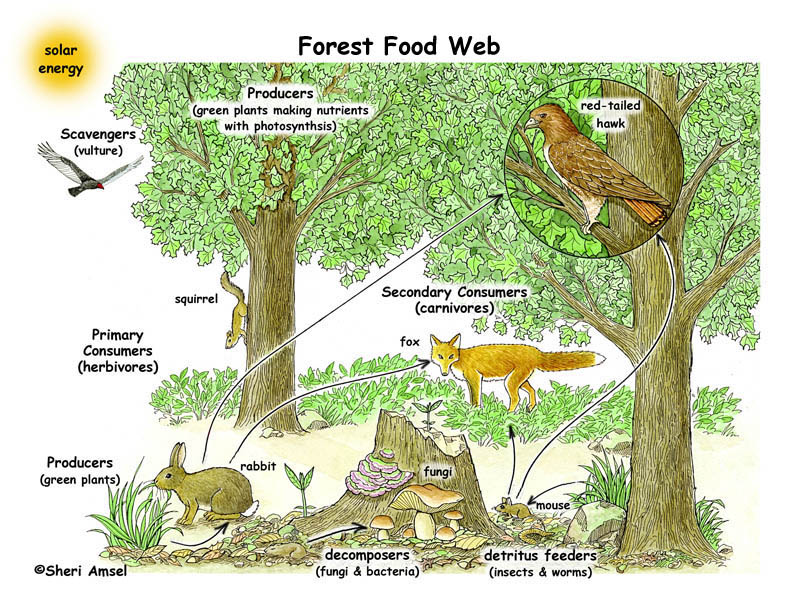
Topic rain forest ecosystem: Explore the rainforest ecosystem, a vibrant cradle of biodiversity where every leaf and creature plays a crucial role in Earth"s environmental harmony.
Table of Content
- What are the characteristics of a rain forest ecosystem?
- Understanding the Rainforest Ecosystem
- Significance of Biodiversity in Rainforests
- Ecosystem Services Provided by Rainforests
- Climate Regulation and Rainforests
- Conservation Efforts and Human Impact
- YOUTUBE: Rainforests 101
- Sustainable Practices and Rainforest Preservation
- Threats to Rainforest Ecosystems: Deforestation, Climate Change, and Pollution
- Unique Flora and Fauna of Rainforests
- Indigenous Peoples and Rainforests: Guardians of the Ecosystem
- Future of Rainforests: Challenges and Solutions
What are the characteristics of a rain forest ecosystem?
A rain forest ecosystem is characterized by several unique features:
- Biodiversity: Rainforests are known for their incredibly rich biodiversity. They support a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth.
- Layers of vegetation: The rainforest is divided into distinct layers, each with its own set of plants and animals. These layers include the emergent layer, canopy layer, understory, and forest floor.
- Tropical climate: Rainforests are typically found in tropical regions near the equator. They experience high average temperatures and high humidity throughout the year.
- Abundant rainfall: Rainforests receive a significant amount of rainfall, often more than 100 inches per year. This consistent precipitation contributes to the lush, dense vegetation.
- Complex food web: The interconnectedness of plants and animals in the rainforest creates a complex food web. Many species rely on specific relationships for their survival.
- Endangered species: Due to deforestation and habitat destruction, many rainforest ecosystems are home to endangered species. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these vulnerable populations.
- Medicinal value: Rainforests have provided a wealth of medicinal plants and compounds that have been used by indigenous communities and have revolutionized modern medicine.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Rainforest Ecosystem
The rainforest ecosystem is a complex and vibrant web of life, encompassing a diverse range of flora and fauna. These ecosystems are primarily found in the equatorial region and are known for their dense vegetation and high rainfall. Rainforests play a crucial role in maintaining the Earth"s climate, air quality, and biodiversity.
- Biological Diversity: Rainforests are home to more than half of the world"s plant and animal species, even though they cover just 6% of the Earth"s surface.
- Climate Regulation: They help regulate the world"s temperature and weather patterns by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
- Water Cycle: Rainforests contribute to the global water cycle by releasing water vapor into the atmosphere, creating rainfall both locally and globally.
