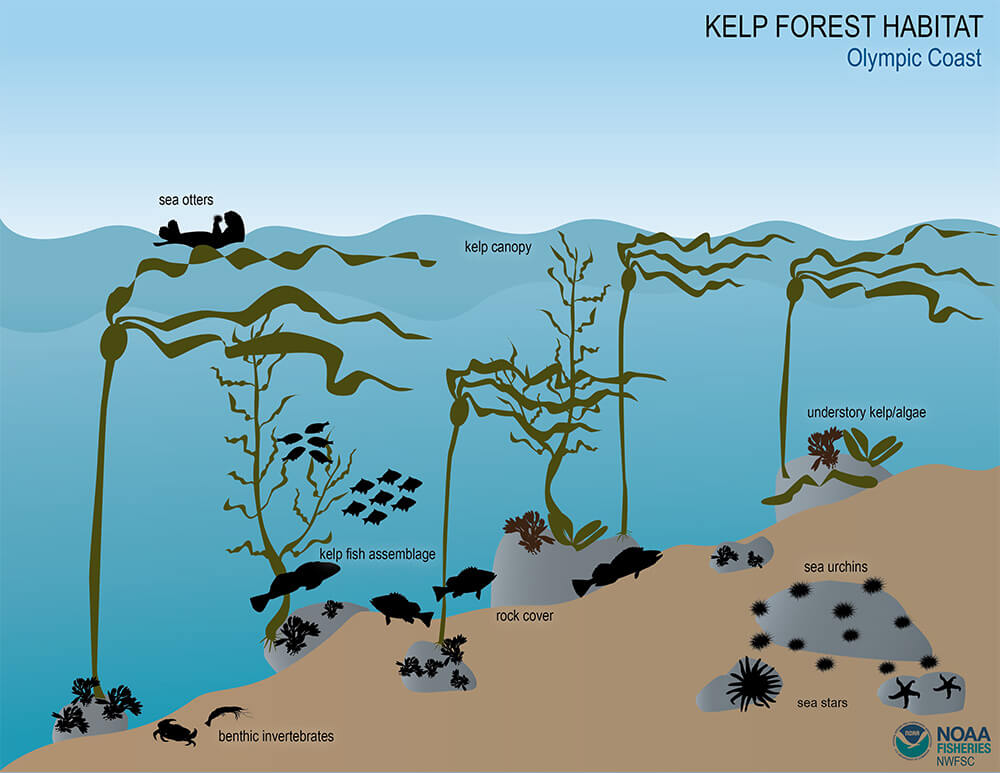
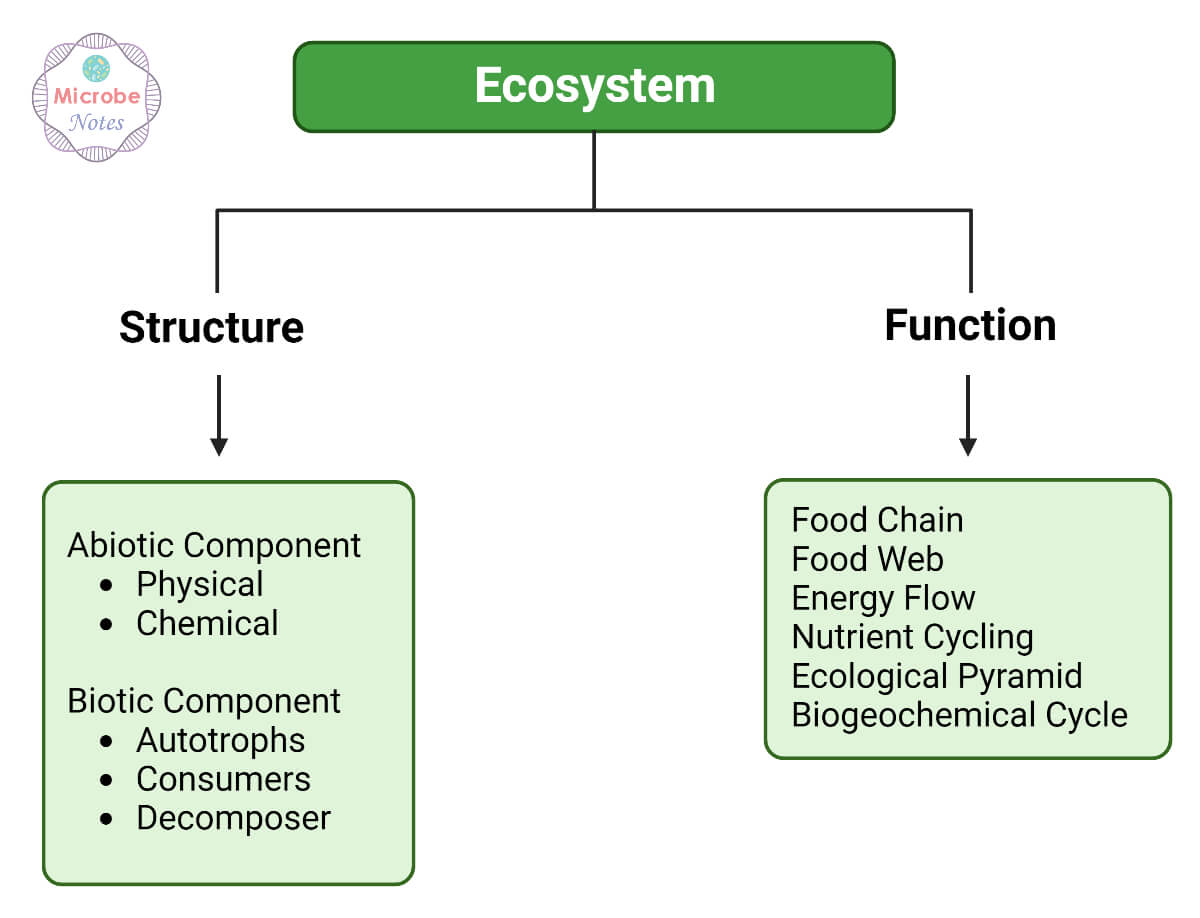
Topic meaning of ecosystem services: Discover the essence of ecosystem services, nature"s invaluable gifts that sustain and enrich our lives, from clean air to fertile soil.
Table of Content
- What are examples of provisioning services in relation to the meaning of ecosystem services?
- Definition and Importance of Ecosystem Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Cultural, and Supporting
- The Role of Ecosystem Services in Human Well-being
- Case Studies: Real-world Examples of Ecosystem Services
- Threats to Ecosystem Services and the Impact of Environmental Degradation
- Conservation Efforts and the Role of Policy in Protecting Ecosystem Services
- YOUTUBE: Ecosystem Services by Dr. Krishnanand
- Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services
- The Future of Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities
What are examples of provisioning services in relation to the meaning of ecosystem services?
Provisioning services are a type of ecosystem service that refers to the tangible benefits that humans obtain directly from ecosystems. These services are essential for human survival and well-being. Examples of provisioning services include:
- Food: This is one of the most crucial provisioning services provided by ecosystems. It includes fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and fish that we obtain from nature.
- Water: Ecosystems play a vital role in regulating the water cycle and providing clean water for drinking, irrigation, and other needs.
- Medicinal Plants: Many plants in ecosystems have medicinal properties and are used in traditional medicine or serve as sources for pharmaceuticals.
- Wood and Fiber: Trees and other vegetation in ecosystems provide timber for construction, paper products, and other materials.
- Fuel: Ecosystems also supply biomass and resources for fuel, such as firewood and charcoal, which are essential for cooking and heating in many parts of the world.
