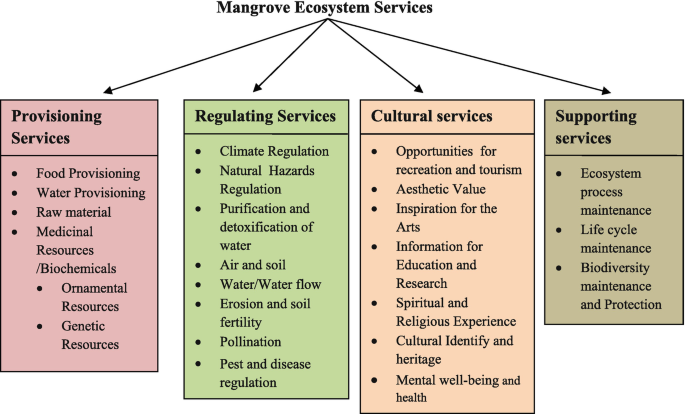
Topic what animals live in grasslands: Explore the vast, vibrant world of grasslands, where a diverse array of animals thrive in these expansive ecosystems, from majestic mammals to exquisite birds.
Table of Content
- What animals live in grasslands?
- Overview of Grassland Habitats
- Common Grassland Mammals
- Unique Birds in Grasslands
- Reptiles and Amphibians Found in Grasslands
- Insects and Other Invertebrates
- Adaptations of Grassland Animals
- YOUTUBE: 9 Animals That Live in Grasslands
- Threats to Grassland Animals and Conservation Efforts
- Role of Predators in Grassland Ecosystems
- Migration Patterns of Grassland Animals
- Interaction Between Grassland Animals and Their Environment
What animals live in grasslands?
Animals that live in grasslands include:
- Zebras
- Giraffes
- Lions
- Cheetahs
- Antelopes
- Buffaloes
- Elephants
READ MORE:
Overview of Grassland Habitats
Grassland habitats, sprawling across continents, are ecosystems characterized by vast open lands dominated by grasses. They are found in regions where rainfall is enough to support grasses, but not enough for large trees to thrive. Grasslands are crucial for biodiversity, supporting a wide range of animals adapted to these open environments.
- Tropical Grasslands: Also known as savannas, these are warm year-round, with seasonal rains and dry periods. They host a variety of large mammals and birds.
- Temperate Grasslands: Experience more extreme temperature differences between seasons. These areas are home to many grazing mammals, burrowing animals, and a rich variety of birds.
- Montane Grasslands: Found in mountainous regions, these grasslands support species adapted to cooler climates and rugged terrain.
Grasslands play a key role in the earth"s carbon cycle, soil fertility, and provide grazing grounds for animals. They are also important for human agriculture and have been used for centuries for grazing domesticated animals and growing crops.

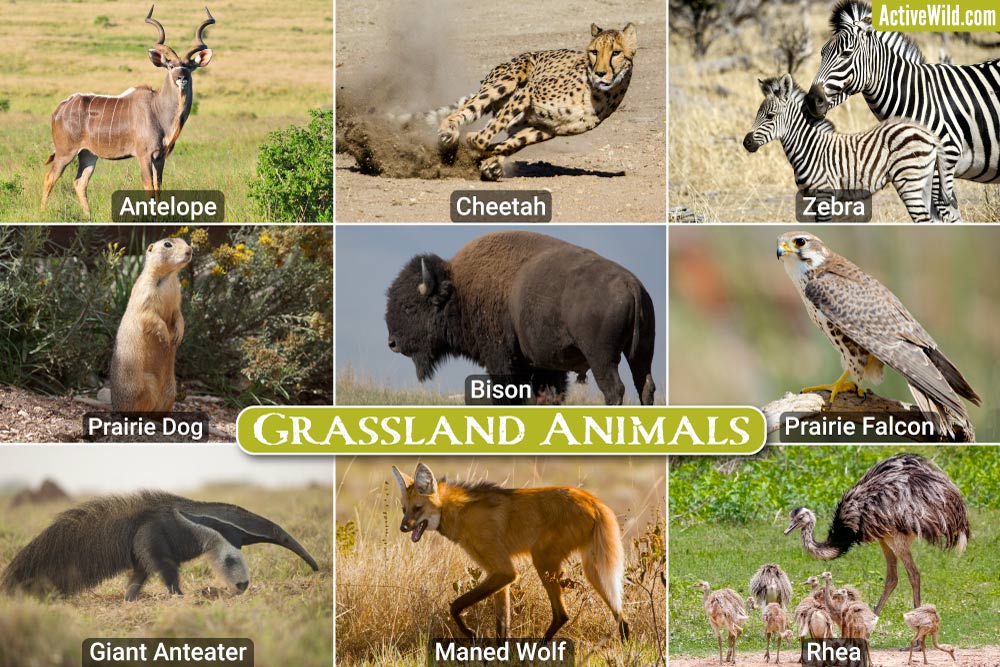
Common Grassland Mammals
Grasslands are teeming with a variety of mammals that have adapted to live in these open habitats. These mammals range from small rodents to large herbivores and include some of the most iconic species on our planet.
