Topic name three ecosystem services provided by biodiversity: Discover the vital roles of biodiversity through "Name Three Ecosystem Services Provided by Biodiversity," highlighting nature"s unparalleled contributions to our planet"s health and prosperity.
Table of Content
- What are three ecosystem services provided by biodiversity?
- Provisioning Services
- Regulating Services
- Cultural Services
- Supporting Services
- Importance of Biodiversity in Agriculture
- Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Services
- YOUTUBE: Understanding Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services Across Urban Landscapes
- Strategies for Protecting and Enhancing Ecosystem Services
What are three ecosystem services provided by biodiversity?
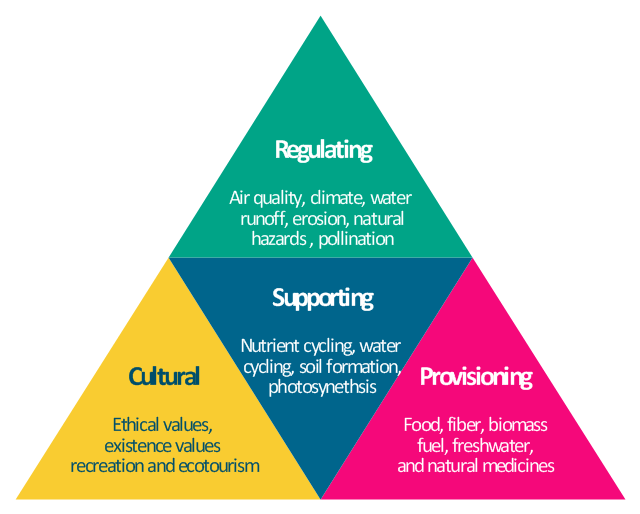
Three ecosystem services provided by biodiversity are:
- Pollination: Biodiversity plays a critical role in pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of plants. Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds facilitate the transfer of pollen between flowers, leading to the production of fruits and seeds.
- Nutrient Cycling and Soil Maintenance: Biodiversity helps in the recycling of nutrients within ecosystems. Different organisms break down dead organic matter and convert it into nutrients that can be used by other living organisms. This nutrient cycling process maintains soil fertility and sustains plant growth.
- Regulation of Climate and Water: Biodiversity contributes to the regulation of climate by influencing processes such as carbon sequestration and water cycling. Forests, for example, store carbon dioxide and help in mitigating climate change. Additionally, vegetation aids in water absorption, reducing the risk of floods and maintaining water quality.
READ MORE:
Provisioning Services
Biodiversity plays a critical role in providing provisioning services, essential benefits that nature offers to humans, directly contributing to our survival and quality of life. These services include a wide range of resources that we depend on daily.
- Food Production: Ecosystems support the growth of a wide variety of plants and animals used for food, medicines, and spices, underpinning the agriculture and fisheries industries. This includes fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and dairy products derived from biodiversity.
- Fresh Water: Biodiversity is key in regulating the water cycle through natural filtration and storage, ensuring the supply of fresh water for drinking, irrigation, and sanitation.
- Raw Materials: Forests, wetlands, and marine ecosystems provide timber, fiber, fuel, and other raw materials for construction, clothing, and energy, demonstrating the tangible value of biodiversity to our economies and livelihoods.
- Medicinal Resources: Many pharmaceuticals are derived from compounds found in plants, animals, and fungi. The diversity of life forms contributes to the development of life-saving medicines, including antibiotics and cancer therapies.
These provisioning services are not only crucial for our physical well-being but also for economic activities, underlining the importance of conserving biodiversity to sustain and enhance these vital resources.

Regulating Services
Biodiversity"s regulating services are crucial for maintaining the balance and health of the Earth"s ecosystems. These natural processes and cycles, facilitated by the diverse life forms on our planet, play a key role in stabilizing the environment and making it habitable for humans.
- Climate Regulation: Forests and oceans act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, which helps to regulate global climate. Diverse ecosystems thus play a vital role in mitigating climate change.
- Water Purification: Wetlands filter pollutants from water, maintain water clarity, and control water flow, ensuring the availability of clean water for drinking, agriculture, and recreation.
- Pollination: A wide variety of insects, birds, and mammals pollinate plants, which is essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, and seeds, contributing significantly to food security and agriculture.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiverse ecosystems can regulate diseases by controlling the populations of carriers or pathogens. For example, certain species can help limit the spread of Lyme disease by controlling deer or rodent populations that host ticks.
- Natural Hazard Regulation: Vegetation covers, such as forests and grasslands, help stabilize soil and reduce the risk and severity of natural disasters like floods and landslides.
These services underscore the importance of preserving biodiversity to ensure that natural systems continue to function effectively, providing critical services that benefit humanity and all life on Earth.
Cultural Services
Biodiversity enriches our lives in numerous ways, contributing to the cultural and spiritual services that nature offers. These services are deeply interwoven with our identity, well-being, and the aesthetic value we find in nature, underscoring the intrinsic connection between humans and the natural world.
- Recreational and Ecotourism Opportunities: Natural landscapes and wildlife provide spaces for recreational activities, such as hiking, bird watching, and photography, as well as ecotourism, which supports local economies and promotes conservation awareness.
- Aesthetic Inspiration: The diversity of life inspires artists, musicians, and writers, fueling creativity and cultural expression. This inspiration is evident in countless works of art, literature, and music that celebrate the beauty of the natural world.
- Spiritual and Religious Values: Many cultures and religions draw spiritual significance from biodiversity, recognizing certain species, natural sites, and landscapes as sacred or spiritually important.
- Educational Value: Nature serves as an outdoor classroom, offering endless opportunities for learning and discovery. Biodiversity and ecosystems teach us about the complexities of life and our place within the natural world.
- Heritage and Identity: For many communities, local biodiversity is a source of cultural identity and heritage, closely linked to traditional knowledge, customs, and languages that have been passed down through generations.
Through these cultural services, biodiversity not only sustains our physical existence but also enriches our psychological and emotional well-being, connecting us to the earth and to each other in profound ways.