- Cultural Value: Indigenous communities have lived in harmony with these forests for thousands of years, relying on them for shelter, food, and medicine.
Rainforests are divided into four main layers: the emergent layer, the canopy, the understory, and the forest floor, each hosting unique species adapted to their specific environment. The canopy, a dense ceiling of leaves and branches, plays a pivotal role in sheltering the layers below and supporting diverse wildlife.
Despite their importance, rainforests face significant threats from deforestation, mining, and agriculture, leading to habitat loss and species extinction. Protecting these ecosystems is critical for preserving the planet"s biodiversity and combating climate change.

Significance of Biodiversity in Rainforests
Rainforests are known as the world"s most vibrant hotspots of biodiversity, teeming with an unparalleled variety of life forms. They are crucial for the health and well-being of our planet for several key reasons:
- Genetic Resources: Rainforests are a treasure trove of genetic material, providing the raw materials for breeding programs and genetic engineering, which can lead to medical and scientific breakthroughs.
- Ecosystem Services: The diverse ecosystems within rainforests contribute to climate regulation, water purification, pollination, and disease control, directly supporting global agricultural productivity and human health.
- Climate Stability: The dense vegetation of rainforests plays a critical role in carbon sequestration, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Resilience and Adaptation: High biodiversity enhances ecosystem resilience, improving the ability of rainforest ecosystems to recover from and adapt to environmental changes and natural or human-induced disturbances.
Biodiversity in rainforests is not just about the variety of species but also about the complex ecological interactions between them. These interactions create a finely balanced network that sustains the forest"s health and its ability to function and provide services critical to life on Earth.
However, this biodiversity is under threat from deforestation, habitat fragmentation, climate change, and pollution, which underscores the urgent need for conservation efforts. Protecting rainforests and their biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecological balance, supporting indigenous cultures, and preserving the natural heritage for future generations.
Ecosystem Services Provided by Rainforests
Rainforests are vital to the health of our planet, offering a wide range of ecosystem services that benefit not just their local environments but the global community as well. These services include:
- Climate Regulation: Rainforests help stabilize the global climate by absorbing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, thereby reducing the impact of climate change.
- Air Quality: The dense vegetation of rainforests produces large quantities of oxygen, contributing significantly to the Earth"s oxygen supply and improving air quality.
- Water Regulation: Rainforests play a key role in the water cycle by absorbing rainfall and releasing water vapor into the atmosphere, which can affect weather patterns locally and globally.
- Soil Protection: The roots of rainforest trees help prevent soil erosion, while the leaf litter on the forest floor enriches the soil with nutrients.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Rainforests are home to an immense variety of species, many of which are not found anywhere else on Earth, contributing to global biodiversity.
- Medicinal Resources: A significant proportion of modern medicines are derived from plants and animals found in rainforests, highlighting their importance in healthcare and pharmaceutical research.
- Cultural and Recreational Value: Rainforests offer significant cultural, educational, and recreational value, supporting eco-tourism and serving as a source of inspiration and spiritual significance for many communities.
Despite their critical importance, rainforests around the world are under threat from deforestation, agriculture, and urban development. It is imperative that we recognize the value of the services provided by rainforests and take action to protect these irreplaceable ecosystems for future generations.

Climate Regulation and Rainforests
Rainforests play a pivotal role in regulating the Earth"s climate, acting as the lungs of our planet. They are essential in the global climate system, performing several key functions:
- Carbon Sequestration: Rainforests absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, storing carbon in their biomass and soil, thus mitigating climate change.
- Temperature Regulation: The dense canopy of rainforests helps regulate surface temperature, both locally and globally, by providing shade and releasing water vapor that cools the air.
- Water Cycle: Rainforests contribute to the regulation of the water cycle by transpiring water, which forms clouds and influences rainfall patterns across the globe.
- Albedo Effect: The dark surface of rainforests absorbs sunlight, affecting the albedo (reflectivity) of the Earth"s surface and influencing global temperature.
The destruction of rainforests, however, poses a significant threat to their ability to regulate the climate. Deforestation leads to increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, reduced biodiversity, and changes in rainfall patterns, exacerbating global warming and climate change. Therefore, protecting rainforests is not only crucial for maintaining biodiversity but also for the stability of the Earth"s climate.
