Topic eastern sahara desert: Embark on an enlightening journey through the Eastern Sahara Desert, a realm of breathtaking landscapes and rich cultural heritage, beckoning adventurers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Table of Content
- What is the climate like in the Eastern Sahara Desert?
- Geographical Overview of the Eastern Sahara
- Climate and Weather Patterns
- Flora and Fauna of the Eastern Sahara
- Historical Significance and Archaeological Sites
- Current Human Inhabitance and Culture
- Challenges and Environmental Concerns
- YOUTUBE: When the Sahara Was Green
- Tourism in the Eastern Sahara
- Economic Importance and Natural Resources
- Future Perspectives and Conservation Efforts
What is the climate like in the Eastern Sahara Desert?
The climate in the Eastern Sahara Desert is characterized by extreme aridity and high temperatures. Rainfall in this region is minimal and sporadic, resulting in a hyper-arid environment.
Here are some key features of the climate in the Eastern Sahara Desert:
- Hyper-arid region with very little rainfall
- Sparsely vegetated with mostly rock and sand
- Wide temperature variations
The Eastern Sahara Desert experiences minimal rainfall, meaning that water availability is extremely limited. This leads to a lack of vegetation cover, with the landscape mainly consisting of rock and sand. The absence of significant plant life further contributes to the aridity of the region.
Temperature variations in the Eastern Sahara Desert are dramatic. During the day, temperatures can soar to extremely high levels, often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit). However, at night, temperatures can drop significantly, resulting in a large diurnal temperature range.
READ MORE:
Geographical Overview of the Eastern Sahara
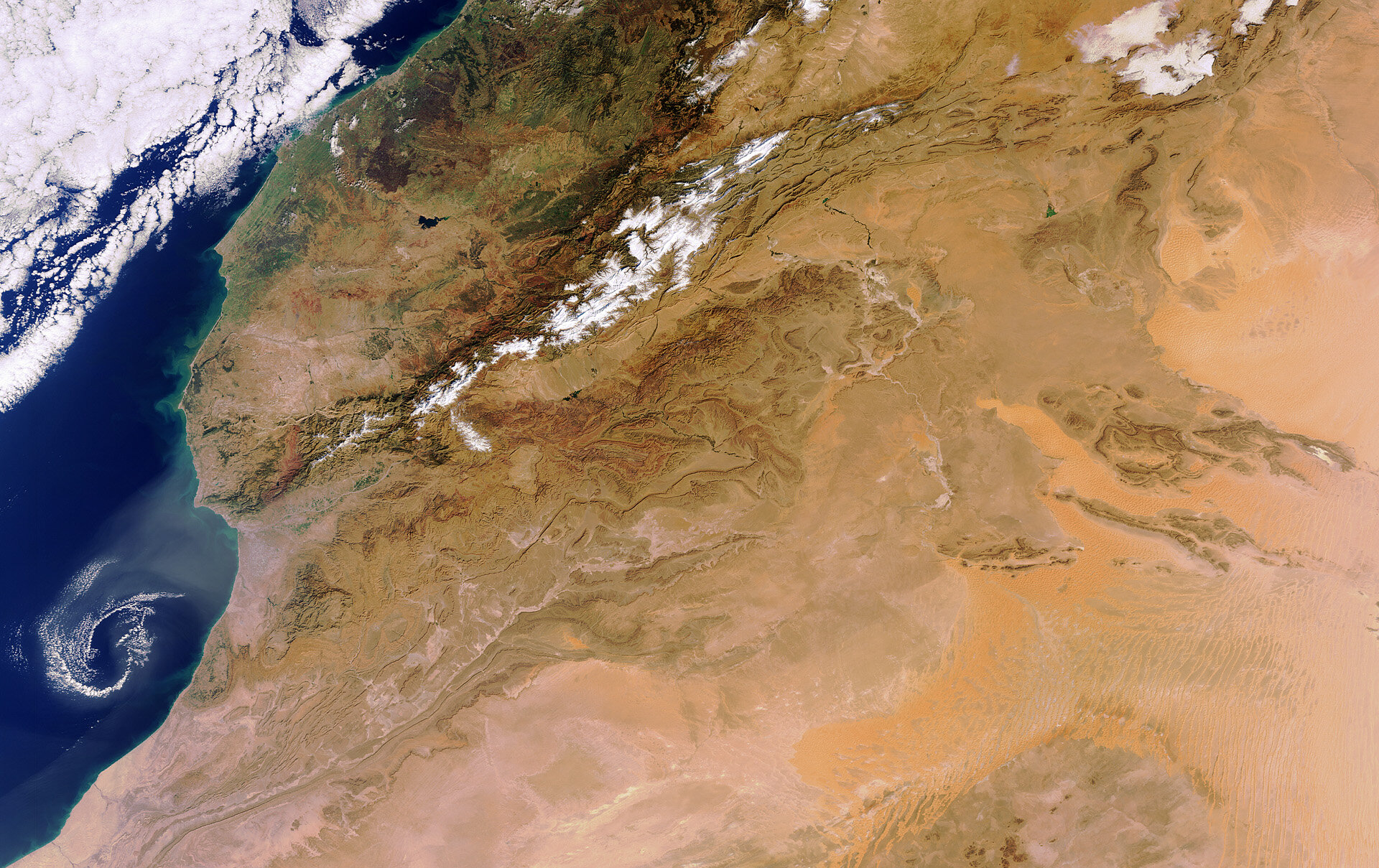
The Eastern Sahara, the eastern part of the vast Sahara Desert, is a region of stark beauty and diverse landscapes. Stretching from the Nile River in the west to the Red Sea and Gulf of Suez in the east, it covers a significant portion of northeastern Africa.
- Location and Size: Encompassing areas of Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, and Ethiopia, this expansive desert spans over 223,000 square kilometers.
- Topography: Unlike the more uniform Western Sahara, the Eastern Sahara boasts a varied terrain with mountainous regions, large areas of sand dunes, stone plateaus, and occasional oases.
- Mountain Ranges: Some of the rocky hills in this area reach heights of over 1,900 meters, providing a dramatic contrast to the surrounding plains.
- River Influence: The Nile River, forming the western boundary of the Eastern Sahara, plays a crucial role in the ecosystem and climate of the region.
