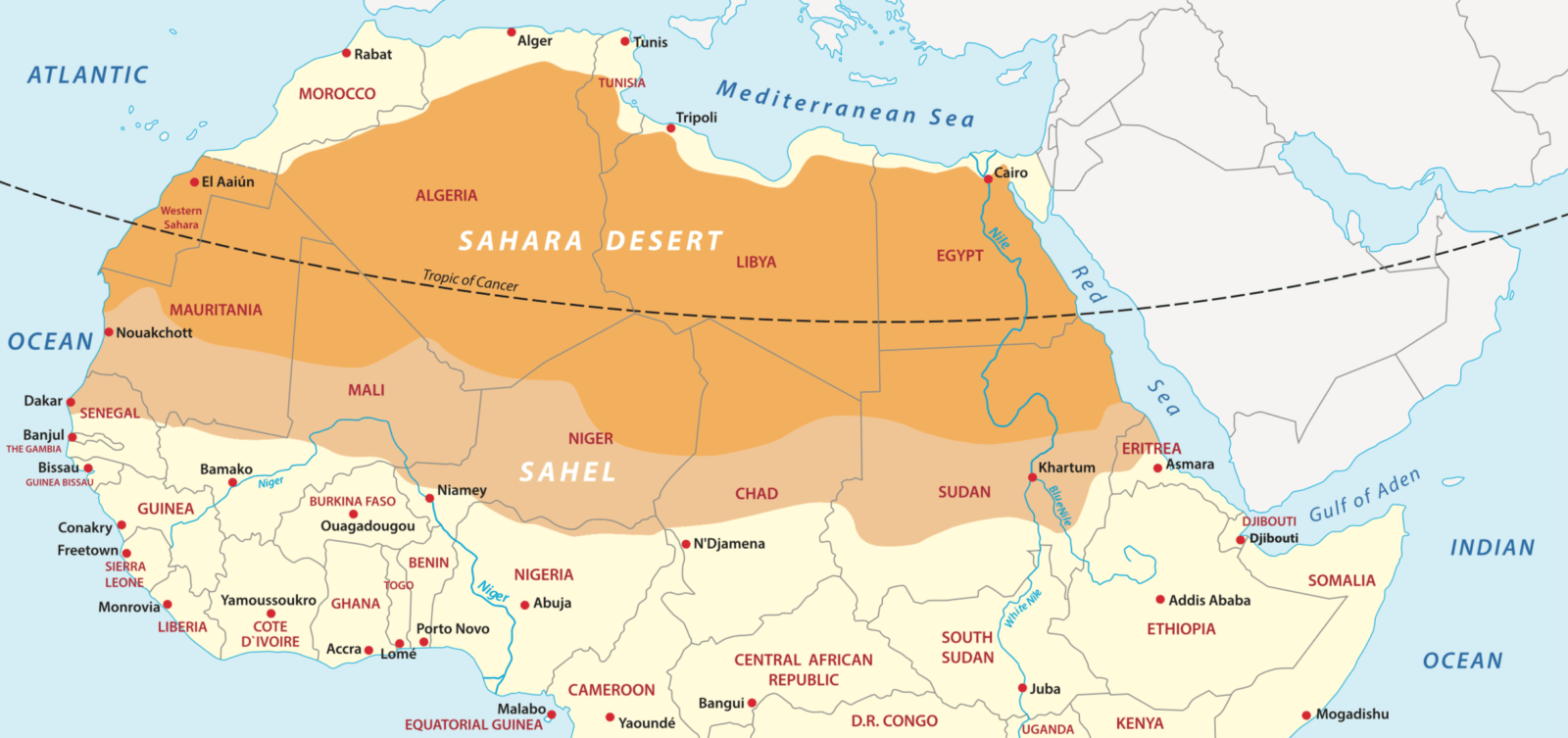
The Sahara Desert is located in the northern part of Africa and covers a significant portion of the continent.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of its location:
- The Sahara Desert is the largest desert in the world, stretching approximately 3000 miles (4800 km) from east to west.
