Topic are insects vertebrates or invertebrates: Discover the intriguing realm of insect biology as we delve into whether insects are vertebrates or invertebrates, unveiling a world of diverse and fascinating creatures that challenge our understanding of life"s complexities.
Table of Content
- Are insects considered vertebrates or invertebrates?
- Defining Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- Characteristics of Invertebrates
- Insects as Invertebrates
- Diversity and Classification of Invertebrates
- Examples of Invertebrate Animal Groups
- Key Differences Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates
- YOUTUBE: Vertebrate vs Invertebrate | Types of Animals | What\'s the Difference?
- Physical and Biological Traits of Invertebrates
- Significance of Invertebrates in the Animal Kingdom
Are insects considered vertebrates or invertebrates?
Insects are considered invertebrates.
Here is a step-by-step explanation:
- First, let\'s clarify the difference between vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone or spine, while invertebrates are animals that do not have a backbone or spine.
- Insects, such as butterflies, beetles, bees, and stick insects, are classified as invertebrates because they do not have a backbone or spine.
- One key characteristic of insects is their exoskeleton, which is a hard, external covering that provides support and protection.
- The presence of wings is a common feature among insects, and although other invertebrates may have wings, if an invertebrate has wings, it is considered an insect.
- On the other hand, vertebrates include animals like mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, as they all have a backbone.
- Overall, insects are a diverse group of invertebrates and play crucial roles in ecosystems as pollinators, decomposers, and prey for other animals.
Therefore, based on the information, insects are classified as invertebrates.
READ MORE:
Defining Vertebrates and Invertebrates
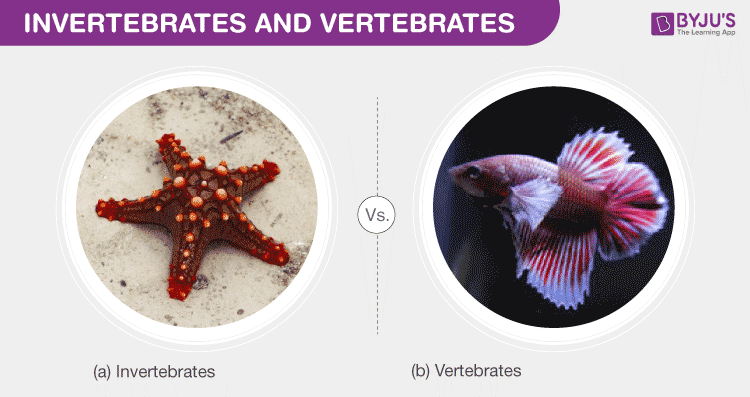
Vertebrates and invertebrates represent two fundamental divisions within the animal kingdom. Vertebrates are characterized by the presence of a backbone or spinal column, encompassing a wide range of animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. This internal skeleton provides structural support and protection for vital organs. In contrast, invertebrates lack a backbone. This diverse group includes insects, arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, cnidarians, and sponges.
- Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of body sizes and structures, from microscopic organisms to large species like the colossal squid. Their lack of a backbone has led to the development of other structural features like exoskeletons, found in arthropods, providing protection and support.
- While vertebrates generally have more complex and organized nervous systems, invertebrates often possess simpler systems. For example, many invertebrates have compound eyes and exhibit varying forms of body symmetry.
- The majority of animal species, estimated at around 97%, are invertebrates. This highlights their vast diversity and adaptability across different environments.
Understanding the distinctions between vertebrates and invertebrates not only aids in categorizing the vast array of animal life but also provides insights into their evolutionary paths and ecological roles.

Characteristics of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, encompassing a vast majority of animal species, display a range of fascinating characteristics that set them apart from vertebrates. These creatures, including insects, lack a backbone or spinal column, a defining trait of vertebrates.
- Exoskeleton: Many invertebrates, such as arthropods, possess an exoskeleton made of chitin, providing structural support and protection.
- Diverse Body Plans: Invertebrates exhibit a wide array of body structures and sizes, ranging from microscopic organisms to large species like the colossal squid.
- Variety in Circulatory Systems: Most invertebrates have an open circulatory system, in contrast to the closed systems found in vertebrates.
- Sensory Organs: Invertebrates often have unique sensory organs, like compound eyes in insects, adapted to their specific environments.
