Topic biodiversity and ecosystem services: Discover the vital role of biodiversity in sustaining ecosystem services, from climate regulation to enhancing human well-being, and explore innovative conservation strategies to safeguard our planet"s natural heritage.
Table of Content
- What is the role of the IPBES in assessing knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services globally?
- Importance of Biodiversity for Ecosystem Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Cultural, and Supporting
- Role of Biodiversity in Climate Regulation and Carbon Sequestration
- Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Human Well-being and Economic Value
- Conservation Strategies and Sustainable Management of Ecosystems
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity Science for Environment Policy
What is the role of the IPBES in assessing knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services globally?
The role of the IPBES in assessing knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services globally can be summarized as follows:
- Regular and Timely Assessments: The IPBES is tasked with performing regular and timely assessments of knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services at the global level. This includes gathering and synthesizing information on the state of biodiversity, the services ecosystems provide, and the interlinkages between them.
- Interlinkages Analysis: The IPBES focuses on understanding the interconnected nature of biodiversity and ecosystem services. By examining how biodiversity supports key processes and directly influences the delivery of ecosystem services, the organization helps identify the importance of preserving natural systems.
- Science-Policy Interface: As an intergovernmental body, the IPBES serves as a bridge between the scientific community and policymakers. It provides authoritative assessments that help inform decision-making at local, national, and international levels, aiming to promote the sustainable use of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Through its assessments and reports, the IPBES plays a crucial role in raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and ecosystem services, highlighting their contributions to human well-being and the need for conservation efforts. By providing a platform for scientific consensus and policy dialogue, the IPBES contributes to global efforts to safeguard biodiversity and sustainably manage ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Importance of Biodiversity for Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of ecosystems, species, and genetic material within the environment, playing a crucial role in the functionality and resilience of ecosystems. It underpins the delivery of essential services such as pollination, climate regulation, flood control, soil fertility, and the production of food, fuel, fiber, and medicines. These ecosystem services are fundamental to human well-being, supporting our economies and societies.
The intricate relationships within biodiversity contribute to the stability and productivity of ecosystems. Higher levels of biodiversity enhance ecosystem multifunctionality, which refers to the ability of an ecosystem to provide multiple services simultaneously. This includes the regulation of diseases, water quality, and the decomposition of waste, among other services.
However, biodiversity is under threat due to human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and the introduction of invasive species. These pressures lead to a decline in biodiversity, which in turn affects the capacity of ecosystems to provide vital services. The loss of biodiversity and the degradation of ecosystem services have serious implications for human needs and the sustainability of our planet.
Conservation and sustainable management practices are essential to protect and enhance biodiversity. This involves preserving natural habitats, restoring degraded ecosystems, and integrating biodiversity considerations into various sectors such as agriculture, forestry, and urban planning. Global and regional policies, including the EU Biodiversity Strategy, aim to halt and reverse biodiversity loss through targeted actions and improved policy implementation.
The importance of biodiversity extends beyond the immediate provision of ecosystem services; it is also about maintaining the resilience and adaptive capacity of ecosystems in the face of environmental changes. Therefore, safeguarding biodiversity is not only about preserving the natural world but also about ensuring a sustainable future for humanity.

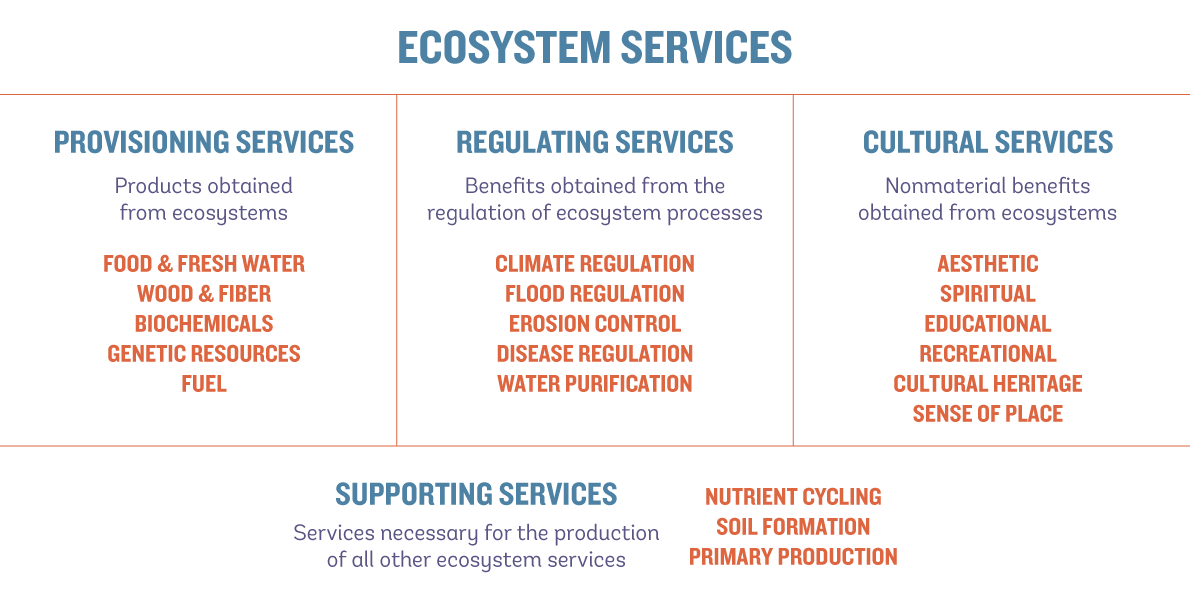
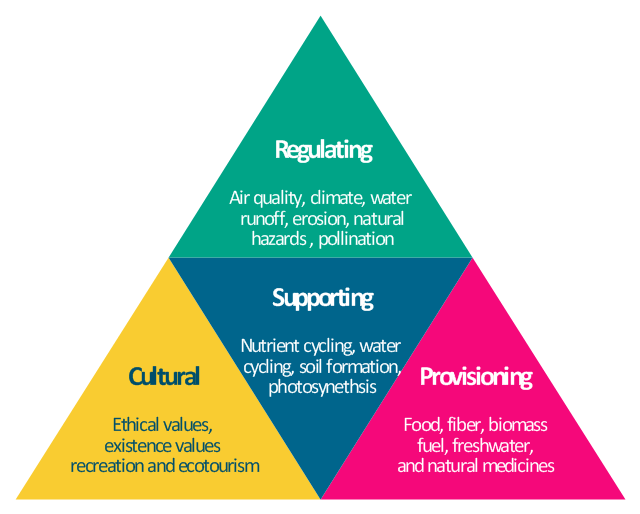
Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Cultural, and Supporting
Ecosystem services, crucial for human well-being and economic prosperity, are categorized into four main types:
- Provisioning Services: These include the direct products from ecosystems such as food, fiber, water, and medicinal resources.
- Regulating Services: These services include climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation, and water purification, which are essential for maintaining the health of our planet.
- Cultural Services: Ecosystems provide cultural or aesthetic benefits, recreational experiences, and spiritual enrichment.
- Supporting Services: These are the natural processes that maintain other services, including nutrient cycling, soil formation, and primary production.
These ecosystem services are interlinked, supporting life and human civilization, and underline the importance of conserving and restoring biodiversity and ecosystems.
Role of Biodiversity in Climate Regulation and Carbon Sequestration
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, plays a pivotal role in regulating the climate and sequestering carbon, thus mitigating the impacts of climate change. Ecosystems rich in biodiversity, such as forests, oceans, and wetlands, act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Forests, particularly, are crucial in this process, removing billions of tons of carbon annually, contributing significantly to reducing the net amount of greenhouse gases.
- Biodiverse ecosystems also regulate environmental conditions, ensuring the balance and health of our planet.
- These systems offer resilience against climate change effects, with diverse species playing various roles in adaptation and survival strategies, enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Conservation and sustainable management of these natural resources are vital for maintaining their role in climate regulation and carbon sequestration, highlighting the importance of global efforts to protect and restore ecosystems.
Understanding and preserving biodiversity is not just about conserving nature, but is intrinsically linked to our survival and the health of the planet.

