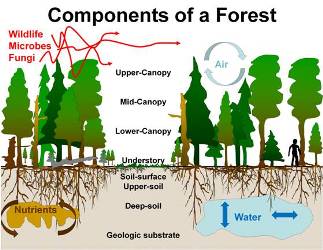
Topic ecosystem services forests: Discover the vital role of ecosystem services forests play in sustaining life on Earth, offering invaluable benefits from climate regulation to water purification and beyond.
Table of Content
- What is the role of forest ecosystems in providing ecosystem services?
- Importance of Forests for Ecosystem Services
- Types of Ecosystem Services Provided by Forests
- Forest Management and Conservation Strategies
- The Role of Forests in Climate Change Mitigation
- Economic Benefits of Forest Ecosystem Services
- Challenges in Valuing and Protecting Forest Ecosystem Services
- YOUTUBE: Forest Ecosystem Services Management
- Case Studies: Successful Forest Conservation Efforts
- Future Directions for Research and Policy
- How Individuals and Communities Can Support Forest Ecosystem Services
What is the role of forest ecosystems in providing ecosystem services?
Forest ecosystems play a crucial role in providing a wide range of ecosystem services that are vital for both the environment and human society. These ecosystem services include:
- Provisioning Services: Forests serve as a source of numerous tangible resources that humans depend on, such as timber, fuelwood, food (fruits, nuts, mushrooms), and medicinal plants.
- Regulating Services: Forests help regulate various natural processes and provide essential services, such as:
- Climate regulation by sequestering carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
- Water regulation by absorbing and storing rainfall, reducing soil erosion, and maintaining water quality.
- Climate and weather regulation by influencing air temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns.
- Prevention of natural disasters as they act as buffers against floods, landslides, and avalanches.
- Cultural Services: Forests have immense cultural value and provide recreational opportunities for people to engage in activities like hiking, camping, birdwatching, and nature photography. They also hold spiritual and aesthetic significance for many cultures.
- Supporting Services: Forest ecosystems provide a foundation for other ecosystems by creating and maintaining soil fertility and nutrient cycling. They also serve as habitats for a rich diversity of plant and animal species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the planet.
In summary, forest ecosystems are essential in providing provisioning, regulating, cultural, and supporting services that contribute to the well-being of both humanity and the environment.
READ MORE:
Importance of Forests for Ecosystem Services
Forests are the backbone of the planet"s ecological health, providing essential services that benefit both the environment and human populations. These services are crucial for sustainability, biodiversity, and our overall well-being.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Forests are home to a vast majority of the world"s terrestrial biodiversity, offering habitat, food, and protection for countless species.
- Climate Regulation: Through photosynthesis, forests sequester carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Water Regulation and Purification: Forests play a key role in water cycles, filtering pollutants and ensuring the supply of clean water.
- Soil Protection: Tree roots stabilize soil, reducing erosion and improving fertility, which is crucial for agriculture and natural vegetation.
- Air Quality Improvement: Forests filter harmful pollutants from the air, contributing to the health of all living organisms.
- Recreational and Cultural Services: Beyond their ecological roles, forests offer spaces for recreation, spiritual enrichment, and cultural practices.
Understanding and preserving these ecosystem services is essential for maintaining the planet"s health and ensuring a sustainable future for all inhabitants.

Types of Ecosystem Services Provided by Forests
Forests deliver a diverse array of ecosystem services, categorized into four main types, each vital for the environment and human well-being.
- Provisioning Services: These include tangible resources that forests provide, such as:
- Wood and timber for construction and energy
- Non-timber forest products like fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants
- Freshwater resources
- Regulating Services: Forests contribute to the regulation of environmental conditions, offering:
- Climate regulation through carbon sequestration
- Air quality improvement by filtering pollutants
- Water regulation and purification services
- Pollination of crops and natural vegetation
- Supporting Services: Fundamental processes that support other ecosystem services, including:
- Soil formation and fertility
- Nutrient cycling and waste decomposition
- Habitat provision for biodiversity conservation
- Cultural Services: Non-material benefits that enhance human well-being, such as:
- Recreational and eco-tourism opportunities
- Spiritual and religious values
- Educational and research opportunities
- Aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art, and design
Each of these services underscores the multifaceted value forests offer, emphasizing the need for their protection and sustainable management.
