Topic ecosystem services provided by forests: Discover the invaluable ecosystem services provided by forests, from purifying our air to regulating climates, showcasing nature"s pivotal role in sustaining life on Earth.
Table of Content
- What are the ecosystem services provided by forests?
- Provisioning Services: Food, Fiber, and Freshwater
- Regulating Services: Climate Regulation, Flood Control, and Disease Regulation
- Supporting Services: Soil Formation, Nutrient Cycling, and Oxygen Production
- Cultural Services: Recreational, Aesthetic, and Spiritual Benefits
- Biodiversity Conservation: Habitat for Species and Genetic Diversity
- Carbon Sequestration and Storage: Combatting Climate Change
- YOUTUBE: Introduction to Urban Forest Ecosystem Services
- Water Filtration and Purification: Ensuring Clean Water Supplies
- Air Quality Improvement: Filtering Pollutants and Producing Oxygen
- Erosion Prevention and Soil Stabilization: Maintaining Land Health
- Recreational and Educational Opportunities: Enhancing Human Well-being
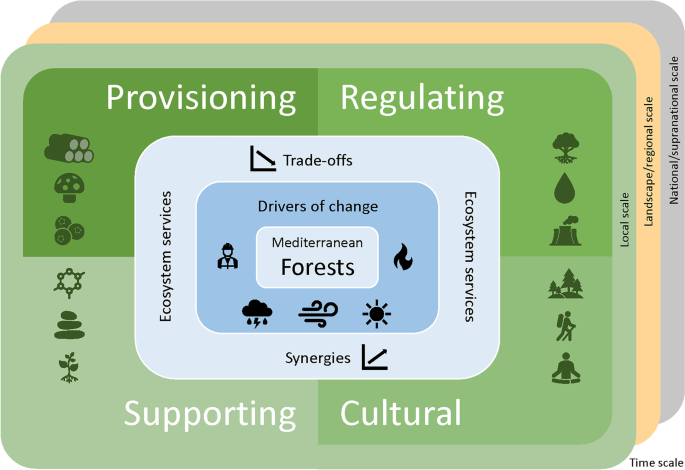
What are the ecosystem services provided by forests?
Forests are vital ecosystems that provide a wide range of valuable services to both humans and the environment. Some of the key ecosystem services provided by forests include:
- Climate regulation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth\'s climate. They absorb carbon dioxide through the process of photosynthesis, helping to mitigate the impacts of greenhouse gases and climate change.
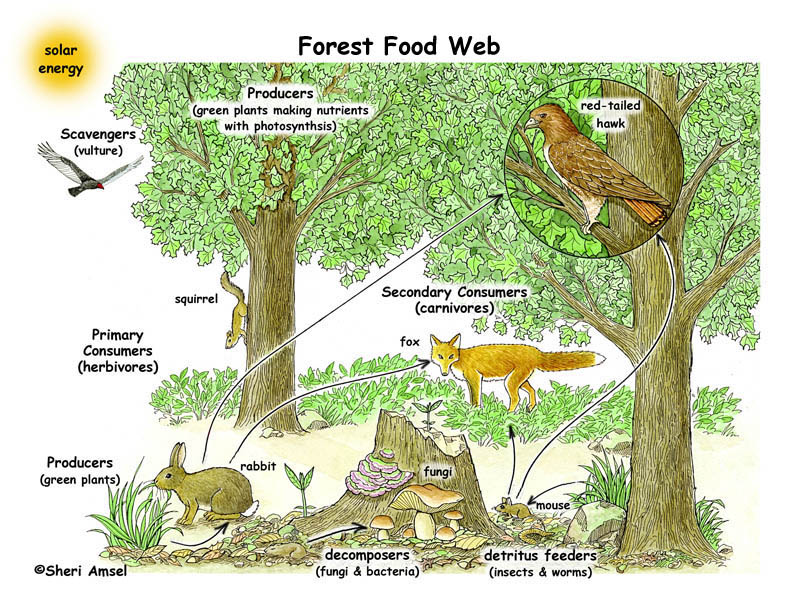
- Biodiversity support: Forests are home to a diverse array of plant and animal species. They provide habitat and shelter for numerous wildlife, contributing to the preservation and maintenance of biodiversity.