Supporting Services
Supporting services form the foundation of all ecosystems, underpinning their ability to provide the other services (provisioning, regulating, and cultural) that we directly benefit from. These fundamental processes include the cycles and systems that sustain life on Earth.
- Nutrient Cycling: Biodiversity plays a critical role in the movement and transformation of nutrients through ecosystems, ensuring the availability of essential elements for plant growth and soil fertility.
- Soil Formation and Maintenance: Organisms contribute to the formation of soil and its maintenance, affecting its structure, fertility, and composition. This process is vital for plant growth and carbon sequestration.
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen as a byproduct, is fundamental for life on Earth. It is the basis for most of the energy supply within ecosystems.
- Water Cycling: Biodiversity influences the global water cycle, including precipitation and evaporation processes, playing a significant role in water availability across different ecosystems.
- Primary Production: This is the production of organic compounds from atmospheric or aquatic carbon dioxide, principally through the process of photosynthesis. It forms the base of the food web, supporting all other life forms.
These supporting services are essential for the maintenance of life on Earth, illustrating the deep interconnections between biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. By preserving biodiversity, we ensure the resilience and continued provision of all ecosystem services.
Importance of Biodiversity in Agriculture
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in agriculture by supporting numerous functions that are essential for food production and ecosystem health. This diversity among and within plant and animal species contributes significantly to the sustainability and resilience of agricultural systems.
- Pest and Disease Control: A diverse ecosystem promotes natural control mechanisms for pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Diverse landscapes support a variety of predators and competitors that help manage pest populations.
- Soil Health: Biodiversity contributes to soil structure and fertility. Different organisms play specific roles in nutrient cycling, organic matter decomposition, and soil aeration, which are vital for crop growth.
- Pollination Services: Many crops depend on pollinators such as bees, birds, and bats for fruit and seed production. Biodiversity ensures the availability of these critical pollination services, directly influencing crop yields and quality.
- Genetic Diversity: The genetic diversity within crop species is crucial for breeding programs, enabling the development of new varieties with improved yield, nutritional quality, and resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses.
- Agroecosystem Resilience: Diverse agricultural systems are more resilient to adverse conditions such as drought, flooding, and climate change. Biodiversity can buffer against environmental fluctuations, ensuring more stable food production.
Enhancing biodiversity in agricultural landscapes is therefore a key strategy for sustainable agriculture, contributing to food security, environmental conservation, and resilience to changing climates.

Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are under increasing pressure from various challenges and threats that can significantly impact their ability to support life and human well-being. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing strategies to protect and sustain these vital services.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Expansion of urban areas, agriculture, and infrastructure development leads to the loss of habitats and divides ecosystems into smaller, isolated patches. This fragmentation affects biodiversity, disrupts ecosystem processes, and reduces the capacity to provide services.
- Climate Change: Alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events can shift ecosystem dynamics, affecting their ability to offer services such as carbon sequestration, flood regulation, and maintaining biodiversity.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal can degrade ecosystems, harming wildlife and reducing the quality of the services they can provide, such as clean water and air.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete, predominate, or bring diseases to native species, disrupting ecosystem balance and diminishing its services, such as pollination and natural pest control.
- Overexploitation of Resources: Unsustainable logging, fishing, and hunting, along with excessive water extraction, can deplete natural resources, leading to a decline in ecosystem services, including provisioning services like food, timber, and fresh water.
Addressing these challenges requires coordinated global, regional, and local efforts to implement sustainable management practices, conservation initiatives, and policies that protect natural habitats and the services they provide.
Understanding Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services Across Urban Landscapes
Explore the fascinating world of ecosystem services in this enlightening video, showcasing the intricate balance of nature and how it benefits all living beings. Witness the vital role these services play in ensuring a healthy environment for generations to come.
Linking Biodiversity, Ecosystem Function, Ecosystem Services, and Human Wellbeing
Linking Biodiversity, Ecosystem Function, Ecosystem Services, and Human Wellbeing: The Landscape Sustainability Science ...
READ MORE:
Strategies for Protecting and Enhancing Ecosystem Services
To safeguard and improve the ecosystem services provided by biodiversity, it is crucial to implement a range of strategies that address current challenges and threats. These strategies can help ensure the sustainability and resilience of ecosystems for future generations.
- Conservation and Restoration: Protecting existing natural habitats and restoring degraded ones are foundational steps in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services. Establishing protected areas and reforestation projects are examples of this approach.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing sustainable practices in forestry, agriculture, fishing, and water use can reduce the impact on ecosystems and ensure the continued provision of essential services.
- Pollution Reduction: Minimizing pollution through better waste management, reducing the use of harmful chemicals in agriculture, and promoting clean energy sources can protect ecosystems from degradation.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Strategies such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and developing climate-resilient ecosystems can help mitigate the effects of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Integrated Land Use Planning: Coordinating land use decisions by considering ecological values and services can help balance development needs with the preservation of ecosystems.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem services can foster a culture of sustainability and stewardship.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that protect ecosystems and promote sustainable practices is crucial for the long-term preservation of ecosystem services.
By adopting these strategies, societies can work towards a sustainable future where ecosystem services are protected and enhanced, benefiting both the environment and human well-being.
Embracing biodiversity"s ecosystem services illuminates pathways to a sustainable future, enhancing our resilience and enriching our lives. Together, we can protect nature"s gifts, ensuring a healthy planet for generations to come.