- Climate: Characterized by hyper-arid conditions, the Eastern Sahara receives minimal rainfall, creating an environment of extreme dryness and heat.
Despite its harsh climate, the Eastern Sahara"s unique geographical features make it a region of interest for scientists, adventurers, and those fascinated by its enduring natural beauty.

Climate and Weather Patterns
The Eastern Sahara, known for its extreme climatic conditions, exhibits a hyper-arid climate, characterized by minimal rainfall and high temperatures.
- Rainfall: This region receives less than 25 millimeters of rain annually, mostly during winter, with some areas experiencing years without any precipitation.
- Temperature Variations: Summer temperatures can soar, often exceeding 40°C (104°F), while winter temperatures are cooler, sometimes dropping to 0°C (32°F) at night.
- Seasonal Changes: The climate is marked by two distinct seasons - a torrid summer and a milder winter. However, temperature fluctuations between day and night can be extreme in both seasons.
- Wind Patterns: The region is also known for its strong wind patterns, including the hot, dry "Khamsin" wind, which can cause sandstorms and significantly impact visibility and air quality.
- Humidity Levels: Humidity is generally low throughout the year, contributing to the arid conditions and making the heat more bearable.
This harsh climate shapes the landscape and living conditions in the Eastern Sahara, making it one of the most challenging yet intriguing environments on Earth.
Flora and Fauna of the Eastern Sahara
The Eastern Sahara is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, adapted to its harsh desert conditions.
- Plant Life: The Sahara contains around 500 species of plants, many of which grow near oases and wadis. These plants have adapted to the arid conditions with features like long roots to access water and seeds that can remain dormant for years.
- Notable Plant Species: Among these are Adenium obesum, Artemisia herba-alba, and Balanites aegyptiaca, each uniquely adapted to the desert environment.
- Animal Diversity: The region supports 70 species of mammals, 90 species of birds, and 100 species of reptiles, along with various arthropods.
- Mammals: Notable mammals include the Barbary sheep, oryx, anubis baboon, spotted hyena, dama gazelle, and the well-known dromedary camel, vital for desert nomads.
- Birds and Reptiles: The Sahara hosts ostriches, secretary birds, Nubian bustards, and raptors, along with reptiles like cobras, chameleons, skinks, and in some regions, crocodiles.
- Adaptations: The harsh climate of the Sahara has led to remarkable adaptations in its wildlife, including nocturnal lifestyles, heat-resistant features, and efficient water utilization.
