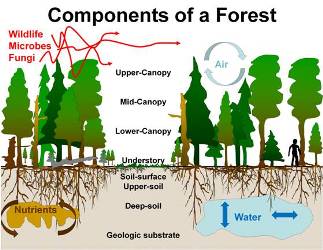
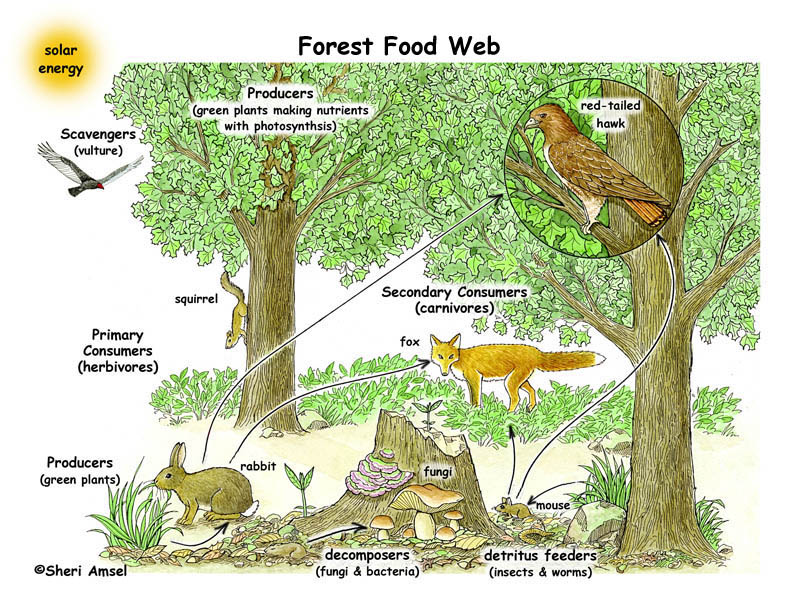
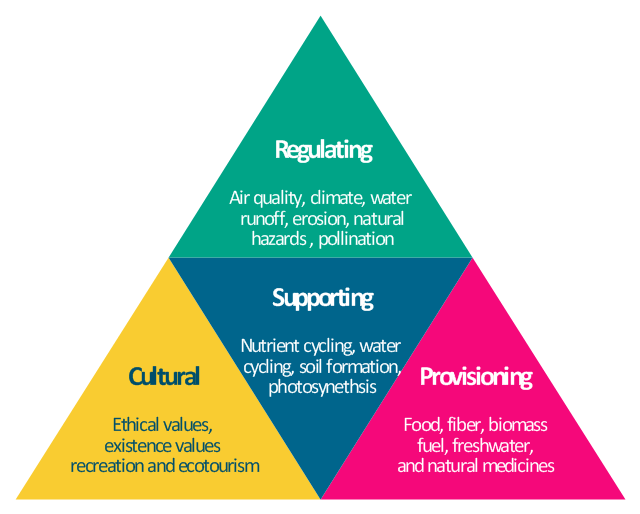
Topic identify one provisioning service of forest ecosystems: Discover the critical role of forest ecosystems in providing provisioning services, from timber to medicinal resources, and how these natural treasures support our lives and the planet.
Table of Content
- What is one provisioning service of forest ecosystems?
- Overview of Provisioning Services in Forest Ecosystems
- Key Provisioning Service: Timber and Wood Products
- Food Resources from Forests: Game, Berries, and Mushrooms
- Water Provisioning: The Role of Forests in Water Cycle Regulation
- Medicinal Resources: Pharmaceuticals and Herbal Medicines
- Non-Timber Forest Products: Fiber, Resins, and Dyes
- YOUTUBE: Forest Ecosystem Services: Valuing All the Benefits from Forests
- Energy Resources: Biomass Fuels and Bioenergy
- Economic Importance of Forest Provisioning Services
- Conservation Efforts to Sustain Forest Provisioning Services
What is one provisioning service of forest ecosystems?
One provisioning service of forest ecosystems is the provision of timber, which is a valuable resource obtained directly from forests.
