Topic are there more vertebrates or invertebrates: Embark on a fascinating journey to explore whether vertebrates or invertebrates dominate our planet, unveiling the incredible diversity and complexity of Earth"s animal kingdom.
Table of Content
- Are there more vertebrates or invertebrates in the animal kingdom?
- Overview of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Comparison of Species Numbers and Diversity
- Environmental Roles and Ecological Importance
- Evolutionary Perspective: Origins and Adaptations
- YOUTUBE: Vertebrate vs invertebrate: Types of animals, What\'s the difference?
- Size Range and Habitat Distribution
- Conservation Status: Threats and Protections
- Human Impact and Interaction with Both Groups
- Future Research and Unexplored Aspects
Are there more vertebrates or invertebrates in the animal kingdom?
Based on the Google search results and scientific data, it can be concluded that:
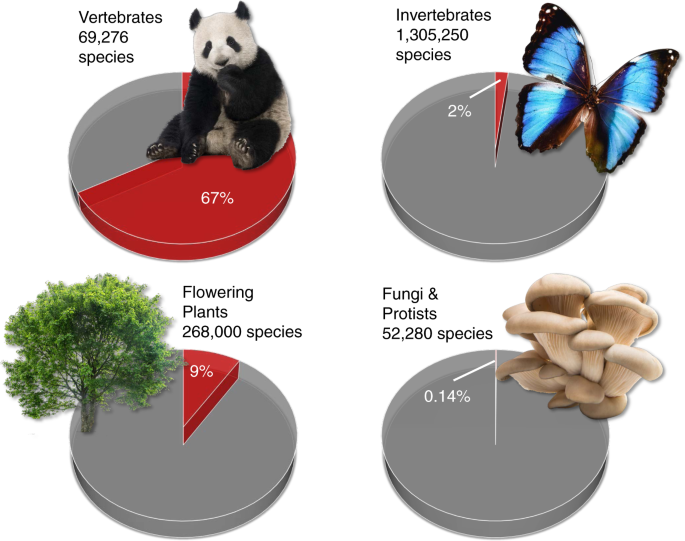
- Only five percent of all known animal species are vertebrates or animals with backbones.
- The vast majority, approximately 95 percent, of animal species are invertebrates.
- Invertebrates include insects, aquatic animals like jellyfish or sea creatures, and many more.
- The number of known vertebrate species may increase over time as more are discovered, but invertebrates are likely to continue dominating the animal kingdom by a wide margin.
- Both vertebrates and invertebrates have a diverse range of species and play important roles in various ecosystems.
READ MORE:
Overview of Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Delving into the animal kingdom reveals a vast diversity, primarily split between vertebrates and invertebrates. These two groups are distinguished by fundamental anatomical differences, each encompassing a wide range of species with unique characteristics.
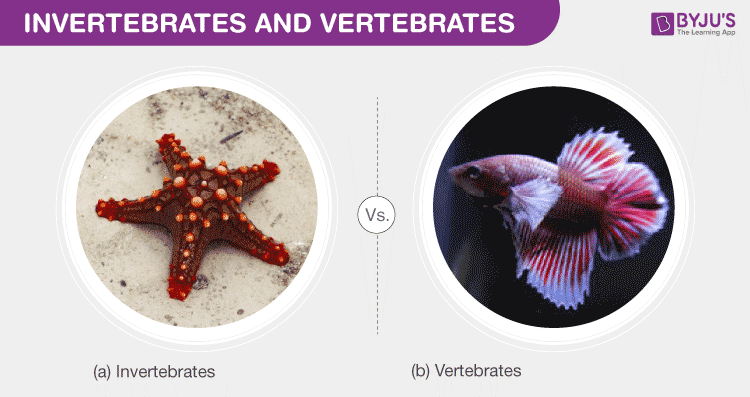
- Vertebrates: Characterized by the presence of a vertebral column or spine, vertebrates include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. This group is known for its complex nervous system and advanced sensory organs.
- Invertebrates: Lacking a spinal column, invertebrates comprise a much larger portion of animal species. This diverse group includes insects, arachnids, mollusks, crustaceans, and more, varying greatly in size, habitat, and biological traits.
Understanding these two classifications not only provides insight into their biological makeup but also sheds light on their evolutionary paths, ecological roles, and the ways in which they interact with their environments.

Comparison of Species Numbers and Diversity
When comparing the sheer numbers and diversity between vertebrates and invertebrates, the scales tip significantly towards one group. This comparison highlights the incredible variety and adaptability of life forms on our planet.
