Topic how are invertebrates and vertebrates alike: Explore the fascinating world where invertebrates and vertebrates converge, revealing the astonishing similarities that unite these diverse creatures of the Animal Kingdom.
Table of Content
- How are invertebrates and vertebrates alike?
- Basic Overview and Classification
- Physical Structures and Body Systems
- Reproduction and Life Cycles
- Environmental Adaptations and Habitats
- Diet and Nutrition
- Role in Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- YOUTUBE: Vertebrate vs Invertebrate: Types of Animals and the Difference
- Conservation and Environmental Impact
- Scientific and Research Applications
- Cultural and Societal Significance
- Future Directions in Study and Research
How are invertebrates and vertebrates alike?
Invertebrates and vertebrates share several similarities:
- Both invertebrates and vertebrates are multicellular organisms.
- They are composed of eukaryotic cells.
- Both groups of animals are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain nutrition by consuming organic matter.
- Both have sense organs that allow them to perceive their environment.
- They have the ability to reproduce, although the methods of reproduction may vary between different species.
READ MORE:
Basic Overview and Classification
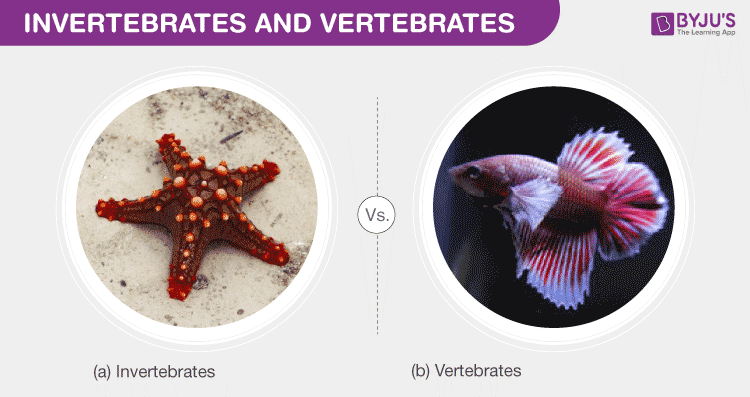
In the animal kingdom, creatures are broadly classified into invertebrates and vertebrates. This classification is primarily based on the presence or absence of a vertebral column or backbone. Invertebrates, constituting about 97% of all animal species, lack a vertebral column. This group includes diverse creatures like insects, mollusks, and crustaceans. Vertebrates, making up the remaining 3%, possess a vertebral column and include classes such as mammals, birds, fish, amphibians, and reptiles.
- Invertebrates:
- Lack a backbone or spinal column.
- Show both bilateral and radial symmetry.
- Include phyla like Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida.
- Vertebrates:
- Possess a backbone made of vertebrae.
- Always show bilateral symmetry.
- Encompass groups like mammals, birds, and fish.
Both groups play crucial roles in their ecosystems and demonstrate a wide range of adaptations that allow them to thrive in various environments. Despite their differences, they share common characteristics such as multicellularity, eukaryotic cells without cell walls, and similar modes of reproduction.

Physical Structures and Body Systems
Invertebrates and vertebrates, though diverse in form, share several key structural and physiological traits. Both groups have evolved complex body systems to adapt to their environments, despite the fundamental difference of a vertebral column in vertebrates.
- Body Symmetry: Both typically exhibit bilateral symmetry, providing efficient movement and sensory perception.
- Nervous System: Each has a developed nervous system, crucial for sensory input, motor control, and internal communication.
- Reproductive Systems: Sexual reproduction is common, with variations in reproductive strategies across species.
- Respiratory Systems: Both have specialized organs or structures for gas exchange, with variations like gills in aquatic species or lungs in terrestrial species.
- Circulatory System: Vertebrates generally have a closed circulatory system, while invertebrates may have open or closed systems.
- Muscular System: Both groups possess a muscular system for movement, though the complexity varies significantly.
Despite these similarities, the diversity in physical structures and body systems is vast. Invertebrates range from simple sponges to complex cephalopods, while vertebrates include species from fish to mammals, each adapted to its unique ecological niche.
Reproduction and Life Cycles
Both invertebrates and vertebrates share fundamental aspects in their reproductive processes and life cycles, despite their diverse biological structures.
- Sexual Reproduction: Most species in both groups reproduce sexually, involving the fusion of male and female gametes.
- Egg-Laying and Live Birth: Many invertebrates lay eggs, as do some vertebrates like birds and reptiles. Mammals, a vertebrate group, are known for live births.
- Development Stages: Both groups undergo various stages of development, from embryos to adults, although the complexity and duration of these stages can vary widely.
- Metamorphosis: Invertebrates like insects undergo drastic changes through metamorphosis, while vertebrate development is generally more gradual and less transformative.