- It fills most of Northern Africa, spanning across multiple countries.
- The desert extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east.
- To the north, it is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlas Mountains of the Maghreb region.
- To the south, the Sahara Desert gradually transitions into the Sahel region, which is a semi-arid transitional zone.
- The Nile Valley, known for its fertility, is one of the few areas within the desert that supports significant human settlements.
Overall, the Sahara Desert\'s location in Africa encompasses a vast expanse of arid land, making it an iconic feature of the continent.
READ MORE:
Overview of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, an awe-inspiring landscape, stands as the largest hot desert in the world. Stretching across North Africa, it serves as a natural wonder with a rich tapestry of ecosystems, cultures, and histories.
- Geographical Span: Covering over 9 million square kilometers, the Sahara extends across multiple African countries, offering a diverse range of terrains from vast sand dunes to rocky plateaus.
- Climate Variability: The Sahara is characterized by its arid climate, with extreme temperature variations. It experiences minimal rainfall and intense sunlight, creating a unique and challenging environment.
- Ecological Diversity: Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara is home to a variety of wildlife and plant species, each uniquely adapted to the desert environment.
- Cultural Significance: The desert has been a cradle for various nomadic tribes throughout history, each contributing to the rich cultural tapestry that defines the Sahara today.
- Historical Importance: The Sahara has played a pivotal role in human history, serving as a trade route and a center for learning and civilization in ancient times.
Exploring the Sahara offers a journey into an enigmatic and ever-changing landscape, revealing the resilience of life and the enduring allure of one of Earth"s greatest natural wonders.

Geographical Location and Size
The Sahara Desert, renowned as a geographical marvel, is the world"s largest hot desert, spanning several countries in North Africa. Its vastness and varied landscapes offer a glimpse into the earth"s incredible diversity.
- Immense Scale: Encompassing approximately 9 million square kilometers, the Sahara Desert is roughly the size of the United States, making it a significant geographical landmark.
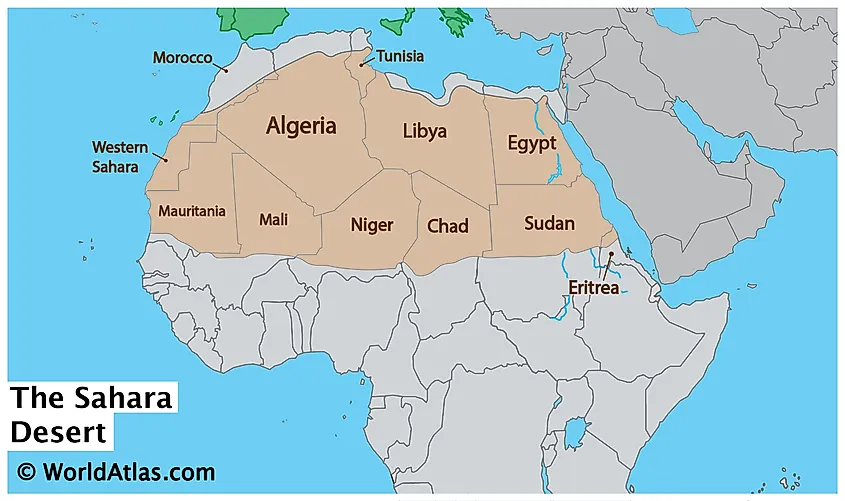
- Spanning Continents: The desert stretches across several countries, including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
- Natural Boundaries: It is bordered by the Atlas Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Red Sea to the east, and transitions into the Sahel region to the south.
- Varied Terrain: Contrary to popular belief, the Sahara is not just a sandy expanse. It features diverse landscapes, including dunes, mountains, plateaus, and oases.
