Topic define ecosystem service: Explore the invisible threads connecting humanity to nature through ecosystem services, the vital benefits our environment generously provides for our survival and well-being.
Table of Content
- What are ecosystem services and how do they benefit humans?
- Understanding Ecosystem Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services
- Importance of Ecosystem Services to Human Well-being
- Examples of Ecosystem Services
- Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Services
- Conservation and Sustainable Management of Ecosystem Services
- YOUTUBE: Understanding Ecosystem Services
- The Role of Policy and Governance in Ecosystem Service Conservation
What are ecosystem services and how do they benefit humans?
Ecosystem services refer to the various benefits that humans receive from healthy ecosystems and the natural environment. These services are classified into four main categories: provisioning, regulating, supporting, and cultural services.
- Provisioning services: These are the tangible products that ecosystems provide, such as food, water, timber, and medicine.
- Regulating services: Ecosystems help regulate important processes like climate, water purification, pollination, and natural hazard mitigation.
- Supporting services: These services are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, such as soil formation, nutrient cycling, and habitat creation.
- Cultural services: Ecosystems also provide intangible benefits like recreational opportunities, spiritual and aesthetic values, and cultural heritage.
The benefits of ecosystem services to humans are vast and essential for sustaining life on Earth. These services contribute to human well-being, economic development, and overall quality of life in various ways:
- Ecosystem services support agriculture by providing fertile soil, clean water, and pollination for crops.
- Forests and wetlands act as natural filters, purifying water and maintaining clean water sources for human consumption.
- Healthy ecosystems help regulate climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events.
- Biodiversity in ecosystems provides resilience against diseases, pests, and environmental changes that could threaten human health and food security.
- Ecosystems offer recreational opportunities for people to enjoy nature, reducing stress and promoting physical and mental well-being.
In conclusion, understanding and preserving ecosystem services are crucial for sustainable development and ensuring a harmonious relationship between humans and the environment. By recognizing the benefits that ecosystems provide, we can make informed decisions to protect and manage natural resources for the benefit of current and future generations.
READ MORE:
Understanding Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the multitude of benefits that nature provides to humanity, underpinning our very existence, health, and prosperity. These services are often taken for granted but are crucial for our survival and the health of our planet.
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, fresh water, wood, fiber, and genetic resources.
- Regulating Services: Nature"s role in regulating climate, floods, disease, wastes, and water quality.
- Cultural Services: Non-material benefits obtained from ecosystems such as spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, recreation, and aesthetic values.
- Supporting Services: These are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and water cycling.
Understanding these services helps us recognize the direct and indirect benefits we receive from ecosystems, emphasizing the need for sustainable interaction with our environment.
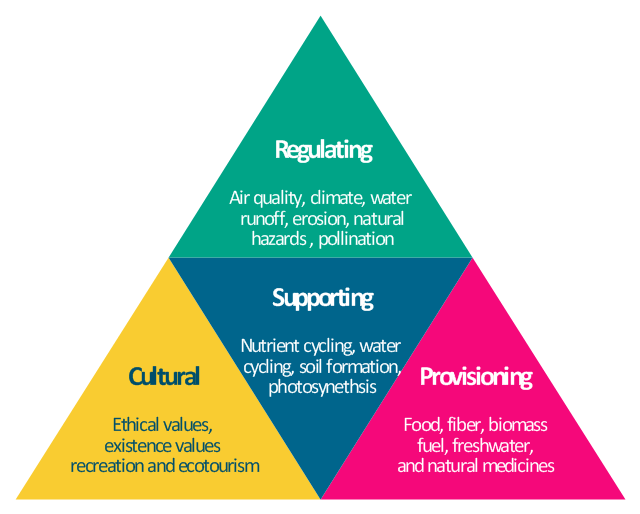
Types of Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits provided by ecosystems that contribute to making human life both possible and worth living. These services are categorized into four main types, each essential for our well-being and the health of our planet:
- Provisioning Services: The products obtained from ecosystems, including food, water, timber, fiber, and genetic resources. These are the raw materials that support human survival and economic activity.
- Regulating Services: The benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes, such as climate regulation, flood control, disease regulation, and water purification. These services help maintain the environment"s balance and ensure its resilience against disturbances.
- Cultural Services: The non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences. Cultural services include tourism, outdoor recreation, and cultural heritage.
- Supporting Services: These are services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services, including soil formation, photosynthesis, primary production, nutrient cycling, and water cycling. They underpin the functioning of the ecosystem and its ability to provide services.
Recognizing these types helps in understanding how ecosystems contribute to our lives and highlights the importance of their conservation and sustainable management.
Importance of Ecosystem Services to Human Well-being
The significance of ecosystem services extends far beyond their intrinsic environmental value, playing a pivotal role in ensuring human well-being and survival. These services are vital for several reasons:
- Supporting Daily Needs: Provisioning services like food, clean water, and air are foundational for human health and daily sustenance.
- Maintaining Environmental Balance: Regulating services such as climate control, flood mitigation, and disease regulation help maintain the stability and safety of our environments.
- Contributing to Economic Development: Many industries rely on natural resources and ecosystem services, including agriculture, forestry, fishing, and tourism, driving economic growth and employment.
- Enhancing Quality of Life: Cultural services offer recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits, improving mental health, community well-being, and overall quality of life.
