Topic location of the sahara desert: Discover the mesmerizing Sahara Desert, a vast landscape of mystery and beauty, spanning across North Africa and holding centuries of untold stories within its sands.
Table of Content
- What is the location of the Sahara Desert?
- The Extent and Location of the Sahara Desert
- Historical Transformation: From a Green Land to a Desert
- Unique Geological Features Underneath the Sahara
- The Nile River"s Relationship with the Sahara
- Climate and Environmental Challenges in the Sahara
- Cultural and Historical Impact of the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Sahara Desert: The Actual Size Revealed
- Modern-Day Challenges and Opportunities in the Sahara
- Exploring the Mystique of the Sahara: Travel and Adventure
What is the location of the Sahara Desert?
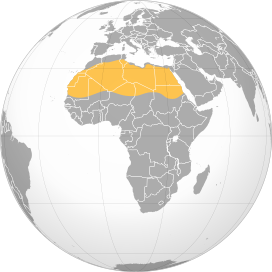
The Sahara Desert is located in northern Africa.
Here are some key details about its location:
- The Sahara Desert spans across several countries including Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia.
- It is situated between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Red Sea to the east.
- The desert is roughly bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Sahel region to the south.
- It covers a vast area of approximately 9.2 million square kilometers (3.6 million square miles), making it the largest hot desert in the world.
- The Sahara stretches approximately 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometers) from east to west.
- The latitude and longitude coordinates for the Sahara Desert are approximately 25.284266° N, 14.438434° E.
The Sahara Desert is renowned for its extreme aridity, vast stretches of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and sparse vegetation.
READ MORE:
The Extent and Location of the Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert, renowned as the world"s largest hot desert, covers an expansive area roughly the size of the United States. Encompassing over 9.2 million square kilometers, it stretches across North Africa, creating a vast landscape that is both awe-inspiring and formidable.
- Geographical Spread: The desert spans several countries, including Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan, and Tunisia. Each region within the Sahara has its unique characteristics and landscapes.
- North Africa"s Dominant Feature: Dominating North Africa, the Sahara is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Atlas Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Red Sea to the east, and the Sahel region to the south.
- Varied Terrain: Contrary to popular belief, the Sahara is not just a vast expanse of sand. It consists of diverse terrains including sand dunes, gravel plains, dry valleys, and salt flats. Only about 25% of the Sahara is sandy, with some of the world"s highest dunes.
- Climate and Environment: Known for its harsh climate, the Sahara experiences extreme temperatures, dry conditions, and minimal rainfall. This environment has shaped a unique ecosystem, home to various plant and animal species adapted to these conditions.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Throughout history, the Sahara has been a crucible for various cultures and peoples. It has served as a trade route, a place of exploration, and a canvas for ancient civilizations, leaving behind a rich tapestry of archaeological and cultural heritage.
Understanding the vastness and diversity of the Sahara Desert is crucial for appreciating its role in shaping the environmental, cultural, and historical narratives of North Africa and beyond.

Historical Transformation: From a Green Land to a Desert
The Sahara Desert"s transformation from a lush, green landscape to the arid expanse we know today is a remarkable journey through time. This transition occurred over several millennia, influenced by climatic and ecological changes.
- Ancient Green Sahara: Evidence suggests that between 11,000 and 5,000 years ago, the Sahara was not a desert but a verdant region with lakes, rivers, and abundant wildlife like gazelles and hippos.
- Climatic Shifts: The transformation began due to Earth’s slow orbital changes, which gradually reduced the region"s rainfall, leading to a drier climate.
- Vegetation and Wildlife: During its green phase, the Sahara supported a variety of vegetation and wildlife, which is depicted in rock art and archaeological findings in the region.
- Human Settlement: This lush environment enabled human settlement and cultivation, influencing early African cultures and civilizations, including Ancient Egypt.
- Gradual Desertification: The gradual reduction in rainfall and shifting climate conditions led to the desertification of the Sahara, transforming it into the vast desert we see today.
- Archaeological Significance: The remnants of this green past are still visible in archaeological sites, offering insights into the ancient Sahara and its transformation.
This historical transformation of the Sahara Desert stands as a testament to the dynamic nature of Earth"s climate and ecosystems, reminding us of the ever-changing face of our planet.
Unique Geological Features Underneath the Sahara
Beneath the Sahara Desert lies a world of extraordinary geological features, each telling a story of the Earth"s ancient past and providing insights into the present and future of this vast landscape.
- Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System: One of the most significant features is the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System, a vast underground water storage system that spans several countries beneath the Sahara. This aquifer is one of the largest in the world, holding ancient "fossil" water.
