Topic location sahara desert: Embark on a journey through the Sahara Desert, a realm of awe-inspiring landscapes and rich history, unfolding the secrets of its strategic location and the diverse cultures that thrive amidst its vast dunes.
Table of Content
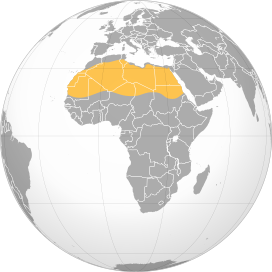
Where is the Sahara Desert located?
The Sahara Desert is located in northern Africa.
It spans across several countries, including:
- Algeria
- Chad
- Egypt
- Libya
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Morocco
- Niger
- Western Sahara
- Sudan
- Tunisia
With a total area of approximately 9 million square kilometers, the Sahara is the largest desert in the world.
READ MORE:
Geographical Overview
The Sahara Desert, an immense expanse of arid terrain, stands as the largest hot desert in the world. Spanning across the northern stretch of Africa, it covers approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, creating a natural barrier that shapes the geography and cultures of the continent.
- Location: Predominantly situated in North Africa, the Sahara stretches from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. It encompasses several countries including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
- Climate Zones: The Sahara is characterized by its diverse climate zones. The northern regions experience a subtropical arid climate with two rainy seasons, while the southern areas are more tropical and receive just one rainy season.
- Physical Features: The desert is home to varied landscapes, from vast sand dunes to rocky plateaus and mountain ranges. The Sahara"s iconic sand dunes, known as ergs, cover only about 15% of its area.
- Biomes: Bordering the Sahara are the Sahel to the south, a semi-arid region acting as a transitional zone, and the Mediterranean and Atlas Mountains to the north, offering contrasting environments.
- Historical Impact: Historically, the Sahara has been a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. Its location and challenging environment have played a significant role in the development and history of the African continent.
The Sahara"s sheer size and geographical diversity make it a subject of continuous fascination and study, profoundly impacting the climate, ecology, and cultures of the surrounding regions.

Climatic Conditions
The Sahara Desert is renowned for its extreme climatic conditions, which vary significantly across its vast expanse. Its climate is one of the key elements defining the life and landscape of this region.
- Temperature Extremes: The Sahara is known for some of the most extreme temperature variations on the planet. Daytime temperatures often soar above 50°C (122°F), while at night, they can plummet dramatically, especially in the winter months.
- Rainfall Patterns: Rainfall in the Sahara is scarce and irregular. The northern and southern fringes of the desert receive minimal annual rainfall, typically between 4 and 10 inches, while central parts often experience years without any rainfall.
- Wind Patterns: The desert is also characterized by its powerful wind systems, which can cause severe sandstorms and dust devils. These winds play a significant role in shaping the desert"s landscape and climate.
- Seasonal Variability: While generally hot and dry, the Sahara experiences some seasonal variability. The north experiences a subtropical climate with two rainy seasons, whereas the south has a more tropical climate with one rainy season.
- Climatic Changes Over Time: Historically, the climate of the Sahara has undergone dramatic shifts. Studies have shown that it alternates between arid and more humid phases, greatly affecting the flora and fauna of the region.
The harsh climatic conditions of the Sahara, with its searing heat and scarce rainfall, have shaped both the natural environment and human adaptation strategies in this vast desert landscape.
Ecology and Biodiversity
The Sahara Desert, often perceived as a lifeless expanse, is in fact a dynamic ecosystem with a unique array of biodiversity adapted to its challenging environment.
- Varied Ecosystems: The Sahara encompasses several ecological regions, each with distinct characteristics. These include the Atlantic Coastal Desert, the North Saharan steppe and woodlands, the central Sahara Desert region, the South Saharan steppe and woodlands, and the West Saharan Montane Xeric Woodlands.
- Plant Life: Despite harsh conditions, the Sahara is home to approximately 2,800 species of plants. Adaptations like short growth to reduce wind exposure, thick stems for water storage, and long roots for moisture absorption are common. Key species include acacia trees, date palms, and various shrubs and grasses.
- Animal Species: The desert supports a range of fauna, including mammals like the addax antelope, gazelles, and the fennec fox; reptiles such as the horned viper; and various bird species. These animals have adapted to survive in extreme heat and aridity.
- Endemic Species: The Sahara hosts a number of endemic species, particularly among its plant life, showcasing the unique evolutionary paths taken in this isolated environment.
- Environmental Challenges: The fragile ecosystem of the Sahara faces threats from climate change, human activities, and desertification, impacting the delicate balance of life here.
Understanding the ecology and biodiversity of the Sahara is crucial for its conservation, highlighting the need for sustainable practices to protect this unique and ancient landscape.

Landscape and Topography
The Sahara Desert"s landscape and topography are as diverse as they are expansive, offering a stunning array of geographical features.
- Sand Dunes: Often the most iconic image of the Sahara, these dunes, or "ergs", cover only a fraction of the desert but are among its most visually striking features. They vary in shape and size, with some reaching heights of up to 150 meters.
