Topic explain how biodiversity affects ecosystem services: Discover the pivotal role of biodiversity in shaping our world, as it fuels ecosystem services essential for human survival and the planet"s health. This exploration unveils the intricate connections between life"s variety and nature"s bounty.
Table of Content
- How does biodiversity impact the provision of ecosystem services?
- Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
- Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity
- Role of Soil Biodiversity in Ecosystem Services
- Biodiversity"s Influence on Human Health and Nutrition
- Stabilizing Effects of Biodiversity on Ecosystems
- Management Strategies for Ecosystems and Biodiversity Conservation
- YOUTUBE: Biodiversity, Ecosystems, Ecosystem Services: TEEB at YALE
- Global Efforts and Policies for Biodiversity Conservation
- Case Studies on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
How does biodiversity impact the provision of ecosystem services?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in determining the provision of ecosystem services, which are the benefits that humans derive from nature. Here\'s how biodiversity impacts the provision of ecosystem services:
- Resilience and Stability: Higher biodiversity within an ecosystem leads to a more stable and resilient environment. A diverse range of species can better withstand environmental changes, such as climate fluctuations or pest outbreaks. This resilience ensures that ecosystem services, such as water purification, soil fertility, and carbon sequestration, remain consistent and functional.
- Pollination and Plant Growth: Biodiversity, especially in terms of pollinators like bees and butterflies, is essential for the pollination of plants. This process is vital for the reproduction of many plant species, leading to improved crop yields and overall plant growth. Ecosystem services such as crop pollination are directly influenced by the presence of diverse pollinator species.
- Nutrient Cycling: Diverse communities of microorganisms, fungi, and other decomposers are responsible for nutrient recycling within ecosystems. These organisms break down organic matter, releasing essential nutrients back into the soil for plants to use. The efficiency of nutrient cycling directly affects ecosystem services related to soil fertility and productivity.
- Climate Regulation: Biodiverse ecosystems play a key role in regulating the Earth\'s climate. Forests, wetlands, and other biodiverse habitats sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, diverse plant species can influence local weather patterns, such as rainfall distribution and temperature regulation, impacting ecosystem services like climate control and air quality.
- Disease Regulation: Biodiversity can act as a natural defense against the spread of diseases. When ecosystems are rich in species diversity, certain species can act as buffers against disease-causing organisms. For example, predators that feed on disease-carrying organisms help regulate their populations, reducing the risk of disease outbreaks. This aspect of biodiversity significantly influences ecosystem services related to human health and disease prevention.
READ MORE:
Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Functioning
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, plays an essential role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems. It contributes to ecosystem resilience, productivity, and stability, influencing climate regulation, water purification, soil fertility, and pollination. The richness of species ensures that ecosystems can withstand environmental changes and stresses, providing a buffer against disturbances and helping to sustain the ecosystem services upon which human societies depend.
- Resilience: Diverse ecosystems are more resilient, better able to recover from disruptions such as natural disasters or human-induced changes. This resilience protects and enhances ecosystem services.
- Productivity: Higher biodiversity leads to greater productivity, where ecosystems can produce more biomass, contributing to carbon sequestration, oxygen production, and the foundation of food chains.
- Stability: Biodiversity stabilizes ecosystems through seasonal variations and unpredictable events, ensuring a consistent delivery of ecosystem services.
- Nutrient Cycling: A variety of organisms contributes to the decomposition of organic material and the cycling of nutrients, crucial for soil health and plant growth.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Biodiversity supports the processes of pollination and seed dispersal, which are vital for food production and ecosystem health.
The intricate interdependencies within ecosystems mean that the loss of any species can have unforeseen negative effects on ecosystem functioning and the services it provides. Thus, conserving biodiversity is not just about preserving nature for its own sake but is critical for maintaining the natural systems that humans rely on for survival and well-being.