- Remnants of Prehistoric Mega-Lakes: The Sahara once hosted mega-lakes, evidenced by geological formations and sediment layers. These ancient lakes existed thousands of years ago when the climate was more favorable for water accumulation.
- Subterranean Water Table: The water table beneath the Sahara varies in depth, ranging from 100 to 250 meters. Accessing this water source through wells has been a crucial survival strategy for inhabitants over centuries.
- Rich Mineral Deposits: The Sahara"s subsoil is rich in minerals, including phosphate, iron ore, and uranium, contributing significantly to the economies of the desert"s bordering countries.
- Ancient River Networks: Fossilized river networks buried beneath the sand reveal the Sahara"s green past. These riverbeds, now dry, once supported extensive ecosystems.
- Diverse Landforms: The Sahara"s underground landscape is as varied as its surface, with features like sandstone plateaus, basins, and even volcanic structures contributing to its geological diversity.
The underground realm of the Sahara Desert is a treasure trove of geological wonders, offering a unique glimpse into the history of our planet and the dynamic forces that shape our natural world.

The Nile River"s Relationship with the Sahara
The Nile River, flowing through the eastern part of the Sahara Desert, forms a unique ecological and historical relationship with this vast arid region. This relationship is multifaceted, influencing both the environment and the civilizations that have thrived along its banks.
- A Lifeline in the Desert: The Nile serves as a crucial source of water, making the lands along its banks fertile and habitable, starkly contrasting with the surrounding desert.
- Historical Significance: The river played a vital role in the development of ancient civilizations, most notably Ancient Egypt, providing resources essential for survival and prosperity.
- Ecological Impact: The Nile creates a narrow strip of lush, green land through the desert, supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna adapted to this unique environment.
- Cultural Connection: Over centuries, the Nile has been a source of inspiration, sustenance, and livelihood for the people living in its vicinity, deeply influencing cultural and social practices.
- Geographical Influence: The river has shaped the landscape, with its annual floods depositing nutrient-rich silt along its banks, fostering agricultural activities in an otherwise inhospitable region.
- Modern-day Challenges: Contemporary issues such as water rights, dam constructions, and climate change impact the Nile"s flow and, consequently, its relationship with the Sahara.
The Nile River"s relationship with the Sahara is a testament to the dynamic interplay between natural environments and human civilizations, highlighting the river"s role as a life-giving force amidst one of the world"s harshest landscapes.
Climate and Environmental Challenges in the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, known for its extreme climate, faces numerous environmental challenges that affect both its ecosystem and the human populations that inhabit its fringes.
- Extreme Temperatures: The Sahara is characterized by some of the hottest temperatures on Earth, often exceeding 50°C (122°F). These extreme conditions pose challenges for wildlife, vegetation, and human habitation.
- Minimal Rainfall: As one of the driest regions in the world, the Sahara receives very little rainfall, averaging less than 3 inches annually. This scarcity of water makes it a challenging environment for sustaining life.
- Desertification: The expansion of desert conditions into surrounding arable lands, a process known as desertification, is a major environmental concern, threatening the livelihoods of millions who live at the desert margins.
- Water Scarcity: Access to freshwater is a significant challenge. The discovery of underground aquifers offers some relief, but these resources are limited and non-renewable.
- Sand Dune Movement: The shifting of sand dunes, driven by wind, can engulf settlements and agricultural lands, causing environmental and economic damage.
- Biodiversity Threats: The harsh conditions of the Sahara pose threats to its unique wildlife, many species of which are adapted to the extreme environment but are vulnerable to changes in their habitat.
- Climate Change Impact: The Sahara is particularly susceptible to the effects of climate change, which can exacerbate existing challenges like temperature extremes and water scarcity.
The climate and environmental challenges in the Sahara underscore the need for sustainable and adaptive strategies to preserve this unique ecosystem and support the communities that depend on it.

Cultural and Historical Impact of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, more than just a vast expanse of sand, has played a significant role in shaping the cultural and historical narratives of the civilizations that have interacted with it throughout history.
- Cradle of Ancient Civilizations: The Sahara has been home to various ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Berbers, and Nubians, each leaving their unique mark on history.
- Trade Routes: Historically, the Sahara was a hub for trans-Saharan trade routes, connecting North Africa with Sub-Saharan Africa. These trade routes facilitated the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas.
- Archaeological Richness: The desert is dotted with archaeological sites, offering insights into human life thousands of years ago, including rock art, ruins, and ancient settlements.