- Reproduction: Invertebrates employ various reproductive strategies, from simple asexual reproduction to complex life cycles involving multiple stages.
- Habitats: These animals are found in nearly every habitat on Earth, from deep ocean floors to high in the atmosphere.
- Role in Ecosystems: Invertebrates play crucial roles in ecosystems, such as pollinators, decomposers, and as a part of the food chain.
Understanding the characteristics of invertebrates not only provides insights into a major part of the animal kingdom but also highlights their essential roles in maintaining ecological balance.
Insects as Invertebrates
Insects, a vast and diverse group of animals, are classified as invertebrates. This classification is based on their lack of a vertebral column, a characteristic feature of vertebrates. Insects exhibit several unique features that align with common invertebrate traits.
- Exoskeleton: Insects have an exoskeleton made of chitin, providing support and protection, typical of many invertebrates.
- Body Structure: Insects have a segmented body, typically divided into head, thorax, and abdomen, with three pairs of legs and a pair of antennae.
- Reproduction: Most insects reproduce sexually, with diverse and often complex life cycles, including stages like larva, pupa, and adult.
- Sensory Organs: Insects commonly have compound eyes and a range of sensory organs adapted for their specific environments and needs.
- Diversity: Insects represent the largest group within the animal kingdom in terms of species diversity, with millions of different species.
- Ecological Roles: As invertebrates, insects play crucial roles in various ecosystems, including pollination, decomposition, and serving as a food source for other animals.
The study of insects as invertebrates provides valuable insights into the broader understanding of invertebrate biology and the essential roles these creatures play in our world.

Diversity and Classification of Invertebrates
The invertebrate category encompasses a vast array of animals, characterized by their lack of a vertebral column. This group demonstrates remarkable diversity in terms of size, habitat, and biological traits.
- Phyla: Invertebrates are classified into several phyla, including Arthropoda (insects, arachnids, crustaceans), Mollusca (snails, clams, cephalopods), Annelida (earthworms, leeches), and many more.
- Size Variation: Invertebrates range from microscopic organisms, like certain nematodes and rotifers, to large species such as the giant squid.
- Habitats: They inhabit diverse environments from deep oceans to terrestrial landscapes, showcasing adaptability and resilience.
- Reproductive Strategies: Invertebrates exhibit a variety of reproductive methods, from simple asexual reproduction to complex metamorphosis in insects.
- Ecological Importance: These creatures play vital roles in ecosystems, such as pollination, decomposition, and as a significant part of food webs.
- Evolutionary Significance: Studying invertebrates offers insights into evolutionary biology, as they represent some of the earliest forms of life on Earth.
This diverse group"s classification and study help us understand the biological complexities and ecological dynamics of life on our planet.
Examples of Invertebrate Animal Groups
Invertebrates, representing the majority of animal species on Earth, are divided into numerous groups, each with unique characteristics. Here are some key examples:
- Arthropods: This is the largest phylum of invertebrates, including insects (like bees and butterflies), arachnids (such as spiders and scorpions), crustaceans (like crabs and lobsters), and myriapods (centipedes and millipedes).
- Mollusks: Mollusks are a diverse group that includes snails, slugs, octopuses, and clams. They are known for their soft bodies, which in many species are protected by a hard shell.
- Annelids: This group includes segmented worms such as earthworms and leeches. They play a crucial role in soil health and are known for their segmented body structure.
- Echinoderms: Including starfish, sea urchins, and sand dollars, echinoderms are known for their radial symmetry and a unique water vascular system used for movement and feeding.
- Cnidarians: This group includes jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones, characterized by their stinging cells used for capturing prey and defense.
- Sponges: Sponges are simple, porous animals that filter feed by drawing water through their bodies. They are found in a variety of marine and freshwater environments.
Each of these groups contributes significantly to ecological balance and biodiversity, showcasing the incredible variety of life forms within the invertebrate classification.

Key Differences Between Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Understanding the distinction between vertebrates and invertebrates is crucial in the study of biology. Here are the key differences:
- Skeletal Structure: Vertebrates have an internal skeleton with a spine made of vertebrae, whereas invertebrates lack this kind of vertebral column. Instead, many invertebrates have an exoskeleton or no skeleton at all.