Forest Management and Conservation Strategies
Effective forest management and conservation strategies are essential to preserve ecosystem services and biodiversity. These approaches are diverse, tailored to local environments and global sustainability goals.
- Sustainable Forestry Practices: Implementing logging methods that minimize environmental impact, promote regrowth, and maintain biodiversity.
- Protected Areas Establishment: Designating national parks, nature reserves, and wilderness areas to protect forest ecosystems from exploitation and degradation.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas and establishing forests on lands that have not been previously forested to restore ecosystem services.
- Community-based Management: Involving local communities in the decision-making process, recognizing their dependence on forest resources for livelihoods and cultural identity.
- Integrated Land Use Planning: Coordinating forest conservation with agricultural and urban development to minimize habitat fragmentation and land-use conflicts.
- Ecosystem-based Management: Approaching forest management with the goal of maintaining ecological processes and resilience, ensuring long-term sustainability of ecosystem services.
- Policy and Legislation: Developing and enforcing laws and policies that promote forest conservation, sustainable use, and equitable benefit-sharing.
- International Cooperation: Participating in global and regional initiatives aimed at forest conservation, climate change mitigation, and biodiversity protection.
Through these strategies, it"s possible to balance the ecological, social, and economic values of forests, securing their benefits for future generations.
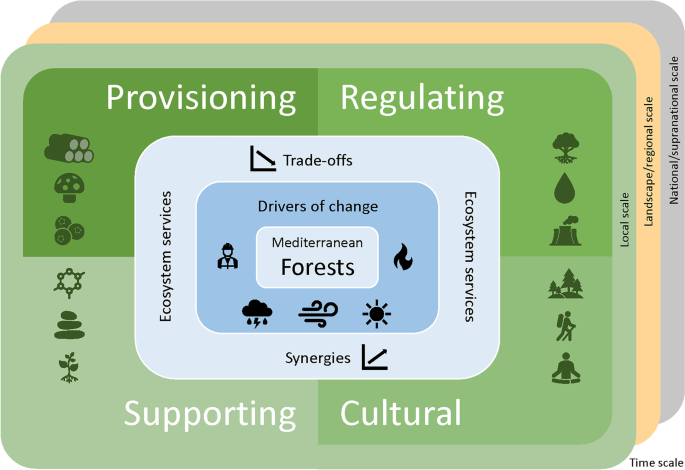
The Role of Forests in Climate Change Mitigation
Forests play a pivotal role in the global strategy to mitigate climate change, leveraging their natural processes to reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and enhance resilience to climate impacts.
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, storing carbon in trees, soil, and vegetation. This process is vital in reducing the net amount of greenhouse gases.
- Carbon Storage: Mature forests serve as significant carbon sinks, storing carbon accumulated over decades or centuries. Protecting these forests is crucial to prevent the release of stored carbon.
- Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+): International efforts aim to incentivize forest conservation and sustainable management, recognizing their value in carbon sequestration.
- Climate Regulation: Beyond carbon, forests influence climate through the regulation of water cycles and the reflection of sunlight, contributing to cooling of the planet.
- Enhancing Resilience: By maintaining forest health and diversity, ecosystems are better equipped to withstand and recover from climate-related disturbances, supporting overall climate resilience.
- Sustainable Forest Management: Implementing practices that ensure the long-term health and productivity of forest ecosystems contributes to their ability to sequester carbon, while also providing other ecosystem services.
- Policy and International Collaboration: Developing policies and engaging in international cooperation to protect forests, promote reforestation, and integrate forests into climate change strategies.
