Topic mammals are vertebrates or invertebrates: Exploring the fascinating world of mammals reveals a key question: are these diverse creatures vertebrates or invertebrates? This article delves into their unique biological classification, shedding light on the remarkable features that define mammals within the animal kingdom.
Table of Content
- Are mammals vertebrates or invertebrates?
- Defining Characteristics of Mammals
- The Vertebrate Classification of Mammals
- Anatomical Features of Mammals as Vertebrates
- Distinguishing Mammals from Invertebrates
- The Evolutionary Biology of Mammalian Vertebrates
- Examples of Mammalian Vertebrates in Different Habitats
- YOUTUBE: The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates - Educational Videos for Kids
- Comparative Analysis: Mammals vs. Invertebrate Species
- Role of Mammals in Ecosystems as Vertebrates
- Conservation Efforts for Mammalian Vertebrates
- Future Research Directions in Mammalian Vertebrate Biology
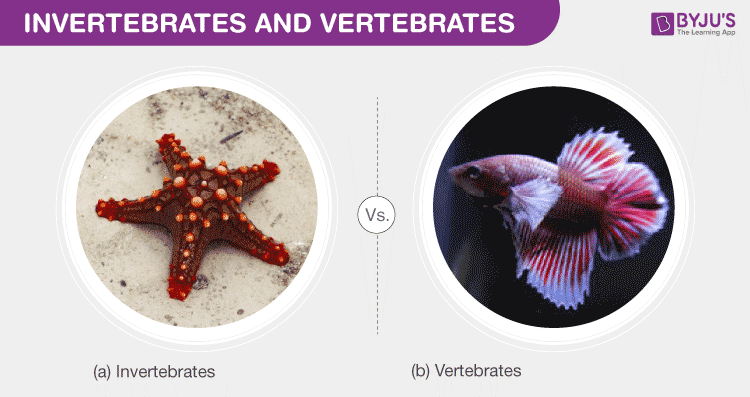
Are mammals vertebrates or invertebrates?
Mammals are vertebrates.
- Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone or spinal column.
- Mammals belong to the class Mammalia, which is a group of vertebrates.
- Some common characteristics of mammals include having hair or fur, being warm-blooded, and nursing their young with milk.
- Examples of mammals include humans, dogs, cats, elephants, and dolphins.
So, in summary, mammals are vertebrates.
READ MORE:
Defining Characteristics of Mammals
Mammals are a diverse group of animals known for their unique features that distinguish them from other vertebrates. Understanding these characteristics helps clarify their classification in the animal kingdom.
- Mammary Glands: Mammals are the only animals with mammary glands that produce milk to nourish their young.
- Hair or Fur: All mammals have some form of hair or fur on their bodies, though it varies greatly among species.
- Warm-Blooded: Mammals are endothermic, maintaining a constant body temperature regardless of the environment.
- Four-Chambered Heart: Mammals possess a four-chambered heart, which allows for efficient circulation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Lungs for Breathing: Mammals use lungs to breathe, which is efficient for oxygen exchange.
- Specialized Teeth: Most mammals have differentiated teeth (incisors, canines, molars) adapted for various diets.
- Advanced Nervous System: Mammals typically have a well-developed brain and nervous system, enabling complex behaviors and intelligence.
- Live Birth: Most mammals give birth to live young, except for the egg-laying monotremes like the platypus and echidna.
- Three Middle Ear Bones: Mammals have three distinct middle ear bones (malleus, incus, stapes) for hearing.
- Neocortex: A region of the brain, the neocortex, is involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, and generation of motor commands.

The Vertebrate Classification of Mammals
Mammals are scientifically classified as vertebrates due to their distinct skeletal and physiological features. This classification places them in a larger group of animals that share common characteristics.
- Presence of a Backbone: Central to their classification as vertebrates, mammals possess a vertebral column, or backbone, made of individual vertebrae that protect the spinal cord.
- Endoskeleton Structure: Mammals have an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) that includes bones and cartilage, providing support and facilitating movement.
- Skull and Brain Protection: The mammalian skull encases and protects the brain, a defining characteristic of vertebrates.
