Topic vertebrate invertebrate: Delve into the fascinating world of biology as we compare and contrast vertebrates and invertebrates, exploring their unique characteristics, evolutionary journeys, and vital roles in our ecosystems.
Table of Content
- How many animals are invertebrates?
- Understanding Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Key Characteristics of Vertebrates
- Key Characteristics of Invertebrates
- Evolutionary Perspectives
- Diversity and Classification
- Ecological Importance of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- YOUTUBE: Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals - Educational Videos for Kids
- Comparative Anatomy and Physiology
- Role in Ecosystems and Human Life
- Conservation Issues
- Current Research and Future Directions
How many animals are invertebrates?
Approximately 97% of animals on our planet are invertebrates.
Invertebrates are animals without spines or backbones, while vertebrates have a backbone.
They are a diverse group of animals that includes insects, worms, mollusks, crustaceans, and more.
Invertebrates play vital roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and prey for other animals.
Some well-known phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, and cnidarians.
- Arthropods include insects, spiders, crustaceans, and millipedes.
- Mollusks include snails, clams, octopuses, and squids.
- Annelids include earthworms and leeches.
- Cnidarians include jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones.
It is important to protect and conserve the diverse habitats and species of invertebrates to maintain the balance of our ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Understanding Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Vertebrates and invertebrates represent two fundamental divisions in the animal kingdom. Vertebrates, characterized by a backbone or spinal column, include diverse classes like mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. They are known for their complex structures and higher levels of mobility.
In contrast, invertebrates, which lack a vertebral column, encompass a vast array of species including insects, arachnids, mollusks, crustaceans, and echinoderms. These creatures are incredibly diverse, adapting to various environments, and play vital roles in ecological systems.
- Biological Classification: Understanding their taxonomy and evolutionary links.
- Anatomical Differences: Exploring the structural distinctions between vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Behavioral and Ecological Impact: Examining their roles in ecosystems and their interactions with other species.
- Adaptations: How these groups have evolved to thrive in their respective habitats.
- Conservation Challenges: Addressing the threats and preservation efforts for both vertebrates and invertebrates.
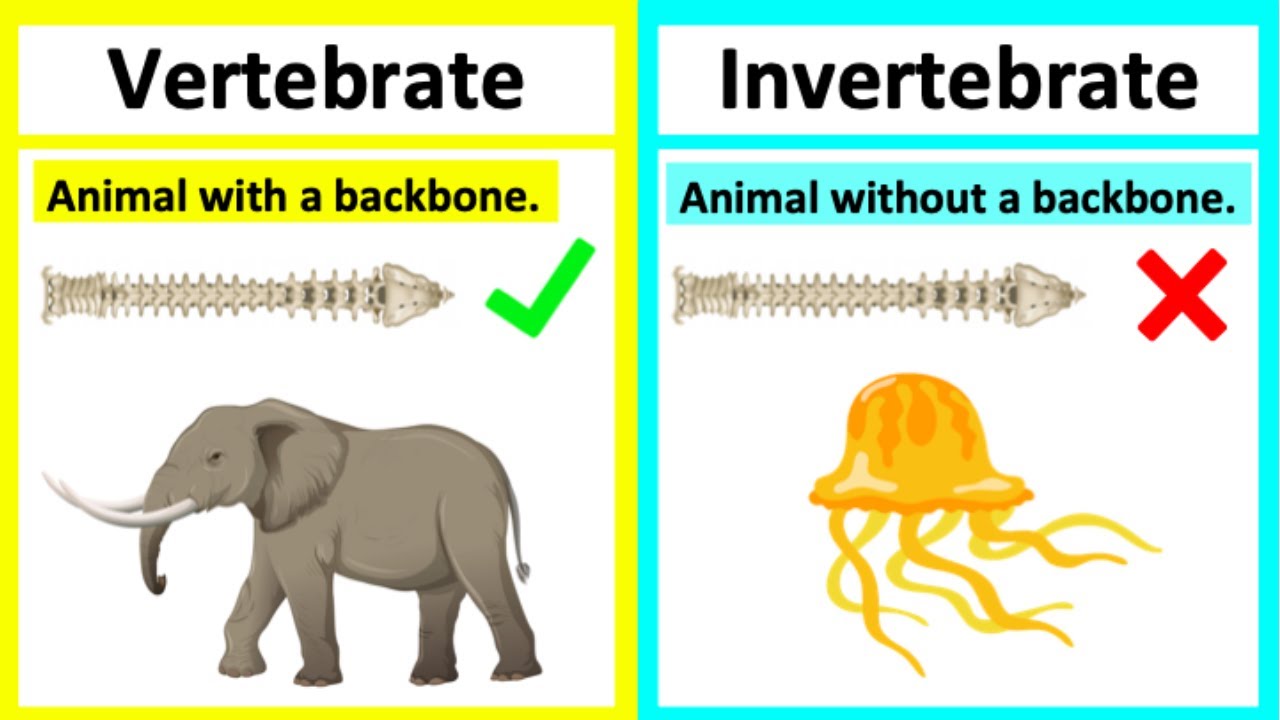
Key Characteristics of Vertebrates
Vertebrates are distinguished by a series of unique features that set them apart from invertebrates. The most defining characteristic is the presence of a vertebral column or spine, providing structural support and protection for the spinal cord.
