Topic the location of sahara desert: Embark on a journey across the Sahara Desert, the world"s largest hot desert, spanning across North Africa. This article unveils the Sahara"s diverse landscapes, historical significance, and ecological wonders, exploring its pivotal role in shaping regional and global narratives.
Table of Content
- What is the size and location of the Sahara Desert?
- Geographical Extent of the Sahara Desert
- Historical Transformation of the Sahara
- The Nile River and the Sahara
- Unique Features of the Sahara
- Human Interaction with the Sahara
- Flora and Fauna of the Sahara
- YOUTUBE: Sahara Desert: The Actual Size Revealed
- Environmental Challenges and Opportunities
What is the size and location of the Sahara Desert?
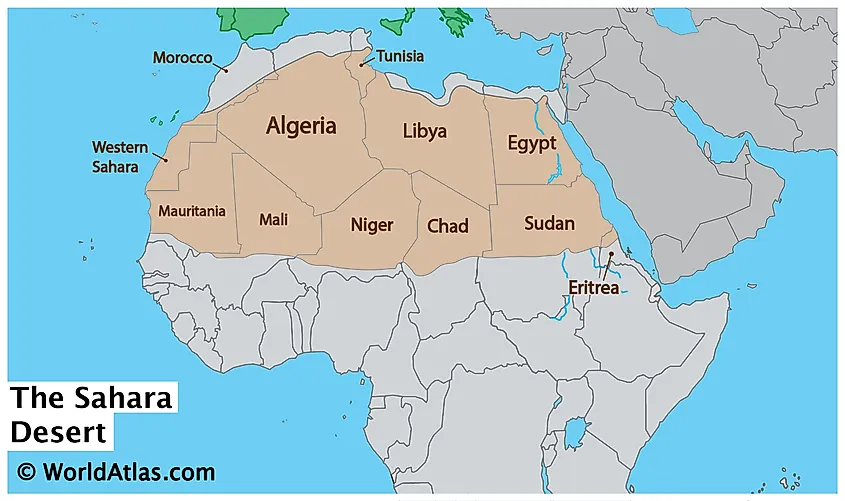
The Sahara Desert is the largest hot desert in the world, spanning across North Africa. It covers an area of approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 square miles).
The approximate coordinates of the Sahara Desert are 25.284266° latitude and 14.438434° longitude.
Here is a summary of the Sahara Desert\'s size and location:
- Size: Approximately 9,200,000 square kilometers (3,600,000 square miles)
- Location: North Africa
- Coordinates: 25.284266° latitude, 14.438434° longitude
READ MORE:
Geographical Extent of the Sahara Desert
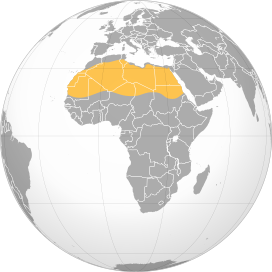
The Sahara Desert, an emblem of mystique and vastness, is the largest hot desert in the world, stretching across North Africa. Covering approximately 9.2 million square kilometers, it extends from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west.
- Spanning 11 countries, the Sahara"s boundaries include Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
- The desert"s northern boundary is marked by the Atlas Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea, while its southern edge is defined by the Sahel, a semi-arid region that forms a transitional zone between the Sahara and sub-Saharan Africa.
- Distinctive for its varied topography, the Sahara comprises not only iconic sand dunes, but also mountain ranges like the Tibesti and the Hoggar, salt flats, and even the occasional oasis.
- The desert"s climate varies from hyper-arid in its central part to arid in the northern and southern fringes, where minimal rainfall sustains a sparse vegetation cover.
Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara has been a crucible for ancient cultures and remains a region of fascination and study, offering a unique blend of natural beauty and historical depth.

Historical Transformation of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert"s history is a tale of ecological transformation, marked by periods of lush greenery and arid desertification. This dynamic past reveals a Sahara drastically different from the one we see today.
- Approximately 11,000 to 5,000 years ago, during the African Humid Period, the Sahara experienced a significantly wetter climate. This period saw the region flourish with vegetation, lakes, and rivers, fostering early human settlements.
