Topic ecosystem services forests provide: Discover the vital role forests play in providing ecosystem services, sustaining biodiversity, and supporting human well-being for a harmonious and sustainable future.
Table of Content
- What are the ecosystem services that forests provide?
- Provisioning Services: Food, Water, Timber, and Fiber
- Regulating Services: Climate Regulation, Water Purification, and Disease Control
- Supporting Services: Soil Formation, Nutrient Cycling, and Pollination
- Cultural Services: Recreational, Spiritual, and Educational Benefits
- Carbon Sequestration and Storage: Combating Climate Change
- Biodiversity Conservation: Habitat for Wildlife
- YOUTUBE: Managing Forests Sustainably for Ecosystem Services
- Water Cycle Regulation: Maintaining Hydrological Systems
- Erosion Control and Sediment Retention: Protecting Landscapes and Water Quality
- Air Quality Improvement: Filtering Pollutants
- Social and Economic Benefits: Livelihoods and Economic Contributions
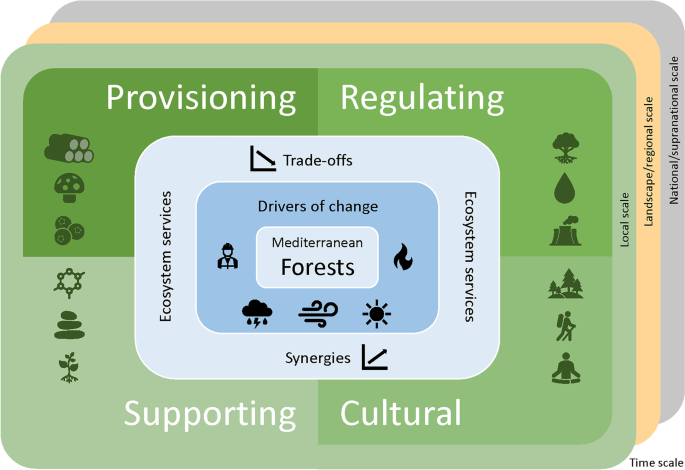
What are the ecosystem services that forests provide?
Forests provide a wide range of ecosystem services that are essential for the well-being of both humans and the environment. These services include:
- Carbon sequestration: Forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in trees and soil, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Water regulation: Forests act as natural water filters, preventing erosion and improving water quality. They also regulate the water cycle, preventing floods and droughts.
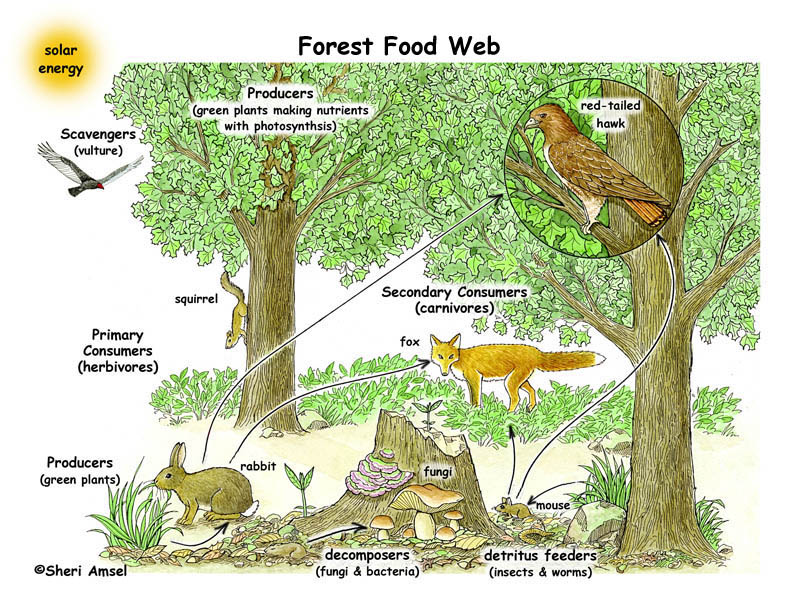
- Biodiversity support: Forests are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, contributing to global biodiversity and serving as habitat for countless organisms.
- Air purification: Through the process of photosynthesis, forests release oxygen and absorb pollutants, playing a crucial role in purifying the air we breathe.
- Soil protection: Forests help prevent soil erosion by providing a protective cover and stabilizing the soil structure with their roots.
- Nutrient cycling: Forests facilitate the cycling and recycling of nutrients, ensuring the fertility of the soil and supporting the growth of diverse plant species.