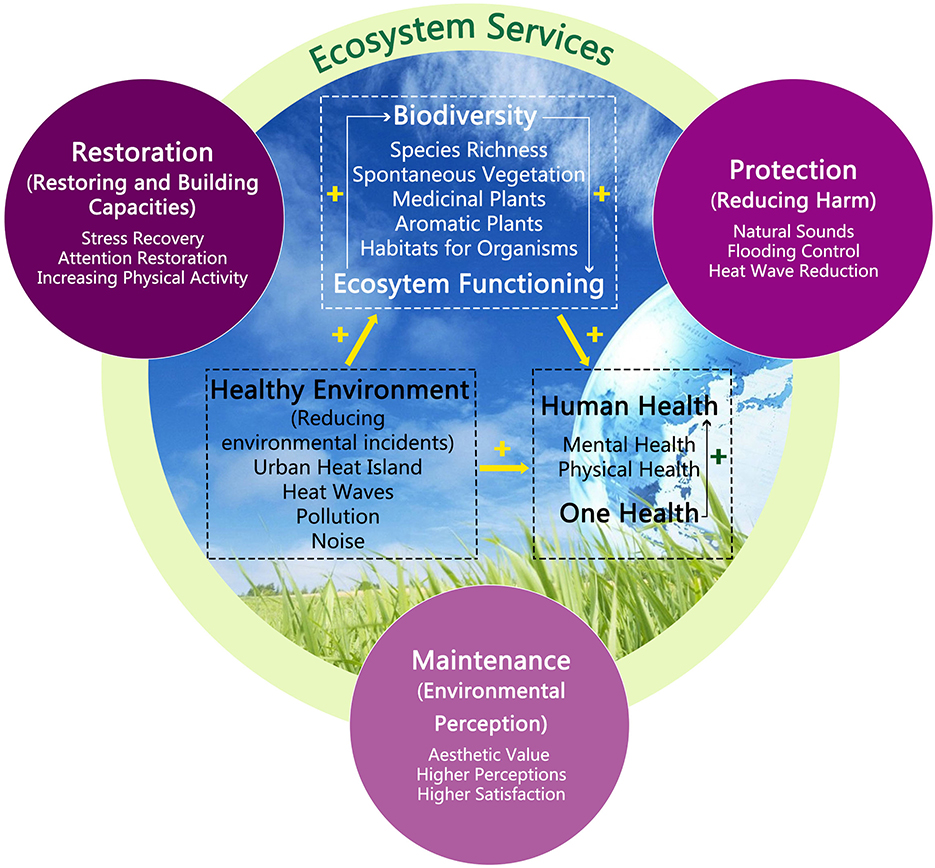
Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity
Climate change significantly impacts ecosystem services and biodiversity, altering the balance of ecosystems worldwide. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events disrupt the delicate interplay between species and their habitats, leading to shifts in biodiversity that can compromise ecosystem services.
- Alteration of Habitats: Climate change can lead to habitat loss, degradation, and shifts in habitat ranges, directly affecting biodiversity and ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
- Changes in Species Distribution: As temperatures rise, species may migrate to cooler areas, altering ecosystem composition and function. This can disrupt the provision of ecosystem services, such as fisheries and forestry.
- Increased Stress on Species: Higher temperatures and altered precipitation patterns increase stress on species, potentially leading to decreased biodiversity and loss of ecosystem services.
- Impact on Pollination: Changes in climate can affect the timing of flowering and pollinator activity, disrupting pollination services critical for food production and ecosystem health.
- Water Cycle Disruption: Climate change impacts the global water cycle, affecting the availability and quality of water for drinking, agriculture, and habitat for aquatic biodiversity.
Adaptation and mitigation strategies are crucial for reducing the impact of climate change on ecosystems and biodiversity. Protecting and restoring natural habitats, conserving water resources, and implementing sustainable land use practices can help maintain ecosystem services and biodiversity in the face of climate change.
Role of Soil Biodiversity in Ecosystem Services
Soil biodiversity is fundamental to the functioning of ecosystems, underpinning a wide array of services vital for life on Earth. The myriad organisms living within the soil, from bacteria and fungi to insects and worms, play critical roles in nutrient cycling, soil formation, and the regulation of greenhouse gases. These activities not only support plant growth, including agricultural crops, but also contribute to water filtration, pest control, and climate regulation.
- Nutrient Cycling: Soil organisms decompose organic matter, converting it into forms usable by plants, thereby facilitating nutrient cycling and enhancing soil fertility.
- Soil Structure Maintenance: The activities of soil organisms, such as earthworms burrowing through the soil, help maintain and improve soil structure, which is crucial for plant root growth and water infiltration.
- Disease Suppression: The diversity of soil microorganisms can suppress plant pathogens, reducing the incidence of plant diseases and supporting healthy crop yields.