- The Sahara"s green era was characterized by lush grasslands, abundant wildlife, and a network of water bodies that supported varied flora and fauna.
- Evidence of this green Sahara is found in prehistoric cave paintings and archaeological sites, showcasing a rich cultural history that thrived in this once fertile landscape.
- The transition to the arid desert as we know it today began around 5,000 years ago, driven by gradual climatic shifts. This change saw a reduction in rainfall and a shift in vegetation patterns, leading to the spread of the desert landscape.
- The Sahara"s transformation is a critical subject in the study of climate change, offering insights into the natural cycles of the Earth and the impact of these changes on human civilizations.
Today"s Sahara, while harsh and inhospitable, continues to fascinate scientists and historians, as it holds keys to understanding the Earth"s climatic history and human adaptation to changing environments.
The Nile River and the Sahara
The interplay between the Nile River and the Sahara Desert is a fascinating aspect of North Africa"s geography. This relationship highlights the Nile"s role as a life-giving artery amidst the vast, arid Sahara.
- The Nile River, known as the world"s longest river, flows through the eastern Sahara, creating a fertile ribbon in contrast to the surrounding desert. This juxtaposition shapes the ecology and human habitation in the region.
- Historically, the Nile has been a cradle of civilization, with ancient Egyptians flourishing on its banks, owing to the fertile land made possible by the river’s annual flooding.
- The river"s presence in the Sahara has created unique ecosystems and oases that support a variety of flora and fauna, serving as vital habitats in the heart of the desert.
- Along its course through the Sahara, the Nile forms significant geographical features such as the Nile Delta and the Nubian Desert, contributing to the diverse landscape of the region.
- The river has also been crucial for modern-day economies and cultures in the Sahara, supporting agriculture, fishing, and transportation, and remains a vital source of life in the desert.
The Nile River"s journey through the Sahara is a testament to the resilience of nature and human societies, thriving in an environment where contrasts between water and desert create a unique and dynamic ecosystem.

Unique Features of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, famed for its vastness and extreme conditions, is home to a multitude of unique and fascinating features. These characteristics not only define its landscape but also its ecological and cultural significance.
- The Sahara is predominantly known for its enormous sand dunes, or ergs, which can reach heights of up to 180 meters. The most iconic of these is the Great Erg of Algeria.
- Contrary to popular belief, sand dunes cover only about 25% of the Sahara"s surface. The majority of the desert consists of rocky plateaus, barren stone plateaus known as hamadas, which are more extensive than the sand seas.
- One of the Sahara"s most striking features is the Tibesti Mountains in Chad, home to the highest peak in the desert, Emi Koussi, a dormant volcano.
- The Sahara also contains unique geological formations such as the Aïr Mountains in Niger and the Richat Structure in Mauritania, often referred to as the "Eye of the Sahara."
- Oases, vital to life in the desert, dot the Sahara. These are lush, fertile areas where groundwater reaches the surface, creating a stark contrast with the surrounding arid landscape.
- The desert is not devoid of life; it supports a variety of flora and fauna specially adapted to the harsh environment. This includes the fennec fox, addax antelope, and various species of reptiles and birds.
- Archaeological discoveries like prehistoric rock paintings in the Tassili n"Ajjer region of Algeria reveal the Sahara"s rich human history and evolution.
These features make the Sahara a place of endless intrigue and scientific interest, offering insights into both the past and the future of our planet"s environmental dynamics.
Human Interaction with the Sahara
The Sahara Desert has been a stage for human activity and culture for thousands of years. Despite its harsh environment, it has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations, trade routes, and unique adaptations of human life.
- The Sahara has been inhabited since prehistoric times, with evidence of human life dating back to the Neolithic era. Rock paintings and engravings in regions like Tassili n"Ajjer in Algeria provide a glimpse into the lives of these early inhabitants.
- The introduction of the camel, around the 1st millennium BC, revolutionized life in the Sahara, facilitating trade across the desert, notably the trans-Saharan trade routes that connected the Mediterranean civilizations with Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Historic Saharan cities like Timbuktu in Mali and Ghadames in Libya flourished as trading and learning centers in medieval times, playing crucial roles in the cultural and economic exchanges between different regions.