READ MORE:
Definition and Importance of Ecosystem Services
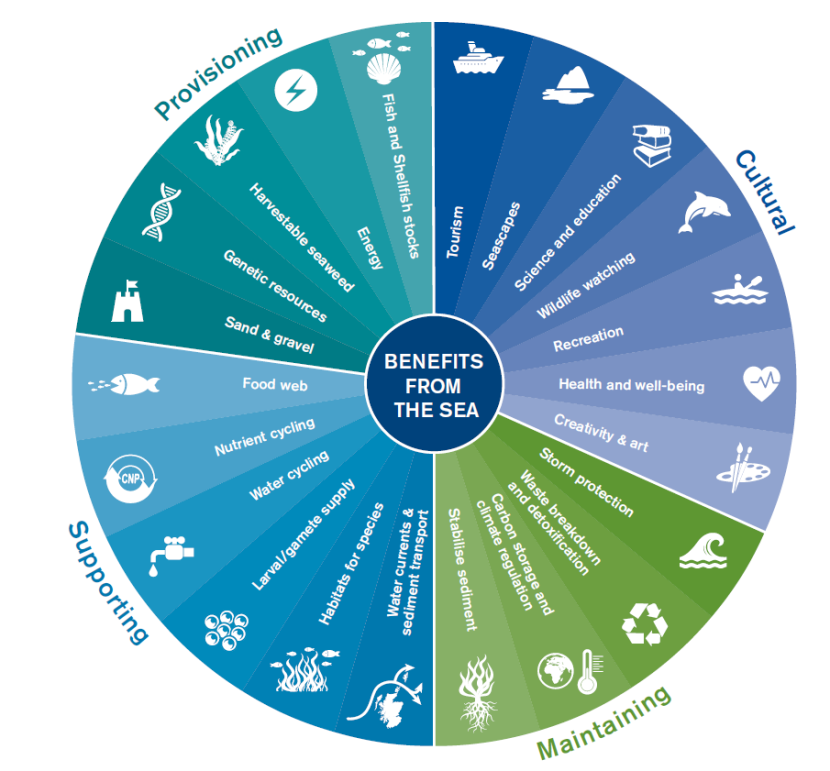
Ecosystem services are the benefits that nature provides to humanity, essential for survival and quality of life. These services are broadly categorized into four main types: provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural services.
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood, fiber, and genetic resources.
- Regulating Services: Natural processes regulated by ecosystems, such as climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation, and water purification.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, and nutrient cycling.
- Cultural Services: Non-material benefits obtained from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, recreation, and aesthetic experiences, contributing to the well-being and quality of life.
The importance of ecosystem services cannot be overstated. They play a crucial role in sustaining the Earth"s life support systems, underpinning economies, and enhancing human well-being. Despite their invaluable contributions, many ecosystem services are under threat due to environmental degradation and unsustainable practices. Recognizing, valuing, and conserving ecosystem services is vital for long-term environmental sustainability and human prosperity.
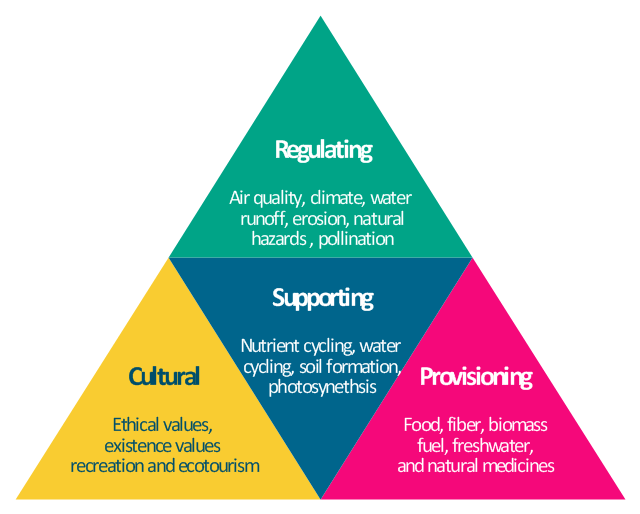
Types of Ecosystem Services: Provisioning, Regulating, Cultural, and Supporting
Ecosystem services, the myriad benefits ecosystems provide to humans, are vital for our survival and well-being. These services are classified into four main categories, each playing a unique role in our lives and the environment.
- Provisioning Services offer essential resources:
- Food - fruits, vegetables, fish, and game.
- Water - for drinking, irrigation, and sanitation.
- Raw materials - wood, fibers, and biofuels.
- Genetic resources - for crop improvement and medical research.
- Regulating Services maintain ecosystem balance:
- Climate regulation - through carbon sequestration and temperature control.
- Flood regulation - by forests and wetlands.
- Disease control - through natural predators of pests.
- Water purification - by wetlands filtering pollutants.
- Supporting Services underpin all other services:
- Soil formation - creating the foundation for plant growth.