- Rocky Plateaus: Large stretches of the Sahara are covered by rocky, barren plateaus known as "hamadas", which are elevated areas of largely bedrock surface.
- Mountain Ranges: The desert is home to several mountain ranges, such as the Tibesti Mountains in Chad and the Ahaggar Mountains in Algeria. These ranges include some of the highest points in the Sahara.
- Depressions and Basins: The Sahara contains various depressions and basins, the most famous being the Qattara Depression in Egypt, which lies below sea level.
- Oases: Scattered across the desert, oases are vital for sustaining life. These fertile areas, where water is available, support a variety of plant and animal life and human settlements.
- River Valleys: While predominantly arid, the Sahara has river valleys such as the Nile Valley, which play a crucial role in supporting life in these regions.
This diverse topography not only shapes the physical appearance of the Sahara but also influences the climate, ecology, and human activities within the desert.
Human Presence and Culture
The Sahara Desert is not just a natural wonder but also a cradle of diverse human cultures and historical legacies.
- Indigenous Peoples: The Sahara has been home to various indigenous groups for thousands of years. Notable among them are the Tuareg, Berber, and Bedouin peoples, each with unique cultural traditions, languages, and lifestyles.
- Adaptation to the Environment: Life in the Sahara is shaped by the desert"s harsh conditions. These communities have adapted with nomadic lifestyles, traditional knowledge of water sources, and unique architectural styles to cope with the extreme climate.
- Historical Trade Routes: Historically, the Sahara was a hub for trans-Saharan trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods and culture between North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa. This trade significantly influenced the cultural and economic development of the region.
- Archaeological Sites: The Sahara is dotted with archaeological sites, including rock art, which provide insights into the prehistoric communities that once thrived in this now harsh environment.
- Modern Changes: Contemporary life in the Sahara has been influenced by modern developments. The discovery of natural resources like oil and minerals has led to urbanization and a shift from traditional nomadic lifestyles to more settled ways of living.
This rich tapestry of human presence and culture in the Sahara underscores the resilience and adaptability of its inhabitants in one of the world"s most challenging environments.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation
The Sahara Desert faces significant environmental challenges that require concerted efforts for conservation and sustainable management.
- Climate Change: The impacts of global climate change are profoundly felt in the Sahara, with rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns exacerbating desertification and affecting the delicate balance of its ecosystems.
- Desertification: The expansion of desert landscapes, partly due to human activities such as overgrazing and deforestation, threatens the livelihoods of millions of people living at the desert"s margins and leads to loss of biodiversity.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity is a major concern in the Sahara, where access to sustainable and clean water sources is critical for the survival of both human populations and wildlife.
- Conservation Efforts: Various conservation projects aim to protect the Sahara"s unique ecosystems. These include establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable land use practices, and preserving the habitats of endangered species.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial, as their knowledge and participation are key to sustainable environmental management and the protection of the Sahara"s natural heritage.
Addressing these environmental challenges is vital for ensuring the sustainability of the Sahara Desert, not only as a natural wonder but also as a habitat for diverse species and home to human communities.
Sahara Desert Size: Unveiling its True Magnitude
\"Discover the significance of size as we delve into mind-boggling facts about the largest creatures on our planet. Get ready to be amazed by the sheer magnitude and beauty of these incredible beings in our captivating video!\"
Sahara Desert Ecosystems Explored
\"Embark on an awe-inspiring journey through the intricate web of life in Earth\'s diverse ecosystems. Watch our mesmerizing video to witness the breathtaking harmony and delicate balance that exists between all living organisms, showcasing the beauty and resilience of our planet.\"
READ MORE:
Travel and Exploration
Exploring the Sahara Desert offers a unique and unforgettable adventure for travelers, combining natural beauty, cultural richness, and historical significance.
- Guided Tours: For a safe and informed journey, guided tours are recommended. Experienced guides can navigate the challenging terrain and provide insights into the desert"s history and ecology.
- Popular Destinations: Key destinations include the majestic sand dunes of Erg Chebbi in Morocco, the ancient rock art in Algeria"s Tassili n"Ajjer, and the bustling markets of Timbuktu in Mali.
- Adventure Activities: The Sahara offers a range of activities such as camel trekking, sandboarding, and star-gazing, allowing travelers to immerse themselves in the desert experience.
- Cultural Experiences: Visitors can experience the rich cultures of the Sahara"s inhabitants, including music, crafts, and traditional cuisine, providing a deeper understanding of the region"s heritage.
- Environmental Considerations: Travelers are encouraged to be mindful of the fragile ecosystem, respecting wildlife and adhering to sustainable tourism practices to minimize their environmental impact.
The allure of the Sahara Desert lies in its vast, unspoiled landscapes and the opportunity to witness a way of life that has persisted for centuries, offering a truly unique travel experience.
The Sahara Desert, a vast canvas of natural wonder and cultural heritage, beckons as a testament to the enduring allure of Earth"s majestic landscapes, inviting endless exploration and discovery in its sun-kissed dunes and timeless horizons.