- Carbon Sequestration: Soil biodiversity plays a key role in carbon sequestration, with soil organisms breaking down organic matter and storing carbon in the soil, thereby contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Water Regulation: Healthy, biodiverse soils absorb and filter water, reducing runoff and pollution, and thus maintaining water quality and availability.
The conservation of soil biodiversity is thus essential for sustaining ecosystem services that humans and all life forms depend on. Practices such as reduced tillage, cover cropping, and organic farming can help preserve and enhance soil biodiversity, ensuring the continued provision of these critical ecosystem services.

Biodiversity"s Influence on Human Health and Nutrition
Biodiversity is a cornerstone of human health and nutrition, providing a vast array of foods rich in different nutrients essential for human well-being. Diverse ecosystems support the production of a wide range of foods, from fruits and vegetables to grains and meats, contributing to a balanced diet and enhancing food security. Moreover, natural ecosystems play a crucial role in purifying air and water, controlling pests and diseases, and providing medicinal resources that underpin traditional and modern medicines.
- Dietary Diversity: Biodiversity offers a variety of foods, ensuring a wider intake of essential nutrients, which is crucial for preventing malnutrition and non-communicable diseases.
- Medicinal Resources: A significant proportion of pharmaceuticals are derived from biological diversity, emphasizing the importance of conserving ecosystems for health care and disease prevention.
- Pollination Services: Pollinators such as bees and butterflies are vital for the production of many fruits, vegetables, and nuts, contributing to food diversity and nutritional quality.
- Ecosystem Services: Clean water and air, provided by diverse ecosystems, are fundamental for human health. Forests and wetlands, for example, filter pollutants and pathogens, reducing the risk of disease.
- Genetic Diversity: The genetic diversity within plant and animal species is key to resilience against pests and diseases, ensuring the sustainability of food sources.
Protecting biodiversity is therefore essential for sustaining the ecosystems that provide these critical services. Conservation efforts and sustainable management of natural resources not only safeguard our planet"s health but also ensure that current and future generations have access to nutritious foods and medicinal resources needed for a healthy life.
Stabilizing Effects of Biodiversity on Ecosystems
The stability of ecosystems is significantly enhanced by biodiversity. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to environmental changes and disturbances, such as climate fluctuations, pests, and diseases. This resilience is crucial for maintaining ecosystem services, such as air and water purification, soil fertility, and climate regulation, which are essential for life on Earth.
- Resilience to Environmental Changes: Biodiversity allows ecosystems to adapt to and recover from adverse conditions, maintaining ecosystem functionality even in the face of stressors.
- Reduction of Pest and Disease Outbreaks: A diverse set of species can limit the spread of pests and diseases, reducing their impact on ecosystem services.
- Enhanced Productivity and Recovery: Diverse ecosystems tend to be more productive and can recover from disturbances more quickly than less diverse systems.
- Maintenance of Ecosystem Services: The variety of life helps to ensure the continued provision of essential services, such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and decomposition.
- Buffer Against Climate Variability: Biodiversity can act as a buffer against climate variability and extreme events, protecting land and aquatic ecosystems.
Therefore, the conservation of biodiversity is not only a matter of preserving the natural beauty and the myriad of species on our planet but is also critical for ensuring the stability and resilience of ecosystems on which humans and all life depend.
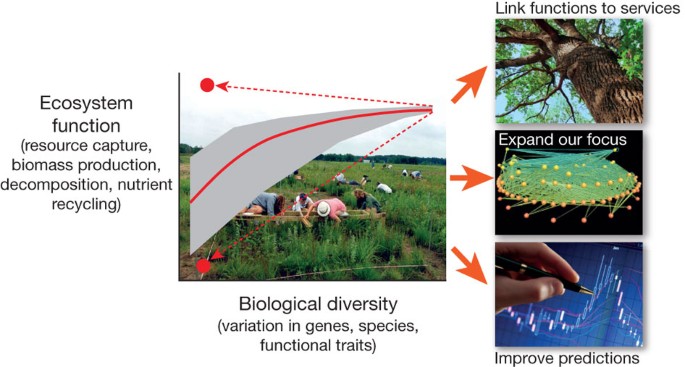
Management Strategies for Ecosystems and Biodiversity Conservation
Effective management strategies for ecosystems and biodiversity conservation are crucial for maintaining the balance of our natural world. These strategies involve a combination of science-based policies, community engagement, and sustainable practices designed to protect and restore biodiversity while supporting ecosystem services.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and enforcing protected areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine sanctuaries to safeguard habitats and species.