Through these mechanisms, forests emerge as a critical ally in the fight against climate change, highlighting the importance of their preservation and sustainable management.
Economic Benefits of Forest Ecosystem Services
The economic benefits of forest ecosystem services are vast and varied, contributing significantly to the global economy and supporting the livelihoods of billions of people worldwide.
- Raw Materials: Forests provide essential raw materials such as timber, paper, and natural fibers, which are foundational to numerous industries.
- Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs): Beyond timber, forests supply a wealth of products like fruits, nuts, honey, and medicinal plants, which are crucial for the economy of rural communities.
- Water Regulation Services: By maintaining water cycles, forests contribute to the availability of clean water, which is essential for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
- Climate Regulation: The role of forests in carbon sequestration has economic implications through carbon trading markets, providing financial incentives for forest conservation.
- Tourism and Recreation: Forests attract tourists seeking natural beauty and adventure, generating significant revenue for local and national economies through ecotourism and recreational activities.
- Job Creation: Sustainable forestry, conservation projects, and ecotourism are important sources of employment, often in rural areas where job opportunities may be limited.
- Natural Disaster Mitigation: Forests act as natural barriers against disasters like floods and landslides, reducing economic losses and protecting infrastructure and communities.
- Health Benefits: Forest ecosystems support health by purifying air and water, which reduces healthcare costs and supports productivity through the well-being of the population.
Quantifying the economic value of these services emphasizes the need for sustainable management and conservation of forests to secure these benefits for current and future generations.

Challenges in Valuing and Protecting Forest Ecosystem Services
While the importance of forest ecosystem services is widely recognized, valuing and protecting these services presents several challenges.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient understanding among policymakers and the public about the comprehensive benefits that forests provide can lead to undervaluation and neglect.
- Economic Pressures: Immediate economic gains from deforestation and land conversion for agriculture or urban development often overshadow the long-term benefits of forest conservation.
- Difficulty in Quantification: Measuring the economic value of ecosystem services is complex, making it hard to incorporate these values into decision-making processes.
- Policy and Institutional Barriers: Inadequate policies, lack of enforcement, and weak governance structures can hinder effective forest management and conservation efforts.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change exacerbates threats to forests through increased frequency and intensity of wildfires, pests, and diseases, challenging conservation efforts.
- Conflicts over Land Use: Competing interests for forest lands, including mining, agriculture, and infrastructure projects, can lead to degradation of forest ecosystems.
- Global Market Dynamics: International demand for commodities like palm oil and soybean drives deforestation, complicating local and national conservation strategies.
- Investment and Financing Gaps: Adequate funding for conservation and sustainable management of forests is often lacking, limiting the implementation of effective strategies.
Addressing these challenges requires integrated approaches that balance economic, social, and environmental objectives, along with strong international cooperation and investment in sustainable forest management.
Forest Ecosystem Services Management
\"Discover the secrets of effective management in our empowering video! Unlock your leadership potential and learn valuable strategies to increase productivity, motivate your team, and achieve outstanding results in your organization.\"
Sustaining Forest Ecosystem Services
\"Join us in our enlightening video on sustaining a better future! Explore innovative solutions, eco-friendly practices, and actionable steps to ensure the long-term health of our planet. Together, we can make a lasting and positive impact on the world.\"
Case Studies: Successful Forest Conservation Efforts
Across the globe, innovative strategies and collaborative efforts have led to significant successes in forest conservation. These case studies highlight the impact of effective management and conservation practices.
- Costa Rica"s Payment for Ecosystem Services Program: By financially compensating landowners for conserving their forests, Costa Rica has dramatically reversed its deforestation rates, enhancing biodiversity and promoting sustainable land use.
- The Amazon Fund in Brazil: This initiative supports projects that prevent, monitor, and combat deforestation while promoting the preservation and sustainable use of the Amazon rainforest, showing how international funding can aid in large-scale forest conservation.