- Complex Organ Systems: Mammals have highly developed organ systems, including a circulatory system with a heart, a digestive system, and respiratory organs, all typical of vertebrates.
- Central Nervous System: Vertebrates, including mammals, possess a well-developed central nervous system, with the spinal cord running through the vertebral column.
- Advanced Sensory Organs: Mammals, like other vertebrates, have complex sensory organs for vision, hearing, and smell, allowing for sophisticated interaction with their environment.
- Reproductive Systems: The reproductive systems of mammals are characteristic of vertebrates, with most species giving birth to live young and a few laying eggs.
This classification as vertebrates underlines the evolutionary path of mammals and their shared traits with other vertebrate species, setting them apart from invertebrates in the animal kingdom.
Anatomical Features of Mammals as Vertebrates
Mammals exhibit several anatomical features that not only define their identity as vertebrates but also distinguish them within this classification. These features are essential for various functions ranging from movement to sensory perception.
- Vertebral Column: Mammals have a distinct vertebral column, which is flexible and supports the body"s structure, allowing for a range of movements.
- Four Limbed Structure: Most mammals have a four-limbed structure, with limbs evolving to suit different modes of life, like walking, flying, or swimming.
- Specialized Teeth: Unlike many vertebrates, mammals have a set of differentiated teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, suited to their varied diets.
- Fur or Hair: A unique characteristic of mammals is the presence of hair or fur, which provides insulation and aids in temperature regulation.
- Mammary Glands: One of the defining features of mammals is mammary glands, which produce milk to nourish their young.
- Diaphragm: Mammals possess a diaphragm, a muscular partition between the chest and abdominal cavity, aiding in effective breathing.
- Three Middle Ear Bones: Mammals have three middle ear bones - the malleus, incus, and stapes, which aid in sound transmission.
- Warm-Blooded Metabolism: As vertebrates, mammals are endothermic, regulating their internal body temperature regardless of external conditions.
- Highly Developed Brain: Mammals have a well-developed brain, particularly the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for complex behaviors and cognitive abilities.
These anatomical features underscore the complexity and adaptability of mammals within the vertebrate category, highlighting their evolutionary success across various habitats.

Distinguishing Mammals from Invertebrates
Understanding the differences between mammals and invertebrates is crucial in the study of biology. Mammals, as vertebrates, have distinct characteristics that set them apart from invertebrates in several key aspects.
- Internal Skeleton: Mammals have an internal skeleton made of bones, including a backbone, which is absent in invertebrates.
- Nervous System: Mammals possess a complex central nervous system, including a brain enclosed in a skull, whereas invertebrates have a simpler nervous system.
- Presence of Hair or Fur: One of the defining features of mammals is their hair or fur, a trait not found in invertebrates.
- Warm-Blooded Metabolism: Mammals are endothermic, maintaining a constant body temperature, unlike most invertebrates.
- Respiratory System: Mammals breathe through lungs, whereas invertebrates may have gills, tracheae, or other breathing mechanisms.
- Reproductive System: Most mammals give birth to live young and nourish them with milk from mammary glands, unlike invertebrates, which often lay eggs.
- Size and Complexity: Generally, mammals tend to be larger and more complex organisms compared to many invertebrates.
- Life Span: Mammals typically have longer life spans than most invertebrates.
- Sensory Capabilities: Mammals often have advanced sensory capabilities, including complex vision and hearing, which are more developed than those of most invertebrates.
These distinctions highlight the evolutionary divergence between mammals and invertebrates, with mammals exhibiting a higher level of complexity and adaptation in their anatomical and physiological traits.
The Evolutionary Biology of Mammalian Vertebrates
The evolutionary journey of mammals from early vertebrates is a fascinating story of biological adaptation and diversification. Understanding this evolution helps in comprehending how mammals developed their unique characteristics.
- Origin from Synapsids: Mammals evolved from synapsids, a group of reptiles, around 300 million years ago, leading to the divergence from reptilian ancestors.
- Therapsids Transition: During the Permian and Triassic periods, therapsids, often called "mammal-like reptiles", emerged, showing early mammalian traits.