- Sustainable Land Use Practices: Implementing sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fishing practices that conserve biodiversity while meeting human needs.
- Restoration Projects: Undertaking ecosystem restoration projects to rehabilitate degraded habitats and reintroduce native species.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting carbon sequestration projects to protect ecosystems from its adverse effects.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in the preservation of natural resources.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and implementing laws and policies that promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research and monitoring biodiversity to inform conservation strategies and adapt them as necessary.
These strategies, combined with international cooperation and public awareness campaigns, form the backbone of efforts to conserve biodiversity and ensure the sustainability of ecosystem services for future generations.
Biodiversity, Ecosystems, Ecosystem Services: TEEB at YALE
Biodiversity: Explore the breathtaking world of biodiversity in this captivating video showcasing the beauty and importance of our planet\'s diverse ecosystems and species. Join us on a journey of discovery and admiration for the wonders of nature. Energy: Discover the limitless possibilities of sustainable energy sources in this inspiring video that will leave you feeling hopeful and empowered to make a positive impact on the environment. Get ready to be amazed by the power of innovation and renewable energy solutions.
Food Webs and Energy Pyramids: Bedrocks of Biodiversity
Explore food chains, food webs, energy pyramids, and the power of biodiversity in this ecology video by the Amoeba Sisters!
Global Efforts and Policies for Biodiversity Conservation
Global efforts and policies for biodiversity conservation are pivotal in addressing the decline in biodiversity across the world. International agreements, national strategies, and local actions work in tandem to protect natural habitats, species, and the ecosystem services they provide. These efforts aim to mitigate impacts from threats such as habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation of resources.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): A global agreement adopted by 196 countries, focusing on the conservation of biological diversity, the sustainable use of its components, and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources.
- Paris Agreement: Although primarily focused on climate change, the Paris Agreement has significant implications for biodiversity conservation by addressing the role of ecosystems in sequestering carbon.
- Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES): Provides assessments on biodiversity and ecosystem services, informing policy and decision-making processes at the global level.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Goals 14 and 15 specifically aim to conserve and sustainably use ocean resources and manage forests, combat desertification, halt and reverse land degradation, and halt biodiversity loss.
- Global Biodiversity Framework: Efforts to create a unified framework for biodiversity conservation, aiming to protect 30% of the planet"s land and oceans by 2030.
- National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs): Developed by countries in line with the CBD, these plans outline specific actions to conserve and protect biodiversity.
Through these and other initiatives, the global community seeks to reverse biodiversity loss and ensure the preservation of ecosystem services for future generations. Collaboration across nations, sectors, and communities is critical to achieving these goals.

READ MORE:
Case Studies on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Exploring case studies from around the world highlights the critical role of biodiversity in maintaining ecosystem services and underscores the impacts of human activities on natural systems. These examples illustrate successful conservation efforts and the ongoing challenges in preserving biodiversity.
- The Amazon Rainforest: Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in global climate regulation by sequestering carbon dioxide. Conservation efforts here focus on protecting vast areas from deforestation and degradation.
- The Great Barrier Reef: This marine ecosystem supports a diverse range of species and offers significant economic benefits through tourism and fisheries. Protection strategies include water quality improvements and reef restoration projects.
- The Serengeti-Mara Ecosystem: Known for its annual wildebeest migration, this ecosystem"s biodiversity supports not just a variety of species but also local and national economies through ecotourism. Conservation efforts aim to balance human development with wildlife protection.
- Madagascar"s Rainforests: Home to unique biodiversity, including many endemic species, Madagascar faces challenges from deforestation and habitat loss. Conservation projects here often involve community-based approaches to sustainable development.
- The Sundarbans Mangrove Forest: This critical habitat for the Bengal tiger also protects coastal regions from storm surges. Efforts to conserve the Sundarbans include sustainable resource management and climate adaptation measures.
These case studies demonstrate the intricate connections between biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human well-being. They show that conserving biodiversity is not only about protecting species but also about ensuring the health of ecosystems that people rely on for their livelihoods, security, and resilience against climate change.
Embracing the symbiosis between biodiversity and ecosystem services illuminates a path toward sustainable living and conservation. This journey not only safeguards our natural heritage but also ensures a resilient and vibrant planet for future generations.