- Endoskeleton: Composed of bones or cartilage, providing support and facilitating movement.
- Complex Nervous System: Advanced brain and spinal cord, enabling refined sensory and motor functions.
- Closed Circulatory System: Including a heart that pumps blood through a network of vessels.
- Respiratory System: Lungs or gills for gas exchange, essential for sustaining high metabolic rates.
- Reproductive Systems: Mostly internal fertilization, with diverse reproductive strategies across species.
These features contribute to the vast diversity of vertebrates, which include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, each adapting to their unique environments and ecological niches.
Key Characteristics of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, a diverse group lacking a vertebral column, encompass the majority of animal species on Earth. They exhibit a remarkable range of forms, sizes, and habitats, contributing significantly to ecological diversity.
- Lack of Backbone: The absence of a vertebral column is a defining feature.
- Varied Body Structures: Invertebrates display a wide range of body plans, from simple to complex.
- Diverse Reproduction: Methods range from simple asexual reproduction to complex sexual reproduction.
- Exoskeletons in Many Species: For protection and support, many invertebrates have an external skeleton.
- Significant Ecological Roles: From pollinators to decomposers, invertebrates are crucial in various ecosystems.
Groups like insects, arachnids, mollusks, and crustaceans are prominent examples of invertebrates, each adapted to their unique ecological niches.
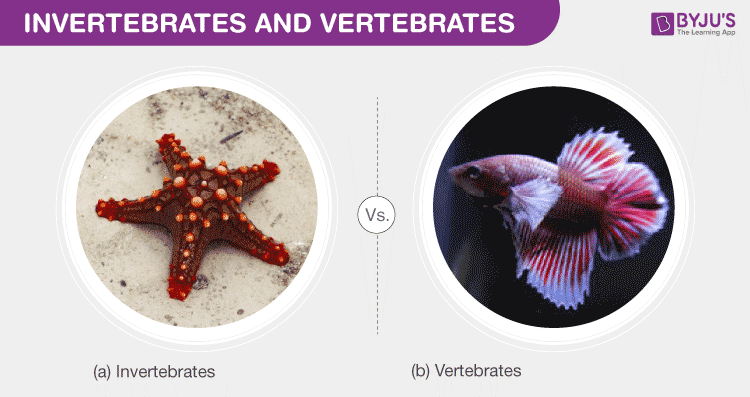
Evolutionary Perspectives
The evolutionary journey of vertebrates and invertebrates is a captivating tale of biological development over millions of years. It highlights the adaptability and diversity of life on Earth.
- Early Origins: Invertebrates are some of the oldest known organisms, with fossils dating back hundreds of millions of years.
- Development of Vertebrates: The transition from invertebrates to vertebrates marked a significant evolutionary step, introducing complex structures like the spinal column.
- Diversification: Both groups have undergone extensive diversification, adapting to a wide range of environments and ecological niches.
- Evolutionary Innovations: The evolution of various body plans, systems, and behaviors in these groups demonstrates nature"s creativity and resilience.
This evolutionary perspective provides insights into the complexity and interconnectedness of life, emphasizing the importance of both vertebrates and invertebrates in the natural world.
Diversity and Classification
The animal kingdom is broadly divided into vertebrates and invertebrates, each with its own intricate classification system and vast diversity.
- Vertebrate Classification: This group is further divided into five main classes - mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, each with distinctive characteristics and evolutionary histories.
- Invertebrate Diversity: Comprising about 97% of all animal species, invertebrates include numerous groups like insects, mollusks, arachnids, annelids, and echinoderms.
- Species Richness: Invertebrates, especially insects, represent the majority of animal biodiversity on Earth, with an immense variety of species adapted to almost every environment.
- Classification Challenges: The complexity and diversity within these groups pose ongoing challenges and opportunities for scientific exploration and classification.
This section explores the classification systems, highlighting the rich diversity within both vertebrates and invertebrates and their importance in the natural world.

Ecological Importance of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Vertebrates and invertebrates play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. Their interactions within ecosystems are complex and vital for environmental health.
- Role in Food Webs: Both vertebrates and invertebrates are integral components of food webs, serving as predators, prey, and decomposers.
- Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Invertebrates like bees and butterflies are essential for pollination, while some vertebrates aid in seed dispersal.
- Soil Aeration and Fertility: Earthworms and other invertebrates improve soil quality, crucial for plant growth.
- Indicator Species: Many vertebrates and invertebrates serve as indicators of environmental health, signalling changes in ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Maintenance: The diversity within these groups contributes significantly to the overall biodiversity of habitats.