- Geographical Coordinates: Positioned predominantly between 20° N and 30° N latitudes and 15° W and 30° E longitudes, the Sahara plays a crucial role in the region"s climate and ecology.
This vast desert, with its sheer size and geographic diversity, continues to captivate scientists, adventurers, and nature enthusiasts alike, revealing the endless wonders of our planet.
Countries Encompassing the Sahara
The Sahara Desert"s immense expanse crosses several nations, each contributing to its diverse landscape and cultural tapestry. This vast desert landscape is shared among numerous African countries, each with its unique connection to this majestic desert.
- Algeria: Covering a significant portion of Algeria, the Sahara"s landscapes here vary from sand dunes to rocky plateaus.
- Chad: Home to diverse wildlife, Chad"s part of the Sahara includes the stunning Tibesti Mountains.
- Egypt: The Sahara here features some of the most famous archaeological sites, including parts of the Nile Valley civilization.
- Libya: The Libyan Desert, a part of the Sahara, is known for its extreme aridity and vast sand seas.
- Mali: Mali"s Sahara region is rich in history and culture, featuring legendary cities like Timbuktu.
- Mauritania: Hosting unique landscapes, Mauritania"s portion of the Sahara includes the eye-catching Adrar Plateau.
- Morocco: The Moroccan Sahara is a blend of historical sites and diverse ecosystems.
- Niger: The Sahara covers much of northern Niger, presenting a mix of desert landscapes and cultural heritage.
- Sudan: Sudan"s Sahara region is known for its arid landscapes and historical significance.
- Tunisia: The Tunisian Sahara offers a mix of desert dunes and oases, featuring unique flora and fauna.
- Western Sahara: This disputed territory features some of the Sahara"s most iconic desert landscapes.
Together, these countries frame the Sahara, each contributing to the desert"s grandeur and mystique, making it a symbol of natural and cultural diversity.
Physical Features and Topography
The Sahara Desert is not just a vast expanse of sand; it is a region of diverse topography and unique physical features. This magnificent desert is characterized by a variety of landscapes, each with its own distinct beauty and challenges.
- Sand Dunes (Ergs): Perhaps the most iconic feature, these large areas of sand dunes, such as the Grand Erg Oriental, can rise to heights of over 150 meters.
- Rocky Plateaus (Hamadas): These are extensive stretches of largely barren, hard, rocky plateaus, providing a stark contrast to the soft sand dunes.
- Mountain Ranges: The Sahara is home to several mountain ranges like the Tibesti Mountains in Chad, which include the highest peak in the desert, Emi Koussi.
- Depressions and Oases: The desert also features depressions like the Qattara Depression in Egypt and numerous oases, providing essential water sources.
- Gravel Plains (Reg): These are vast, wind-swept plains covered with sand and gravel, more common in the desert’s margins.
- Dry Valleys (Wadis): Seasonal rivers form these valleys, which are often dry but can fill rapidly during rare rainfalls.
- Salt Flats (Chotts): These are flat areas where salt crusts form over the ground, often found in the desert"s northern regions.
Each of these features contributes to the Sahara’s breathtaking scenery and formidable environment, making it a place of both great beauty and extreme conditions.
Climatic Conditions
The Sahara Desert is known for its extreme climate, which is one of the most challenging aspects of this vast region. The desert experiences some of the most extreme weather conditions on the planet, influencing both its landscape and the life that resides within it.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is characterized by some of the highest temperatures recorded on earth, often exceeding 50°C (122°F) in the summer, while winter temperatures can drop below freezing.
- Rainfall: It is one of the driest regions in the world, with some parts not seeing rain for years at a time. Annual rainfall is generally less than 3 inches.
- Diurnal Temperature Variation: The desert experiences significant temperature swings between day and night, due to the lack of humidity and vegetation to retain the day"s heat.
- Wind Patterns: The Sahara is also known for its strong winds, including the hot, dry, and dusty Harmattan wind, which can dramatically affect the climate and visibility.