This unique ecosystem, though appearing barren at first glance, teems with life that has ingeniously adapted to the extreme desert conditions.

Historical Significance and Archaeological Sites
The Eastern Sahara Desert holds a treasure trove of historical significance and archaeological wonders that shed light on ancient civilizations and their way of life.
- Ancient Civilizations: The Eastern Sahara has been a cradle for various ancient civilizations, with evidence of human habitation dating back to prehistoric times. This region has contributed significantly to our understanding of the early development of human societies in Africa.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Various archaeological sites have been uncovered, revealing fascinating aspects of life in ancient times. These include pre-Islamic oasis settlements, remnants of early agricultural practices, and evidence of trade and migration.
- Rock Art and Engravings: The discovery of rock art in places like Farafra provides insights into the artistic expressions of ancient people. These artworks, which include depictions of animals and boats, have been linked to cultural influences from both Africa and the Near East.
- Use of Advanced Technologies: Modern archaeological efforts in the Eastern Sahara have benefited from advanced technologies like imaging radar and remote sensing, enabling the exploration of buried sites and landscapes without extensive excavation.
- Significance in Human History: The findings in the Eastern Sahara contribute significantly to our understanding of human history, including the transition from foraging to farming, and the complex interactions between different ancient cultures.
This region continues to be a focal point for archaeologists and historians, offering glimpses into the rich and varied past of one of the world"s most intriguing deserts.
Current Human Inhabitance and Culture
The Eastern Sahara, despite its harsh climate, is home to resilient communities that have adapted to the desert environment, preserving rich cultural traditions.
- Nomadic Tribes: The region is predominantly inhabited by nomadic tribes who have historically traversed the desert, such as the Bedouins. These communities are known for their deep knowledge of the land and survival skills in arid conditions.
- Way of Life: The lifestyle in the Eastern Sahara is largely shaped by the environment. Nomadic herding, oasis farming, and trading are common practices. The inhabitants often move in search of water and grazing lands for their livestock.
- Cultural Traditions: The culture of the Sahara"s inhabitants is rich in oral traditions, including storytelling, poetry, and music. These traditions are often passed down through generations, preserving the history and values of the community.
- Modern Influences: In recent times, some of the Eastern Sahara"s inhabitants have started to settle in more permanent communities. This shift has brought modern amenities and technologies, though many still maintain their traditional ways.
- Challenges: The communities in the Eastern Sahara face several challenges, including limited access to resources like water and education. Environmental changes and political factors also impact their traditional way of life.
The Eastern Sahara is not just a vast desert; it"s a place of cultural richness and resilience, where communities continue to thrive and preserve their heritage against the odds.
Challenges and Environmental Concerns
The Eastern Sahara faces significant environmental and societal challenges that impact both the ecosystem and the human populations residing there.
- Climate Conditions: The region experiences extreme weather conditions, with high temperatures often exceeding 30°C, and minimal annual rainfall, making it one of the harshest environments on Earth.
- Biodiversity Threats: Despite the sparse vegetation and fauna, the area is a habitat for unique species. However, the hyper-arid conditions, along with human activities, pose threats to this biodiversity.
- Human Impact: The inhabitants, mainly nomadic tribes, face challenges due to water scarcity, political instability, and changing environmental conditions. Their traditional ways of life are increasingly under pressure.
- Natural Resource Exploitation: Activities such as oil and gas extraction have escalated in recent years, leading to environmental degradation and posing risks to the fragile desert ecosystem.
- Renewable Energy Potential: There are opportunities for environmental improvement through renewable energy projects. Research suggests that large-scale wind and solar farms could increase local rainfall and vegetation, offering some respite to the arid conditions.
- Conservation Efforts: Priorities for the next decade include establishing cross-boundary protected areas, promoting sustainable ecotourism, and implementing research and monitoring schemes to protect the desert"s natural and cultural heritage.
The Eastern Sahara Desert is a region of stark contrasts, where the challenges of a changing climate and human impact intersect with opportunities for sustainable development and conservation.
When the Sahara Was Green
Green: \"Discover the beauty of the lush green landscapes in our latest video, showcasing the serene natural surroundings that will leave you feeling refreshed and rejuvenated. Let\'s immerse ourselves in the calming shades of green together!\" Largest: \"Prepare to be awed by the sheer magnitude captured in our video of the world\'s largest structures and natural wonders. From towering skyscrapers to vast waterfalls, this visual feast will leave you mesmerized.\"
Sahara: The Largest Desert On Earth Journeys To The Ends Of The Earth Real History
The Sahara is the biggest desert on earth ... it takes its name from the Arab word for \"emptiness\". In the dead heart of that ...