- Lifespan: Lifespans vary greatly within both invertebrates and vertebrates, ranging from a few days in some insects to over a century in some vertebrates.
These reproductive strategies and life cycles are crucial for the survival and adaptation of both invertebrates and vertebrates in their respective environments.
Environmental Adaptations and Habitats
Invertebrates and vertebrates demonstrate remarkable adaptability in diverse environments, leveraging unique physical and physiological traits to thrive in various habitats.
- Adaptation to Environments:
- Invertebrates, lacking a backbone, show tremendous diversity in their adaptations, inhabiting environments from deep oceans to arid deserts.
- Vertebrates, with their internal skeletons, adapt to a wide range of habitats, including aquatic, terrestrial, and aerial environments.
- Structural Adaptations:
- Some invertebrates like the horseshoe crab and octopus have structures that function similarly to a backbone, aiding in their environmental adaptation.
- Vertebrates, such as birds, have developed wings for flight, while aquatic vertebrates like fish have adapted fins for swimming.
- Physiological Adaptations:
- Both groups have developed various respiratory and circulatory adaptations suitable for their specific habitats, like gills in aquatic species and lungs in terrestrial species.
- The nervous systems in vertebrates are more complex and organized, aiding in their adaptability to diverse environments.
- Ecological Roles:
- Invertebrates and vertebrates play crucial roles in their ecosystems, with many species being key to ecological balance and biodiversity.
- Both groups are integral in food chains, serving as prey and predators, and contribute to various ecological processes.
Overall, the adaptability of invertebrates and vertebrates to their environments underscores the evolutionary success of these groups in the animal kingdom.
Diet and Nutrition
Both invertebrates and vertebrates exhibit diverse dietary habits, reflecting their adaptive evolution in various ecosystems.
- Variety in Diet:
- Invertebrates encompass a wide range of feeding habits, including herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, detritivores, and parasites.
- Vertebrates also show diverse diets, from the carnivorous habits of lions to the herbivorous nature of elephants.
- Adaptations for Feeding:
- Specific adaptations in both groups match their dietary needs. For example, some invertebrates like butterflies have specialized mouthparts for sucking nectar.
- Vertebrates such as birds exhibit a variety of beak shapes suited to their specific diets, from seeds to insects.
- Internal Digestion:
- Both invertebrates and vertebrates have evolved complex digestive systems to efficiently process their food.
- While some invertebrates have simpler digestive tracts, vertebrates typically have more advanced and specialized digestive systems.
Understanding the diet and nutrition of invertebrates and vertebrates provides insights into their ecology, behavior, and evolutionary history.

Role in Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Invertebrates and vertebrates play integral roles in maintaining the balance and diversity of ecosystems worldwide.
- Ecosystem Services:
- Invertebrates like bees and butterflies are vital for pollination, supporting the growth of plants and crops.
- Vertebrates such as birds and fish contribute to seed dispersal and pest control, enhancing ecosystem health.
- Biodiversity:
- Invertebrates, representing a vast majority of animal species, contribute significantly to global biodiversity.
- Vertebrates, though fewer in number, add to biodiversity through a wide range of species, each with unique roles in their habitats.
- Food Webs:
- Both invertebrates and vertebrates are crucial components of food webs, either as predators, prey, or both.
- Their interactions within food webs help maintain ecological balance and species diversity.
- Indicator Species:
- Certain invertebrates and vertebrates serve as indicator species, helping gauge the health of ecosystems.
- Changes in their populations can signal shifts in environmental conditions, guiding conservation efforts.
Understanding the roles of invertebrates and vertebrates in ecosystems is essential for conservation and sustainable environmental management.
Vertebrate vs Invertebrate: Types of Animals and the Difference
Get ready to embark on an exciting journey through the fascinating world of animals! From cute and cuddly to wild and powerful, this video will introduce you to a variety of incredible creatures, giving you a closer look at their unique traits and behaviors. Prepare to be amazed by the wonders of the animal kingdom! Watch now and let your love for animals soar!
Vertebrates and Invertebrates: An Overview
Wondering what this video has in store for you? Allow us to give you a captivating overview. With stunning visuals and expert narration, this video will take you on a virtual tour of breathtaking landscapes, historical landmarks, and hidden gems from all around the world. Sit back, relax, and let the beauty of this overview mesmerize you – it\'s an experience you won\'t want to miss! Click play and let the adventure begin!
Conservation and Environmental Impact
Conservation efforts for both invertebrates and vertebrates are crucial for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity.
- Conservation Challenges:
- Invertebrates, often overlooked in conservation, are vital for ecosystem functions like pollination and nutrient cycling.
- Vertebrates, including endangered species, require habitat protection and restoration to prevent extinction.