- Timber, also known as wood, is used for various purposes such as construction, furniture making, and paper production.
- Forests act as a natural source of timber, providing a renewable and sustainable supply of wood.
- Timber from forests contributes to the economy by supporting the timber industry and creating employment opportunities.
- Additionally, the use of timber from forests can help reduce the carbon footprint compared to alternative materials like concrete or steel.
Overall, the provision of timber is an essential provisioning service of forest ecosystems, supporting various industries and contributing to sustainable development.
READ MORE:
Overview of Provisioning Services in Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems are invaluable to human well-being, offering a wide array of provisioning services that are fundamental to our survival and quality of life. These services include the supply of food, fiber, water, and medicinal resources, among others. Understanding these services helps in appreciating the direct benefits forests provide to humanity and underscores the importance of conserving these vital ecosystems.
- Timber and Wood Products: Forests are a primary source of timber used in construction, furniture, and paper products, showcasing their critical economic value.
- Food Resources: Forests offer a variety of foods including fruits, nuts, mushrooms, and honey, contributing to food security and dietary diversity.
- Water Supply: By regulating the water cycle, forests ensure the availability of clean water for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
- Medicinal Resources: Many modern medicines are derived from plants found in forests, highlighting their role in health care and pharmaceuticals.
- Non-Timber Forest Products: Beyond timber, forests provide other goods like resin, latex, and essential oils, which have various commercial and traditional uses.
Each of these provisioning services plays a crucial role in supporting both local economies and global environmental health. By identifying and valuing these services, we can take steps towards sustainable forest management and conservation efforts that benefit us all.

Key Provisioning Service: Timber and Wood Products
Timber and wood products stand out as one of the most significant provisioning services provided by forest ecosystems. This service not only supports economic development but also plays a vital role in cultural practices and construction industries worldwide. Forests serve as the backbone for the timber industry, supplying raw materials for furniture, construction, paper, and numerous other products essential to daily life.
- Sustainable Harvesting: Sustainable forestry practices ensure a balance between timber production and the maintenance of forest health and biodiversity.
- Economic Impact: The timber industry contributes significantly to the economies of many countries, providing employment opportunities and income for millions of people.
- Construction Material: Wood, being a durable and versatile material, is widely used in construction, offering environmental benefits such as carbon sequestration.
- Paper and Packaging: Wood pulp is the primary ingredient in paper production, highlighting the importance of forests in the packaging and publishing industries.
- Cultural Significance: Wood products are integral to many cultural practices, from traditional building techniques to artistic expressions.
The sustainable management of forest resources for timber and wood products is crucial for preserving these ecosystems" integrity while fulfilling global demand. Through responsible practices, we can continue to benefit from this vital provisioning service without compromising the health of our planet"s forests.
Food Resources from Forests: Game, Berries, and Mushrooms
Forests are not just about trees and timber; they are vital sources of food. Offering a bounty of game, berries, and mushrooms, forests provide nutritious, diverse, and often unique foods that are essential to the diets of local communities and wildlife. These resources contribute significantly to food security, cultural traditions, and even commercial food industries.
- Game: Forests are habitats for various wildlife, including deer, rabbits, and birds, which are important sources of meat for many communities, combining subsistence hunting with traditions and conservation.
- Berries: Wild berries, such as blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are harvested for their nutritional value, rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting health and well-being.
- Mushrooms: Forests are rich in a variety of mushrooms, esteemed not only for their culinary value but also for their medicinal properties. Foraging for mushrooms is a cultural activity in many societies, contributing to biodiversity knowledge and sustainable living.
These food resources underscore the importance of forests beyond wood and timber, highlighting the need for sustainable management practices that protect these ecosystems while ensuring the continued availability of vital food sources. Through responsible stewardship, forests can continue to nourish and sustain life in numerous ways.

Water Provisioning: The Role of Forests in Water Cycle Regulation
Forests play a pivotal role in the global water cycle, acting as natural water reservoirs that ensure the availability of clean water for ecosystems, agriculture, and human consumption. The intricate relationship between forests and water cycles highlights the essential provisioning service of water regulation and supply.
