Topic what animals are in the grasslands: Discover the vibrant world of grassland ecosystems, where diverse animals thrive in vast, open landscapes, offering a glimpse into nature"s remarkable adaptability and beauty.
Table of Content
- What animals rely on prairie grasses for survival in the grasslands?
- Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
- Iconic Grassland Mammals
- Bird Species in Grasslands
- Reptiles and Amphibians of Grassland Habitats
- Insects and Other Invertebrates
- Adaptations to Grassland Life
- YOUTUBE: 9 Animals That Live in Grasslands
- Threats to Grassland Animals and Conservation Efforts
What animals rely on prairie grasses for survival in the grasslands?
Animals that rely on prairie grasses for survival in the grasslands include:
- Prairie dogs
- Bison
- Elk
- Deer
- Pronghorns
READ MORE:
Overview of Grassland Ecosystems
Grasslands, sprawling across the globe, are ecosystems characterized by wide open spaces filled with grasses, herbs, and shrubs, hosting a rich diversity of life. These biomes, varying from the savannas of Africa to the prairies of North America, play a crucial role in supporting a variety of species due to their fertile soil and seasonal rainfall patterns.
- Types of Grasslands: Includes tropical savannas, temperate grasslands, and polar grasslands, each with distinct climates and life forms.
- Climate and Geography: Typically found between deserts and forests, grasslands receive moderate rainfall, enough to sustain grasses but not enough for large trees to dominate.
- Biodiversity: Home to many species, from large herbivores like bison and zebras to predators such as lions and wolves, alongside numerous bird, insect, and plant species.
- Importance: Essential for ecosystems services such as soil preservation, carbon sequestration, and serving as grazing grounds for livestock, while also being habitats for numerous endangered species.
Grasslands are not just about the grass; they are vibrant ecosystems that support complex interactions among plants, animals, and their environment, playing a significant role in the Earth"s ecological balance.
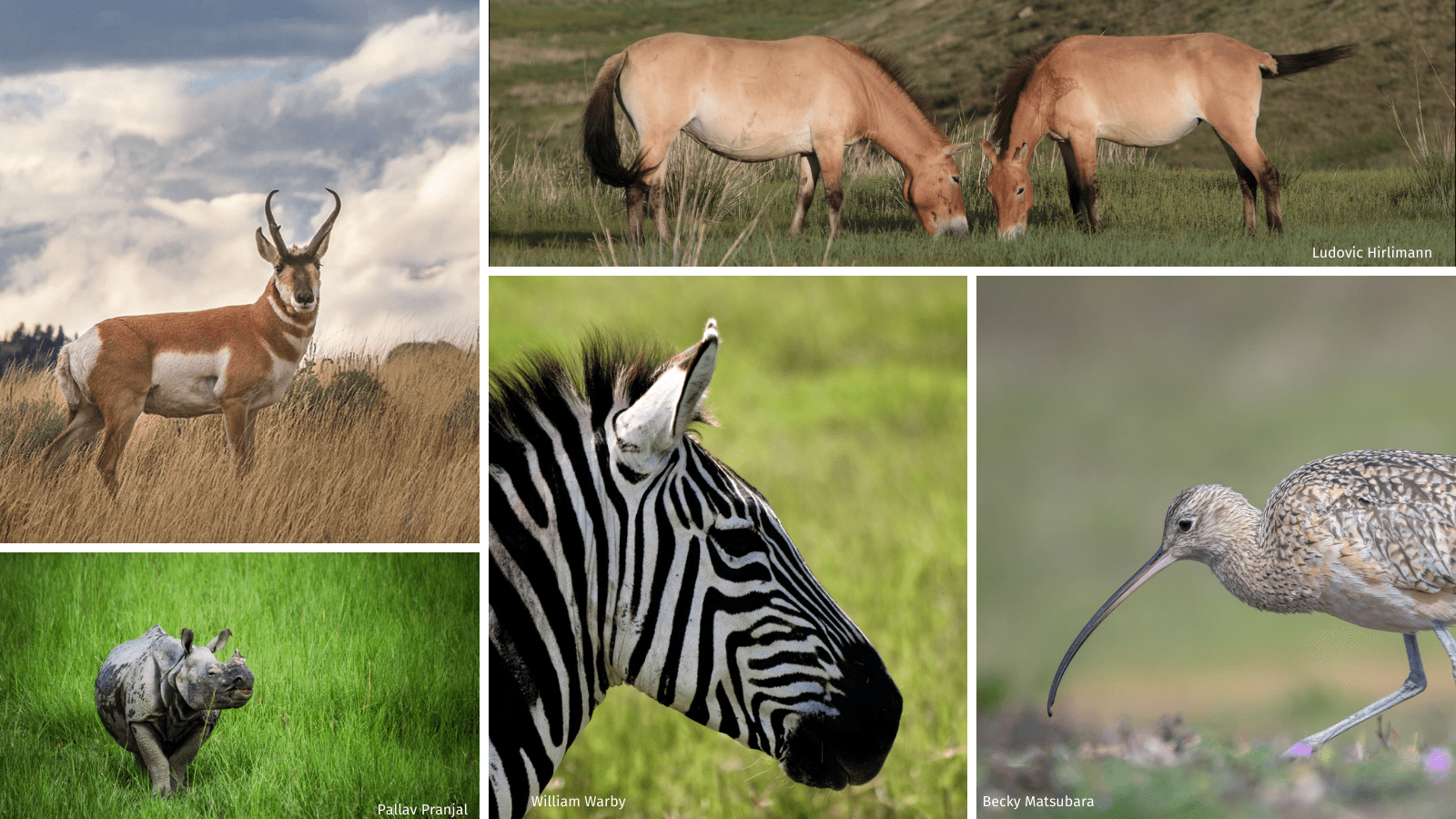

Iconic Grassland Mammals
Grasslands around the world are teeming with a variety of mammals, each adapted to thrive in the open, grassy landscapes. These mammals play a pivotal role in maintaining the ecological balance, serving as both predators and prey within their respective ecosystems.