- Water purification: Forests act as natural filters, helping to purify and regulate the quality of water. The trees and vegetation trap and absorb pollutants, preventing them from entering water bodies and ensuring clean water supplies.
- Flood control: The dense canopy and root systems of forests help regulate water flow and reduce the risk of flooding. They absorb and store excess rainwater, releasing it slowly into rivers and streams, thereby minimizing flood damage.
- Soil conservation: Forests play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion. The tree roots bind the soil and reduce the risk of landslides and erosion caused by wind and water, helping to maintain the fertility and health of the soil.
- Timber and non-timber forest products: Forests provide a sustainable source of timber for construction and wood products. They also offer non-timber forest products such as fruits, nuts, medicinal plants, and resins, which are essential for livelihoods and cultural practices.
- Recreation and tourism: Forests offer numerous opportunities for outdoor recreational activities like hiking, camping, bird-watching, and nature exploration. They attract visitors and contribute to local economies through nature-based tourism.
These are just a few examples of the valuable ecosystem services provided by forests. They highlight the importance of protecting and conserving these ecosystems for the benefit of both present and future generations.
READ MORE:
Provisioning Services: Food, Fiber, and Freshwater
Forests play a crucial role in providing essential resources for human survival and economic activities. They are the source of a wide variety of provisioning services that benefit societies around the globe.
- Food: Forests are a rich source of fruits, nuts, mushrooms, and other edible products, supporting the diets of millions of people worldwide. They also provide habitat for game and fish, crucial for protein intake in many communities.
- Fiber: Wood from forests is a primary material for construction and paper production. Bamboo and other fibrous plants offer sustainable alternatives for clothing, utensils, and other household items.
- Freshwater: Forests play a key role in the water cycle, regulating the availability of freshwater. They help in filtering and recharging groundwater supplies, ensuring clean water for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
These provisioning services are not only vital for the sustenance of local communities but also have global economic implications, emphasizing the need to manage and conserve forest ecosystems sustainably.

Regulating Services: Climate Regulation, Flood Control, and Disease Regulation
Forests are indispensable in maintaining the balance of our planet"s environment, offering critical regulating services that impact our climate, water systems, and health.
- Climate Regulation: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing carbon in their biomass. This process is vital for mitigating the effects of climate change. Additionally, forests influence local and global weather patterns through their impact on the water cycle and temperature regulation.
- Flood Control: Trees and forest soils play a significant role in water absorption and storage, reducing runoff and the risk of floods. Forested watersheds are crucial for preventing soil erosion and sedimentation in rivers and lakes, thereby safeguarding communities and biodiversity.
- Disease Regulation: Forests contribute to disease regulation by supporting diverse ecosystems that can limit the spread of pathogens. Healthy forests are associated with reduced transmission rates of diseases like Lyme disease and malaria, as they provide habitat for predator species that control populations of disease vectors, such as ticks and mosquitoes.
Through these regulating services, forests not only protect the environment but also support human well-being by stabilizing climate conditions, reducing disaster risks, and contributing to health regulation.
Supporting Services: Soil Formation, Nutrient Cycling, and Oxygen Production
Forests are foundational to the health of our planet, providing essential supporting services that underpin all other ecosystem functions and services.
- Soil Formation: Forest ecosystems are vital for soil formation. The decomposition of fallen leaves, branches, and dead organisms contributes to the development of rich, fertile soil. This process not only helps in creating the ground we depend on for agriculture but also supports diverse terrestrial life forms.
- Nutrient Cycling: Forests play a critical role in nutrient cycling, ensuring the transfer and recycling of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium through their ecosystems. Trees absorb these nutrients from the soil, which are then returned to the ground through leaf litter and decomposition, maintaining ecosystem health and productivity.
- Oxygen Production: Through the process of photosynthesis, forests are major producers of oxygen, a by-product of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This oxygen is essential for the survival of most life forms on Earth, highlighting the crucial role forests play in sustaining life.
These supporting services are the backbone of ecological resilience, enabling not just the survival of countless species, including humans, but also enhancing the quality of the environment in which we live.
Cultural Services: Recreational, Aesthetic, and Spiritual Benefits
Forests enrich our lives beyond their material contributions, offering profound cultural services that nourish the human spirit and enhance our well-being.