- Natural Filtration: Forests filter rainwater, improving water quality by trapping pollutants and sediments, ensuring cleaner water sources for downstream communities and ecosystems.
- Regulation of Water Flow: By absorbing rainfall, forests reduce surface runoff, mitigating the risk of floods. During dry periods, they release stored water, helping to maintain river flows.
- Climate Regulation: Forests influence local and global climates, affecting precipitation patterns. They play a crucial role in ensuring adequate rainfall for agricultural lands and urban areas.
- Supporting Biodiversity: Forest watersheds are habitats for diverse aquatic and terrestrial species, supporting ecosystems that rely on quality water environments.
- Sustainable Water Use: Promoting sustainable forestry practices helps protect water resources, ensuring their availability for future generations.
The provisioning service of water by forests is indispensable, underlining the need for conservation and sustainable management of these ecosystems. Protecting forests means safeguarding water resources vital for life on Earth.
Medicinal Resources: Pharmaceuticals and Herbal Medicines
Forests are treasure troves of medicinal resources, providing a vast array of plants and herbs that have been used for centuries in traditional and modern medicine. These natural pharmacies offer crucial ingredients for pharmaceuticals, herbal supplements, and holistic remedies, highlighting the indispensable role of forest ecosystems in global health and wellness.
- Source of Pharmaceutical Compounds: Many prescription drugs are derived from compounds found in forest plants, including cancer treatments, pain relievers, and antimalarials.
- Herbal Medicines: Forests contribute to traditional medicine practices worldwide, offering natural remedies that are used to treat a wide range of ailments.
- Biodiversity and Drug Discovery: The rich biodiversity of forests provides a vast genetic library for scientists to discover new medicinal compounds, with countless species yet to be studied.
- Conservation and Sustainable Use: Sustainable harvesting and conservation of medicinal plants ensure the longevity of these resources for future generations.
- Integrating Traditional Knowledge: Recognizing and integrating traditional ecological knowledge in forest management helps preserve medicinal practices and promotes sustainable use of these resources.
The provision of medicinal resources by forests underscores the need for their protection and sustainable management. Preserving these natural pharmacies is vital for health care, scientific research, and maintaining the balance of ecosystems around the world.

Non-Timber Forest Products: Fiber, Resins, and Dyes
Forests provide a wide range of non-timber products that are essential for various industries, traditional practices, and daily living. These products, including fibers, resins, and dyes, are derived from the diverse flora found within forest ecosystems, showcasing the versatility and richness of forest resources beyond timber.
- Fiber: Plants like bamboo, jute, and flax are harvested from forests for their fibers, which are used in making textiles, ropes, and other materials.
- Resins: Forest trees produce resins that have numerous uses, including as adhesives, in varnishes, and in medicinal products. Pine resin, for example, is widely used for its sticky and waterproofing properties.
- Dyes: Natural dyes extracted from forest plants and fungi are used in the textile industry, offering sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes.
- Economic and Cultural Value: These non-timber products contribute significantly to the livelihoods of local communities and hold cultural significance in many societies.
- Sustainable Management: Sustainable harvesting of non-timber forest products is crucial for the conservation of forest ecosystems and the continuation of these resources for future generations.
The importance of non-timber forest products extends beyond their economic value, playing a crucial role in the sustainability and biodiversity of forest ecosystems. Ensuring the protection and sustainable use of these resources is essential for maintaining the balance between human needs and environmental health.