- Recreation and tourism: Forests offer recreational opportunities like hiking, camping, and wildlife observation. They attract tourists and provide economic benefits to local communities.
- Wood and non-timber forest products: Forests are a source of timber for construction, furniture, and paper production. They also provide non-timber forest products like medicinal plants, fruits, and nuts.
These are just a few examples of the important ecosystem services that forests provide. Their preservation and sustainable management are crucial for the well-being of our planet and future generations.
READ MORE:
Provisioning Services: Food, Water, Timber, and Fiber
Forests are nature"s powerhouse, offering a bounty of essential resources that support life and livelihoods. They are crucial for the well-being of humanity, providing a wide range of materials and resources.
- Food: Forests offer a diverse array of edible products—fruits, nuts, mushrooms, and honey, contributing to the food security of millions worldwide.
- Water: They play a key role in the hydrological cycle, filtering and regulating the water that fills our rivers and quenches our thirst.
- Timber: The sustainable management of forests yields timber, a renewable resource essential for construction, furniture, and energy.
- Fiber: Forests provide natural fibers like bamboo and rattan, as well as raw materials for paper and textile industries.
These provisioning services are not only fundamental for survival but also underpin economies around the globe, emphasizing the importance of conserving and sustainably managing our forests.

Regulating Services: Climate Regulation, Water Purification, and Disease Control
Forests act as the Earth"s thermostat and its water filter, providing critical regulatory services that maintain ecological balance and protect human health.
- Climate Regulation: Through photosynthesis, forests absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, thus playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. They also regulate temperature and rainfall patterns, supporting global and local climates.
- Water Purification: Forest ecosystems naturally filter water, removing pollutants and sediments, ensuring the availability of clean water for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation.
- Disease Control: By maintaining healthy ecosystems, forests can help control diseases. They are home to a diverse range of species, some of which are natural predators of disease vectors like mosquitoes.
These regulating services underscore the intrinsic value of forests in sustaining life on Earth, highlighting the need for their protection and sustainable management.
Supporting Services: Soil Formation, Nutrient Cycling, and Pollination
Forests are foundational to Earth"s life-support systems, facilitating essential processes that underpin all other ecosystem services.
- Soil Formation: Forests contribute to the formation of fertile soil through the decomposition of organic matter, which enriches the soil and supports diverse plant life.
- Nutrient Cycling: They play a critical role in nutrient cycling, with trees and other plants absorbing nutrients from the soil and returning them through leaf litter and other organic debris.
- Pollination: Forests are vital habitats for pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and birds, which are essential for the reproduction of many plant species, supporting food security and biodiversity.
These supporting services are crucial for ecosystem health and resilience, emphasizing the importance of maintaining forest ecosystems for the benefit of all life on Earth.
Cultural Services: Recreational, Spiritual, and Educational Benefits
Forests enrich our lives beyond their material contributions, offering profound cultural, recreational, spiritual, and educational benefits.
- Recreational Benefits: Forests provide unparalleled opportunities for recreation, from hiking and birdwatching to camping and photography, offering people a chance to relax, exercise, and connect with nature.
- Spiritual Benefits: Many cultures and religions regard forests as sacred spaces, places for contemplation, renewal, and spiritual connection.
- Educational Benefits: They serve as living classrooms, where students and researchers can learn about ecology, conservation, and the complex interdependencies within natural systems.
These cultural services highlight the integral role forests play in human well-being, culture, and heritage, underscoring the need to preserve these invaluable resources for future generations.
Carbon Sequestration and Storage: Combating Climate Change
Forests are frontline warriors in the battle against climate change, playing a critical role in carbon sequestration and storage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, converting carbon into biomass and storing it in their trunks, branches, leaves, and roots, effectively removing greenhouse gases from the air.
- Carbon Storage: Mature forests act as carbon sinks, storing vast amounts of carbon for centuries. This storage is not just limited to the trees themselves but extends to the forest soil, which holds significant carbon reserves.
- Climate Change Mitigation: By reducing the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere, forests mitigate the greenhouse effect, helping to stabilize global temperatures and climate patterns.
This ability of forests to sequester and store carbon is a natural solution to climate change, highlighting the importance of preserving existing forests and restoring degraded ones.

Biodiversity Conservation: Habitat for Wildlife
Forests are vital for the preservation of biodiversity, providing essential habitats for a wide range of wildlife species.
- Habitat for Wildlife: Forests offer shelter, food, and breeding grounds for countless species, including many that are endangered or have specialized habitats, contributing to the richness of life on Earth.