- Recreational Benefits: Forests provide a natural playground for activities like hiking, birdwatching, and camping, offering people a chance to reconnect with nature. These recreational opportunities promote physical health, reduce stress, and enhance mental well-being.
- Aesthetic Benefits: The beauty of forest landscapes inspires artists, photographers, and nature lovers alike. The aesthetic value of forests contributes to our quality of life by offering scenic vistas that evoke feelings of peace and wonder.
- Spiritual Benefits: For many cultures and individuals, forests are sacred spaces that offer spiritual connection and renewal. They are places of tranquility and meditation, where one can seek solitude, reflection, and a deeper sense of purpose.
Through these cultural services, forests play an essential role in human culture and identity, providing spaces for recreation, inspiration, and spiritual connection that are invaluable to societies worldwide.
Biodiversity Conservation: Habitat for Species and Genetic Diversity
Forests are critical for maintaining global biodiversity, serving as the home for a vast array of species and preserving genetic diversity vital for ecosystem resilience and human well-being.
- Habitat for Species: Forests provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds for millions of species, including many that are endangered. They support a complex web of life, from the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem"s functioning.
- Genetic Diversity: The diverse conditions within forests, from tropical rainforests to boreal forests, foster an incredible range of plant and animal genetics. This genetic diversity is crucial for adaptation to changing environments and for the resilience of ecosystems against pests and diseases.
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting forests is synonymous with conserving biodiversity. Conservation strategies include establishing protected areas, sustainable management practices, and restoration efforts to ensure forests continue to provide habitat for species and maintain genetic diversity.
As guardians of biodiversity, forests not only support the web of life but also the ecological services that sustain human societies, highlighting the importance of conserving these vital ecosystems for future generations.

Carbon Sequestration and Storage: Combatting Climate Change
Forests play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change through their ability to absorb and store carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during the process of photosynthesis, converting it into biomass and storing it in their trunks, branches, leaves, and root systems. This natural process reduces the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, helping to combat climate change.
- Carbon Storage: Forests act as carbon reservoirs, locking away carbon for decades or even centuries. Mature forests, in particular, are highly efficient at storing large amounts of carbon, making the conservation of existing forests and the restoration of degraded ones crucial strategies for climate mitigation.
- Enhancing Forest Carbon Sinks: Sustainable forest management practices, reforestation, and afforestation efforts are key to enhancing the capacity of forests to sequester and store carbon. By promoting the growth of forests, we can significantly increase their role in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
Through carbon sequestration and storage, forests serve as a critical defense against climate change, underscoring the importance of preserving and expanding forested areas worldwide.
Introduction to Urban Forest Ecosystem Services
Explore the mesmerizing beauty of the urban forest in this captivating video. Discover how nature thrives in the midst of concrete jungles, and learn about the importance of preserving these green havens for future generations.
Sustainable Forest Management: Maximizing Ecosystem Services
Dive into the world of sustainable forest management with this enlightening video. Gain insights into innovative techniques that ensure the health and vitality of our forests, while promoting responsible and eco-friendly practices. Join the movement towards a greener and more sustainable future through the power of responsible forest management.
Water Filtration and Purification: Ensuring Clean Water Supplies
Forests play a crucial role in water filtration and purification, providing an essential ecosystem service that supports clean water supplies for both human consumption and natural ecosystems. Through a combination of soil absorption, plant uptake, and microbial decomposition, forests naturally filter and clean the water that flows through their root systems, significantly reducing pollutants before they reach water bodies.
- Natural Filtration: As rainwater and surface runoff move through forest soils, contaminants such as sediments, nutrients, and pollutants are trapped and filtered out. This natural filtration process improves water quality by reducing the load on man-made water treatment plants.
- Soil and Vegetation Role: Forest soils and vegetation play a key role in absorbing and breaking down pollutants. Trees and plants take up nutrients and chemicals, further purifying the water through their root systems.
- Microbial Activity: The forest floor and soil are rich in microorganisms that decompose organic matter and detoxify harmful substances, contributing to the natural purification process.
- Protection Against Erosion: Forests prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the soil with their roots. This not only maintains soil health but also prevents sediments from entering waterways and affecting water quality.
- Wetlands and Riparian Zones: Wetlands and riparian zones within and adjacent to forests act as natural water filters, absorbing pollutants and providing habitat for species that contribute to the ecosystem"s ability to purify water.