Forest Ecosystem Services: Valuing All the Benefits from Forests
\"Discover the fascinating world of timber in this captivating video! From the diverse range of tree species to the sustainable practices of harvesting, you\'ll gain a newfound appreciation for the beauty and importance of this natural resource.\"
Sven Mutke: Non-wood Provisioning Services from Mediterranean Forest Ecosystems
\"Unlock the secrets of nature\'s medicine cabinet in this eye-opening video on medicinal plants. Learn about the incredible healing properties of herbs, roots, and flowers that have been used for centuries to promote health and well-being. Don\'t miss out on this empowering journey!\"
Energy Resources: Biomass Fuels and Bioenergy
Forests play a crucial role in providing renewable energy resources through biomass fuels and bioenergy, contributing to sustainable energy solutions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Biomass from forests includes wood, wood waste, and plant material, which can be converted into energy for heating, electricity, and fuel, showcasing the potential of forests in the global energy mix.
- Wood and Wood Waste: The most common form of biomass, used directly for heating and cooking or converted into bioenergy through combustion processes.
- Energy Crops: Fast-growing plants like switchgrass and willow are cultivated in forest areas to produce biomass energy, offering a sustainable alternative to non-renewable energy sources.
- Biogas Production: Decomposition of organic forest waste can produce biogas, a renewable energy source used for electricity generation and heating.
- Carbon Neutrality: Biomass fuels are considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth phase.
- Sustainable Management: Sustainable harvesting and management practices ensure that forest biomass use does not compromise forest health, biodiversity, or carbon sequestration capabilities.
By harnessing the power of biomass fuels and bioenergy, forests offer a pathway towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving energy sustainability. The development of technologies and policies supporting the sustainable use of forest-derived biomass is essential for maximizing its benefits for the environment and society.

Economic Importance of Forest Provisioning Services
The provisioning services provided by forest ecosystems are not only vital for ecological balance and biodiversity but also have significant economic implications. These services contribute to the livelihoods of billions of people worldwide, supporting industries, enhancing food security, and fostering sustainable development. Understanding the economic importance of forest provisioning services is essential for formulating policies that promote environmental stewardship and economic prosperity.
- Contribution to Livelihoods: Forests support the livelihoods of over 1.6 billion people globally, providing essential resources for survival and economic activities.
- Source of Raw Materials: Forests supply raw materials to various industries, including timber, paper, pharmaceuticals, and textiles, driving economic growth and innovation.
- Food Security: Forests contribute to food security by providing a source of nutritious foods, such as fruits, nuts, and game, particularly in rural areas.
- Income Generation: The sale and trade of forest products offer income opportunities for local communities, often serving as a primary income source in remote areas.
- Ecotourism and Recreation: Forests attract tourists seeking natural beauty, adventure, and relaxation, generating revenue for local economies and promoting conservation.
- Energy Production: Biomass from forests is a renewable energy source, contributing to energy security and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
The economic importance of forest provisioning services underscores the need for sustainable management practices that balance economic gain with ecological preservation. Investing in the sustainable use of forest resources can lead to long-term economic benefits and resilience against climate change and environmental degradation.
READ MORE:
Conservation Efforts to Sustain Forest Provisioning Services
The sustainability of forest provisioning services is crucial for the well-being of humanity and the health of our planet. Conservation efforts are essential to ensure that forests continue to provide their myriad of benefits for future generations. These efforts involve a combination of local, national, and international initiatives aimed at preserving forest ecosystems while enabling sustainable use of their resources.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and managing protected forest areas to conserve biodiversity and safeguard ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Management Practices: Implementing sustainable forestry practices that balance resource extraction with conservation, such as selective logging and agroforestry.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees to restore degraded areas and expand forest cover, enhancing carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, recognizing their dependence on forest resources and their role in sustainable management.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing policies and laws that promote sustainable forest management and protect critical habitats.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating across borders to address global challenges such as climate change and illegal logging, ensuring the preservation of forests worldwide.
Conservation efforts to sustain forest provisioning services are imperative for maintaining ecological balance, supporting economic development, and ensuring that forests can continue to fulfill their critical roles in providing food, water, medicine, and other essential services. Through collective action and sustainable practices, we can ensure the resilience and longevity of these vital ecosystems.
Embracing the myriad provisioning services of forest ecosystems illuminates paths towards sustainable living and conservation, ensuring these natural treasures continue to enrich our lives and the planet for generations to come.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)