- Invertebrates: Invertebrates account for an overwhelming majority of animal species. Estimates suggest that they make up about 97% of all animal species. This group"s diversity is unparalleled, ranging from microscopic organisms to larger species like squids and starfish.
- Vertebrates: Although vertebrates are more familiar to us and include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, they represent only a small fraction of animal species. Despite their lower numbers, vertebrates are often more studied and understood.
This stark contrast in species numbers is a testament to the evolutionary success of invertebrates, capable of thriving in virtually every habitat on Earth. The diversity within these groups speaks to the vast array of ecological niches and evolutionary strategies employed by life on our planet.
Environmental Roles and Ecological Importance
Both vertebrates and invertebrates play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance. Vertebrates, such as mammals, birds, and fish, often serve as key species in their ecosystems, influencing the survival and distribution of other organisms. Invertebrates, comprising over 90% of all animal species, are integral to various ecological processes.
Key Roles of Invertebrates
- Pollination: Many invertebrates, especially insects like bees, are vital pollinators for numerous plant species, including those important for human agriculture.
- Decomposition: Invertebrates such as earthworms and certain insects play a significant role in decomposing organic matter, enriching soil fertility.
- Food Web Support: As a primary link in food chains, invertebrates serve as food for various vertebrates, sustaining the energy flow in ecosystems.
Key Roles of Vertebrates
- Predation and Control: Vertebrates like birds and fish maintain ecological balance by controlling invertebrate populations and serving as predators or prey in food chains.
- Seed Dispersion: Many vertebrates, including mammals and birds, are essential for the dispersal of seeds, aiding in plant propagation and diversity.
- Ecosystem Engineers: Certain vertebrates modify their environments significantly, creating habitats for other organisms (e.g., beavers building dams).
Both groups are under threat from human activities, and their conservation is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecological health. The intricate interdependence between vertebrates and invertebrates highlights the importance of preserving both groups for a balanced and functioning ecosystem.
Evolutionary Perspective: Origins and Adaptations
The evolutionary journey of vertebrates and invertebrates highlights the rich diversity and complexity of life on Earth. Vertebrates, characterized by their backbone, and invertebrates, notable for their lack thereof, represent distinct evolutionary paths with unique adaptations and origins.
Evolution of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, constituting a vast majority of animal species, exhibit an incredible range of diversity. Their evolution is believed to have begun with simple organisms, possibly small aquatic worms or even single-celled creatures. Over time, these early forms diversified into a multitude of species, including insects, arachnids, mollusks, crustaceans, and more. The Cambrian period, around 500 million years ago, marked a significant diversification of invertebrate species, although their exact origin remains a subject of ongoing research.
Evolution of Vertebrates
Vertebrate evolution traces back to the emergence of chordates around 540 million years ago. These early chordates, characterized by notochords, eventually developed complex structures like gills, eyes, and brains. The evolution of vertebrates can be divided into major stages, including the appearance of jawed fish in the Silurian period, the rise of amphibians at the end of the Devonian period, and the diversification of reptiles during the Carboniferous period. These evolutionary stages set the foundation for the emergence of mammals and the rich diversity of vertebrate species we observe today.
Distinct Characteristics and Adaptations
- Physical Structure: Vertebrates possess an internal skeleton made of bones or cartilage, while invertebrates often rely on external structures like shells or exoskeletons for support.
- Nervous System: Vertebrates have a centralized nervous system with a spinal cord and brain, whereas invertebrates use nerve cells and ganglia for coordination.
- Habitat and Behavior: Vertebrates are generally more active and mobile due to their skeletal structure, while invertebrates are incredibly diverse in their habitat preferences, occupying virtually every ecological niche.
This evolutionary narrative underscores the intricate and dynamic history of life on our planet, revealing how vertebrates and invertebrates have adapted and thrived in diverse environments over millions of years.
Vertebrate vs invertebrate: Types of animals, What\'s the difference?
Come and explore the fascinating world of animals in this captivating video! From majestic lions to adorable dolphins, witness the beauty and diversity of nature\'s creations. Get ready to embark on an unforgettable journey with these incredible creatures!
The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates, Educational Videos for Kids
Expand your knowledge and have fun with these educational videos! Get ready to dive into a world of science, history, and fascinating discoveries. Whether you\'re a curious learner or an avid explorer, these videos will ignite your thirst for knowledge and leave you craving more!