Tourism in the Eastern Sahara
The Eastern Sahara, with its unique landscapes and rich cultural heritage, offers a variety of attractions for tourists seeking adventure and a glimpse into traditional desert life.
- Desert Expeditions: Visitors can embark on guided tours to explore the vast dunes, rugged mountains, and serene oases. Camel trekking and 4x4 desert safaris are popular ways to experience the desert"s majesty.
- Cultural Experiences: Tourists have the opportunity to interact with local nomadic tribes, learn about their way of life, and experience traditional music, dance, and cuisine.
- Historical Sites: The Eastern Sahara is home to numerous archaeological sites, including ancient rock art, ruins, and historical settlements that offer a window into the region"s past civilizations.
- Stargazing: The clear desert skies provide ideal conditions for stargazing, allowing visitors to marvel at the night sky"s beauty, untouched by light pollution.
- Eco-Tourism: There are initiatives to promote sustainable tourism practices that respect the delicate desert ecosystem and support local communities.
- Seasonal Variations: The best time to visit is between October and April, when the temperatures are milder, making outdoor activities more enjoyable.
Tourism in the Eastern Sahara is not just about the awe-inspiring landscapes; it"s an immersive experience that connects visitors with the timeless spirit of the desert.

Economic Importance and Natural Resources
The Eastern Sahara Desert, though predominantly arid, holds significant economic value and natural resources that are vital to the surrounding regions.
- Natural Resources: The desert is rich in minerals, including phosphates and ores. In some areas, there are significant reserves of oil and natural gas, which contribute substantially to the economies of neighboring countries.
- Agriculture: While challenging, agriculture is practiced in oases where irrigation is possible. These areas produce dates, figs, and other crops that are crucial for local communities.
- Renewable Energy Potential: The vast open spaces and high solar irradiance make the Eastern Sahara an ideal location for solar energy projects, which could provide sustainable energy solutions.
- Tourism: The unique landscapes, rich history, and cultural heritage of the Eastern Sahara attract tourists, contributing to the local economy through eco-tourism and cultural tourism.
- Trade Routes: Historically, the Sahara has been a crossroads for trade routes connecting various parts of Africa. These routes are still used for the trade of goods and contribute to the region"s economic activity.
- Challenges: Despite its potential, the harsh climate and remote location pose significant challenges to the exploitation and sustainable management of these resources.
The Eastern Sahara"s natural resources and economic activities play a crucial role in the livelihoods of the local populations and have the potential for future development, especially in renewable energy and sustainable tourism.
READ MORE:
Future Perspectives and Conservation Efforts
Looking ahead, the Eastern Sahara faces both challenges and opportunities in terms of conservation and sustainable development.
- Wildlife Conservation: Organizations like Sahara Conservation are actively working to protect the region"s unique wildlife, such as the critically endangered dama gazelle and the scimitar-horned oryx, which has been brought back from the brink of extinction.
- Great Green Wall Initiative: This ambitious project aims to combat desertification across Africa, including areas in the Sahara and Sahel. It focuses on localized approaches like agroforestry and reforestation to restore degraded land and promote biodiversity.
- Water Management: In response to climate change, there are efforts to revive ancient irrigation systems like lkhttarts to sustain oasis agriculture and combat desertification. This approach supports the local communities" livelihood and conserves the unique oasis ecosystems.
- Species Reintroduction: Efforts to reintroduce species like the addax and the scimitar-horned oryx into their native habitats are ongoing. These conservation actions also involve local communities and aim to maintain the balance between human activities and wildlife needs.
- Adaptation and Sustainability: Future conservation efforts in the Sahara will need to focus on adapting to changing environmental conditions while integrating the needs of local communities. Sustainable management of natural resources and habitat conservation are key.
The future of the Eastern Sahara involves a concerted effort towards sustainable development, conservation of its unique biodiversity, and adaptation to the changing climate, ensuring the region remains a vital and vibrant ecosystem.
The Eastern Sahara Desert, a land of extreme beauty and profound challenges, offers a unique window into both the past and future of our world, beckoning adventurers and conservationists alike to explore its mysteries and protect its legacy.