- Environmental Impact:
- Both invertebrates and vertebrates are affected by environmental changes like climate change, habitat loss, and pollution.
- Their decline can indicate ecosystem health, necessitating measures to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Role in Biodiversity:
- Protecting invertebrates and vertebrates supports biodiversity, which is essential for ecological resilience and human well-being.
- Conservation strategies must address the needs of both groups to ensure a comprehensive approach to ecosystem preservation.
- Sustainable Practices:
- Encouraging sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and urban development can reduce negative impacts on these animal groups.
- Public awareness and education about the importance of invertebrates and vertebrates can bolster conservation efforts.
Effective conservation of invertebrates and vertebrates is essential for sustaining the intricate web of life that they support.

Scientific and Research Applications
Invertebrates and vertebrates are extensively used in scientific and medical research, providing vital insights into biological processes and human health.
- Model Organisms:
- Invertebrates like fruit flies and nematodes are key model organisms in genetics and developmental biology due to their simple structure, short lifespans, and ease of genetic manipulation.
- Vertebrates such as mice and zebrafish are widely used in biomedical research for studying human diseases, drug testing, and understanding developmental processes.
- Ecological Studies:
- Studying invertebrates and vertebrates helps scientists understand ecological dynamics, species interactions, and the impact of environmental changes on biodiversity.
- These studies are crucial for conservation biology, helping to develop strategies to protect endangered species and habitats.
- Evolutionary Biology:
- Research on invertebrates and vertebrates provides insights into evolutionary processes, helping to trace the development of complex life forms and understand genetic variations.
- This research is essential for understanding the history of life on Earth and the mechanisms driving evolution.
- Biotechnology and Medicine:
- Invertebrates and vertebrates contribute to advancements in biotechnology, including the development of new medical treatments, vaccines, and diagnostic tools.
- Studying their biological processes has led to breakthroughs in understanding human physiology and diseases.
The study of invertebrates and vertebrates in scientific and medical research continues to be a cornerstone of advancements in our understanding of life sciences.
Cultural and Societal Significance
The presence and symbolism of invertebrates and vertebrates in human culture and society highlight their importance beyond biological aspects.
- Cultural Symbolism:
- Invertebrates like butterflies often symbolize transformation and rebirth in various cultures, while spiders can represent creativity or mystery.
- Vertebrates such as eagles and lions are frequently used as national symbols, signifying strength and leadership.
- Religious and Mythological References:
- Many religions and mythologies feature invertebrates and vertebrates, attributing them with spiritual meanings or using them in storytelling to impart moral lessons.
- Impact on Human Lifestyle:
- Invertebrates like bees play a crucial role in agriculture through pollination, directly affecting food production and economy.
- Vertebrates such as domesticated animals (dogs, cats, livestock) have profound impacts on human lifestyle, companionship, and work.
- Conservation Awareness:
- The portrayal of invertebrates and vertebrates in media and literature often raises awareness about conservation issues and the need to protect endangered species and habitats.
- Educational Value:
- Both invertebrates and vertebrates are integral in educational settings, teaching about biodiversity, ecosystems, and the importance of environmental stewardship.
Understanding the cultural and societal significance of invertebrates and vertebrates enhances our appreciation of biodiversity and its relevance to human life.

READ MORE:
Future Directions in Study and Research
Future research in the study of invertebrates and vertebrates holds promising potential for advancing our understanding of biology, ecology, and medicine.
- Genomic Research:
- Advancements in genomic technologies may provide deeper insights into the genetic makeup of both invertebrates and vertebrates, enhancing our understanding of evolutionary biology and biodiversity.
- Climate Change Impact Studies:
- Research on how climate change affects these groups can lead to better strategies for conservation and understanding ecological dynamics under changing environmental conditions.
- Biomedical Applications:
- Continued study of vertebrates and invertebrates, especially at the molecular and cellular levels, can lead to breakthroughs in disease treatment and medical technology.
- Ecological and Environmental Monitoring:
- Both groups can serve as indicators in environmental monitoring, aiding in the assessment of ecosystem health and the impacts of human activities.
- Technological Biomimicry:
- Studying the unique physical and behavioral traits of invertebrates and vertebrates can inspire innovative designs in technology, engineering, and materials science.
- Interdisciplinary Research:
- The integration of different scientific disciplines, such as genomics, ecology, and informatics, can lead to a more holistic understanding of these animal groups and their roles in the natural world.
The exploration of invertebrates and vertebrates will continue to be a vital part of scientific discovery, offering endless opportunities for new knowledge and applications.
In conclusion, exploring the similarities between invertebrates and vertebrates enriches our understanding of the animal kingdom, highlighting the interconnectedness and diversity of life that thrives on our planet.