This section highlights the indispensable roles that both vertebrates and invertebrates play in ecological processes and the sustenance of life on Earth.
Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals - Educational Videos for Kids
Get ready to be amazed by the incredible world of animals! Watch this captivating video and discover the beauty and diversity of nature\'s creatures. From majestic lions to tiny hummingbirds, you\'ll be left in awe of their unique abilities and fascinating behaviors. Don\'t miss out on this opportunity to learn and be entertained!
Vertebrate vs Invertebrate | Types of Animals | What\'s the Difference?
Curious about the difference between two similar concepts? This engaging video is here to provide you with all the answers. Explore the nuances and distinctions that set them apart, and gain a deeper understanding of the intricacies of the subject. With clear explanations and captivating visuals, this video will leave you with a newfound knowledge and a eagerness to learn more. Don\'t miss out on this enlightening experience!
Comparative Anatomy and Physiology
Comparing the anatomy and physiology of vertebrates and invertebrates reveals fascinating insights into the diversity of life forms and their adaptations to various environments.
- Structural Differences: Vertebrates possess an internal skeleton including a spine, while invertebrates may have an external skeleton (exoskeleton) or no rigid structure.
- Nervous System: Vertebrates typically have a more complex nervous system, including a well-developed brain and spinal cord, compared to the simpler systems in invertebrates.
- Reproductive Systems: Vertebrates generally have internal fertilization and a variety of reproductive strategies, whereas invertebrates exhibit a wide range of reproductive methods, including both internal and external fertilization.
- Respiration: Vertebrates breathe through lungs or gills, while invertebrates use a variety of methods, such as tracheae, gills, or through their skin.
- Circulatory System: Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system with a heart, whereas invertebrates can have open or closed systems, or none at all in simpler organisms.
This section explores the key anatomical and physiological differences and similarities between vertebrates and invertebrates, highlighting how these traits are suited to their specific lifestyles and environments.

Role in Ecosystems and Human Life
Vertebrates and invertebrates play integral roles in ecosystems and have significant impacts on human life. Understanding these roles is key to appreciating our interconnectedness with nature.
- Ecosystem Services: These animals contribute to critical ecosystem functions like pollination, decomposition, soil aeration, and nutrient cycling.
- Food Sources: Both vertebrates and invertebrates serve as vital food sources for humans and other animals, maintaining food chain dynamics.
- Biodiversity Indicators: Their presence and health indicate the overall health of ecosystems, signaling environmental changes and potential threats.
- Scientific Research: They provide invaluable insights into biological processes and environmental studies, contributing to medical, environmental, and genetic research.
- Cultural and Economic Impact: From being part of cultural symbols to contributing to economies through activities like fishing and beekeeping, these creatures deeply impact human societies.
This section highlights the indispensable roles of vertebrates and invertebrates in maintaining ecological balance and their profound influence on various aspects of human life.
Conservation Issues
Conservation of vertebrates and invertebrates is critical for maintaining ecological balance. Many species face threats from human activities, requiring urgent attention and action.
- Habitat Loss: Deforestation, urbanization, and pollution lead to significant habitat loss for both vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Climate Change: Global warming affects breeding patterns, migration routes, and habitats, posing a serious threat to many species.
- Overexploitation: Overfishing, hunting, and poaching have drastically reduced populations of numerous vertebrates, while overuse of pesticides harms invertebrate populations.
- Conservation Efforts: Efforts include habitat protection, legal regulations, and breeding programs, but more comprehensive measures are needed globally.
- Awareness and Education: Promoting awareness about the importance of these creatures and their conservation is essential for their survival.
This section discusses the major conservation challenges faced by vertebrates and invertebrates and the efforts required to protect these vital components of our ecosystems.

READ MORE:
Current Research and Future Directions
Current research in the field of vertebrate and invertebrate biology is incredibly diverse, addressing various ecological, genetic, and conservation issues. Future directions point towards a more integrated and sustainable approach.
- Genetic and Molecular Studies: Advancements in genetic research are unraveling the complexities of these organisms, offering insights into their evolution and adaptation mechanisms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Research is increasingly focusing on how climate change is affecting both vertebrates and invertebrates, influencing their behavior, distribution, and survival.
- Conservation Technologies: Development of new technologies for monitoring and conserving species, including habitat restoration and wildlife tracking methods.
- Sustainable Practices: Emphasis on creating sustainable interactions between humans and these animal groups, balancing ecological needs with economic activities.
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: Combining various fields such as ecology, biotechnology, and environmental science for a holistic understanding and protection of biodiversity.
This section explores the forefront of research in vertebrate and invertebrate studies, highlighting the innovative approaches and future challenges in understanding and preserving these essential components of our natural world.
In exploring the intricate world of vertebrates and invertebrates, we uncover the rich tapestry of life on Earth, highlighting the need for conservation and appreciation of these remarkable creatures in our shared ecosystem.