- Community Forest Management in Nepal: Nepal"s approach to forest management involves local communities in the conservation and use of forests, leading to improved forest conditions, livelihoods, and biodiversity conservation.
- Great Green Wall in Africa: An ambitious project aimed at combating desertification, the Great Green Wall is a belt of vegetation stretching across Africa, which helps in restoring degraded lands, enhancing food security, and improving resilience to climate change.
- REDD+ Projects Worldwide: The Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) initiative has funded projects in multiple countries, demonstrating how carbon finance can be used to encourage forest conservation while benefiting local communities.
These examples underscore the potential for successful forest conservation through innovative funding mechanisms, community involvement, and international cooperation, providing valuable lessons for future efforts.

Future Directions for Research and Policy
To ensure the continued provision of ecosystem services by forests and to enhance their role in global environmental sustainability, research and policy must evolve to address emerging challenges and opportunities.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Data Collection: Developing advanced technologies and methodologies for monitoring forest health and ecosystem services to inform policy and management decisions.
- Integrated Management Approaches: Promoting policies that support integrated landscape management, balancing conservation with sustainable development to benefit both the environment and local communities.
- Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation: Focusing research on how forests can best be managed to adapt to and mitigate climate change, including the role of forests in carbon sequestration and storage.
- Valuation of Ecosystem Services: Advancing methods for the economic valuation of forest ecosystem services to better reflect their true value in policy and decision-making processes.
- Policy Coherence and Coordination: Ensuring that forest conservation and management policies are coherent and coordinated across different sectors and levels of government to avoid conflicting objectives and maximize synergies.
- Community-based Conservation Strategies: Strengthening the role of local communities in forest management, recognizing their knowledge and dependence on forest resources, and ensuring their participation in decision-making processes.
- International Collaboration: Enhancing international cooperation to address transboundary forest management issues, share knowledge and best practices, and mobilize resources for conservation and sustainable management.
- Innovative Financing Mechanisms: Exploring new funding models to support forest conservation and sustainable management, including payments for ecosystem services, green bonds, and environmental impact investments.
Addressing these directions through collaborative research and policy-making can significantly contribute to the preservation and enhancement of forest ecosystem services for future generations.
READ MORE:
How Individuals and Communities Can Support Forest Ecosystem Services
Individuals and communities play a crucial role in supporting and enhancing the ecosystem services provided by forests. Through proactive engagement and sustainable practices, everyone can contribute to the conservation and restoration of forest ecosystems.
- Participate in Reforestation Projects: Joining or organizing tree planting activities helps increase forest cover and restore degraded lands.
- Adopt Sustainable Living Practices: Reducing waste, recycling, and using forest products responsibly can minimize the impact on forest resources.
- Support Eco-friendly Products: Purchasing products certified by sustainable forestry initiatives encourages businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Engage in Community-Based Forest Management: Being actively involved in local forest management practices ensures that forests are used sustainably and equitably.
- Educate and Raise Awareness: Spreading knowledge about the importance of forest ecosystem services and the threats they face can mobilize others to take action.
- Advocate for Forest Conservation: Supporting policies and initiatives that aim to protect and conserve forest ecosystems ensures that they continue to provide essential services.
- Practice and Promote Eco-tourism: Engaging in and advocating for responsible tourism practices protects forests while supporting local economies.
- Invest in Conservation: Donations to organizations working on forest conservation can provide the necessary resources for their projects.
By taking these steps, individuals and communities not only help in preserving forest ecosystem services but also contribute to global environmental sustainability and the well-being of future generations.
Embracing the incredible value of forest ecosystem services is essential for our planet"s health and our future. Together, through conservation and sustainable practices, we can protect these natural treasures for generations to come.