- African Elephants: The largest land mammals, these gentle giants roam the African savannas, shaping the landscape as they feed on trees and grasses.
- North American Bison: Once roaming the Great Plains in vast herds, bison are a symbol of the American prairie, vital for the grassland"s health and biodiversity.
- African Lions: Top predators of the African grasslands, lions play a crucial role in controlling the population of herbivores and maintaining the ecosystem"s balance.
- Asian Steppe Saiga Antelope: Known for their distinctive bulbous nose, these critically endangered antelopes are adapted to the harsh conditions of the Eurasian steppes.
- Australian Kangaroos: Symbolic of the Australian outback, kangaroos are marsupials that graze on grasses and herbs, with unique adaptations for long-distance hopping.
These mammals, among others, are integral to the grassland biome, each contributing to the dynamic and complex web of life that defines these vast, open ecosystems.
Bird Species in Grasslands
Grasslands serve as a vital habitat for a diverse array of bird species, each adapted to life in these expansive habitats. From ground-nesting birds to majestic raptors, grasslands provide a rich tapestry of avian life that contributes to the ecological diversity and balance of these ecosystems.
- Greater Prairie-Chicken: A symbol of North American grasslands, these birds are known for their unique mating dances and booming calls during the breeding season.
- Red-tailed Hawk: These raptors soar above grasslands, using their keen eyesight to spot prey from high above. They are crucial for controlling rodent populations.
- African Secretary Bird: Standing tall on long legs, these birds of prey hunt snakes and rodents, walking through the grasslands of Africa.
- Sarus Crane: The world"s tallest flying birds, found in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, rely on wet grasslands for breeding and feeding.
- Eastern Meadowlark: Known for their distinctive yellow breast and melodious songs, meadowlarks are a common sight in North American grasslands.
These bird species, among others, play essential roles in grassland ecosystems, from pollination and seed dispersion to controlling pest populations, showcasing the interconnectedness of life within these biomes.

Reptiles and Amphibians of Grassland Habitats
Reptiles and amphibians are integral components of grassland ecosystems, playing key roles in the food chain and contributing to the biological diversity of these habitats. These cold-blooded creatures are well-adapted to the varying conditions of grasslands around the world.
- Gopher Tortoise: A keystone species in North American grasslands, known for its burrowing activity that creates habitats for other species.
- Rattlesnakes: Predators that play a crucial role in controlling rodent populations, rattlesnakes are well-suited to the dry conditions of many grassland areas.
- Grassland Frogs: Species like the Plains Leopard Frog thrive in the moist areas of grasslands, contributing to insect control and serving as prey for larger animals.
- Eastern Collared Lizard: Colorful and agile, these lizards are found in open, sunny areas where they hunt insects and other small prey.
- Common Toad: Found across various grasslands, these amphibians are vital for controlling insect populations, benefiting agricultural areas especially.
These reptiles and amphibians, with their diverse diets and behaviors, enhance the ecological dynamics of grasslands, demonstrating the complexity and resilience of these ecosystems.
Insects and Other Invertebrates
Insects and other invertebrates play pivotal roles in grassland ecosystems, acting as pollinators, decomposers, and food sources for a variety of animals. These small creatures are essential for the health and sustainability of grasslands worldwide.
- Grasshoppers and Locusts: These insects are among the most visible in grasslands, serving as important food sources for birds and reptiles.
- Bees and Butterflies: Crucial for pollination, these invertebrates support the growth of plants, which in turn sustain other wildlife in the grassland.
- Ants: Known for their complex social structures, ants play key roles in soil aeration and decomposition, contributing to the health of the grassland ecosystem.
- Spiders: Acting as natural pest controllers, spiders help maintain balanced insect populations within grasslands.
- Earthworms: Essential for soil health, earthworms improve soil structure and fertility, benefiting the vast array of plant life found in grasslands.