- Nomadic tribes, such as the Tuareg and Bedouins, have adapted to the Sahara"s challenging conditions for centuries, developing unique cultural practices and knowledge of the desert.
- In modern times, the Sahara is not only home to various indigenous communities but also the site of significant economic activities like oil extraction in Algeria and Libya, and phosphate mining in Western Sahara.
- Recent initiatives aim to harness the Sahara"s vast potential for solar energy production, reflecting a new chapter in the human use of this vast desert.
The Sahara Desert remains a testament to human resilience and adaptability, embodying a rich tapestry of history, culture, and continuous interaction between nature and human ingenuity.
Flora and Fauna of the Sahara
The Sahara Desert, often perceived as a lifeless expanse, surprisingly hosts a variety of flora and fauna uniquely adapted to its extreme environment. This diverse ecosystem is a testament to the resilience of life.
- The flora of the Sahara includes various species of drought-resistant plants like acacia trees, date palms, and various types of grasses and shrubs. These plants have adapted to conserve water and survive in the harsh desert conditions.
- Among the notable fauna, the Sahara is home to the fennec fox, known for its large ears that help dissipate heat. Other mammals include the addax antelope, dorcas gazelle, and the endangered Saharan cheetah.
- Reptiles are well-represented in the Sahara, with species like the horned viper and the Sahara sand viper, along with various types of lizards and skinks, adapted to the hot and dry climate.
- Bird species such as the ostrich, Namaqua dove, and several raptor species thrive in the desert, often near oases which provide essential water sources.
- Despite the scarcity of water, the Sahara features occasional oases that support higher biodiversity, including various species of birds, insects, and even amphibians.
- The Sahara also has a unique array of invertebrates, including scarab beetles and the Saharan silver ant, known for its ability to survive in extreme temperatures.
The flora and fauna of the Sahara Desert are examples of nature"s adaptability, with each species playing a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of this extreme environment.
Sahara Desert: The Actual Size Revealed
Discover the wonders of size as this video takes you on a journey through the mesmerizing landscapes of the world\'s largest and smallest creatures. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible diversity and beauty that exists in our natural world.
Sahara Desert: Countries it Covers
Embark on an exhilarating adventure to explore the diverse cultures and breathtaking landscapes of countries around the world. From bustling cities to serene countryside, this video will transport you to new and exciting destinations, igniting your wanderlust like never before.
READ MORE:
Environmental Challenges and Opportunities
The Sahara Desert faces significant environmental challenges, but these also present unique opportunities for sustainable development and innovation in adapting to extreme conditions.
- One of the major challenges in the Sahara is desertification, the process where fertile land becomes desert typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture. This threatens the livelihoods of local communities and the ecosystem.
- Climate change poses another challenge, exacerbating water scarcity, and altering the delicate balance of desert ecosystems. It leads to more extreme temperature fluctuations and impacts the already scarce water resources.
- Overexploitation of resources, including water extraction and mining activities, has also put pressure on the Sahara"s environment, leading to habitat degradation and biodiversity loss.
- However, the Sahara offers significant opportunities for renewable energy, particularly solar power. Its vast, sunlit landscapes are ideal for large-scale solar farms, which could generate clean energy for local use and potential export.
- There are also efforts to combat desertification through sustainable land management practices, including reforestation and the establishment of protected areas to conserve native species and habitats.
- Eco-tourism presents another opportunity, encouraging a sustainable approach to tourism that fosters environmental awareness and provides economic benefits to local communities while minimizing ecological footprints.
The Sahara Desert, while facing environmental challenges, also serves as a canvas for innovative solutions in sustainability and conservation, offering lessons on resilience and adaptation in the face of adversity.
In exploring the Sahara Desert"s diverse landscapes, rich history, and dynamic ecosystems, we uncover a world of wonders that transcends its arid reputation, inviting us to appreciate the resilience and beauty inherent in one of Earth"s most extraordinary places.