- African Elephants: Majestic giants that roam the savannas, playing a critical role in maintaining the ecosystem.
- American Bison: Once roamed North American prairies in vast numbers and are a symbol of the grasslands.
- Zebras: Known for their distinctive stripes, these animals are a common sight in African grasslands.
- Gazelles and Antelopes: Swift and agile, these animals are adapted to the open spaces, providing them the visibility to spot predators.
- Prairie Dogs: These social rodents live in extensive burrow systems in North American grasslands.
- Lions: As top predators, lions play a crucial role in the grassland ecosystem by controlling the population of other animals.
These mammals are integral to the grassland ecosystem, contributing to the balance and biodiversity of these habitats. They are involved in seed dispersal, soil aeration, and serve as prey and predators within their ecological niches.
Unique Birds in Grasslands
Grasslands serve as a vital habitat for a diverse array of bird species, many of which are uniquely adapted to this environment. These birds range from large raptors to small seed-eaters, each playing an important role in the ecosystem.
- Bustards: Including the critically endangered Great Indian Bustard, these ground-dwelling birds are among the heaviest flying birds native to grassland areas.
- Sarus Crane: The tallest flying bird in the world, found in Indian subcontinent grasslands, known for its impressive size and elegant mating dances.
- Secretary Bird: A large, mostly terrestrial bird of prey, famous for its striking appearance and snake-hunting prowess.
- Larks and Sparrows: Small but vital, these birds thrive in grasslands, where their songs fill the air, and they play key roles in seed dispersal.
- Eastern Meadowlark: Known for its distinctive calls and bright yellow belly, it"s a common sight in North American grasslands.
- Red-tailed Hawk: A versatile predator that soars above grasslands, keeping the rodent populations in check.
These birds not only contribute to the biodiversity of grasslands but also aid in pollination, pest control, and act as indicators of the health of these ecosystems.
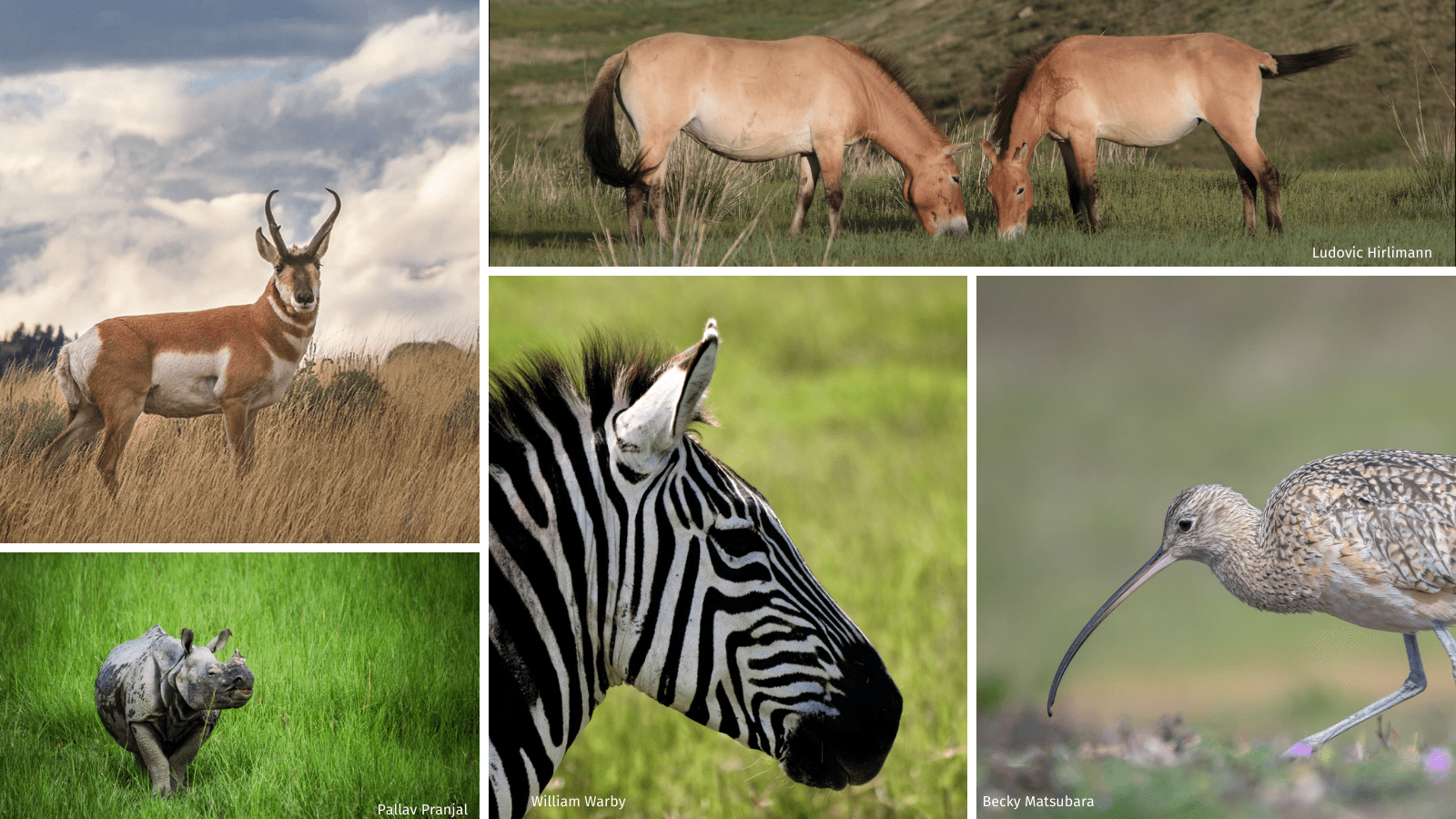

Reptiles and Amphibians Found in Grasslands
Grasslands are not only home to mammals and birds but also provide habitat for a variety of reptiles and amphibians. These cold-blooded creatures are well adapted to the unique challenges of grassland life.
- Rattlesnakes: These venomous snakes are adept at camouflage in the grassy terrain, waiting patiently for their prey.
- Lizards: Including the swift and the collared lizard, these reptiles bask in the sunlit open areas of grasslands.