- Development of Mammalian Features: Over millions of years, therapsids evolved distinct mammalian features like fur, warm-blooded metabolism, and more efficient respiratory and circulatory systems.
- Survival through Mass Extinction: Mammals survived the mass extinction event 65 million years ago that wiped out the dinosaurs, leading to an explosion in mammalian diversity.
- Diversification of Mammals: Post-dinosaur extinction, mammals diversified into the various forms we see today, from tiny shrews to the massive blue whale.
- Adaptation to Environments: Mammals adapted to a wide range of environments, leading to variations in size, shape, and behavior.
- Evolution of Primates: One significant evolutionary path led to the rise of primates, and eventually to humans, highlighting the adaptive success of mammals.
This evolutionary history not only explains the physical traits of mammals but also their ecological diversity and behavioral complexity, underscoring their success as a vertebrate group.

Examples of Mammalian Vertebrates in Different Habitats
Mammals have adapted to a wide variety of habitats across the world, showcasing their remarkable versatility and evolutionary success. Below are examples of mammalian vertebrates thriving in diverse environments.
- Tropical Rainforests: Species like the Sloth and the Orangutan are adapted to life in dense, humid rainforests, with unique traits for arboreal living.
- Deserts: The Fennec Fox and the Camel, with adaptations like water conservation and temperature regulation, thrive in arid desert conditions.
- Oceans: Marine mammals such as the Blue Whale and the Dolphin have evolved for aquatic life, exhibiting streamlined bodies and modified limbs for swimming.
- Arctic Regions: Polar Bears and Walruses, equipped with insulating fat and fur, are well-adapted to cold Arctic climates.
- Mountains: The Snow Leopard and the Mountain Goat exhibit adaptations like agility and warmth retention for life in mountainous terrains.
- Grasslands: Animals such as the African Elephant and the American Bison are suited to the vast grasslands, with adaptations for long-distance foraging.
- Urban Environments: Species like the Raccoon and the Pigeon have successfully adapted to urban settings, showcasing the adaptability of mammals.
These examples underscore the evolutionary adaptability of mammals, enabling them to occupy a wide range of ecological niches and habitats around the globe.
The Animal Kingdom: Vertebrates and Invertebrates - Educational Videos for Kids
Discover the fascinating world of animals through this captivating video! Get ready to be awed by the incredible diversity of species and their unique behaviors. From cuddly pets to exotic creatures, this video will surely leave you in awe of the wonders of the animal kingdom.
Animal Classification: The Vertebrates Song
Have you ever wondered how scientists classify living organisms? This enlightening video provides a clear and concise explanation of the classification system used to categorize animals. Unravel the secrets of taxonomy and learn how scientists group organisms based on their characteristics and evolutionary relationships. Expand your knowledge and dive into the fascinating world of classification!
Comparative Analysis: Mammals vs. Invertebrate Species
The comparison between mammals and invertebrate species highlights significant differences in anatomy, physiology, and ecological roles. This comparative analysis provides insights into the distinct evolutionary paths of these two broad classifications of animals.
- Skeletal Structure: Mammals have an internal skeleton with a backbone, while invertebrates lack a vertebral column, often having an exoskeleton or no skeleton at all.
- Nervous System Complexity: Mammals possess a highly developed central nervous system, in contrast to the simpler systems found in most invertebrates.
- Reproduction: Most mammals give birth to live young and nurse them with milk, whereas invertebrates exhibit a wide range of reproductive strategies, often involving egg laying.
- Size and Lifespan: Generally, mammals are larger and have longer lifespans compared to many invertebrates.
- Metabolic Rate: Mammals are endothermic, maintaining a constant body temperature, which is rare in invertebrates.
- Sensory Abilities: Mammals typically have advanced sensory organs for vision, hearing, and smell, which are more developed than those of most invertebrates.
- Mobility: Mammals show a wide range of locomotion methods on land, air, and water, while invertebrates have diverse but different locomotion adaptations.
- Environmental Adaptation: Both groups exhibit adaptations to their environments, but mammals generally show more complex behavioral and physiological adaptations.