- Nervous System: Vertebrates generally have a more complex nervous system. Invertebrates, while diverse, usually have simpler nervous systems.
- Size and Complexity: Vertebrates tend to be larger and more physically complex than most invertebrates. However, there are exceptions like the colossal squid, an invertebrate that can grow to enormous sizes.
- Reproductive Systems: Vertebrates often have more complex reproductive systems, while invertebrates exhibit a greater variety of reproductive strategies, ranging from asexual to complex sexual reproduction.
- Diversity and Abundance: Invertebrates make up the vast majority of animal species on Earth. They are more abundant and diverse compared to vertebrates.
- Ecological Roles: Both play crucial roles in ecosystems, but invertebrates, being more numerous, often have a broader impact on ecological processes like pollination and decomposition.
These differences highlight the vast diversity of life forms and the unique adaptations each group has developed over millions of years of evolution.
Vertebrate vs Invertebrate | Types of Animals | What\'s the Difference?
Discover the fascinating world of insects in this captivating video! From intricate, vibrant wings to extraordinary abilities, you\'ll be amazed by the diversity and beauty of these tiny creatures. Join us on this educational journey and be inspired by the remarkable lives of insects!
The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates | Educational Videos for Kids
Expand your knowledge with this engaging educational video! Dive into a world of discovery as you learn about fascinating topics that are sure to captivate your curiosity. Whether you\'re a student or a curious mind, this educational video promises to enlighten and entertain you!
Physical and Biological Traits of Invertebrates
Invertebrates, a diverse group of animals without a vertebral column, exhibit a range of physical and biological traits that distinguish them from vertebrates. Understanding these traits provides insight into their adaptations and survival strategies.
- Body Structure: Invertebrates often have bodies with varying levels of complexity, from the simple, porous structure of sponges to the more complex segmented bodies of arthropods.
- Skeletal System: Many invertebrates, such as arthropods, possess an exoskeleton made of chitin, while others, like jellyfish, lack any rigid skeletal structure.
- Nervous System: The nervous systems in invertebrates range from simple nerve nets in cnidarians to more complex systems in cephalopods like octopuses.
- Sensory Organs: Invertebrates may have specialized sensory organs, such as the antennae in insects for detecting chemical signals, or the eyespots in flatworms for light perception.
- Reproductive Strategies: Reproductive methods vary widely, including asexual reproduction in some species and complex life cycles involving metamorphosis in others.
- Respiration: Respiratory structures vary, from gills in aquatic invertebrates to tracheal systems in insects, adapted to their specific environments.
- Movement: Modes of locomotion are diverse, including crawling, flying, swimming, and even passive drifting in currents for some marine species.
- Ecological Roles: Invertebrates play key roles in ecosystems, such as pollinators, decomposers, and as prey for other species.
These traits showcase the incredible adaptability and evolutionary success of invertebrates in various environments across the planet.

READ MORE:
Significance of Invertebrates in the Animal Kingdom
Invertebrates, though often overlooked, play a pivotal role in the animal kingdom and the broader ecosystem. Their significance can be understood through various aspects:
- Biodiversity: Invertebrates constitute the majority of animal biodiversity, with millions of species varying in size, shape, and habitat. This diversity is crucial for the balance and resilience of ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Services: Many invertebrates are key pollinators, decomposers, and soil engineers. They contribute to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and the pollination of plants, including many human food crops.
- Food Web: Serving as a primary food source for numerous vertebrates, invertebrates are integral to the food chain. Their abundance supports a variety of higher trophic levels, maintaining ecological balance.
- Environmental Indicators: Many invertebrate species are sensitive to environmental changes, making them effective bioindicators for assessing ecosystem health and the impact of human activities.
- Scientific Research: Invertebrates are used in scientific research to study genetics, development, disease, and ecology, providing insights applicable to other life forms, including humans.
- Cultural and Economic Value: Invertebrates also have cultural significance in many societies and contribute economically, particularly through activities like silk production and pollination.
The study and preservation of invertebrates are essential for maintaining ecological integrity and understanding the complex web of life on our planet.
In conclusion, the exploration of whether insects are vertebrates or invertebrates opens a window into the astounding diversity of life, underscoring the significance of every creature in the intricate tapestry of our natural world.