- Tortoises: Grassland tortoises, such as the Gopher Tortoise, dig burrows that provide homes for themselves and other species.
- Frogs and Toads: Species like the Grassland Frog thrive in moist areas of grasslands, contributing to the ecosystem’s diversity.
- Skinks: These smooth-skinned lizards are often found skittering through the underbrush, hunting insects.
These reptiles and amphibians play critical roles in grassland ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey, and contributing to the ecological balance by controlling insect populations and providing food sources for other animals.
Insects and Other Invertebrates
Insects and other invertebrates are the unsung heroes of grassland ecosystems, playing crucial roles in pollination, soil aeration, and as a food source for other animals.
- Bees and Butterflies: Essential pollinators that contribute to the health of grassland plants and the broader ecosystem.
- Grasshoppers and Crickets: Abundant in grasslands, these insects are a vital food source for a variety of animals.
- Ants: Their complex colonies aerate the soil and contribute to nutrient cycling, supporting plant growth.
- Spiders: Act as natural pest controllers, maintaining the balance of insect populations in grasslands.
- Earthworms: Improve soil structure and fertility by breaking down organic matter and enhancing nutrient availability.
These invertebrates are integral to the grassland ecosystem, supporting its complexity and productivity through their diverse roles.

Adaptations of Grassland Animals
Animals inhabiting the grasslands have evolved a variety of adaptations to survive and thrive in these open environments. These adaptations help them to find food, avoid predators, and cope with the climate.
- Camouflage: Many grassland animals have coats or skins that blend into the grassy landscape, making them less visible to predators.
- Speed and Agility: Open landscapes require fast movement to escape predators. Animals like antelopes and gazelles are incredibly swift and agile.
- Burrowing: Many small mammals and reptiles burrow into the ground to escape extreme weather and predators.
- Migratory Behavior: Some species migrate across vast distances to find food and breeding grounds, adapting to seasonal changes.
- Social Structures: Many grassland animals, such as prairie dogs and elephants, form complex social structures for better protection and resource allocation.
- Long Legs: Birds and mammals may have long legs for wading through grass and spotting predators from a distance.
These adaptations ensure the survival of grassland species, demonstrating the intricate balance of nature and the evolution of species to fit their environment.