- Nutrient cycling - recycling essential elements for life.
- Photosynthesis - producing oxygen and food.
- Biodiversity - supporting ecosystems" resilience and productivity.
- Cultural Services enrich human life:
- Recreational experiences - hiking, birdwatching, and outdoor activities.
- Spiritual and religious values - nature as a source of inspiration.
- Educational values - learning about nature and ecosystems.
- Aesthetic appreciation - landscapes, flora, and fauna.
Understanding these types of ecosystem services highlights the intricate ways in which humans depend on and interact with the natural world. It underscores the importance of conserving and sustainably managing our ecosystems to ensure these services continue to support life on Earth.
The Role of Ecosystem Services in Human Well-being
The role of ecosystem services in enhancing human well-being is profound and multifaceted. These natural services are not only essential for survival but also for the quality of life and the socio-economic development of communities worldwide.
- Health Benefits: Clean air, water, and access to healthy foods directly contribute to physical health and prevent diseases. Natural spaces and recreational services support mental health by reducing stress and enhancing mood.
- Economic Support: Many industries, such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism, directly rely on ecosystem services. These services contribute to economic development and job creation, supporting livelihoods globally.
- Social and Cultural Value: Cultural services provide recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits that enrich human life, foster community identity, and support educational opportunities.
- Resilience and Security: Ecosystem services play a crucial role in regulating climate, reducing disaster risk (e.g., floods, landslides), and ensuring food and water security, thereby enhancing community resilience.
- Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship: Supporting and regulating services, such as nutrient cycling and climate regulation, are vital for maintaining the health of the planet and ensuring the sustainability of resources for future generations.
By recognizing and valuing the essential role of ecosystem services in human well-being, societies can make more informed decisions that promote environmental conservation, sustainable management, and equitable access to these services for all.

Case Studies: Real-world Examples of Ecosystem Services
Illustrating the value of ecosystem services through real-world examples helps to highlight their critical role in sustaining life and human societies. Here are several case studies that showcase the diverse benefits ecosystems provide.
- The Amazon Rainforest - Biodiversity and Climate Regulation: Known as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a critical role in carbon sequestration, significantly influencing global climate regulation. Its vast biodiversity also serves as a source of medicines and genetic materials.
- The Great Barrier Reef - Tourism and Coastal Protection: Australia"s Great Barrier Reef, the world"s largest coral reef system, supports a tourism industry worth billions of dollars annually and provides significant coastal protection against storm surges and erosion.
- The Sundarbans Mangrove Forest - Storm Protection and Livelihoods: The Sundarbans in Bangladesh and India offer protection against cyclones and flooding for millions of people. Mangroves also support fisheries and forestry, underpinning local economies.
- Urban Green Spaces - Health and Well-being: Parks and green spaces in cities around the world offer recreational opportunities, improve air quality, and have been shown to enhance physical and mental health for urban populations.
- Wetlands - Water Purification and Biodiversity: Wetlands act as natural water filters, removing pollutants from surface water. They are also hotspots of biodiversity and support a wide range of plant and animal species.
These case studies underscore the indispensable benefits of ecosystem services to humanity. Protecting and restoring ecosystems is not just about conserving nature; it"s about safeguarding our future.
Threats to Ecosystem Services and the Impact of Environmental Degradation
The integrity and functionality of ecosystems, upon which humans and all life depend, face significant threats from a range of human activities. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the impact of environmental degradation.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Expanding urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural encroachment lead to the loss of critical habitats, reducing biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and waste disposal disrupt ecosystem processes and diminish the quality of the services provided.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns, rising temperatures, and increased frequency of extreme weather events impact ecosystems" ability to provide services like climate regulation and disaster risk reduction.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable fishing, hunting, logging, and mining deplete resources faster than they can regenerate, undermining provisioning services and biodiversity.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can outcompete native species, disrupt ecosystems, and lead to the loss of native biodiversity and ecosystem services.