- Microclimates: Despite its overall aridity, the Sahara has varied microclimates. These are influenced by factors such as altitude, proximity to the Atlantic Ocean or the Mediterranean Sea, and the presence of mountain ranges.
Understanding the climatic conditions of the Sahara is crucial for grasping the challenges and adaptations of both human and wildlife that inhabit this extreme environment.

Ecological Regions and Biodiversity
The Sahara Desert, spanning over 3.6 million square miles across northern Africa, is not only a vast expanse of sand but also a region of diverse ecological zones and rich biodiversity. Contrary to popular belief, the Sahara is not a homogeneous desert landscape; it comprises several ecological regions, each with its unique flora and fauna.
Major Ecological Zones
- Oasis Ecosystems: Scattered across the desert, oases are vibrant hubs of life. They are home to date palms, various fruit trees, and crops, sustained by natural springs or wells.
- Mountain Ranges: The Sahara includes significant mountain ranges like the Atlas Mountains in Morocco and Algeria and the Tibesti Mountains in Chad. These highlands harbor distinct species adapted to cooler and wetter conditions.
- Sand Dunes and Plains: Iconic for their vast dunes, these areas also support specially adapted species that can survive extreme conditions.
- Rocky Plateaus: These regions offer a harsh landscape, where only the hardiest of species can thrive.
Flora and Fauna
The Sahara"s plant life is predominantly xerophytic, adapted to arid conditions. Many plants are ephemerals, blooming spectacularly soon after rare rains. Animal life in the Sahara includes mammals like the Fennec fox, reptiles like the Sahara horned viper, and a variety of bird species. Nomadic pastoralists also graze their livestock in the region, adapting to the challenging environment.
Adaptation and Survival
Life in the Sahara has adapted in remarkable ways to cope with the extreme environment. Many animals are nocturnal, avoiding the intense daytime heat. Plants have adapted to conserve water, and people have historically relied on nomadic lifestyles and oasis farming to survive.
Environmental Challenges
While the Sahara is resilient, it faces environmental challenges such as climate change, which impacts rainfall patterns and temperatures, potentially affecting its delicate ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the Sahara"s unique biodiversity. These include protecting endangered species, preserving natural habitats, and sustainable management of natural resources.
The Sahara Desert Ecosystems
Ecosystems: Explore the diverse beauty and intricate connections within ecosystems in this captivating video. From lush rainforests to vibrant coral reefs, witness the wonders of nature come to life like never before. Mauritania: Immerse yourself in the rich culture and stunning landscapes of Mauritania through this visually stunning video. From the Sahara desert dunes to the bustling markets of Nouakchott, experience the vibrant tapestry of this West African gem.
Mauritania: Where The Sahara Desert Meets the Ocean
In human cultures in general, and perhaps particularly in Africa, the landscape is the first shrine of tradition. From the sand dunes ...
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Sahara Desert has been a cradle of historical and cultural evolution for millennia, influencing and shaping the civilizations of North Africa and beyond. This vast desert has been a witness to the rise and fall of empires, a crossroads for trade routes, and a canvas for ancient art and architecture.
Ancient Civilizations
- The Nile Valley Civilization thrived on the Sahara"s eastern edge, utilizing the fertile lands for agriculture and establishing a lasting cultural and architectural legacy.
- Berber Tribes have historically inhabited the Sahara, developing unique cultural practices adapted to desert life.
- Remnants of the Garamantes Civilization in modern-day Libya show advanced irrigation systems and fortifications.
Trade Routes and Caravans
The Sahara was central to the trans-Saharan trade, connecting sub-Saharan Africa with the Mediterranean world. Caravans of camels transported gold, salt, and other goods, fostering economic and cultural exchanges.
Rock Art and Archaeology
- The Sahara boasts a rich collection of rock art, revealing insights into the prehistoric environment and human life.