This comparison underscores the diversity of life and the unique evolutionary adaptations that have enabled both mammals and invertebrates to thrive in their respective ecological niches.

Role of Mammals in Ecosystems as Vertebrates
Mammals, as vertebrates, play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Their presence and activities have significant impacts on the ecological balance and biodiversity in their habitats.
- Pollinators: Some mammals, like bats and certain primates, serve as pollinators, helping in the reproduction of flowering plants.
- Seed Dispersers: Many mammals, including squirrels and elephants, are vital for seed dispersal, aiding in the propagation of numerous plant species.
- Predators and Prey: As predators, mammals like lions and wolves maintain the balance of species in their habitats. As prey, they support the food web, providing sustenance for other wildlife.
- Soil Aeration and Fertilization: Activities of burrowing mammals, such as moles and gophers, enhance soil aeration and fertilization, promoting plant growth.
- Ecosystem Engineers: Species like beavers alter landscapes by building dams, creating wetlands that benefit a variety of species.
- Indicator Species: Certain mammals act as indicator species, signaling the health of their ecosystems, which is crucial for conservation efforts.
- Carbon Storage: Large mammals, particularly in marine environments like whales, contribute to carbon storage, playing a role in climate regulation.
- Cultural and Economic Value: Many mammals have cultural significance and provide economic benefits through ecotourism and as part of human livelihoods.
The diverse roles of mammals highlight their importance in maintaining ecological integrity and the need for their conservation to sustain healthy ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts for Mammalian Vertebrates
Conservation of mammalian vertebrates is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance. Various strategies and initiatives have been employed to protect and preserve these vital creatures and their habitats.
- Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, reserves, and sanctuaries to provide safe habitats for wildlife and preserve biodiversity.
- Legislation and Policies: Enacting laws and regulations to protect endangered species and regulate hunting, trade, and habitat destruction.
- Breeding Programs: Implementing captive breeding and reintroduction programs to increase population numbers of endangered species.
- Habitat Restoration: Undertaking habitat restoration projects to repair and reestablish ecosystems vital for mammalian survival.
- Research and Monitoring: Conducting scientific research and monitoring to understand species" needs, threats, and effective conservation measures.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, promoting sustainable practices and wildlife coexistence.
- Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of mammalian conservation and the threats they face.
- International Collaboration: Cooperating across borders to address challenges such as climate change and illegal wildlife trade that affect global mammal populations.
Through these concerted efforts, there is hope to preserve the diverse and invaluable species of mammalian vertebrates for future generations.

READ MORE:
Future Research Directions in Mammalian Vertebrate Biology
The field of mammalian vertebrate biology continues to evolve, with several key areas poised for significant advancements. Future research will likely focus on understanding and addressing the challenges faced by these species in a rapidly changing world.
- Genetic and Genomic Studies: Advancements in genetic and genomic research can provide deeper insights into mammalian evolution, diversity, and conservation strategies.
- Climate Change Impact: Investigating the effects of climate change on mammalian species, particularly in terms of habitat shifts, population dynamics, and adaptation mechanisms.
- Ecological Interactions: Exploring the complex ecological interactions of mammals with other species and their environments, including the impact of human activities.
- Disease Ecology: Studying the emergence and spread of diseases among mammal populations, including zoonotic diseases that impact both wildlife and human health.
- Behavioral Studies: Conducting in-depth research on mammalian behavior, social structures, and communication to understand their ecological roles and social dynamics.
- Conservation Technologies: Developing and applying innovative technologies for conservation efforts, including habitat monitoring, population tracking, and genetic conservation.
- Integration of Indigenous Knowledge: Incorporating traditional ecological knowledge in research and conservation strategies to enhance understanding and respect for local ecosystems.
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: Encouraging interdisciplinary research combining biology, ecology, technology, and social sciences to address complex conservation challenges.
These future research directions will not only expand our knowledge of mammalian vertebrates but also aid in the development of more effective conservation practices to safeguard these species for the future.
In conclusion, the exploration of mammals as vertebrates unveils a remarkable journey through evolution, showcasing their unique adaptations and crucial roles in ecosystems, and highlights the ongoing importance of their study and conservation.