The degradation of ecosystem services not only affects the environment but also has profound implications for human well-being, economic stability, and social structures. Addressing these threats requires coordinated global efforts, including conservation, sustainable management, and restoration initiatives to ensure the long-term viability of our planet"s ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts and the Role of Policy in Protecting Ecosystem Services
Effective conservation and policy strategies are essential for safeguarding ecosystem services and ensuring their benefits continue to support human well-being and biodiversity. Strategic approaches and policy frameworks can significantly impact the preservation and restoration of vital ecosystems.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and effectively managing protected areas to conserve biodiversity hotspots and critical habitats for ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing practices that allow for the sustainable use of natural resources, ensuring that ecosystem services are not depleted over time.
- Restoration Projects: Engaging in ecosystem restoration to rehabilitate degraded areas, enhancing their capacity to provide ecosystem services.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Developing policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase ecosystem resilience to the impacts of climate change.
- Integrating Ecosystem Services into Economic Planning: Recognizing the economic value of ecosystem services in national and global economies, and incorporating this value into development planning and decision-making processes.
- Community Involvement and Indigenous Rights: Involving local communities and respecting the rights of indigenous peoples in conservation efforts, recognizing their knowledge and stake in the sustainability of ecosystems.
- International Agreements: Participating in global treaties and agreements aimed at environmental protection and the conservation of biodiversity, such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
By prioritizing ecosystem service conservation in policy-making and planning, societies can ensure the long-term health and productivity of ecosystems, securing the essential services they provide for future generations.
Ecosystem Services by Dr. Krishnanand
Biodiversity: Dive into the mesmerizing world of biodiversity where a myriad of plants, animals, and ecosystems coexist in harmony. Explore the beauty of nature and learn about the importance of preserving our diverse environment in this captivating video. Conservation: Join us on a journey to discover the inspiring efforts of conservationists working tirelessly to protect our planet\'s precious wildlife and natural resources. Be part of the solution and witness the positive impact of conservation in action in this heartwarming video.
The Importance of Ecosystem Services
This video is about The Importance of Ecosystem Services.
Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services
Assigning economic value to ecosystem services is crucial for understanding their contribution to the economy and for making informed decisions about environmental conservation and sustainable use. This valuation helps highlight the often-overlooked economic importance of natural systems and the services they provide.
- Direct Use Value: The tangible benefits obtained from ecosystem services, such as food, raw materials, and recreational opportunities, which have direct market prices.
- Indirect Use Value: The services that support life indirectly, like climate regulation, flood control, and pollination, which are more challenging to price but essential for economic activities.
- Non-use Value: Values not associated with direct or indirect use, including the existence value (value of knowing that a natural environment exists) and bequest value (value of preserving natural environments for future generations).
- Integrated Assessment Models: Tools used to estimate the economic impacts of ecosystem changes on human well-being, combining ecological and economic data.
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES): Mechanisms that provide financial incentives to landowners or local communities to conserve and restore ecosystem services.
Valuing ecosystem services in economic terms facilitates their integration into policy-making and development planning, ensuring that the benefits of ecosystems are recognized and maintained for sustainable development and human welfare.

READ MORE:
The Future of Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of ecosystem services faces both significant challenges and opportunities. Addressing these effectively will require innovative approaches, collaborative efforts, and a commitment to sustainable development.
- Climate Change: As a major challenge, climate change threatens the stability and functionality of ecosystems worldwide. Adapting to these changes while mitigating further impacts is crucial.
- Biodiversity Loss: Protecting and restoring biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem resilience and the services they provide.
- Sustainable Management: Developing and implementing sustainable management practices for land, water, and resources will help preserve ecosystem services for future generations.
- Technological Advancements: Technology offers new opportunities for monitoring and managing ecosystems more effectively, from satellite imaging to data analytics.
- Policy and Governance: Strong policy frameworks and governance structures are needed to integrate ecosystem service valuation into economic systems and decision-making processes.
- Community Engagement and Education: Engaging communities and educating the public about the importance of ecosystem services can foster greater environmental stewardship.
- International Cooperation: Global challenges require global solutions. International cooperation is vital for addressing cross-border environmental issues and promoting sustainable practices worldwide.
Despite the challenges, the future also holds immense opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and progress towards a more sustainable and resilient world. Embracing these opportunities will be key to ensuring the continued provision of ecosystem services.
Embracing the vital role of ecosystem services promises a sustainable future, fostering harmony between humanity and nature for generations to come.