9 Animals That Live in Grasslands
Grasslands: Explore the vast beauty of grasslands in this captivating video, showcasing the tranquility and diversity of flora and fauna that call this ecosystem home. Immerse yourself in the natural wonder of grasslands. Habitats: Delve into the intricate web of habitats around the world in this fascinating video, highlighting the unique environments and animals that rely on them for survival. Witness the beauty and importance of protecting these diverse habitats.
All About Habitats: Kids\' Guide to Tundra, Deserts, Grasslands, Forests, and More
Join us for an exciting science lesson on Habitats with the \"All About Habitats\" video. This educational video explores the ...
Threats to Grassland Animals and Conservation Efforts
Grassland ecosystems face numerous threats that endanger the animals living within them. However, concerted conservation efforts are underway to protect these habitats and their inhabitants.
- Habitat Loss: Expansion of agriculture, urban development, and mining reduces grassland areas, leading to loss of habitat for many species.
- Climate Change: Alters precipitation patterns and temperatures, affecting the availability of water and food sources in grasslands.
- Overgrazing: Livestock can overgraze, damaging the grasslands and making them unsuitable for native wildlife.
- Poaching and Hunting: Illegal hunting of grassland animals for meat, horns, or as trophies poses a significant threat.
- Invasive Species: Non-native plants and animals can disrupt the ecological balance, outcompeting native species for resources.
Conservation efforts include creating protected areas, sustainable land management practices, restoration projects to rehabilitate degraded lands, and legal protections for threatened species. Education and community involvement are also crucial in promoting the conservation of grasslands and their unique wildlife.

Role of Predators in Grassland Ecosystems
Predators play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of grassland ecosystems. They help control the population of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and ensuring vegetation remains abundant and diverse.
- Natural Population Control: By preying on the weakest members, predators help maintain healthy populations of prey species.
- Biodiversity Support: Predation pressure can lead to greater biodiversity, as it prevents any one species from dominating the ecosystem.
- Disease Regulation: Predators often target sick and diseased animals, reducing the spread of illness.
- Behavioural Effects: The presence of predators can alter the behaviour of herbivores, affecting their feeding patterns and movements, which in turn influences the structure and composition of vegetation.
Conserving predators is vital for the stability of grassland ecosystems. Efforts to protect these important animals, including legal protections and habitat conservation, are essential for preserving the intricate balance of life in grasslands.
Migration Patterns of Grassland Animals
Many grassland animals undertake remarkable migrations, moving across vast distances in search of food, water, and breeding grounds. These migrations are critical for the survival of species and the health of grassland ecosystems.
- Seasonal Movements: Animals like the wildebeest in the Serengeti migrate in response to seasonal rainfall patterns, traveling hundreds of miles in massive herds.
- Bird Migration: Grassland birds, including the Sandhill Crane, migrate to breeding grounds in the north during spring and return south for winter.
- Altitudinal Migration: Some species, like the Montane grassland animals, move to higher elevations during warmer months and return to lower areas in colder periods.
- Impact of Climate Change: Changing climate conditions are affecting migration patterns, with some species altering their routes and timing in response to temperature and precipitation changes.
Understanding and protecting these migration routes is essential for the conservation of grassland ecosystems, ensuring that animals can continue these vital journeys that sustain their populations and the biodiversity of their habitats.

READ MORE:
Interaction Between Grassland Animals and Their Environment
The dynamic relationship between grassland animals and their environment is a fascinating study of adaptation, survival, and ecological balance. These interactions ensure the sustainability of grassland ecosystems worldwide.
- Herbivory and Plant Growth: Grazing by herbivores like bison and antelopes promotes new plant growth, maintains plant diversity, and can prevent bush encroachment.
- Seed Dispersal: Animals such as birds and small mammals play a crucial role in dispersing seeds, facilitating plant regeneration and spread.
- Soil Aeration and Fertilization: The movement and feeding behavior of animals such as earthworms and burrowing mammals improve soil health and structure.
- Predation and Population Control: Predators maintain healthy prey populations, ensuring that no single species dominates, which could lead to ecosystem imbalance.
- Mutualism: Some grassland species engage in mutualistic relationships, such as pollinators with flowering plants, which benefit both parties and enhance biodiversity.
This intricate web of interactions highlights the importance of each species in maintaining the health and resilience of grassland ecosystems. Conservation efforts are vital to preserve these relationships amid changing environmental conditions.
Discovering the remarkable animals of grasslands reveals the beauty and complexity of these ecosystems, urging us to appreciate and protect these vital habitats for future generations.