Through their diverse activities, insects and other invertebrates are fundamental to the productivity and diversity of grassland ecosystems, showcasing the intricate web of life that thrives within these habitats.
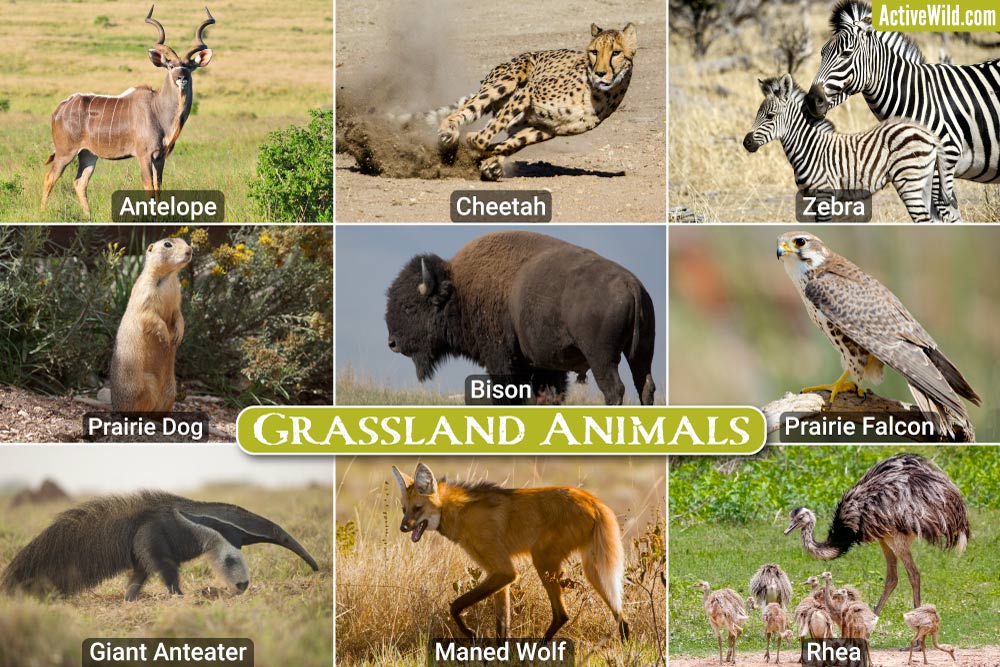

Adaptations to Grassland Life
Animals and plants in grasslands have evolved unique adaptations to survive in an environment characterized by wide open spaces, periodic droughts, and occasional fires. These adaptations ensure their survival and success in these dynamic ecosystems.
- Large Herbivores: Animals like bison and zebras have developed strong teeth and digestive systems to feed on tough grasses, while their large, flat feet help them move easily over soft, uneven terrain.
- Predators: Lions, cheetahs, and other predators have adapted for speed and stealth, crucial for hunting in the open landscapes where hiding places are scarce.
- Burrowing Animals: Many small mammals and reptiles burrow underground to escape the heat of the day, conserve moisture, and hide from predators.
- Camouflage: Grassland birds and insects often have coloring that blends into their environment, helping them avoid predation.
- Fire Adaptation: Some grassland plants have seeds that only germinate after a fire, ensuring their species" survival and regeneration of the ecosystem.
These adaptations not only highlight the resilience of grassland species but also the intricate balance and interdependence of life within these ecosystems.
9 Animals That Live in Grasslands
\"Discover the fascinating world of animals in our captivating video! From playful puppies to majestic elephants, you\'ll be amazed by the beauty and diversity of the animal kingdom. Watch now and let these adorable creatures warm your heart!\"
What Animals Live in Grasslands
\"Step into the breathtaking beauty of the grasslands in our mesmerizing video! Experience the vast open spaces, vibrant wildflowers, and graceful wildlife that call these plains home. Immerse yourself in the serenity of the grasslands today!\"
READ MORE:
Threats to Grassland Animals and Conservation Efforts
Grassland ecosystems face various threats that impact the diverse species living within them. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these habitats and ensure the survival of grassland animals.
- Habitat Loss: Expansion of agriculture, urban development, and mining reduces grassland areas, leading to loss of habitat for many species.
- Climate Change: Altered rainfall patterns and temperatures affect grass growth and water availability, impacting food sources for herbivores and the entire food chain.
- Overgrazing: Unsustainable livestock farming practices can lead to soil erosion and degradation of grasslands, diminishing the quality of habitat for native species.
- Pollution: Pesticides and other chemicals used in farming can contaminate water sources and soil, harming grassland wildlife.
- Conservation Efforts: Protected areas, sustainable land management practices, and conservation programs aim to restore and preserve grassland ecosystems. Initiatives include rewilding projects, community-based conservation, and legal protections for key species and habitats.
By addressing these threats through concerted conservation efforts, we can safeguard the future of grassland ecosystems and the incredible diversity of life they support.
Exploring the grasslands reveals a world of incredible diversity and resilience. By understanding and protecting these ecosystems, we ensure a rich natural heritage for future generations to cherish and learn from.