Size Range and Habitat Distribution
The animal kingdom exhibits a vast range of sizes and habitats, with significant differences between vertebrates and invertebrates. Invertebrates, which comprise about 95% of all known animal species, display an extensive size range, from microscopic organisms to larger species like jellyfish and octopuses. Vertebrates, though fewer in number, also show a wide size range, from small birds and fish to large mammals like elephants and whales.
Habitat Distribution of Invertebrates
- Invertebrates are found in nearly every environment on Earth, from deep ocean floors to high mountain peaks.
- They adapt to a wide range of habitats, including soil, water, and air.
- Examples include insects in forests, mollusks in oceans, and arachnids in desert areas.
Habitat Distribution of Vertebrates
- Vertebrates inhabit diverse environments, from aquatic ecosystems to terrestrial habitats.
- They are typically found in environments suitable for their specific needs, such as birds in air, fish in water, and mammals in various terrestrial settings.
- Some vertebrates are adapted to extreme conditions, like penguins in cold climates and camels in deserts.
This distribution and diversity in size and habitat reflect the adaptability and evolutionary success of both vertebrates and invertebrates across the globe.

Conservation Status: Threats and Protections
Both vertebrates and invertebrates face various conservation challenges, but their vast differences in diversity and biological characteristics lead to distinct conservation needs and strategies.
Conservation of Invertebrates
- Invertebrates, making up a significant portion of biodiversity, are crucial in ecosystems for functions like pollination and soil aeration.
- Threats to invertebrates include habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, impacting their survival and the ecosystems they support.
- Conservation efforts for invertebrates often focus on habitat protection and restoration, along with research to understand their roles in ecosystems.
Conservation of Vertebrates
- Vertebrates, often more visible and studied, face threats from habitat loss, hunting, and climate change.
- They play key roles in their ecosystems as predators, prey, and ecological engineers.
- Conservation efforts for vertebrates include legal protections, habitat conservation, and specific species recovery programs.
The conservation of both vertebrates and invertebrates is vital for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. A holistic approach, considering the interconnectedness of all species, is essential for effective conservation.
Human Impact and Interaction with Both Groups
Human activities have significantly impacted both vertebrates and invertebrates, with varying consequences for each group. Our interactions range from detrimental to beneficial, influencing their survival and ecosystems.
Impact on Vertebrates
- Habitat Alteration: Urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation have led to habitat loss for many vertebrate species.
- Overexploitation: Hunting, fishing, and trade have caused population declines in numerous vertebrate species, sometimes leading to extinction.
- Conservation Efforts: Humans have established wildlife reserves, breeding programs, and legal protections to conserve and restore vertebrate populations.
Impact on Invertebrates
- Pollution: Pesticides and other chemicals have detrimental effects on invertebrate populations, particularly pollinators like bees.
- Climate Change: Global warming affects invertebrates" habitats and life cycles, impacting ecological balances.
- Scientific Research and Education: Invertebrates are often studied for scientific research, and conservation awareness programs aim to highlight their importance.
Understanding and mitigating human impact on these groups is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. Responsible stewardship and informed conservation strategies are necessary for the coexistence of humans, vertebrates, and invertebrates.
READ MORE:
Future Research and Unexplored Aspects
The exploration of vertebrates and invertebrates presents vast opportunities for future research, particularly in understanding their evolutionary paths, ecological roles, and responses to environmental changes.
Research Areas in Vertebrates
- Genetic and Evolutionary Studies: Deepening the understanding of the evolutionary history of vertebrates, from the emergence of chordates to the diversification of major classes like mammals, birds, and fish.
- Behavioral and Ecological Research: Examining the complex behaviors of vertebrates in varying ecosystems to understand their roles as apex predators, prey, and ecological engineers.
- Conservation Biology: Focusing on endangered species and habitats, studying the impacts of human activities, and developing strategies for conservation and restoration.
Research Areas in Invertebrates
- Diversity and Taxonomy: Exploring the immense diversity of invertebrates, which constitute a majority of animal species, to understand their classification and evolutionary relationships.
- Environmental Adaptations: Investigating how invertebrates adapt to different habitats and environmental changes, including studies on their physiology and life cycles.
- Role in Ecosystems: Understanding the ecological importance of invertebrates in processes like pollination, soil formation, and as part of the food web.
These research areas highlight the need for continued and expanded scientific inquiry into both vertebrates and invertebrates, to uncover the complexities of their existence and ensure their conservation in a rapidly changing world.
Exploring the fascinating world of vertebrates and invertebrates reveals a tapestry of life far richer than imagined. Join us in uncovering the wonders and complexities of these diverse creatures that shape our planet"s ecosystems.