Impact of Biodiversity Loss on Human Well-being and Economic Value
The loss of biodiversity has profound consequences on human well-being and the global economy, undermining the natural systems upon which we depend. Ecosystem services, which include provisioning, regulating, cultural, and supporting services, are critically dependent on biodiversity. The degradation of these services can lead to:
- Reduced food security due to the loss of pollinators affecting crop yields and diversity.
- Increased vulnerability to natural disasters as ecosystems like wetlands and forests play key roles in mitigating floods and stabilizing climates.
- Diminished medicinal resources, with a significant percentage of pharmaceuticals deriving from biological materials.
- Loss of cultural, recreational, and spiritual values associated with natural landscapes.
- Decreased economic opportunities in sectors like tourism, fisheries, and forestry.
- Economic costs associated with the loss of ecosystem services, impacting sectors from healthcare to disaster recovery.
Healthy, diverse ecosystems contribute to the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the natural places we find solace and recreation in. The interconnectedness of species and habitats underlines the essential role of biodiversity in climate regulation and carbon sequestration, highlighting the urgent need for conservation and sustainable management.
Conservation Strategies and Sustainable Management of Ecosystems
Conservation strategies and sustainable management of ecosystems are crucial for maintaining biodiversity, ensuring ecosystem services, and supporting human well-being. Effective conservation involves a combination of scientific understanding, policy making, and community involvement to protect natural habitats and the species that inhabit them.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and expanding protected areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and marine protected areas to safeguard critical habitats and species.
- Restoration Projects: Initiating ecological restoration projects to rehabilitate degraded ecosystems, such as reforestation efforts, wetland restoration, and coral reef rehabilitation.
- Sustainable Land Use Practices: Promoting sustainable agricultural, forestry, and fishing practices that minimize environmental impact, maintain soil health, and protect water resources.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Implementing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sinks through reforestation and sustainable land management practices.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing traditional knowledge, and providing incentives for sustainable resource use.
- Legislation and Policy: Developing and enforcing environmental laws and policies that protect biodiversity, regulate land use, and reduce pollution.
- International Cooperation: Participating in global biodiversity initiatives and agreements to address transboundary conservation challenges and share best practices.
- Research and Monitoring: Supporting scientific research to monitor ecosystem health, assess the effectiveness of conservation measures, and adapt strategies based on new insights.
- Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of biodiversity and ecosystem services through education programs, media, and community outreach.
- Eco-friendly Technologies: Encouraging the development and adoption of green technologies that reduce environmental impact and enhance resource efficiency.
By integrating these strategies into a coherent framework, we can ensure the sustainable management of ecosystems, preserve biodiversity, and secure the essential services they provide for future generations.

Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity Science for Environment Policy
Conservation: Dive into the mesmerizing world of conservation and witness the incredible efforts to protect our planet\'s precious wildlife and habitats. Join us on a journey of hope and resilience as we work together to preserve our natural wonders for future generations. Sustainability: Discover the inspiring and innovative practices of sustainability that are shaping a brighter future for our planet. From renewable energy to eco-friendly lifestyles, explore the endless possibilities of living in harmony with nature. Watch our video to be part of the solution!
READ MORE:
FAO Policy Series Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity
http://www.fao.org/policy-support The productivity and sustainability of agriculture, forestry and fisheries depend on healthy and ...