Conservation Efforts and Human Impact
Rainforests around the world are under threat due to human activities, but concerted conservation efforts are being made to mitigate these impacts and preserve these vital ecosystems for future generations. Understanding both the negative impacts and the steps being taken to counteract them is essential.
- Deforestation: The cutting down of rainforests for timber, agriculture, and urban development is the primary threat to these ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
- Pollution: Industrial, agricultural, and urban waste can contaminate water sources and soil, affecting both plant and animal life in rainforests.
- Climate Change: The global increase in temperatures and changing weather patterns affect the delicate balance of rainforest ecosystems, impacting species adaptation and survival.
- Conservation Initiatives: Protected areas, sustainable land management practices, and reforestation projects are among the key strategies being employed to conserve rainforests.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, through education and sustainable livelihood programs, ensures the protection of rainforests and their biodiversity.
- International Cooperation: Global agreements and partnerships, like the Paris Agreement, aim to address climate change and deforestation on a worldwide scale.
Conservation efforts require a multi-faceted approach that includes legal protection, sustainable management, scientific research, and international collaboration. By understanding the human impact on rainforests, we can better appreciate the urgency of conservation efforts and the role each of us can play in preserving these irreplaceable ecosystems.

Rainforests 101
Explore the captivating world of ecosystems in this mesmerizing video! Learn about the delicate balance of nature and how all living organisms, big and small, are interconnected. Get ready to be amazed by the beauty and complexity of our planet\'s diverse ecosystems!
Rainforests for Kids | Learn about the two types of rainforests
Calling all curious kids! Join us on a journey of discovery as we dive into the wondrous world of knowledge just for you. From fascinating facts about animals and plants to mind-boggling experiments and fun activities, this video is packed with excitement and learning for our young explorers!
Sustainable Practices and Rainforest Preservation
Sustainable practices are essential for the preservation of rainforest ecosystems, balancing human needs with environmental protection. Implementing these practices ensures the longevity and health of these vital ecosystems for future generations.
- Eco-Friendly Agriculture: Practices such as agroforestry, which combines agriculture and forestry, help maintain forest cover, protect watersheds, and provide habitat for wildlife while producing food.
- Sustainable Logging: Implementing selective logging practices and using certified sustainable timber can reduce the impact on the forest, preserving biodiversity and forest structure.
- Conservation Programs: Establishing protected areas and wildlife sanctuaries helps safeguard biodiversity hotspots and critical habitats from deforestation and degradation.
- Community-Based Management: Involving local communities in the management of forest resources encourages sustainable use and benefits local economies, reducing the pressure to clear forests for agricultural expansion.
- Restoration Efforts: Reforestation and forest rehabilitation projects restore degraded areas, improve ecosystem services, and increase forest connectivity, which is crucial for wildlife.
- Eco-Tourism: Developing eco-tourism as an alternative income source for communities living near rainforests can reduce reliance on destructive practices like logging and mining.
Adopting sustainable practices requires global cooperation, local action, and a commitment to long-term ecological health. By prioritizing rainforest preservation, we can ensure these ecosystems continue to thrive, providing essential services and maintaining global biodiversity.
Threats to Rainforest Ecosystems: Deforestation, Climate Change, and Pollution
Rainforest ecosystems face numerous threats that endanger their biodiversity, functionality, and the global environmental benefits they provide. Addressing these threats is crucial for the preservation of these vital natural resources.
- Deforestation: The clearing of rainforest land for agriculture, logging, and mining leads to habitat loss, species extinction, and contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns disrupt the delicate balance of rainforest ecosystems, affecting species distribution and forest health.
- Pollution: Chemical runoff from agriculture, industrial waste, and plastic pollution harm water quality and soil health, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic life in rainforest regions.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade: The poaching and trafficking of wildlife diminish biodiversity and disrupt ecological balance, threatening endangered species with extinction.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of roads, dams, and urban expansion into rainforest areas fragments habitats, making it difficult for species to survive and migrate.