- Religious and Mythological Significance: The Sahara holds religious and mythological importance for many cultures, often depicted in folklore, songs, and stories passed down through generations.
- Influence on Art and Literature: The stunning landscapes and unique lifestyle of the Sahara have inspired numerous works of art, literature, and music, reflecting the desert"s mystique and beauty.
- Adaptation and Survival: The harsh conditions of the Sahara have shaped the way of life for its inhabitants, leading to unique adaptations in architecture, agriculture, and social organization.
- Modern Cultural Identity: Today, the Sahara continues to influence the cultural identity of the region, playing a vital role in the heritage and traditions of its people.
The Sahara Desert"s cultural and historical impact is profound, echoing through time and continuing to influence contemporary societies around its vast, sandy expanse.
Sahara Desert: The Actual Size Revealed
\"Discover the power of size! Our fascinating video uncovers the wonders of size in the natural world, revealing the incredible variations and adaptations that make every creature unique. Prepare to be amazed by the immense and intricate world of size!\"
Sahara Desert Coverage: Which Countries Does It Extend To?
\"Embark on a thrilling journey across continents with our captivating video on countries. From breathtaking landscapes to diverse cultures, get ready to explore the rich heritage and hidden gems that make each country a fascinating tapestry of experiences. Join us for an unforgettable exploration of our beautiful planet!\"
Modern-Day Challenges and Opportunities in the Sahara
In the modern era, the Sahara Desert faces both significant challenges and unique opportunities that impact its environment, the people who live there, and the global community.
- Environmental Challenges: Ongoing issues such as climate change, water scarcity, and desertification pose severe threats to the fragile ecosystem of the Sahara and its surrounding regions.
- Economic Development: The Sahara offers opportunities in sectors like mining, with rich deposits of minerals and resources, but sustainable practices are necessary to avoid environmental degradation.
- Renewable Energy Potential: The vast, sun-drenched expanses of the Sahara are ideal for solar energy production, presenting opportunities for large-scale renewable energy projects.
- Scientific Research: The unique conditions of the Sahara make it a valuable location for scientific research, including studies on climate change, astronomy, and biodiversity.
- Tourism and Cultural Heritage: The Sahara"s rich cultural heritage and stunning landscapes offer potential for sustainable tourism, which can provide economic benefits while preserving the region"s cultural and natural resources.
- Water Management: Innovative approaches to water management, such as utilizing underground aquifers or desalination, are critical for supporting life in the Sahara.
- Adaptation and Resilience: Communities in and around the Sahara are developing adaptive strategies to cope with environmental changes, preserving their way of life while facing modern challenges.
The Sahara Desert, while presenting daunting challenges, also holds a wealth of opportunities that, if harnessed responsibly, can lead to sustainable development and a better understanding of our planet.
READ MORE:
Exploring the Mystique of the Sahara: Travel and Adventure
The Sahara Desert, with its vast, undulating sands and ancient mysteries, offers a unique and thrilling destination for travelers and adventurers seeking to experience its unique beauty and challenges.
- Camel Trekking: Embark on a traditional camel trek, a quintessential Sahara experience, offering an intimate connection with the desert"s rhythms and landscapes.
- Desert Camping: Experience the magic of a night under the stars, with desert camping that ranges from basic tents to luxurious desert camps.
- 4x4 Desert Safaris: Explore the Sahara"s diverse terrains with a 4x4 safari, an exhilarating way to discover remote areas and hidden wonders of the desert.
- Historical Sites: Visit ancient historical sites, where millennia of history are etched into the desert landscape, from prehistoric rock art to ruins of ancient civilizations.
- Sandboarding and Dune Bashing: For the more adventurous, sandboarding or dune bashing offers a thrilling way to experience the Sahara"s iconic sand dunes.
- Oasis Visits: Explore lush oases, a stark contrast to the arid desert, which provide a glimpse into the desert"s ecosystem and local cultures.
- Photographic Journeys: The Sahara"s dramatic landscapes provide a stunning backdrop for photography enthusiasts, capturing its shifting sands, unique wildlife, and vibrant cultures.
- Cultural Immersion: Engage with local communities and nomadic tribes, gaining insights into their traditions, lifestyle, and the rich heritage of the Sahara.
Traveling in the Sahara Desert is not just a journey across a physical landscape, but an exploration into a world of cultural richness, historical depth, and profound natural beauty.
The Sahara Desert, a marvel of nature, offers a blend of historical richness, cultural depth, and breathtaking landscapes, making it a destination that promises both enlightenment and adventure.