- Archaeological sites like the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria and Tassili n"Ajjer reveal paintings and engravings dating back thousands of years.
Islamic Influence
With the spread of Islam, the Sahara saw the rise of Islamic architecture and scholarly centers, notably in cities like Timbuktu.
Modern Cultural Impact
Today, the Sahara continues to inspire artists, writers, and filmmakers, symbolizing both harsh challenges and serene beauty.
Preserving Heritage
Efforts are ongoing to preserve the Sahara"s rich historical and cultural heritage, safeguarding it for future generations.
Modern Day Sahara
The Sahara Desert today is a dynamic landscape, reflecting both the challenges and opportunities of the modern world. While it retains much of its timeless allure and natural beauty, the Sahara is also a region undergoing significant environmental, social, and economic changes.
Environmental Changes
- Climate Change: The Sahara is experiencing shifts in climate patterns, with some areas seeing increased desertification and others observing unusual rainfall.
- Biodiversity: Efforts are being made to preserve the unique flora and fauna of the Sahara, which face threats from habitat loss and climate change.
Economic Development
- Natural Resources: The Sahara is rich in resources like oil, natural gas, and minerals, attracting global investment and economic activities.
- Renewable Energy: Large-scale renewable energy projects, especially solar power, are being explored, harnessing the Sahara"s vast potential for sustainable energy production.
Social Dynamics
- Traditional Lifestyles: Nomadic tribes continue to traverse the Sahara, maintaining centuries-old cultural practices and herding techniques.
- Urbanization: Increasing urbanization in Sahara-bordering countries is influencing the demographic and economic landscape of the region.
Technology and Connectivity
Advancements in technology are transforming life in the Sahara, with improved communication tools and access to global markets.
Travel and Tourism
The Sahara remains a destination for adventurers and tourists, drawn by its majestic landscapes, rich history, and unique cultural experiences.
Conservation and Sustainability
Conservation initiatives aim to balance the development and preservation of the Sahara, ensuring its resilience and sustainability for future generations.
READ MORE:
Travel and Exploration in the Sahara
Traveling through the Sahara Desert offers an unparalleled opportunity to experience one of the world"s most extraordinary landscapes. From vast sand dunes to ancient cultural sites, the Sahara is a destination that captivates adventurers, historians, and nature lovers alike.
Planning Your Journey
- Best Time to Visit: The best time to explore the Sahara is during the cooler months, typically from October to April, when the temperatures are more tolerable.
- Travel Essentials: Adequate preparation is key. Essentials include a good supply of water, sun protection, appropriate clothing, and navigation tools.
Popular Destinations
- Morocco"s Erg Chebbi: Famous for its stunning orange-colored dunes and camel treks.
- Egypt"s Siwa Oasis: Known for its rich history and unique culture, nestled between the sand and palm trees.
- Algeria"s Tassili n"Ajjer: A UNESCO World Heritage site, home to prehistoric rock art and diverse landscapes.
Activities and Adventures
- Camel Trekking: A traditional way to experience the desert, offering a unique perspective of the vast landscape.
- 4x4 Safaris: For those seeking an adrenaline rush, off-road safaris provide an exciting way to explore remote areas.
- Stargazing: The Sahara"s clear skies are perfect for astronomical observation and photography.
Cultural Experiences
Visiting local communities and participating in cultural events can enrich your Sahara experience, offering insights into the traditions and lifestyles of the desert inhabitants.
Environmental Responsibility
Travelers are encouraged to practice sustainable tourism, respecting the fragile desert environment and supporting local conservation efforts.
Safety Considerations
While exploring the Sahara, it"s important to be aware of safety. Hiring a local guide, staying informed about regional conditions, and having a reliable means of communication are essential for a safe journey.
Discover the Sahara, a majestic desert spanning Africa, rich in history, culture, and breathtaking landscapes, promising an unforgettable journey into the heart of this vast and enigmatic land.