Combating these threats requires global cooperation, sustainable development practices, and stringent conservation measures. By understanding and mitigating the impacts of human activities, we can work towards securing a healthier future for rainforest ecosystems and the planet as a whole.

Unique Flora and Fauna of Rainforests
Rainforests are renowned for their astonishing biodiversity, hosting a myriad of unique flora and fauna that cannot be found anywhere else on Earth. This incredible diversity is a result of the warm, wet climate that prevails throughout the year.
- Flora: Rainforests are home to over two-thirds of the world"s plant species. Iconic plants include the towering kapok tree, with its vast buttress roots, and the diverse array of epiphytes, such as orchids and bromeliads, which live on the branches of giant trees.
- Fauna: The animal life is equally diverse and specialized. Insects, such as the brilliantly colored butterflies and beetles, are abundant. Birds like the resplendent quetzal and the harpy eagle soar through the canopy, while the forest floor is home to mammals such as jaguars, tapirs, and the secretive okapi.
- Amphibians and Reptiles: Rainforests are also a haven for a variety of amphibians and reptiles, including poison dart frogs known for their vivid colors and toxic skin, and the anaconda, one of the world"s largest snakes.
Each species plays a crucial role in the rainforest ecosystem, contributing to the complex web of life that maintains the balance of this unique environment. The preservation of rainforest biodiversity is essential for ecological stability, medical research, and the overall health of our planet.
Indigenous Peoples and Rainforests: Guardians of the Ecosystem
Indigenous peoples have been the stewards of rainforest ecosystems for thousands of years, living in harmony with the environment and utilizing sustainable practices that preserve biodiversity. Their traditional knowledge and cultural practices offer invaluable insights into conservation and sustainable use of rainforest resources.
- Traditional Knowledge: Indigenous communities possess a deep understanding of the rainforest"s flora and fauna, which they have used for food, medicine, and shelter. This knowledge is crucial for biodiversity conservation and the discovery of new medicines.
- Sustainable Practices: They employ sustainable hunting, fishing, and agriculture practices that minimize impact on the rainforest, ensuring that ecosystems remain healthy and productive for future generations.
- Conservation Efforts: Indigenous peoples are active in conservation efforts, often leading the fight against deforestation, mining, and other activities that threaten their homes and the rainforest ecosystem.
- Cultural Significance: The rainforest is not just a home but a sacred space for many indigenous communities, imbued with spiritual and cultural significance that guides their interaction with the environment.
The role of indigenous peoples in the preservation of rainforests is increasingly recognized at international levels, leading to collaborations between governments, conservation organizations, and indigenous communities to protect these critical ecosystems. Respecting and integrating their knowledge and rights is key to effective and equitable conservation efforts.

READ MORE:
Future of Rainforests: Challenges and Solutions
The future of rainforests hangs in a delicate balance, facing significant challenges that demand immediate and sustained action. However, there are solutions and strategies being developed and implemented to ensure the preservation and recovery of these vital ecosystems.
- Challenges:
- Deforestation for agricultural expansion, logging, and mining continues to reduce rainforest cover at an alarming rate.
- Climate change exacerbates the vulnerability of rainforests, altering rainfall patterns and increasing the frequency of fires.
- Pollution and illegal wildlife trade further endanger the biodiversity within these ecosystems.
- Solutions:
- Enforcing stronger legal frameworks and international agreements to protect rainforests and regulate resource extraction.
- Supporting sustainable land-use practices that provide economic benefits without harming the environment, such as eco-tourism and agroforestry.
- Investing in reforestation and forest restoration projects to rehabilitate damaged areas and improve ecosystem services.
- Empowering indigenous communities and local populations through inclusive conservation programs that respect their knowledge and rights.
- Leveraging technology for monitoring and management, using satellite imagery and AI to track deforestation and biodiversity loss.
While the challenges are daunting, the collective effort of governments, organizations, communities, and individuals worldwide can make a significant difference. By prioritizing the health of rainforests, we safeguard the future of our planet, ensuring that these ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.
Embracing the beauty and complexity of rainforest ecosystems offers us a path to a sustainable future. By understanding, protecting, and valuing these natural wonders, we can ensure they continue to enrich our planet for generations to come.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)