- Genetic Diversity: They are hotspots of genetic diversity, which is crucial for species adaptation to changing environments and for ecosystem resilience.
- Conservation of Endangered Species: Protecting forests is key to the survival of endangered species, as it preserves their natural habitats and the ecological balance necessary for their continued existence.
The conservation of forest biodiversity is essential not only for wildlife but also for maintaining ecological processes and services that humans rely on, underscoring the need for concerted conservation efforts.
Managing Forests Sustainably for Ecosystem Services
Discover the beauty of living sustainably and learn how to make a positive impact on the environment with this informative and inspiring video. Find out practical tips to incorporate sustainability into your daily life and be part of the change we all need.
Ecosystem Services in Forests: The Thurig Perspective
Dive into the fascinating world of Thurig, a stunning destination that will leave you in awe. Immerse yourself in its breathtaking landscapes, vibrant culture, and rich history through this captivating video that showcases the best of what Thurig has to offer. Get ready to be enchanted!
Water Cycle Regulation: Maintaining Hydrological Systems
Forests are crucial in maintaining and regulating the Earth"s water cycle, ensuring the availability and quality of water resources.
- Regulation of Water Flows: Trees and forest soils act as natural sponges, absorbing rainfall and releasing it slowly into rivers and streams, reducing the risk of floods and droughts.
- Enhancement of Groundwater Recharge: Forested areas facilitate the infiltration of rainwater into the soil, replenishing groundwater supplies crucial for drinking, agriculture, and industry.
- Maintenance of Water Quality: By filtering pollutants and stabilizing soil, forests prevent sediment and contaminants from entering water bodies, ensuring clean water for ecosystems and human use.
This regulation of water cycles by forests is essential for environmental sustainability, supporting ecosystems, human livelihoods, and biodiversity.

Erosion Control and Sediment Retention: Protecting Landscapes and Water Quality
Forests play a pivotal role in safeguarding landscapes and water quality by preventing soil erosion and retaining sediment.
- Prevention of Soil Erosion: Tree roots bind the soil, while the forest canopy reduces the impact of raindrops on the soil, significantly decreasing the risk of soil erosion.
- Sediment Retention: Forests act as natural barriers, trapping sediment that would otherwise be washed into waterways, reducing sedimentation and protecting aquatic habitats.
- Stabilization of Slopes: By anchoring the soil, forests prevent landslides and slope failures, especially in mountainous and hilly regions, protecting downstream communities and infrastructure.
The role of forests in controlling erosion and retaining sediment is indispensable for maintaining ecosystem health, water quality, and landscape stability, highlighting the importance of forest conservation and sustainable management practices.
Air Quality Improvement: Filtering Pollutants
Forests are natural air purifiers, playing a significant role in improving air quality by filtering pollutants and providing cleaner air.
- Absorption of Pollutants: Trees absorb harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter through their leaves, which helps to cleanse the air.
- Production of Oxygen: Through the process of photosynthesis, forests convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, enriching the air we breathe.
- Reduction of Heat Islands: Forests help to moderate temperatures, particularly in urban areas, by providing shade and releasing moisture into the air through transpiration, effectively acting as natural air conditioners.
This vital function of forests in filtering pollutants and improving air quality underscores the importance of protecting and expanding forested areas to ensure healthier environments for all living beings.

READ MORE:
Social and Economic Benefits: Livelihoods and Economic Contributions
Forests provide significant social and economic benefits, underpinning livelihoods and contributing to economies at both local and global levels.
- Source of Livelihoods: Millions of people worldwide depend directly on forests for their livelihoods, through activities such as timber and non-timber forest product harvesting, agriculture, and ecotourism.
- Economic Contributions: The forest industry, including logging, paper production, and furniture manufacturing, plays a critical role in the global economy, generating employment and income.
- Recreational and Tourism Value: Forests attract tourists seeking natural beauty, wildlife, and outdoor activities, contributing to the economic development of local communities.
- Cultural and Educational Value: Forests are places of cultural significance and educational interest, providing opportunities for learning and cultural practices.
The social and economic benefits of forests highlight their importance beyond their ecological roles, emphasizing the need for sustainable management to preserve these benefits for future generations.
Forests are irreplaceable treasures, offering a multitude of ecosystem services vital for our planet"s health and our well-being. Let"s commit to protecting these natural wonders for current and future generations.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/497408077-56af61ff3df78cf772c3c309.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/489034241_5-56af62885f9b58b7d0183204.jpg)