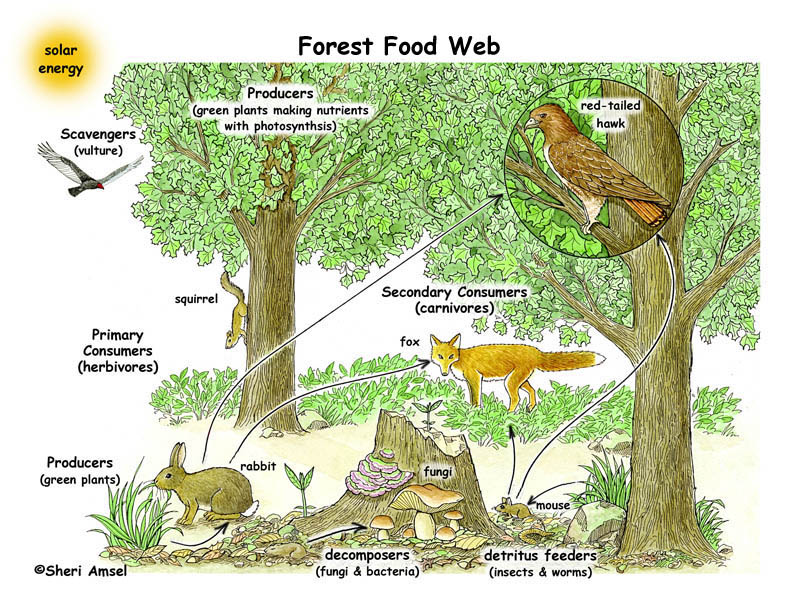
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)




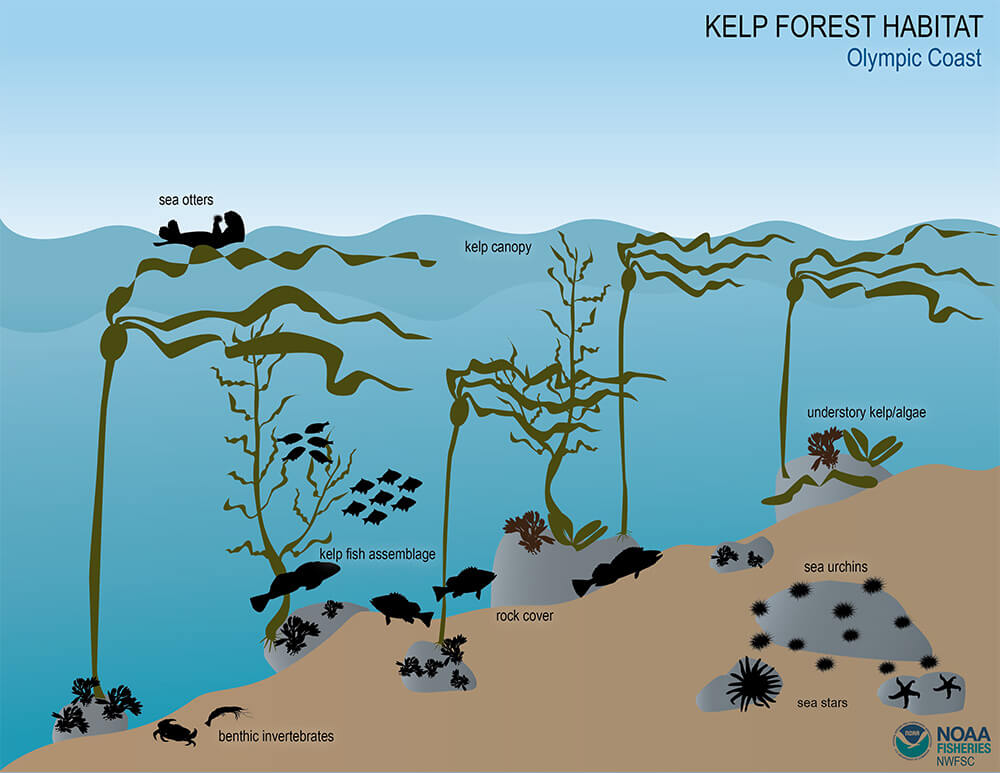



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)