The maintenance and restoration of forest ecosystems are vital for sustaining the natural processes that underpin water filtration and purification. Protecting forests means safeguarding our water supplies, ensuring that communities have access to clean water while supporting biodiversity and ecosystem health.

Air Quality Improvement: Filtering Pollutants and Producing Oxygen
Forests are vital in improving air quality by filtering pollutants and producing oxygen, which is crucial for all living organisms. Through the process of photosynthesis, trees and other vegetation in forests absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing significantly to the oxygen we breathe. This process not only cleans the air but also combats climate change by reducing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a significant role in capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), a major greenhouse gas, thus mitigating climate change.
- Filtering Pollutants: Trees and plants in forests can absorb pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, effectively reducing pollution levels in the air.
- Oxygen Production: Through photosynthesis, forests produce large amounts of oxygen, contributing to the overall health of the planet and its inhabitants.
- Temperature Regulation: By absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen, forests help in regulating the Earth"s temperature, counteracting the urban heat island effect and contributing to global climate regulation.
- Habitat for Biodiversity: Forests provide a habitat for a wide range of species, contributing to biodiversity conservation, which is essential for ecosystem resilience and the provision of ecosystem services.
Maintaining and expanding forested areas is crucial for sustaining the air quality improvement services they provide. Efforts to conserve and restore forests are essential in ensuring that these natural resources continue to benefit the atmosphere and climate, supporting life on Earth.
Erosion Prevention and Soil Stabilization: Maintaining Land Health
Forests play a critical role in preventing soil erosion and stabilizing the soil, which are essential for maintaining land health and supporting diverse ecosystems. The root systems of trees and other vegetation in forests bind the soil, reducing runoff and the loss of soil during heavy rains and floods. This not only maintains soil fertility but also protects water quality by preventing sediments and pollutants from entering waterways.
- Root Systems: The extensive root systems of forest vegetation hold soil in place, reducing displacement caused by water and wind.
- Canopy Cover: The canopy of a forest reduces the impact of raindrops on the soil, lessening the force with which water hits the ground and therefore reducing erosion.
- Organic Matter: Forests contribute organic matter to the soil through fallen leaves and decomposing plant material, which enhances soil structure and its ability to retain water, further reducing erosion.
- Water Infiltration: Healthy forest soils promote water infiltration into the subsurface layers, decreasing surface runoff and erosion risks.
- Protection Against Landslides: In areas prone to landslides, forests can act as a stabilizing force, anchoring the soil and reducing the likelihood of landslide events.
Protecting existing forests and reforesting areas where forests have been lost is vital for erosion prevention and soil stabilization. Sustainable forest management practices are essential to maintaining the balance between forest health and the provision of ecosystem services, including those related to soil and water conservation.

READ MORE:
Recreational and Educational Opportunities: Enhancing Human Well-being
Forests offer a wealth of recreational and educational opportunities that significantly enhance human well-being. These natural environments provide spaces for physical activities, relaxation, and learning, contributing to physical health, mental well-being, and educational enrichment.
- Hiking and Physical Activities: Forests are prime locations for hiking, biking, and other outdoor sports, offering trails that cater to all levels of fitness and adventure, promoting physical health and endurance.
- Nature Observation and Wildlife Photography: They serve as natural habitats for diverse wildlife, offering unique opportunities for nature observation, bird watching, and wildlife photography, fostering a deeper connection with nature.
- Educational Programs: Many forests have visitor centers or educational programs that provide insights into ecological systems, conservation efforts, and the importance of biodiversity, enhancing environmental awareness and stewardship.
- Camping and Picnicking: Offering areas for camping and picnicking, forests provide families and individuals with the chance to spend quality time outdoors, creating lasting memories in natural settings.
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: The natural serenity of forest landscapes supports mindfulness practices and stress reduction, contributing to mental health and emotional well-being.
Recognizing the value of forests in providing these recreational and educational services is crucial for their conservation and the promotion of sustainable use. Encouraging responsible enjoyment of these natural resources ensures that they remain available for future generations, supporting the ongoing health and happiness of communities worldwide.
Discover the myriad benefits forests offer, from climate regulation to recreational joy, underscoring their vital role in sustaining our planet and enriching our lives. Let"s cherish and protect these natural treasures for generations to come.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)