- Ensuring Future Sustainability: Ecosystem services are crucial for sustainability, helping to ensure that future generations have the same or improved access to these essential benefits.
Understanding and preserving ecosystem services is not only a matter of environmental conservation but also a prerequisite for sustainable development, public health, and economic prosperity.

Examples of Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the many ways through which natural ecosystems and the biodiversity within them support and fulfill human life. Here are some concrete examples:
- Pollination of Crops: Insects, birds, and bats play a crucial role in the reproduction of many plants, including many food crops, enhancing food security and agricultural productivity.
- Water Purification: Wetlands, forests, and rivers naturally filter pollutants, reducing the need for costly artificial filtration and providing clean water for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests and oceans absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the impacts of climate change and contributing to the regulation of the Earth"s climate.
- Soil Erosion Control: Vegetation cover and root systems stabilize soil, preventing erosion, reducing loss of fertile land, and supporting agriculture.
- Natural Disaster Mitigation: Ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs act as barriers against storms and tsunamis, protecting coastlines and communities from natural disasters.
- Recreational and Cultural Benefits: Natural parks, landscapes, and seascapes offer recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual benefits, supporting mental and physical health.
These examples highlight the indispensable services provided by ecosystems, emphasizing the need for their protection and sustainable management.
Challenges and Threats to Ecosystem Services
The sustainability of ecosystem services is under threat from various global challenges, posing significant risks to biodiversity, human well-being, and future generations. Key challenges include:
- Climate Change: Alterations in climate patterns can disrupt the provisioning, regulating, and supporting services ecosystems provide, exacerbating vulnerabilities in food security and disaster resilience.
- Habitat Destruction: Urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural expansion lead to the loss of habitats, diminishing biodiversity and the ecosystem services it supports.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution can degrade ecosystems, reducing their ability to provide clean water, air, and fertile soil for agriculture.
- Overexploitation of Resources: Unsustainable fishing, logging, and mining practices can deplete resources faster than they can regenerate, undermining ecosystem services.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can alter ecosystem functions, outcompeting native species and reducing biodiversity.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The decline in species diversity affects ecosystem resilience, reducing its ability to adapt to changes and provide essential services.
Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation, sustainable management practices, and policies that prioritize ecosystem conservation and restoration.

Conservation and Sustainable Management of Ecosystem Services
Ensuring the longevity and resilience of ecosystem services necessitates a strategic approach to conservation and sustainable management. Effective strategies include:
- Protected Areas: Establishing and maintaining protected areas to conserve critical habitats and biodiversity, ensuring the provision of essential ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Land Use Practices: Implementing sustainable agriculture, forestry, and urban planning practices that minimize environmental impact and enhance ecosystem services.
- Restoration Projects: Restoring degraded ecosystems to recover their ability to provide essential services, including reforestation and wetlands restoration.
- Integrated Water Resources Management: Managing water resources in a holistic and sustainable manner to support clean water supply and healthy aquatic ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: Adopting practices and policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change, protecting ecosystems and their services.
- Community Engagement and Education: Involving local communities in conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of ecosystem services and how to sustainably manage them.
- Policies and Legislation: Developing and enforcing policies and laws that promote the conservation and sustainable use of ecosystems and their services.
Through these measures, we can safeguard ecosystem services for future generations, supporting global well-being and biodiversity conservation.
Understanding Ecosystem Services
Explore the beauty and importance of biodiversity in our world through this captivating video. Discover the incredible variety of life forms and ecosystems that make our planet so unique and precious.
READ MORE:
The Role of Policy and Governance in Ecosystem Service Conservation
Policy and governance play critical roles in the conservation of ecosystem services, guiding the sustainable management and protection of ecosystems that provide vital services to humans and the environment. These frameworks establish the rules, regulations, and practices that determine how ecosystems are managed and conserved, aiming to balance human needs with environmental sustainability.
Effective policy and governance mechanisms are essential for:
- Identifying and protecting critical ecosystems that provide essential services.
- Implementing sustainable land use practices that preserve the ability of ecosystems to deliver services.
- Regulating activities that impact ecosystem health, such as pollution, deforestation, and overfishing.
- Encouraging restoration efforts for degraded ecosystems to regain their service provision capacities.
- Facilitating the integration of ecosystem service values into economic systems, promoting incentives for conservation.
- Supporting research and monitoring programs to better understand ecosystem functions and their contributions to human well-being.
- Enhancing public awareness and participation in ecosystem conservation efforts.
- Developing international cooperation to address ecosystem service conservation on a global scale.
Policy tools and governance mechanisms commonly used in ecosystem service conservation include:
- Environmental impact assessments to evaluate the potential effects of development projects on ecosystem services.
- Payment for ecosystem services (PES) schemes that provide financial incentives for the conservation of ecosystem services.
- Legal protections for endangered species and habitats critical for ecosystem service provision.
- Land use planning and zoning regulations to prevent habitat loss and fragmentation.
- International agreements and conventions that promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
Successful conservation and sustainable management of ecosystem services require collaborative efforts among governments, non-governmental organizations, the private sector, local communities, and individuals. By prioritizing ecosystem service conservation in policy and governance, society can ensure the long-term health and resilience of ecosystems that are fundamental to human survival and well-being.






